
by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Feb 18, 2018 | Colonialism & Conquest
Featured image: The Marma, like other tribes of the CHT, have faced years of violence, land-grabbing and intimidation. © Mark McEvoy/Survival International
by Survival International
Two sisters from the Marma indigenous tribe of the Chittagong Hill Tracts in Bangladesh are being held against their will after being raped and sexually assaulted at gun point, allegedly by members of the Bangladesh security forces.
The Jummas, a collective name for the tribes living in the CHT, continue to face endemic violence, land-grabbing and intimidation on their ancestral land. Jumma women and girls are frequently subjected to rape and sexual assault at the hands of Bengali settlers and the armed forces.
The Marma girls, aged 19 and 14, describe men in army uniforms entering their house during a raid in the early hours of January 22. They report that the older sister was raped and the younger was sexually assaulted during an attempted rape.
The army and other security forces have denied the attacks took place, and the authorities are now not allowing the girls to be released from hospital. Their room is being guarded by police who are refusing to allow human rights activists or journalists to talk to the victims.
The sisters fear for their own, and their family’s, safety. Those who have been able to speak to the girls report that they are traumatised, not only by the initial brutal attacks but also by the numerous interrogations by male police officers and the entry of male security personnel into their hospital room throughout the day and night.
The girls speak only their tribal Marma language and have been refused access to familiar indigenous food brought to the hospital by well wishers.
Raja Devasish Roy, the Chakma king, Survival and other human rights activists have called for the girls to be released from the hospital and for the perpetrators to be brought to justice.

by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Jan 30, 2018 | Colonialism & Conquest
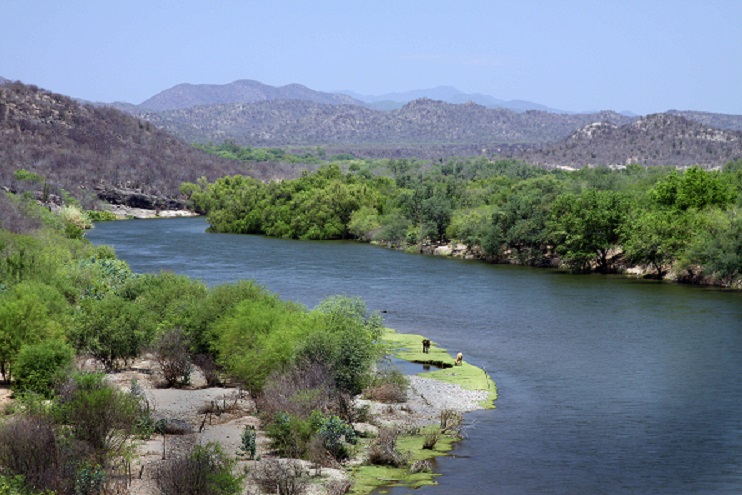
Featured image: The Aguaprieta pipeline crosses the Yaqui River (Río Yaqui), the water source for the Yaqui, an indigenous tribe residing in the Yaqui Valley in Sonora, Mexico. Photo: Tomas Castelazo (CC). As far as one Yaqui community is concerned, the pipeline will never be completed.
by Gabriella Rutherford / Intercontinental Cry
In 2013, Enrique Peña Nieto’s government deregulated Mexico’s energy sector, opening it up to foreign investors for the first time 75 years. In what he called an “historic opportunity”, the Mexican President proclaimed “This profound reform can lift the standards of living for all Mexicans.”
But not everyone stands to see their quality of life materially improve from the deregulated sector. Such is the case for the Yaquí Peoples in Sonora state, Mexico, whose territory is currently home to an 84-kilometre stretch of natural gas pipeline.
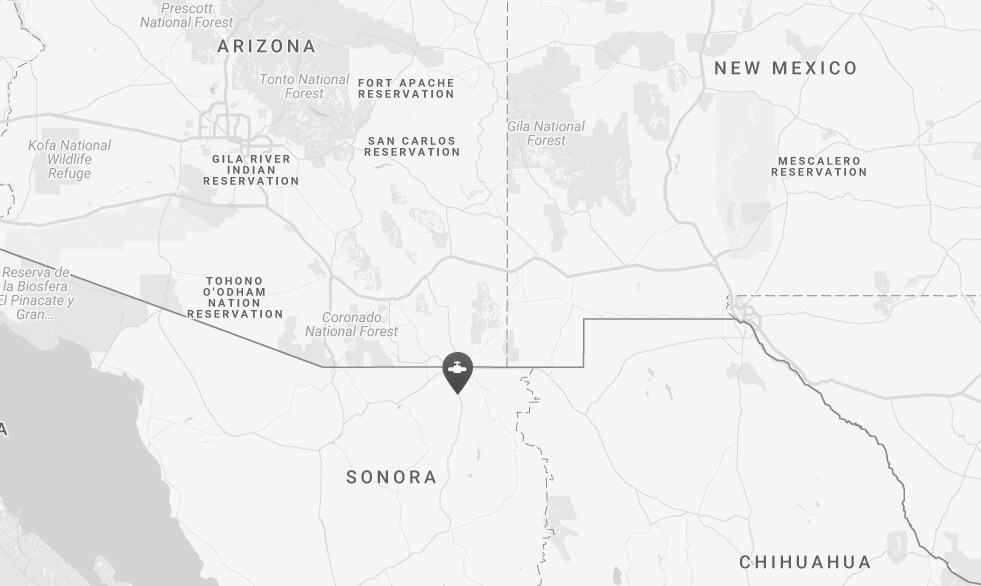
The Aguaprieta (Agua Prieta) pipeline starts out in Arizona and stretches down 833km to Agua Prieta, in the northeastern corner of the Mexican state of Sonora—cutting through Yaqui territory along the way.
Once completed, the pipeline would also cross Yaqui River (Río Yaqui), the Yaqui’s main source of water.
More than a few Yaqui are adamant that they will see no benefits from the project. “The gas pipeline doesn’t help us, it only benefits businessmen, factory owners, but not the Yaqui” said Francisca Vásquez Molina, a Yaquí from the Loma de Bacúm community.
As with Keystone XL and Dakota Access pipelines, the Aguaprieta project comes with its own share of risks.
In addition to the considerable environmental impact that stems from the pipeline’s construction, the high methane content of natural gas could bring on disaster. Rodrigo Gonzalez, natural resources and environmental impact expert, maintains that in the event of a gas explosion all human, plant and animal life within a one-kilometre radius surrounding the explosion would be lost. Anyone within the second kilometre would risk second and third-degree burns.
In the community of Loma de Bacúm, the gas pipeline is just 700 m from houses. In nearby Estación Oroz, it is 591m from a primary school.
Gonzalez has pointed out that another viable route for the pipeline was initially considered by the company that could have avoided Yaqui territory altogether. He suggests this route was ultimately rejected to save costs. “At the beginning of the project, two routes were mooted. That which didn’t cross indigenous territory cost 400 million pesos whilst that which puts Yaquí lives at risk costs 100 million pesos.”
IEnova, the company behind the pipeline, has repeatedly made assurances that all due safety procedures have been followed in construction and that the risk of accidents is minimal but this has not been enough to assuage the fear or anger of everyone opposing the gas pipeline.
In a public statement last year, the group Solidaridad Tribu Yaquí said, “This is a people that say no to a megaproject of death, dispossession and destruction[…]These rich men don’t care about the life of one, two, or three people, much less if they are indigenous… [they] don’t care if the Yaqui culture is exterminated. What is important to these rich men is to conclude the work and pocket all the profits to be brought about by the appropriation of the Yaqui territory.”
Not all Yaquí communities are united in rejecting the gas pipeline, however. Indeed, of the eight Yaquí communities consulted, only the Loma de Bacúm community refused to give their consent to the project. The other seven communities chose to accept the compensation offered. This decision has sadly resulted in tensions between Loma de Bacúm and the other communities. Things reached a critical point in October 2016 where one Yaquí member died and thirty injured in a confrontation involving different Yaquí communities.
Seemingly alone in their struggle, the Loma de Bacúm Yaquí have consistently resisted the Aguaprieta pipeline. In April 2016, they successfully fought to be granted a moratorium on its construction. When, in 2017, it became clear that IEnova, would carry on regardless and that neither federal nor state or authorities could be counted on for support, the Loma de Bacúm community resorted to more drastic measures. On May 21, community members removed cables which had been laid down in the preliminary stages of the gas pipeline construction. Then, after another court ruling that IEnova should remove all infrastructure within 24 hours fell on deaf ears, on August 22 the community went ahead and cut a 25-foot section out of the live gas pipeline, despite the grave risks they ran in doing so. As a result of the community’s actions in August, IEnova was forced to cut off the gas flow in the area and it has remained out of service ever since.
The community has been accused of sabotage and vandalism to IEnova property but the community maintains that IEnova, a company owned by US-based Sempra Energy, is trespassing on their land and holds them responsible for all damage brought on by the construction of a pipeline to which they never consented.
In a video shared on Facebook, one community member explained “If you want to have us killed, there’s no problem. We’re not scared of that… We’re not scared of this company nor this project…All that the Yaquí tribe is asking for is that the law is upheld and that federal and state government respect it. If you want to have us killed, go ahead there’s no problem but we’ll defend our land and that is our right.”
In September 2017, a judge once again found in favour of the Yaquí community ruling that IEnova did not have the right to enter Yaquí territory to repair the gas pipeline. Whether this latest ruling will carry more weight with both local and state authorities than the previous ones remains to be seen.
For the time-being, the stand-off looks set to continue. Loma de Bacúm has made it clear it will not back down until the pipeline is removed or rerouted. “If they want to build a pipeline. that’s fine”, said community spokesperson Guadalupe Flores, “but it will not pass through here.” At the same time, IEnova refuses to accept that one small community can curtail their plan to use Yaquí territory in order to provide electricity to the Comisión Federal de Electricidad (CFE), the country’s largest electric utility. Nor does it seem willing to brazenly defy the court’s latest ruling, at least for the time-being.
The struggle in Loma de Bacúm echoes loudly among all Indigenous Peoples who are grappling to make sure the resource sector cannot run roughshod over human rights and environmental concerns; but it is perhaps loudest in Mexico. Since the new energy policy went into effect, four other pipeline projects have been suspended. Looking ahead, a “shale offensive” is now set to begin later this year should the PRI retain power in July, leading to a proliferation of similar conflicts.

by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Jan 29, 2018 | Colonialism & Conquest
Featured image: Tomas was contacted between 2001 to 2003 and now lives in the Amazon region where one of the deadliest roads has been proposed. © David Hill/Survival International
by Survival International
Peru has approved a law that could devastate several uncontacted Amazon tribes.
The law declares “in the national interest” the construction of roads in the remote Ucayali region that borders Peru and Brazil.
The area lies inside the Uncontacted Frontier, home of the highest concentration of uncontacted tribes on Earth.
Several illegal roads that cut through uncontacted Indians’ lands have already been opened up. Thousands of illegal gold miners operate in the region, and have polluted dozens of rivers with mercury.
Uncontacted tribes face catastrophe unless their land is protected. They have the right to their land under Peruvian and international law.
Road building in the Amazon almost always leads to a devastating influx of settlers, loggers and ranchers.
Pope Francis, speaking from the region just days before the road law was passed, said: “Never before has there been a greater threat to indigenous peoples’ lands.
“We must break with the historical paradigm that sees the Amazon as an inexhaustible resource for other countries, without taking into account its inhabitants.”
Survival is calling on the Peruvian government to scrap road building plans inside the Uncontacted Frontier.
by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Jan 8, 2018 | Colonialism & Conquest
Featured image: A recent epidemic in the Republic of Congo is said to have been aggravated by the loss of indigenous peoples’ resources due to conservation and logging projects. © C. Fornellino Romero/Survival International
by Survival International
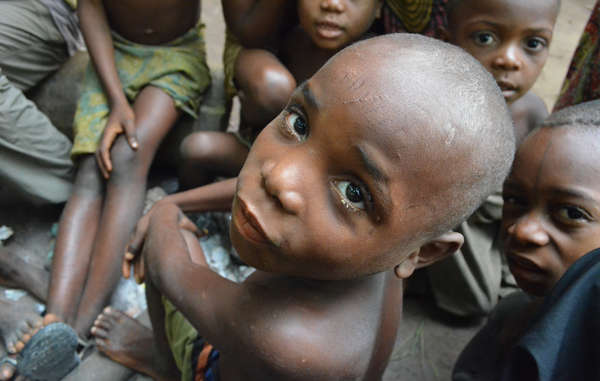
A Congolese organization has recently raised concerns that conservation contributed to the deaths of several dozen children, mostly Bayaka “Pygmies,” during an epidemic in 2016 in the Republic of Congo – the latest in a long line of related reports.
The deaths have been attributed by a medical expert to malaria, pneumonia and dysentery, aggravated by severe malnutrition.
Conservation-related malnutrition among Bayaka children in this region has been reported since 2005 at least, as the Bayaka are prevented from hunting and gathering on their lands by wildlife guards through violence and intimidation.
These guards are funded and equipped by the Wildlife Conservation Society (WCS), one of the world’s largest conservation organizations, and the logging company it has partnered with, CIB. Both organizations have failed to take effective action to prevent abuse.
“The wildlife guards abuse us. They don’t want us to go into the forest. How can we feed our children?” a Bayaka man from Mbandza, the site of the epidemic, told Survival in 2016.
These guards have been accused of abusing Bayaka and stealing their food for over 13 years. One such attack that took place in Mbandza in early 2016 left one man hospitalized.

The Baka and Bayaka’s consent is required by law for any major project on their lands, but this is ignored by WWF and WCS. © Survival International
In this way, the Bayaka are being illegally evicted from their ancestral homelands by threat of violence. As one Bayaka woman explained: “If we go into the forest we eat well there compared to the village. We eat wild yams and honey. We want to go into the forest but they forbid us to. It frightens us. It frightens us.”
Critics have noted that the guards have also failed to protect the wildlife the Bayaka depend on for food, since they have difficulty tackling corruption and the creation of logging roads, the two main drivers of poaching.
Plummeting health has been reported among Bayaka living in the Dzanga-Sangha Protected Areas in the Central African Republic – one of the World Wildlife Fund’s (WWF) flagship projects – since 2006. Conditions encountered among older women “would be considered a public health crisis by international health agencies,” according to research published in 2016.
Increased malnutrition and mortality have been reported among Baka “Pygmies” in Cameroon, where WWF also operates, and among Batwa “Pygmies” in another of WCS’s project sites in east Democratic Republic of Congo.
“Now we are afraid of the anti-poaching squads. Before when a woman gave birth we took her to the forest to help her regain her strength and weight, now we can’t do this. We would take our children to the forest to avoid epidemics. Now we know illnesses we never knew before,” one Baka woman in Cameroon told Survival.
Watch Baka describe the abuse they face as a result of WWF’s conservation projects
Baka health plummets due to conservation
In the Congo Basin, the Baka, Bayaka and dozens of other rainforest peoples are being illegally evicted from their ancestral homelands in the name of conservation. Their health is plummeting as a result.
The big conservation organizations that support these conservation projects, like the World Wildlife Fund (WWF), refuse to abide by basic international standards and secure their consent.
Neither WCS nor WWF has attempted to secure the indigenous peoples’ consent, as basic due diligence and their own human rights policies require.
Survival’s Director Stephen Corry said: “Land theft is a serious and deadly crime, as these reports show. Many associate conservation with reason and compassion but, for Baka and Bayaka, it often means mindless violence and plummeting health. When will WWF and WCS finally start complying with their own human rights policies? ”
Timeline
1996: The organization Berggorilla & Regenwald Direkthilfe finds that malnutrition and mortality has increased among Batwa “Pygmies” since they were evicted from Kahuzi-Biega, a national park in east Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) funded by WCS.
1997: WWF observes that the fact that the Bayaka are banned from hunting or gathering inside the Dzanga-Ndoki Park, the park in the Central African Republic (CAR) that WWF helped to create, “punishes [the Bayaka] severely” and is undermining their food security.
2000: A study finds that the Batwa in Kahuzi-Biega, DRC, are suffering from nutritional deficiencies, because they are no longer able to hunt in the forest, and soaring mortality rates. Malnutrition is particularly pronounced among women and children.
2004: A BBC investigation into CIB’s logging concessions in Congo hears from a Bayaka man: “We get so much suffering because of [wildlife] guards. We can’t go and find things in the forest as we used to. All we hear is hunger.”
2004: Bayaka from another community in Congo report to Greenpeace: “Then we met another white man (WCS) who came to tell us to stop hunting and that the wildlife guards would make sure we did. Now we are afraid to go far in the forest in case the wildlife guards catch us so we have to stay in the village. […] Now we are dying of hunger.”
2005: The Congolese Observatory on Human Rights, the organization that reported on the 2016 epidemic, documents three cases of violent abuse against Bayaka by wildlife guards, and warns that some Bayaka “are dying of hunger.”
2005: A news report recounts how Bayaka in one of CIB’s logging concessions describe being targeted by wildlife guards that mistreat and temporarily imprison them, and how this has led to more frequent malnutrition among children and vulnerable adults.
2006: WWF and its partners commission a report that finds that the Bayaka in Dzanga-Sangha, CAR, are struggling to feed themselves. The Bayaka interviewed for the report state that the conservation project has forced them out of some of their richest hunting and gathering grounds. They report that wildlife guards harass or attack them even when they try to use the reduced areas of land they have left, all the while accepting bribes from the real poachers who were emptying the forest of its wildlife. Some Bayaka women are finding it so hard to find food, the investigator hears, that they have been driven to sex work in the nearby town.
2006: An article in The Lancet cautions that “Pygmy peoples’ health risks are changing as the central African forests, which are the basis for their traditional social structure, culture, and hunter-gatherer economy, are being destroyed or expropriated by […] conservation projects:”
2008: UNICEF warns that the Bayaka’s right to gather resources is being “flouted on the most basic level because indigenous people no longer have access to areas rich in game” due to protected areas in Congo.
2012: An anthropologist with 18 years’ experience working with Bayaka in Congo reports increasingly poor nutrition and increased mortality. He attributes this to the removal of forest resources by loggers and to “conservationists’ exclusionary and draconian management practices.”
2013: A researcher at the University of Oxford reports that the combined impact of conservation and logging have led to poorer health and higher levels of drug and alcohol addiction among the Bayaka. He argues that conservation efforts would benefit from gaining people’s consent
2014: A medical study finds that “punitive anti-poaching measures” and dwindling wildlife have caused health to plummet among Bayaka in Dzanga-Sangha, CAR, particularly among women. “It is disheartening to see health decline so closely tied […] to the conservation management policies of the last twenty-five years,” the study’s authors note.
2015: A doctor with extensive experience working in CIB’s logging concessions reports that: “Aside from wounds inflicted by gorillas, buffalo or other wild animals, my colleague and I also see [gun] wounds in people claiming to have been attacked – sometimes without warning – by the protectors of wildlife: the wildlife guards.”
2015: The same doctor tells Survival: “I find this [wildlife guard violence] a very serious problem and in my opinion most wildlife guards have other motives than protecting the animals to work as a wildlife guard.”
2016: A second doctor with extensive experience working in CIB’s logging concessions describes to Survival the seasonal malnutrition she encounters among Bayaka, which she attributes to repressive conservation policies.
“Pygmy” is an umbrella term commonly used to refer to the hunter-gatherer peoples of the Congo Basin and elsewhere in Central Africa. The word is considered pejorative and avoided by some tribespeople, but used by others as a convenient and easily recognized way of describing themselves.

by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Jan 4, 2018 | Colonialism & Conquest
Featured image: This Baiga woman was evicted from Kanha tiger reserve. © Survival International
by Survival International
India’s National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) is coming under increasing pressure over its illegal order banning the recognition of tribal forest rights in tiger reserves. The order prompted Survival International to launch a global tourism boycott in November.
Information released to Survival has revealed that India’s tribal peoples’ Commission (officially called the National Commission for Scheduled Tribes (NCST)) has directly challenged the NTCA’s order in private meetings in Delhi. The Commission demanded that the NTCA suspend any planned evictions of tribal peoples, who have been dependent on and managed their forests for millennia.
After demanding to meet with the NTCA, the Commission argued that the order violates India’s Forest Rights Act – which guarantees tribal peoples’ rights to their forests. It was intended to address the “historical injustice” against tribes and other “traditional forest dwellers.”
In November, representatives of tribal communities met with many human rights and environment activists in Delhi, amidst mounting concern over the NTCA order.

A Baiga woman works for daily wages on Vedanta’s Bodai-Daldali bauxite mine, Chhattisgarh © Sayantan Bera/Survival
J.K. Thimma, a Jenu Keruba man who lives in Nagarhole National Park, and was present at the meeting, said: “The NTCA order is an attack against our culture and our tradition. This is anti-Constitutional and the NTCA have no right to stop the implementation of an Act passed by the Parliament… This is denial for our existence. The order needs to be withdrawn as soon as possible, it is creating fear among all of us.”
Another tribal man, Shankar Barde from Tadoba Tiger Reserve, said: “After years of restrictions and hardships, finally we were told early this year by the district administration that our rights have been recognized. We were excited… but then we were told by the district administration that NTCA order does not allow our rights to be recognized. This is a complete injustice. Dozens of outsiders are earning large sums of money in our backyard while we struggle to even live with dignity.”
Indian law specifically states that the NTCA does not have the power to “interfere with or affect the rights of local people, particularly… tribes.” Tribal rights are under the jurisdiction of the Ministry of Tribal Affairs.
Despite this, conservation authorities have violated the rights of tribal peoples. Across India, tribal peoples endure harassment, coercion, and illegal eviction from their ancestral homelands in the name of conservation.

Baiga children. Their village was notified with eviction. Achanakmar Tiger Reserve. © Survival
After eviction, tribal people face lives of poverty and exclusion on the fringes of Indian society. Meanwhile, huge numbers of tourists are then invited into tiger reserves, disrupting tiger habitats and making tigers more vulnerable to poaching.
Survival International is leading the global fight against injustice and abuse in the name of protecting wildlife.
Survival’s Director Stephen Corry said: “This order is an attack on India’s tribal peoples – it’s also illegal. Polluting and destructive industries such as uranium mining and tourism are apparently welcome in tiger reserves, but conservationists in India remain determined to kick tribal people off their land. It’s time they partnered with the best conservationists and guardians of the natural world, and stopped persecuting them. Tribal peoples know their land and its animals better than the conservationists.”

by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Jan 2, 2018 | Colonialism & Conquest
by Pam Tau Lee / Intercontinental Cry
The Lumad are Indigenous Peoples in the southern Mindanao region of the Philippines. The term Lumad is short for Katawhang Lumad (Literally: “indigenous people”), a description officially adopted by delegates of the Lumad Mindanao Peoples Federation founding assembly on June 26, 1986. This grew out of a political awakening among tribes during the martial law regime of President Marcos and reflects the collective identity of 18 Lumad ethnic groups. The assembly’s main objectives was to achieve self-determination and governance for their member-tribes within their ancestral domain in accordance with their culture and customary laws.
The Lumad have a traditional ancestral concept of land ownership which is communal private property. Community members have the right utilize any piece of unoccupied land within the communal territory. Lumad ancestral lands include rain forests, hunting grounds, cultivated and uncultivated land and valuable mineral resources (copper, nickel, gold, chromite, coal, gas, cement) below the land.

For decades the Lumad had been forced to physically defend their right to control their ancestral territories against corporate plunder and militarization. Unable to match up to the armed forces of the government and profiteers the Lumad have had to flee their communities; their land has been seized by multinational corporations and logging companies. Wealthy Filipino migrants and multinationals are planting and exporting palm oil, bananas, rubber and pineapple.
Unequipped to understand the modern land tenure system, the Lumad have established schools in their communities supplying knowledge to young adults and youth on how to protect their rights, property and culture. While these schools have always posed a threat, President Duterte has taken the unprecedented step of directing the Department of Education to close them down and has also encouraged the killing and arrest of Lumad teachers, which continues to go unpunished.
The history of violence and unwarranted (extrajudicial) killings of Lumad at the hands of military, paramilitary, and private security forces is in the hundreds, with the arrest and torture Lumad activists in the thousands. Fifty-six percent of Philippine military have been deployed to the Mindanao region. Today many of the Lumad have sought safety and shelter in evacuation centers where they and other victims of war are crowded into small spaces, lacking sanitary conditions and food, and endure harassment by local police including sexual harassment.

Bolstered by the recent visit of Trump to the Philippines who has promised and delivered increased in military funding to the Philippines, President Duterte has extended martial law on the whole island of Mindanao under the guise of war on terrorism and drugs and has launched a full-scale assault on social justice activists throughout the Philippines, including the Lumad people.
Where there is oppression there is resistance. The Lumad have organized protest actions against mining, extrajudicial killings, and the militarization of their communities, and have led “Manilakbayan” people’s caravans from Mindanao to Manila where they have built unity with Moro and peasant communities and other oppressed sectors in Mindanao and, together, have brought these people’s demands to the national capital. There are some young Lumad that say, because the repression suffered by their community is so bad, at times they consider joining the New Peoples Army. In fact, some Lumad do engage in armed resistance to defend their ancestral lands, as Lumad have done since time immemorial, from fending off logging corporations using spears and native weapons to taking up arms with the New Peoples Army as part of the decades long revolutionary struggle led by the Communist Party of the Philippines. The Lumad struggle continues to take many forms—and as state repression and encroachment on ancestral lands has worsened, Lumad resistance has continued to grow.
In October of 2016, the Lumad people sent messages of solidarity to the tribes and Water Protectors at Standing Rock as they clearly understood the universal common struggle of indigenous to protect the land.

In this moment of intense violence, the International Interfaith Humanitarian Mission 3.0 proposes the following recommendations for the victims of the military operations in Marawi City: Continue relief, medical services and psychosocial intervention for the victims; a just recovery and reparations for homes and properties destroyed; make the Duterte government accountable for the death, displacement of residents and destruction of Warawi City; put people over profit in the rehabilitation of Warawi so that the residents can return to their original communities not profit driven development.
Pam Tau Lee is Chair of the International Coalition for Human Rights in the Philippines (ICHRP) – U.S.













