by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Jan 12, 2018 | Agriculture, Building Alternatives
by Frances Moore Lappé / Local Futures
People yearn for alternatives to industrial agriculture, but they are worried. They see large-scale operations relying on corporate-supplied chemical inputs as the only high-productivity farming model. Another approach might be kinder to the environment and less risky for consumers, but, they assume, it would not be up to the task of providing all the food needed by our still-growing global population.
Contrary to such assumptions, there is ample evidence that an alternative approach—organic agriculture, or more broadly “agroecology”—is actually the only way to ensure that all people have access to sufficient, healthful food. Inefficiency and ecological destruction are built into the industrial model. But, beyond that, our ability to meet the world’s needs is only partially determined by what quantities are produced in fields, pastures, and waterways. Wider societal rules and norms ultimately shape whether any given quantity of food produced is actually used to meet humanity’s needs. In many ways, how we grow food determines who can eat and who cannot—no matter how much we produce. Solving our multiple food crises thus requires a systems approach in which citizens around the world remake our understanding and practice of democracy.
Today, the world produces—mostly from low-input, smallholder farms—more than enough food: 2,900 calories per person per day. Per capita food availability has continued to expand despite ongoing population growth. This ample supply of food, moreover, comprises only what is left over after about half of all grain is either fed to livestock or used for industrial purposes, such as agrofuels.1
Despite this abundance, 800 million people worldwide suffer from long-term caloric deficiencies. One in four children under five is deemed stunted—a condition, often bringing lifelong health challenges, that results from poor nutrition and an inability to absorb nutrients. Two billion people are deficient in at least one nutrient essential for health, with iron deficiency alone implicated in one in five maternal deaths.2
The total supply of food alone actually says little about whether the world’s people are able to meet their nutritional needs. We need to ask why the industrial model leaves so many behind, and then determine what questions we should be asking to lead us toward solutions to the global food crisis.
Vast, Hidden Inefficiencies
The industrial model of agriculture—defined here by its capital intensity and dependence on purchased inputs of seeds, fertilizer, and pesticides—creates multiple unappreciated sources of inefficiency. Economic forces are a major contributor here: the industrial model operates within what are commonly called “free market economies,” in which enterprise is driven by one central goal, namely, securing the highest immediate return to existing wealth. This leads inevitably to a greater concentration of wealth and, in turn, to greater concentration of the capacity to control market demand within the food system.
Moreover, economically and geographically concentrated production, requiring lengthy supply chains and involving the corporate culling of cosmetically blemished foods, leads to massive outright waste: more than 40 percent of food grown for human consumption in the United States never makes it into the mouths of its population.3
The underlying reason industrial agriculture cannot meet humanity’s food needs is that its system logic is one of disassociated parts, not interacting elements. It is thus unable to register its own self-destructive impacts on nature’s regenerative processes. Industrial agriculture, therefore, is a dead end.
Consider the current use of water in agriculture. About 40 percent of the world’s food depends on irrigation, which draws largely from stores of underground water, called aquifers, which make up 30 percent of the world’s freshwater. Unfortunately, groundwater is being rapidly depleted worldwide. In the United States, the Ogallala Aquifer—one of the world’s largest underground bodies of water—spans eight states in the High Plains and supplies almost one third of the groundwater used for irrigation in the entire country. Scientists warn that within the next thirty years, over one-third of the southern High Plains region will be unable to support irrigation. If today’s trends continue, about 70 percent of the Ogallala groundwater in the state of Kansas could be depleted by the year 2060.4
Industrial agriculture also depends on massive phosphorus fertilizer application—another dead end on the horizon. Almost 75 percent of the world’s reserve of phosphate rock, mined to supply industrial agriculture, is in an area of northern Africa centered in Morocco and Western Sahara. Since the mid-twentieth century, humanity has extracted this “fossil” resource, processed it using climate-harming fossil fuels, spread four times more of it on the soil than occurs naturally, and then failed to recycle the excess. Much of this phosphate escapes from farm fields, ending up in ocean sediment where it remains unavailable to humans. Within this century, the industrial trajectory will lead to “peak phosphorus”—the point at which extraction costs are so high, and prices out of reach for so many farmers, that global phosphorus production begins to decline.5
Beyond depletion of specific nutrients, the loss of soil itself is another looming crisis for agriculture. Worldwide, soil is eroding at a rate ten to forty times faster than it is being formed. To put this in visual terms, each year, enough soil is washed and blown from fields globally to fill roughly four pickup trucks for every human being on earth.6
The industrial model of farming is not a viable path to meeting humanity’s food needs for yet another reason: it contributes nearly 20 percent of all anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions, even more than the transportation sector. The most significant emissions from agriculture are carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide. Carbon dioxide is released in deforestation and subsequent burning, mostly in order to grow feed, as well as from decaying plants. Methane is released by ruminant livestock, mainly via their flatulence and belching, as well as by manure and in rice paddy cultivation. Nitrous oxide is released largely by manure and manufactured fertilizers. Although carbon dioxide receives most of the attention, methane and nitrous oxide are also serious. Over a hundred-year period, methane is, molecule for molecule, 34 times more potent as a heat-trapping gas, and nitrous oxide about 300 times, than carbon dioxide.7
Our food system also increasingly involves transportation, processing, packaging, refrigeration, storage, wholesale and retail operations, and waste management—all of which emit greenhouses gases. Accounting for these impacts, the total food system’s contribution to global greenhouse gas emissions, from land to landfill, could be as high as 29 percent. Most startlingly, emissions from food and agriculture are growing so fast that, if they continue to increase at the current rate, they alone could use up the safe budget for all greenhouse gas emissions by 2050.8
These dire drawbacks are mere symptoms. They flow from the internal logic of the model itself. The reason that industrial agriculture cannot meet the world’s needs is that the structural forces driving it are misaligned with nature, including human nature.
Social history offers clear evidence that concentrated power tends to elicit the worst in human behavior. Whether for bullies in the playground or autocrats in government, concentrated power is associated with callousness and even brutality not in a few of us, but in most of us.9 The system logic of industrial agriculture, which concentrates social power, is thus itself a huge risk for human well-being. At every stage, the big become bigger, and farmers become ever-more dependent on ever-fewer suppliers, losing power and the ability to direct their own lives.
The seed market, for example, has moved from a competitive arena of small, family-owned firms to an oligopoly in which just three companies—Monsanto, DuPont, and Syngenta—control over half of the global proprietary seed market. Worldwide, from 1996 to 2008, a handful of corporations absorbed more than two hundred smaller independent companies, driving the price of seeds and other inputs higher to the point where their costs for poor farmers in southern India now make up almost half of production costs.10 And the cost in real terms per acre for users of bio-engineered crops dominated by one corporation, Monsanto, tripled between 1996 and 2013.
Not only does the industrial model direct resources into inefficient and destructive uses, but it also feeds the very root of hunger itself: the concentration of social power. This results in the sad irony that small-scale farmers—those with fewer than five acres—control 84 percent of the world’s farms and produce most of the food by value, yet control just 12 percent of the farmland and make up the majority of the world’s hungry.11
The industrial model also fails to address the relationship between food production and human nutrition. Driven to seek the highest possible immediate financial returns, farmers and agricultural companies are increasingly moving toward monocultures of low-nutrition crops such as corn—the dominant US crop—that are often processed into empty-calorie “food products.” As a result, from 1990 to 2010, growth in unhealthy eating patterns outpaced dietary improvements in most parts of the world, including the poorer regions. Most of the key causes of non-communicable diseases are now diet-related, and by 2020, such diseases are predicted to account for nearly 75 percent of all deaths worldwide.12
A Better Alternative
What model of farming can end nutritional deprivation while restoring and conserving food-growing resources for our progeny? The answer lies in the emergent model of agroecology, often called “organic” or ecological agriculture. Hearing these terms, many people imagine simply a set of farming practices that forgo purchased inputs, relying instead on beneficial biological interactions among plants, microbes, and other organisms. However, agroecology is much more than that. The term as it is used here suggests a model of farming based on the assumption that within any dimension of life, the organization of relationships within the whole system determines the outcomes. The model reflects a shift from a disassociated to a relational way of thinking arising across many fields within both the physical and social sciences. This approach to farming is coming to life in the ever-growing numbers of farmers and agricultural scientists worldwide who reject the narrow productivist view embodied in the industrial model.
Recent studies have dispelled the fear that an ecological alternative to the industrial model would fail to produce the volume of food for which the industrial model is prized. In 2006, a seminal study in the Global South compared yields in 198 projects in 55 countries and found that ecologically attuned farming increased crop yields by an average of almost 80 percent. A 2007 University of Michigan global study concluded that organic farming could support the current human population, and expected increases without expanding farmed land. Then, in 2009, came a striking endorsement of ecological farming by fifty-nine governments and agencies, including the World Bank, in a report painstakingly prepared over four years by four hundred scientists urging support for “biological substitutes for industrial chemicals or fossil fuels.”13 Such findings should ease concerns that ecologically aligned farming cannot produce sufficient food, especially given its potential productivity in the Global South, where such farming practices are most common.
Ecological agriculture, unlike the industrial model, does not inherently concentrate power. Instead, as an evolving practice of growing food within communities, it disperses and creates power, and can enhance the dignity, knowledge, and the capacities of all involved. Agroecology can thereby address the powerlessness that lies at the root of hunger.
Applying such a systems approach to farming unites ecological science with time-tested traditional wisdom rooted in farmers’ ongoing experiences. Agroecology also includes a social and politically engaged movement of farmers, growing from and rooted in distinct cultures worldwide. As such, it cannot be reduced to a specific formula, but rather represents a range of integrated practices, adapted and developed in response to each farm’s specific ecological niche. It weaves together traditional knowledge and ongoing scientific breakthroughs based on the integrative science of ecology. By progressively eliminating all or most chemical fertilizers and pesticides, agroecological farmers free themselves—and, therefore, all of us—from reliance on climate-disrupting, finite fossil fuels, as well as from other purchased inputs that pose environmental and health hazards.
In another positive social ripple, agroecology is especially beneficial to women farmers. In many areas, particularly in Africa, nearly half or more of farmers are women, but too often they lack access to credit.14 Agroecology—which eliminates the need for credit to buy synthetic inputs—can make a significant difference for them.
Agroecological practices also enhance local economies, as profits on farmers’ purchases no longer seep away to corporate centers elsewhere. After switching to practices that do not rely on purchased chemical inputs, farmers in the Global South commonly make natural pesticides using local ingredients—mixtures of neem tree extract, chili, and garlic in southern India, for example. Local farmers purchase women’s homemade alternatives and keep the money circulating within their community, benefiting all.15
Besides these quantifiable gains, farmers’ confidence and dignity are also enhanced through agroecology. Its practices rely on farmers’ judgments based on their expanding knowledge of their land and its potential. Success depends on farmers’ solving their own problems, not on following instructions from commercial fertilizer, pesticide, and seed companies. Developing better farming methods via continual learning, farmers also discover the value of collaborative working relationships. Freed from dependency on purchased inputs, they are more apt to turn to neighbors—sharing seed varieties and experiences of what works and what does not for practices like composting or natural pest control. These relationships encourage further experimentation for ongoing improvement. Sometimes, they foster collaboration beyond the fields as well—such as in launching marketing and processing cooperatives that keep more of the financial returns in the hands of farmers.
Going beyond such localized collaboration, agroecological farmers are also building a global movement. La Via Campesina, whose member organizations represent 200 million farmers, fights for “food sovereignty,” which its participants define as the “right of peoples to healthy and culturally appropriate food produced through ecologically sound and sustainable methods.” This approach puts those who produce, distribute, and consume food—rather than markets and corporations—at the heart of food systems and policies, and defends the interests and inclusion of the next generation.
Once citizens come to appreciate that the industrial agriculture model is a dead end, the challenge becomes strengthening democratic accountability in order to shift public resources away from it. Today, those subsidies are huge: by one estimate, almost half a trillion tax dollars in OECD countries, plus Brazil, China, Indonesia, Kazakhstan, Russia, South Africa, and Ukraine.16 Imagine the transformative impact if a significant share of those subsidies began helping farmers’ transition to agroecological farming.
Any accurate appraisal of the viability of a more ecologically attuned agriculture must let go of the idea that the food system is already so globalized and corporate-dominated that it is too late to scale up a relational, power-dispersing model of farming. As noted earlier, more than three-quarters of all food grown does not cross borders. Instead, in the Global South, the number of small farms is growing, and small farmers produce 80 percent of what is consumed in Asia and Sub-Saharan Africa.17
The Right Path
When we address the question of how to feed the world, we need to think relationally—linking current modes of production with our future capacities to produce, and linking farm output with the ability of all people to meet their need to have nutritious food and to live in dignity. Agroecology, understood as a set of farming practices aligned with nature and embedded in more balanced power relationships, from the village level upward, is thus superior to the industrial model. This emergent relational model offers the promise of an ample supply of nutritious food needed now and in the future, and more equitable access to it.
Reframing concerns about inadequate supply is only the first step toward necessary change. The essential questions about whether humanity can feed itself well are social—or, more precisely, political. Can we remake our understanding and practice of democracy so that citizens realize and assume their capacity for self-governance, beginning with the removal of the influence of concentrated wealth on our political systems?
Democratic governance—accountable to citizens, not to private wealth—makes possible the necessary public debate and rule-making to re-embed market mechanisms within democratic values and sound science. Only with this foundation can societies explore how best to protect food-producing resources—soil, nutrients, water—that the industrial model is now destroying. Only then can societies decide how nutritious food, distributed largely as a market commodity, can also be protected as a basic human right.
This post is adapted from an essay originally written for the Great Transition Initiative.
Featured image: TompkinsConservation.org
Endnotes
1. Food and Agriculture Division of the United Nations, Statistics Division, “2013 Food Balance Sheets for 42 Selected Countries (and Updated Regional Aggregates),” accessed March 1, 2015, http://faostat3.fao.org/download/FB/FBS/E; Paul West et al., “Leverage Points for Improving Global Food Security and the Environment,” Science 345, no. 6194 (July 2014): 326; Food and Agriculture Organization, Food Outlook: Biannual Report on Global Food Markets (Rome: FAO, 2013), http://fao.org/docrep/018/al999e/al999e.pdf.
2. FAO, The State of Food Insecurity in the World 2015: Meeting the 2015 International Hunger Targets: Taking Stock of Uneven Progress (Rome: FAO, 2015), 8, 44, http://fao.org/3/a-i4646e.pdf; World Health Organization, Childhood Stunting: Context, Causes, Consequences (Geneva: WHO, 2013), http://www.who.int/nutrition/events/2013_ChildhoodStunting_colloquium_14Oct_ConceptualFramework
_colour.pdf?ua=1; FAO, The State of Food and Agriculture 2013: Food Systems for Better Nutrition (Rome: FAO, 2013), ix, http://fao.org/docrep/018/i3300e/i3300e.pdf.
3. Vaclav Smil, “Nitrogen in Crop Production: An Account of Global Flows,” Global Geochemical Cycles 13, no. 2 (1999): 647; Dana Gunders, Wasted: How America Is Losing Up to 40% of Its Food from Farm to Fork to Landfill (Washington, DC: Natural Resources Defense Council, 2012), http://www.nrdc.org/food/files/wasted-food-IP.pdf.
4. United Nations Environment Programme, Groundwater and Its Susceptibility to Degradation: A Global Assessment of the Problem and Options for Management (Nairobi: UNEP, 2003), http://www.unep.org/dewa/Portals/67/pdf/Groundwater_Prelims_SCREEN.pdf; Bridget Scanlon et al., “Groundwater Depletion and Sustainability of Irrigation in the US High Plains and Central Valley,” Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 109, no. 24 (June 2012): 9320; David Steward et al., “Tapping Unsustainable Groundwater Stores for Agricultural Production in the High Plains Aquifer of Kansas, Projections to 2110,” Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 110, no. 37 (September 2013): E3477.
5. Dana Cordell and Stuart White, “Life’s Bottleneck: Sustaining the World’s Phosphorus for a Food Secure Future,” Annual Review Environment and Resources 39 (October 2014): 163, 168, 172.
6. David Pimentel, “Soil Erosion: A Food and Environmental Threat,” Journal of the Environment, Development and Sustainability 8 (February 2006): 119. This calculation assumes that a full-bed pickup truck can hold 2.5 cubic yards of soil, that one cubic yard of soil weighs approximately 2,200 pounds, and that world population is 7.2 billion people.
7. FAO, “Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Agriculture, Forestry, and Other Land Use,” March 2014, http://fao.org/resources/ infographics/infographics-details/en/c/218650/; Gunnar Myhre et al., “Chapter 8: Anthropogenic and Natural Radiative Forcing,” in Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis (Geneva: Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, 2013), 714, http://www.ipcc.ch/pdf/assessment-report/ar5/wg1/WG1AR5_Chapter08_FINAL.pdf.
8. Sonja Vermeulen, Bruce Campbell, and John Ingram, “Climate Change and Food Systems,” Annual Review of Environment and Resources 37 (November 2012): 195; Bojana Bajželj et al., “Importance of Food-Demand Management for Climate Mitigation,” Nature Climate Change 4 (August 2014): 924–929.
9. Philip Zimbardo, The Lucifer Effect: Understanding How Good People Turn Evil (New York: Random House, 2007).
10. Philip Howard, “Visualizing Consolidation in the Global Seed Industry: 1996–2008,” Sustainability 1, no. 4 (December 2009): 1271; T. Vijay Kumar et al., Ecologically Sound, Economically Viable: Community Managed Sustainable Agriculture in Andhra Pradesh, India (Washington, DC: World Bank, 2009), 6-7, http://siteresources.worldbank.org/EXTSOCIALDEVELOPMENT/Resources/244362-1278965574032/CMSA-Final.pdf.
11. Estimated from FAO, “Family Farming Knowledge Platform,” accessed December 16, 2015, http://www.fao.org/family-farming/background/en/.
12. Fumiaki Imamura et al., “Dietary Quality among Men and Women in 187 Countries in 1990 and 2010: A Systemic Assessment,” The Lancet 3, no. 3 (March 2015): 132–142, http://www.thelancet.com/pdfs/journals/langlo/PIIS2214-109X%2814%2970381-X.pdf.
13. Jules Pretty et al., “Resource-Conserving Agriculture Increases Yields in Developing Countries,” Environmental Science & Technology 40, no. 4 (2006): 1115; Catherine Badgley et al., “Organic Agriculture and the Global Food Supply,” Renewable Agriculture and Food Systems 22, no. 2 (June 2007): 86, 88; International Assessment of Agricultural Knowledge, Science and Technology for Development, Agriculture at a Crossroads: International Assessment of Agricultural Knowledge, Science and Technology for Development (Washington, DC: Island Press, 2009).
14. Cheryl Doss et al., “The Role of Women in Agriculture,” ESA Working Paper No. 11-02 (working paper, FAO, Rome, 2011), 4, http://fao.org/docrep/013/am307e/am307e00.pdf.
15. Gerry Marten and Donna Glee Williams, “Getting Clean: Recovering from Pesticide Addiction,” The Ecologist (December 2006/January 2007): 50–53,http://www.ecotippingpoints.org/resources/download-pdf/publication-the-ecologist.pdf.
16. Randy Hayes and Dan Imhoff, Biosphere Smart Agriculture in a True Cost Economy: Policy Recommendations to the World Bank (Healdsburg, CA: Watershed Media, 2015), 9, http://www.fdnearth.org/files/2015/09/FINAL-Biosphere-Smart-Ag-in-True-Cost-Economy-FINAL-1-page-display-1.pdf.
17. Matt Walpole et al., Smallholders, Food Security, and the Environment (Nairobi: UNEP, 2013), 6, 28, http://www.unep.org/pdf/SmallholderReport_WEB.pdf.

by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Jan 11, 2018 | The Problem: Civilization
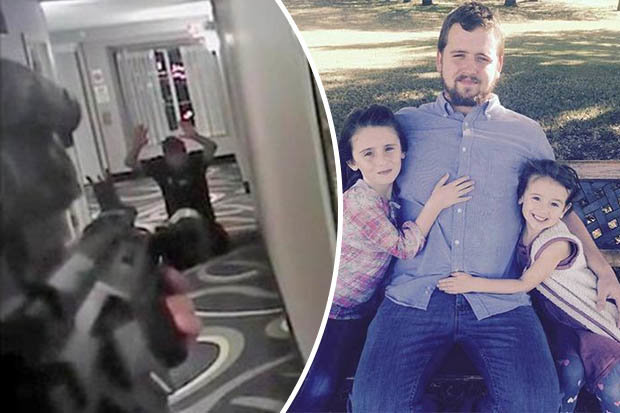
Featured image: Police cam video of Daniel Shaver (pictured at right with his daughters) just before being killed by Mesa, Arizona Police Department officer Philip Brailsford. Brailsford was acquitted of second-degree murder in the case.
by Pray for Calamity
Cold air bites at the tip of my nose and the upper rim of my ears as I crunch across the driveway to the wood pile. Pulling from a rick consisting mostly of ash, I load my arms. We burned through the last rick of wood too quickly. Subzero temperatures moved in right after the winter solstice, and for weeks they held strong, the winds at night drawing the heat from our cabin through every crack and seam. Wool blankets cover the windows, and we trade light for heat. At night we nestle into our bed as a family, buried under our down comforter, which can effectively create an ecosystem all its own. Before sunrise though, I will feel my cheeks getting cold, and I will head to the kitchen to find the last embers of the fire on the verge of extinguishing. In the dark I will snap small sticks with my hands, then feed them into the steel belly of the woodstove, and layer split wood on top of that. I wait, watching, listening. When I am sure that the fire has taken, I head back towards bed with the orange flicker lighting the way.
—
The year has rolled over on the calendars of western humans, and the northern hemisphere has had its shortest day in this particular planetary revolution around the sun. It is a time of transitions and resolutions, reflections of the year passed and goals laid out for the year to come. Personally, I feel that we are in a time of exposure. Open secrets once whispered and acknowledge but never loudly spoken are no longer able to be contained. An obvious example of this is the so-called “me too” movement in which powerful men in politics and entertainment who used their status to sexually assault others were publicly exposed, which then blew open the door for women in a variety of industries and lifestyles to report on the bosses and colleagues who used their positions as leverage to seek and sometimes force sexual attention. Basically, a lot of men in a lot of places of power have been using that power to harass and assault women (and yes, sometimes other men) and a lot of dirty laundry has been aired all at once.
Open secrets are not uncommon in our society. Uncomfortable truths that we all come to know, but fear to speak about lest our murmurings disturb the delicate balance of our universe, and tip the whole order into disarray. One of these open secrets that is getting more and more attention is the fact that the police in the United States are arguably a bigger threat to many people than criminals. With nary a legal or civil consequence for their actions to be had, police killed another thousand or so Americans in 2017. The case of former Mesa, Arizona cop Philip Brailsford being acquitted of murdering Daniel Shaver attracted a lot of attention after the body cam video of the event was released, and the general public viewed what was essentially a snuff film with horror, aghast as Brailsford smugly derided the weeping father Shaver who begged for his life before being murdered. Most of the population now accepts that the police and justice systems by and large treat black Americans far differently, and far worse, than they treat white Americans.
Of course, when a nasty truth comes to light, especially a truth that cuts right through the heart of a person’s – or nation’s – identity, there are those who will flat refuse to believe it. In the case of the many exposed men who have been accused of sexual assault and rape, there are cadres of defenders who nit-pick each case looking to find where the accuser is either lying, or perhaps sought or deserved her treatment. It is just so with the issue of police in America. With each new horror show of a news story, even those complete with heartbreaking video as in the case of Daniel Shaver, there are defenders of the system, professional analyzers who find the moment the victim screwed up by not, in their moments of terror, following some command or by having made some innocuous and unconscious movement of the hand. Then they scream, “See! He deserved to die!”
To these reactionaries desperate to believe that everything is OK, women who are abused and harassed by their bosses and colleagues deserve it if they ever take a meeting with a man alone, and untrained and fearful civilians must act with professional precision while teams of academy graduates laden with military firearms and earning a government wage can ignore standards and statutes alike while engaging in murderous street justice.
However, if we believe all these stories of rape and assault, we then have to start examining our culture and try to understand their source. If we believe that the police are racist and unnecessarily violent and murderous, then we have to start examining our culture and try to understand why. Such digging leads to dangerous places for the egos and identities of many. Our lies are pillars that hold up entire institutions and ways of viewing ourselves and the world around us. We have cursed and damned so many people to live out their days in slums or cages, if we haven’t just flat out killed them. If these sentences of impoverishment, imprisonment, and death were all the extension of a society built on lies, then that would make us some pretty terrible people.
Yes, better to not look down that well.
—
I find myself in a bookstore fairly regularly, and I have noticed that over the past few years, there has been significant growth in the survival magazine market. Of course, there are the homestead magazines, the gardening magazines, the hunting magazines, and the straight up gun fetish magazines, but then the other day I noticed something new. It was a magazine that had on its cover a man, a boy, and a woman, all presumably a family. They carried packs, radios, and firearms. A setting sun painted their faces a golden hue, or who knows, maybe it was a distant nuclear blast, as they stood near a ruined vehicle in some scrubland. The father was handsome with chiseled cheek bones, and the lightest Hollywood smattering of dirt across his brow. In true marketing fashion, this was a magazine with a good looking family surviving a civilization-ending EMP blast, bug out bags in tow.
Seeing this I thought to myself that I think it is basically an open secret now that our society is fucked. We are fucked, and no one is coming to save us. Things are going to get steadily worse and worse until the entire façade of civil life breaks into a series of dysfunctional pieces, and deep down, everybody knows it.
A few weeks ago a friend came over to my house, and as she helped me truck firewood from the front of our land to the house, I made a comment about this to test my theory. I cannot now remember how I snuck it into the conversation, but at some point I said, “We’re fucked,” in regards to the future stability of our climate and the world of human comings and goings. She looked at me with a light, knowing smile, and very sincerely said, “Oh yeah.” I might as well have told her that the sun would set.
Of course, my friends are not exactly going to be a random sampling of the population, and they are all going to fall under an umbrella of social consciousness and ecological concern, to be sure, but the increase in television shows, magazines, and books that all orbit the topic of surviving the collapse of society, to me, is telling. For now, we can treat the topic with a bit of irony should we not find ourselves in like company, and laugh at the commercial selling dehydrated beef stroganoff that one can store in their closet for emergencies.
But the idea is out there. Years’ worth of promised solutions to energy and ecological woes have not been delivered. The fires are worse, the floods are more frequent, and still the powers that be are drilling and scraping for every last bit of hydrocarbon. I think most people assumed that somewhere, some group of serious people was laying out the roadmap of transition, and making sure that it would be implemented. The consequences are rolling in as expected, but the global solutions are nowhere to be found. A few companies absorb government subsidies and put out press releases to keep the investors chomping at the bit, but a look around does not show me a world much different than the one in which I walked as a child thirty years ago.
If it becomes understood that this society as it exists has no future, that would mean we have to ask ourselves serious questions about how, or if, we are going to survive. That is a deep, black well indeed.
—
With a night rain came warm air. Gray morning light expands through the wood revealing a half decayed carpet of leaves. Only islands of snow remain, and they are thin and vulnerable. I have eagerly awaited this warm front. The straw in duck and chicken houses needs tossing, and when out in the animal yards I begin to survey first the damage; a plastic rain collection barrel has burst at its base. Then I look to the work; scraping away the ground in front of every gate and door, as the heave of frozen Earth has made opening and closing most of them quite difficult, and no fix was to be had during zero range temperatures.
Animal gates and hen house doors that cannot be closed again once open are not a problem that can be ignored. Raccoons and foxes are particularly hungry this time of year, I can only imagine. A day or two above freezing are opportunities not to be squandered. Winter is only beginning.

by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Jan 10, 2018 | Human Supremacy
Featured image: Real freedom is not found in the quest to escape limits but in deepening our understanding of our place in a world with limits. EATCUTE / GETTY IMAGES
by Robert Jensen
In a routinely delusional world, what is the most dangerous delusion?
Living in the United States, I’m tempted to focus on the delusion that the United States is the greatest nation in the history of the world – a claim repeated robotically by politicians of both parties.
In a mass-consumption capitalist society, there’s the delusion that if we only buy more, newer, better products we all will be happier – a claim repeated endlessly in commercial propaganda (commonly known as advertising and marketing).
I’m also white, and so it’s understandable to worry about the delusion that white people are superior to non-white people. And as a man, I reflect on the delusion that institutionalized male dominance is our fate, whether asserted to be divinely commanded or evolutionarily inevitable.
But all these delusions that rationalize hierarchies within the human family, and the resulting injustices that flow from those hierarchies, are less frightening to me than modern humans’ delusion that we are not bound by the laws of physics and chemistry, that humans can live beyond the biophysical limits of the ecosphere.
This delusion is not limited to one country, one group, or one political party, but rather is the unstated assumption of everyday life in the high-energy/high-technology industrial world. This is the delusion that we are – to borrow from the title of a particularly delusional recent book – the god species.
This ideology of human supremacy leads us to believe that our species’ cleverness allows us to ignore the limits placed on all life forms by the larger living world, of which we are but one component. What we once quaintly called “environmentalism” – which too often focused on technical solutions to discrete problems rather than challenging human arrogance and the quest for endless affluence – is no longer adequate to deal with the multiple, cascading ecological crises that define our era: climate destabilization, species extinction, soil erosion, groundwater depletion, toxic waste accumulation, and on and on.
Playing god got us into this trouble, and more of the same won’t get us out.
This inability to accept the limits that come with being part of “nature” – a strange term when used to contrast with “human,” as if humans were somehow not part of the natural world – was on my mind as I read two new books about controversial topics that typically are thought of as social, not ecological, issues: Transgender Children and Young People: Born in Your Own Body, edited by Heather Brunskell-Evans and Michele Moore, and Surrogacy: A Human Rights Violation, by Renate Klein.
Both books offer a feminist critique of the ideology and practices of these movements that herald medical/technological “solutions” to struggles with gender norms and infertility.
Brunskell-Evans’ and Moore’s book brings together researchers, activists, mental health practitioners and parents who question such practices as puberty suppression to block the development of secondary sex characteristics as treatment for gender dysphoria. Are such disruptions of a child’s development with powerful drugs warranted, given the lack of testing and absence of a clear understanding of the etiology of transgenderism? The authors challenge what has rapidly become the liberal dogma of embracing medicalized approaches to the very real problem of patriarchal gender norms (the demand that boys must act one way and girls another) that constrain our lives.
Klein marshals research and the testimony of surrogates to point out that another liberal dogma – affluent individuals have a right to “rent a womb” so they may have a child genetically related to them – involves considerable risks for the surrogate mother (sometimes referred to as the “gestational carrier”). The author’s assessment is blunt, but well supported: modern surrogacy is a form of exploitation of women and trafficking in babies.
Both books demonstrate the enduring relevance of the radical branch of feminism that highlights men’s attempts to control and exploit women’s reproductive power and sexuality as a key feature of men’s dominance in patriarchal societies. And both are critical of the naive celebration of high-tech medicine to deal with issues that stem from patriarchy’s rigid, repressive and reactionary gender norms.
Those radical feminist challenges dovetail with a radical ecological critique that reminds us that being alive – being a carbon-based creature that exists within the limits of the ecosphere – means that we should be sceptical of claims that we can magically transcend those limits. The high-energy, high-tech, human-defined world in which we live can lull us into believing that we are like gods in our ability to shape the world, and to shape our own bodies.
Of course, drugs, surgery and medical techniques routinely save lives and improve our lives, in ways that are “unnatural” in some sense. To highlight these questions does not mean that lines are easy to draw between what is appropriate and what is ill-advised. But we invite serious miscalculations when we embrace without critical self-reflection the assumption that we can manipulate our human-centred worlds without concern for the limits of the larger living world.
Many of us have experienced this in end-of-life care decisions for ourselves or loved ones. When are high-tech medical interventions that prolong life without concern for quality of life a mistake? I have had long conversations with friends and family about where the line should be drawn, not only to make my own views clear but to search for collective understanding. The fact that the line is hard to draw, and even harder to face when arriving at it, doesn’t make the question any less relevant. The fact that there is no obvious and easy answer doesn’t mean we can avoid the question.
Elective cosmetic surgery is perhaps the best example of the culture’s rejection of limits. All living things eventually die, and human appearance changes as we age, yet many people search for ways to stave off that aging or to change their appearance for other non-medical reasons. In 2017, Americans spent more than $15 billion on cosmetic procedures (surgical and nonsurgical), 91% of which were performed on women. The two most common surgical procedures are liposuction and breast augmentation. Although some people who get liposuction are overweight, it is not a treatment for obesity, and breast augmentation is rarely related to physical health. These procedures typically are chosen by people seeking to conform to social norms about appearance.
With this humility about high-tech human intervention in mind, how should we understand the experience of feeling at odds with gender norms? How should we reconcile the physical inability to bear children with the desire to have children? There are no obvious or easy answers, but I believe that as a culture we are better served by starting with the recognition that we are not gods, that we cannot endlessly manipulate the world without risking unintended consequences for self and others. How does the rejection of limits impede our ability to first examine and then resist the impositions of patriarchy, to find new understandings of sex/gender and new social relationships for caring for children?
At the planetary level, we have considerable evidence that our faux-god attempts to dominate the ecosphere – which started most dramatically with the invention of agriculture 10,000 years ago and intensified with the exploitation of fossil fuels – now make the future of a large-scale human population uncertain. The lesson some of us take from that is to turn away from the “technological fundamentalism” that leads us to see all problems as having high-energy/high-tech solutions and consider different ways of living within the biophysical limits of the planet.
That same perspective is compelling on the level of these questions around gender and fertility. Here’s a sensible place to start: We should step back from the hyper-individualism of neoliberal ideology and examine more deeply how the institutionalized male dominance of patriarchy has shaped our collective thinking about gender and identity, and about women’s status and parenting. Such reflection reveals that the liberal ideology on transgenderism and surrogacy embraces the technological fundamentalism that embraces medical and market “solutions” rather than enhancing the sense of integrity that we seek.
Integrity is a key concept here because of its two meanings – adherence to moral principles and the state of being whole. We strive to act with integrity, and to maintain the integrity of both the living body and the larger living world. In hierarchical systems that reward domination, such as patriarchy, freedom comes to be understood only at the ability to control, others and the world around us. Andrea Dworkin captures this struggle when she writes:
“Being an object – living in the realm of male objectification – is abject submission, an abdication of the freedom and integrity of the body, its privacy, its uniqueness, its worth in and of itself because it is the human body of a human being.”
Freedom in patriarchy is granted only to those in control, and that control turns other living things into objects, destroying the possibility of integrity-as-moral-principles and integrity-as-wholeness. Real freedom is not found in the quest to escape limits but in deepening our understanding of our place in a world with limits.
Robert Jensen is a professor in the School of Journalism at the University of Texas at Austin and the author of The End of Patriarchy: Radical Feminism for Men.
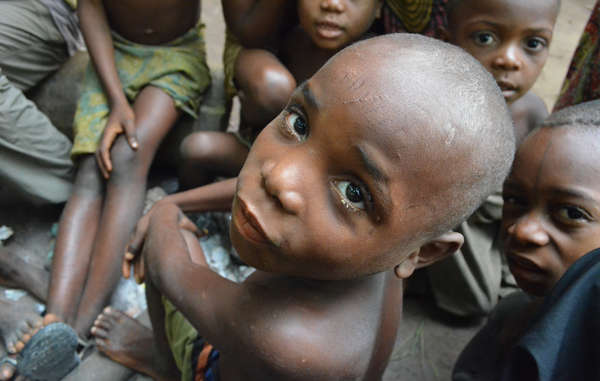
by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Jan 8, 2018 | Colonialism & Conquest
Featured image: A recent epidemic in the Republic of Congo is said to have been aggravated by the loss of indigenous peoples’ resources due to conservation and logging projects. © C. Fornellino Romero/Survival International
by Survival International
A Congolese organization has recently raised concerns that conservation contributed to the deaths of several dozen children, mostly Bayaka “Pygmies,” during an epidemic in 2016 in the Republic of Congo – the latest in a long line of related reports.
The deaths have been attributed by a medical expert to malaria, pneumonia and dysentery, aggravated by severe malnutrition.
Conservation-related malnutrition among Bayaka children in this region has been reported since 2005 at least, as the Bayaka are prevented from hunting and gathering on their lands by wildlife guards through violence and intimidation.
These guards are funded and equipped by the Wildlife Conservation Society (WCS), one of the world’s largest conservation organizations, and the logging company it has partnered with, CIB. Both organizations have failed to take effective action to prevent abuse.
“The wildlife guards abuse us. They don’t want us to go into the forest. How can we feed our children?” a Bayaka man from Mbandza, the site of the epidemic, told Survival in 2016.
These guards have been accused of abusing Bayaka and stealing their food for over 13 years. One such attack that took place in Mbandza in early 2016 left one man hospitalized.

The Baka and Bayaka’s consent is required by law for any major project on their lands, but this is ignored by WWF and WCS. © Survival International
In this way, the Bayaka are being illegally evicted from their ancestral homelands by threat of violence. As one Bayaka woman explained: “If we go into the forest we eat well there compared to the village. We eat wild yams and honey. We want to go into the forest but they forbid us to. It frightens us. It frightens us.”
Critics have noted that the guards have also failed to protect the wildlife the Bayaka depend on for food, since they have difficulty tackling corruption and the creation of logging roads, the two main drivers of poaching.
Plummeting health has been reported among Bayaka living in the Dzanga-Sangha Protected Areas in the Central African Republic – one of the World Wildlife Fund’s (WWF) flagship projects – since 2006. Conditions encountered among older women “would be considered a public health crisis by international health agencies,” according to research published in 2016.
Increased malnutrition and mortality have been reported among Baka “Pygmies” in Cameroon, where WWF also operates, and among Batwa “Pygmies” in another of WCS’s project sites in east Democratic Republic of Congo.
“Now we are afraid of the anti-poaching squads. Before when a woman gave birth we took her to the forest to help her regain her strength and weight, now we can’t do this. We would take our children to the forest to avoid epidemics. Now we know illnesses we never knew before,” one Baka woman in Cameroon told Survival.
Watch Baka describe the abuse they face as a result of WWF’s conservation projects
Baka health plummets due to conservation
In the Congo Basin, the Baka, Bayaka and dozens of other rainforest peoples are being illegally evicted from their ancestral homelands in the name of conservation. Their health is plummeting as a result.
The big conservation organizations that support these conservation projects, like the World Wildlife Fund (WWF), refuse to abide by basic international standards and secure their consent.
Neither WCS nor WWF has attempted to secure the indigenous peoples’ consent, as basic due diligence and their own human rights policies require.
Survival’s Director Stephen Corry said: “Land theft is a serious and deadly crime, as these reports show. Many associate conservation with reason and compassion but, for Baka and Bayaka, it often means mindless violence and plummeting health. When will WWF and WCS finally start complying with their own human rights policies? ”
Timeline
1996: The organization Berggorilla & Regenwald Direkthilfe finds that malnutrition and mortality has increased among Batwa “Pygmies” since they were evicted from Kahuzi-Biega, a national park in east Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) funded by WCS.
1997: WWF observes that the fact that the Bayaka are banned from hunting or gathering inside the Dzanga-Ndoki Park, the park in the Central African Republic (CAR) that WWF helped to create, “punishes [the Bayaka] severely” and is undermining their food security.
2000: A study finds that the Batwa in Kahuzi-Biega, DRC, are suffering from nutritional deficiencies, because they are no longer able to hunt in the forest, and soaring mortality rates. Malnutrition is particularly pronounced among women and children.
2004: A BBC investigation into CIB’s logging concessions in Congo hears from a Bayaka man: “We get so much suffering because of [wildlife] guards. We can’t go and find things in the forest as we used to. All we hear is hunger.”
2004: Bayaka from another community in Congo report to Greenpeace: “Then we met another white man (WCS) who came to tell us to stop hunting and that the wildlife guards would make sure we did. Now we are afraid to go far in the forest in case the wildlife guards catch us so we have to stay in the village. […] Now we are dying of hunger.”
2005: The Congolese Observatory on Human Rights, the organization that reported on the 2016 epidemic, documents three cases of violent abuse against Bayaka by wildlife guards, and warns that some Bayaka “are dying of hunger.”
2005: A news report recounts how Bayaka in one of CIB’s logging concessions describe being targeted by wildlife guards that mistreat and temporarily imprison them, and how this has led to more frequent malnutrition among children and vulnerable adults.
2006: WWF and its partners commission a report that finds that the Bayaka in Dzanga-Sangha, CAR, are struggling to feed themselves. The Bayaka interviewed for the report state that the conservation project has forced them out of some of their richest hunting and gathering grounds. They report that wildlife guards harass or attack them even when they try to use the reduced areas of land they have left, all the while accepting bribes from the real poachers who were emptying the forest of its wildlife. Some Bayaka women are finding it so hard to find food, the investigator hears, that they have been driven to sex work in the nearby town.
2006: An article in The Lancet cautions that “Pygmy peoples’ health risks are changing as the central African forests, which are the basis for their traditional social structure, culture, and hunter-gatherer economy, are being destroyed or expropriated by […] conservation projects:”
2008: UNICEF warns that the Bayaka’s right to gather resources is being “flouted on the most basic level because indigenous people no longer have access to areas rich in game” due to protected areas in Congo.
2012: An anthropologist with 18 years’ experience working with Bayaka in Congo reports increasingly poor nutrition and increased mortality. He attributes this to the removal of forest resources by loggers and to “conservationists’ exclusionary and draconian management practices.”
2013: A researcher at the University of Oxford reports that the combined impact of conservation and logging have led to poorer health and higher levels of drug and alcohol addiction among the Bayaka. He argues that conservation efforts would benefit from gaining people’s consent
2014: A medical study finds that “punitive anti-poaching measures” and dwindling wildlife have caused health to plummet among Bayaka in Dzanga-Sangha, CAR, particularly among women. “It is disheartening to see health decline so closely tied […] to the conservation management policies of the last twenty-five years,” the study’s authors note.
2015: A doctor with extensive experience working in CIB’s logging concessions reports that: “Aside from wounds inflicted by gorillas, buffalo or other wild animals, my colleague and I also see [gun] wounds in people claiming to have been attacked – sometimes without warning – by the protectors of wildlife: the wildlife guards.”
2015: The same doctor tells Survival: “I find this [wildlife guard violence] a very serious problem and in my opinion most wildlife guards have other motives than protecting the animals to work as a wildlife guard.”
2016: A second doctor with extensive experience working in CIB’s logging concessions describes to Survival the seasonal malnutrition she encounters among Bayaka, which she attributes to repressive conservation policies.
“Pygmy” is an umbrella term commonly used to refer to the hunter-gatherer peoples of the Congo Basin and elsewhere in Central Africa. The word is considered pejorative and avoided by some tribespeople, but used by others as a convenient and easily recognized way of describing themselves.

by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Jan 7, 2018 | Biodiversity & Habitat Destruction
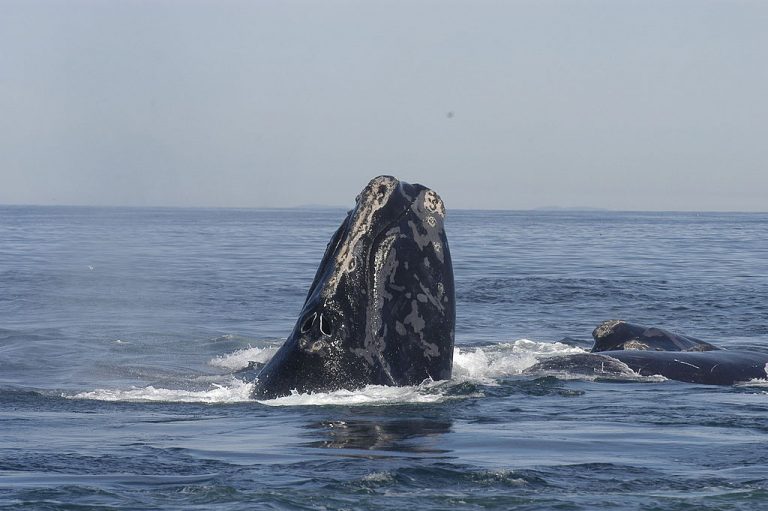
Featured image: The critically endangered North Atlantic right whale is a species of utmost concern should seismic airgun blasting be allowed off the Atlantic coast. Photo Credit: Moira Brown and New England Aquarium.
by Mike Gaworecki / Mongabay
The Trump Administration has unveiled its plan to open nearly all of the United States’ coastal waters to oil and gas drilling.
U.S. Secretary of the Interior Ryan Zinke announced the National Outer Continental Shelf Oil and Gas Leasing Program for 2019-2024 yesterday, which includes a proposal to open up more than 90 percent of the country’s continental shelf waters to future exploitation by oil and gas companies. The draft five-year plan also proposes the largest number of offshore oil and gas lease sales in U.S. history.
“Responsibly developing our energy resources on the Outer Continental Shelf in a safe and well-regulated way is important to our economy and energy security, and it provides billions of dollars to fund the conservation of our coastlines, public lands and parks,” said Secretary Zinke. “Today’s announcement lays out the options that are on the table and starts a lengthy and robust public comment period. Just like with mining, not all areas are appropriate for offshore drilling, and we will take that into consideration in the coming weeks.”
The Obama Administration blocked drilling on about 94 percent of the outer continental shelf, but, in April 2017, Trump issued an executive order that called for a review of the 2017-2022 Five Year Outer Continental Shelf Oil and Gas Leasing Program finalized under Obama in favor of implementing Trump’s so-called “America-First Offshore Energy Strategy.”
The draft five-year plan that has just been released by the Trump Administration’s Interior Department would open up 25 of 26 outer continental shelf regions to drilling. The North Aleutian Basin, which lies off the northern shore of the Alaska Peninsula and extends into the Bering Sea, was the only region exempted from drilling in the new plan, the New York Times reports.
The Interior Department proposes to hold 47 lease sales in those 25 regions — including 19 off the coast of Alaska, 12 in the Gulf of Mexico, nine in the Atlantic Region, and seven in the Pacific Region. “This is the largest number of lease sales ever proposed for the National [Outer Continental Shelf] Program’s 5-year lease schedule,” the Interior Department said in a statement.
Earlier moves by the Trump Administration to open the U.S. Atlantic coast to drillinghave already drawn fierce opposition. An alliance of more than 41,000 businesses and 500,000 fishing families from Florida to Maine was joined by fishery management councils for the Mid-Atlantic, New England, and the South Atlantic regions in speaking out against oil exploration and development in the Atlantic. One of their chief concerns is the incredibly disruptive exploration technique known as seismic airgun blasting, which would need to be used to determine how much oil is actually underneath the floor of the Atlantic Ocean off the U.S. East Coast given that oil drilling has been banned there for decades.
Drilling in the Pacific Ocean off the U.S. West Coast has been banned since a 1969 oil spill in Santa Barbara, California. Local officials there also vowed to fight the Trump Administration’s move to open their coastal waters to the oil and gas industry: “For more than 30 years, our shared coastline has been protected from further federal drilling and we’ll do whatever it takes to stop this reckless, short-sighted action,” California Governor Jerry Brown, Oregon Governor Kate Brown, and Washington Governor Jay Inslee said in a joint statement.
Continue reading at Mongabay

by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Jan 4, 2018 | Colonialism & Conquest
Featured image: This Baiga woman was evicted from Kanha tiger reserve. © Survival International
by Survival International
India’s National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) is coming under increasing pressure over its illegal order banning the recognition of tribal forest rights in tiger reserves. The order prompted Survival International to launch a global tourism boycott in November.
Information released to Survival has revealed that India’s tribal peoples’ Commission (officially called the National Commission for Scheduled Tribes (NCST)) has directly challenged the NTCA’s order in private meetings in Delhi. The Commission demanded that the NTCA suspend any planned evictions of tribal peoples, who have been dependent on and managed their forests for millennia.
After demanding to meet with the NTCA, the Commission argued that the order violates India’s Forest Rights Act – which guarantees tribal peoples’ rights to their forests. It was intended to address the “historical injustice” against tribes and other “traditional forest dwellers.”
In November, representatives of tribal communities met with many human rights and environment activists in Delhi, amidst mounting concern over the NTCA order.

A Baiga woman works for daily wages on Vedanta’s Bodai-Daldali bauxite mine, Chhattisgarh © Sayantan Bera/Survival
J.K. Thimma, a Jenu Keruba man who lives in Nagarhole National Park, and was present at the meeting, said: “The NTCA order is an attack against our culture and our tradition. This is anti-Constitutional and the NTCA have no right to stop the implementation of an Act passed by the Parliament… This is denial for our existence. The order needs to be withdrawn as soon as possible, it is creating fear among all of us.”
Another tribal man, Shankar Barde from Tadoba Tiger Reserve, said: “After years of restrictions and hardships, finally we were told early this year by the district administration that our rights have been recognized. We were excited… but then we were told by the district administration that NTCA order does not allow our rights to be recognized. This is a complete injustice. Dozens of outsiders are earning large sums of money in our backyard while we struggle to even live with dignity.”
Indian law specifically states that the NTCA does not have the power to “interfere with or affect the rights of local people, particularly… tribes.” Tribal rights are under the jurisdiction of the Ministry of Tribal Affairs.
Despite this, conservation authorities have violated the rights of tribal peoples. Across India, tribal peoples endure harassment, coercion, and illegal eviction from their ancestral homelands in the name of conservation.

Baiga children. Their village was notified with eviction. Achanakmar Tiger Reserve. © Survival
After eviction, tribal people face lives of poverty and exclusion on the fringes of Indian society. Meanwhile, huge numbers of tourists are then invited into tiger reserves, disrupting tiger habitats and making tigers more vulnerable to poaching.
Survival International is leading the global fight against injustice and abuse in the name of protecting wildlife.
Survival’s Director Stephen Corry said: “This order is an attack on India’s tribal peoples – it’s also illegal. Polluting and destructive industries such as uranium mining and tourism are apparently welcome in tiger reserves, but conservationists in India remain determined to kick tribal people off their land. It’s time they partnered with the best conservationists and guardians of the natural world, and stopped persecuting them. Tribal peoples know their land and its animals better than the conservationists.”








