
by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Apr 27, 2016 | Biodiversity & Habitat Destruction, Strategy & Analysis
By Zoe Blunt / WildCoast.ca
“I’m in love. With salmon, with trees outside my window, with baby lampreys living in sandy streambottoms, with slender salamanders crawling through the duff. And if you love, you act to defend your beloved.” — Derrick Jensen
Pacific Coast people have always defended the places we love. Most of British Columbia is unceded indigenous land; native peoples have never abandoned, sold, or traded their land away. Many fought fiercely against the power of the British Empire. Cannonballs are sometimes still found embedded in centuries-old trees along the shore – leftovers from the gunboats that tried to suppress indigenous uprisings in the late 1800s.

Nuu-chah-nulth war canoes (Edward Curtis, BC Historical Society)
A century later, descendants of the settlers have joined forces to battle corporate raiders. In the 1980s and 1990s, a groundswell of eco-organizing brought thousands of people together to stop clearcut logging in the cathedral forests of Vancouver Island’s Pacific coast, where timber companies were busy converting ten-thousand-year-old ecosystems into barren stumpfields and pulp for paper.
During those years, police arrested hundreds in Clayoquot Sound and the Walbran Valley at mass civil disobedience protests. Young and old alike sat in the middle of the logging roads and linked arms. The resistance went far beyond the peaceful and symbolic: unknown individuals spiked thousands of trees to make the timber dangerous to sawmills. Shadowy figures burned logging bridges and vandalized equipment. The skirmishes went on for over a decade.
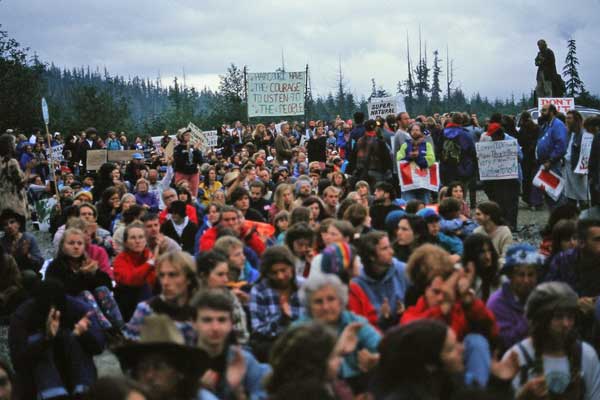

Clayoquot Sound, 1993
We won a few battles. Several coastal valleys are protected as parks. But many of them have been logged. And now the logging companies are coming back for the valleys that remain unprotected.
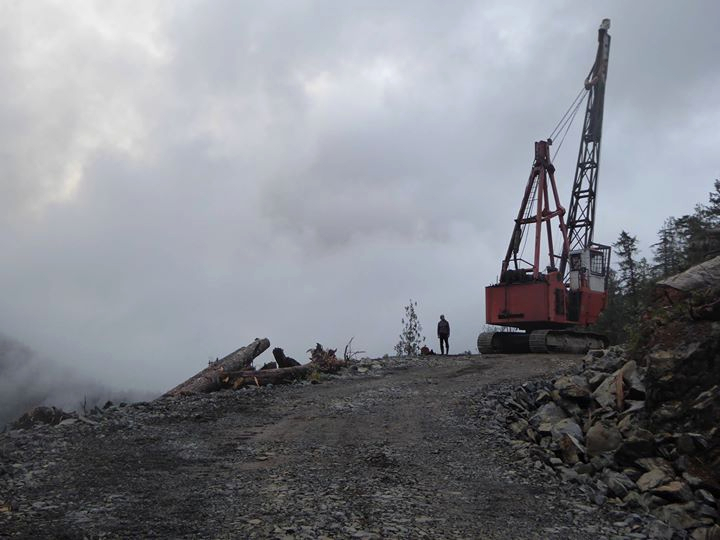
One of the worst corporate offenders is Teal Jones, the company currently bulldozing the majestic Walbran Valley, two hours west of Victoria, BC. They are laying waste to a vibrant rainforest for short-term profit, without the consent of the Pacheedaht First Nation, the Qwa-ba-diwa people, or anyone else outside of government and industry. Teal Jones does not even own the land; it was taken from indigenous people in the name of the BC government sixty years ago.
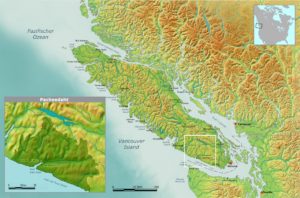
Pacheedaht territory, Vancouver Island BC
This year, the elected leadership of the Pacheedaht First Nation threw its support behind building a longhouse in the contested valley, on the land that has sustained them for countless generations. At the same time, locals are pushing back against the logging by occupying roads and logging sites. This in spite of the company’s court order telling police to arrest anyone who blocks their work. Forest defenders are regrouping, but the destruction continues.
Women for the Walbran and Forest Action Network are ramping up to break the deadlock. We’re hosting direct action trainings to share skills and develop strategies for defending ecosystems. The agenda includes tactics like non-violent civil disobedience, occupying tree-tops, and backcountry stealth. We’ll have info on legal rights, indigenous solidarity, and more.

Tree-sit occupation, Langford BC. (Photo: Ingmar Lee)
Our adversary, Teal Jones, is a relatively small company. Its owners are relying on the police to protect their “right” to strip public forests on Pacheedaht traditional territory. Profit margins are slim, and lawyers are expensive. The forest defenders are poor, but we have community support and a wide array of strategies for beating Teal Jones at its own game. Every tool in the box: we can launch a mass civil disobedience campaign, carry out hit-and-run raids on costly machines, coordinate a knockout legal strategy, or deliver the tried-and-true “death by a thousand cuts” with a combination of tactics.
However it plays out, Teal Jones is on borrowed time in the Walbran. But that’s cold comfort when the machines are mowing down thousand-year-old forests like grass.

Photo: Walbran Central
The forest defenders do have certain advantages. On the practical side, we’re investing in the gear and training that will provide the leverage to win. We have a legal defense fund that’s both a war chest for litigation and a safety net for those who risk their freedom on the front lines. But our best defense is the thousands of people who love this land like life itself. Many live nearby and visit every chance they get, others came once and fell in love, and untold numbers have yet to see the Walbran’s wildlife firsthand, but they hold it in their hearts.

Photo: Walbran Central
Those who love the land are a community. We are the organizers, sponsors, and volunteers who drive this movement forward. Everyone who shares these values can be a part of it; no contribution is too small. We’re going all-out to defend the forests, rivers, bears, cougars, otters, and eagles of the Walbran Valley. They sustain us and we give back by fighting to protect them.

Walbran River, the heart of the Walbran Valley, spring 2016. (Photo: Walbran Central)
Remember: Forest Defenders Are Heroes!

by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Apr 24, 2016 | Mining & Drilling, Protests & Symbolic Acts
Via Censored News
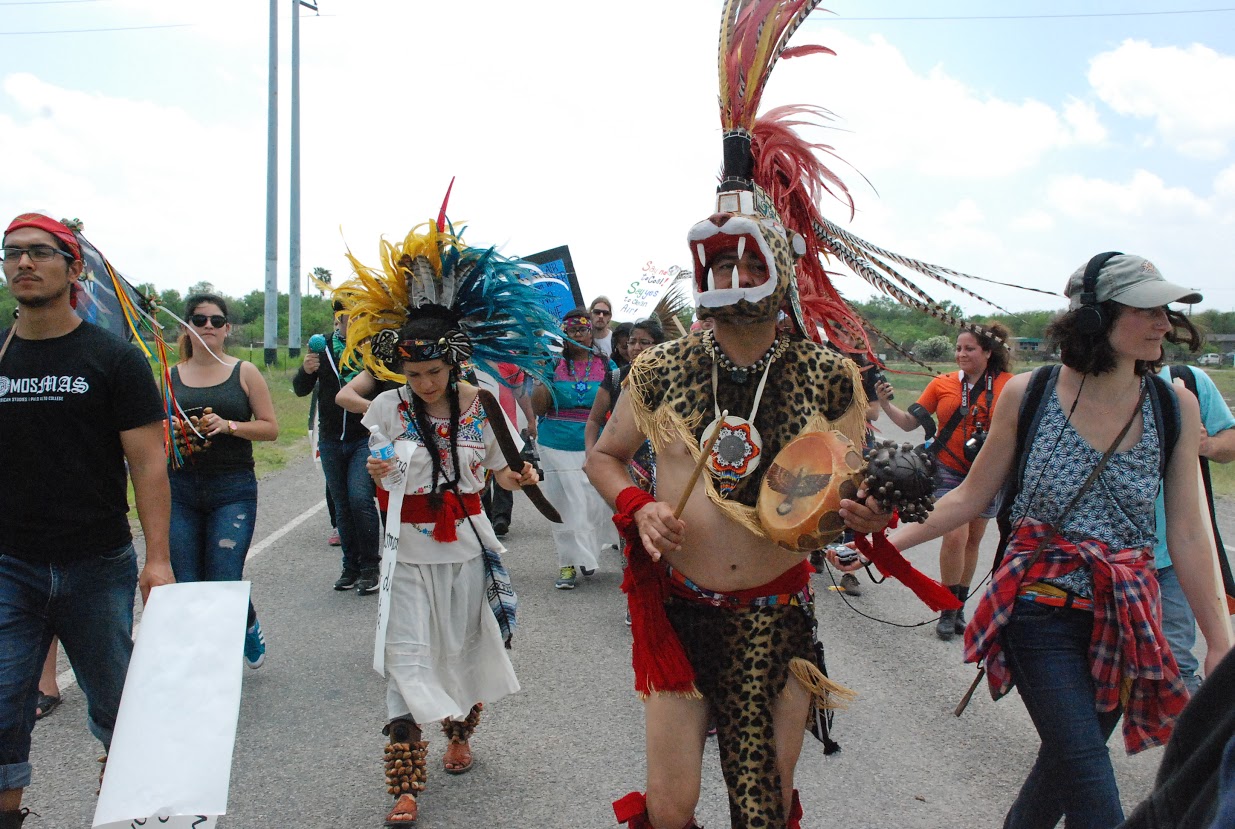
EAGLE PASS, Tex. — Native American Groups gathered today for a historic rally and march to protest the open-pit coal strip mine in Eagle Pass, Tex. The protesters called on the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers to rescind the mine’s permit, halt expansion and protect the land from further destruction. The project, owned by Dos Republicas Coal Partnership, mines lignite coal, which is transported by train from Maverick County across the border to be burned in a Mexican coal-fired power plant. The mine began operating several months ago, despite local opposition, and is harming the ancestral homelands of many Native groups and damaging sacred lands and more than 100 archaeological sites.
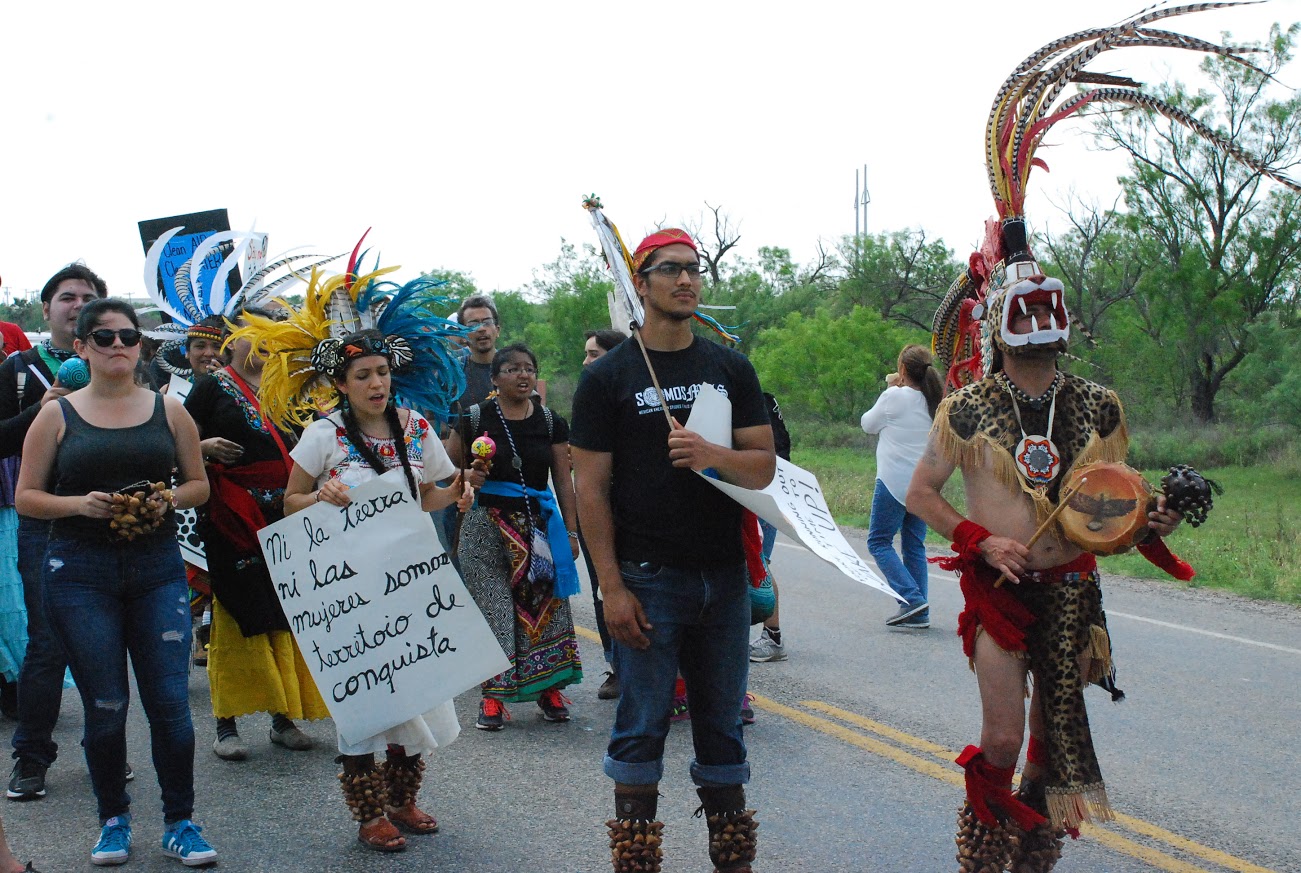

“This mine has already caused irreparable damage, destroying multiple burial sites and erasing our cultural heritage in the process,” said Maria Torres, Tribal Chairwoman of the Pacuache Clan of Texas. “This land is our patrimonial heritage, and it holds the story of our ancient aboriginal people—how we lived and how we died. When we lose access to our land and to the ancient wildlife of the area, from the jaguarundi and ocelot to crucial plant life, we lose part of our heritage and our connection with Mother Earth.”
Many Native groups say they were not properly consulted by Federal agencies as required prior to granting the permits necessary for the coal mine to open. More than eight thousand Eagle Pass residents and allies signed a petition in opposition to the Dos Republicas mine before its opening.

“This project is the worst example of environmental injustice I’ve seen,” said Dr. Jonathan Hook, former Director of Environmental Justice and Tribal Affairs for the EPA, Cherokee Nation citizen and Maverick County resident. “Everything about it is wrong. Given the incomplete processes and potential damage to one of the most vulnerable communities in the country, the Dos Republicas mine should have been stopped before it even started.”
Representatives from the Lipan Apache Band of Texas, Pacuache Band Coahuiltecan Nation, Carrizo-Comecrudo Tribe of Texas, and American Indian Movement of Central Texas were present at the Saturday event, which included Native regalia, drumming, and other cultural expressions along with large banners, signs, and puppets.
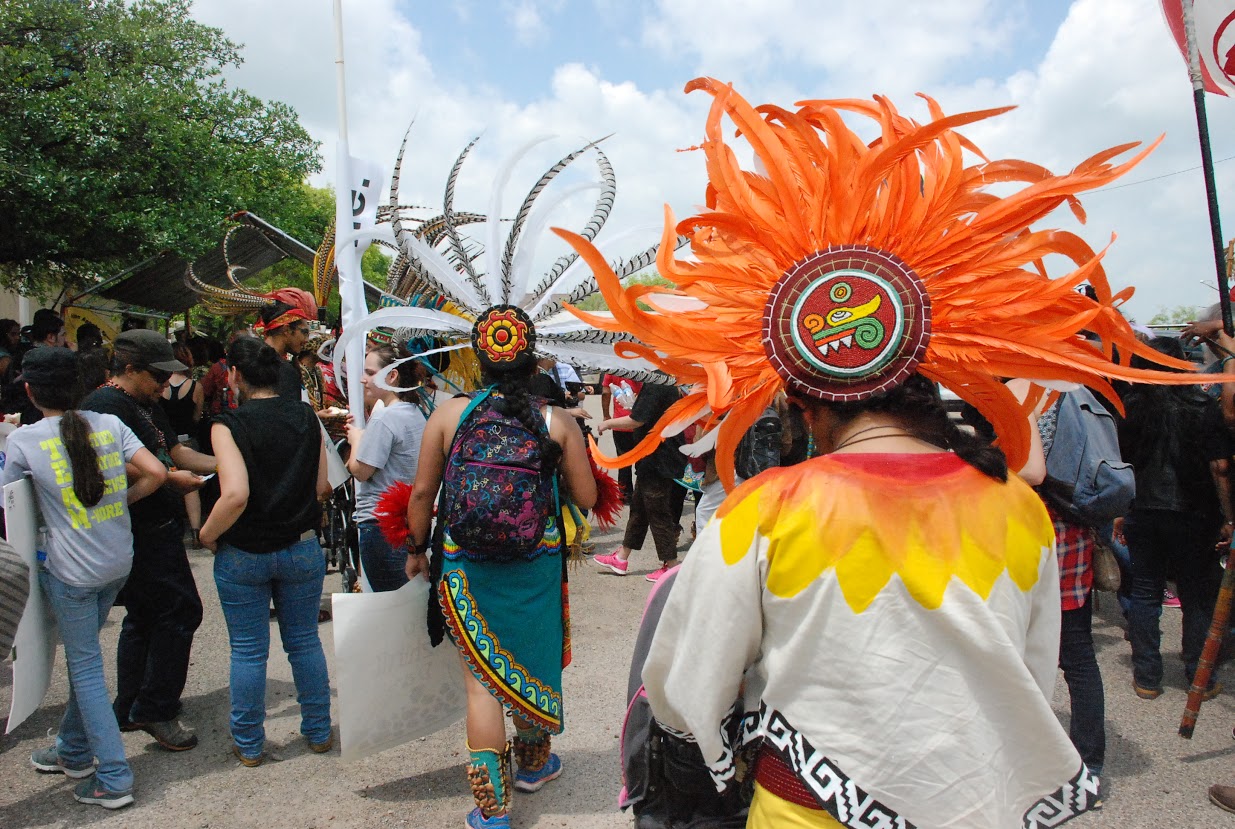

“Native leaders, tribal members and allies from across the country are uniting here today, and they join thousands from the area who are standing up against this disastrous project,” said Dr. Tane Ward, and Native and decolonial organizer working with the Sierra Club. “It’s unclear why the state of Texas has been so supportive of the controversial mining project. Not only does it harm culturally rich and historic land, the Dos Republicas mine threatens the safety and livelihood of those who live nearby all so the coal can be shipped to Mexico and burned in coal plants. It’s time for this dangerous project to be stopped, once and for all.”
Read more about the Dos Replicas Mine at the Sierra Club Lone Star Chapter’s website.

by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Apr 23, 2016 | Mining & Drilling, Repression at Home
By Cultural Survival
At least four people were killed after police opened fire at a massive protest of several thousand villagers in Bangladesh Monday, April 4th, reported the Phulbari Solidarity Group.
“This is a terrible tragedy and major news. It is the largest loss of life at an anti-coal protest in Bangladesh since the tragic deaths in the August 26, 2006 killings at Phulbari, Bangladesh, where three people were killed and 200 injured by paramilitaries. It is the worst overall loss of life in anti-coal protests worldwide since the killings of six people in Jharkhand, India, at two protests in April 2011,” noted Ted Nace, the editor of Coal Swarm.
Professor Anu Muhammd, the Member Secretary of the National Committee to Protect Oil, Gas, Mineral Resources, Power and Port in Bangladesh, noted: “The villagers in Bashkhali have been loud against the destructive plans of S. Alam Group for months because the company wants to build two coal-fired power plants in the area by evicting thousands of villagers and landowners. The coal-businessmen of S. Alam Group, financed by two Chinese firms — SEPCOIII Electric Power and HTG, were fully aware of the strong opposition to the coal-power plant.”
According to the Daily Star, in December 2013, S Alam Group, struck an agreement with SEPCO3 Electric Power Construction Corporation of China to set up a coal-fired power plant in Banshkhali district of Chittagong, Bangladesh. On February 16 this year, the government signed power purchase agreements with two private joint ventures led by S Alam Group to buy electricity at Tk 6.61 per kilowatt-hour from two projects with power generation capacity of 1,224MW. S Alam Group and their Chinese backers plan to initiate the power plant by November 2019 across a 600-acre site. No consultation has taken place with communities members who would be affected. The project will require an investment of $2.4 billion of which $1.75 billion will come from Chinese lenders.
Abu Ahmed was a witness to the police violence, himself being shot in his leg. He said that the villagers had been holding peaceful protests for days after S. Alam, the local conglomerate behind the project, started purchasing land for the plants in the village, which lies on the edge of the Bay of Bengal. But the government did not pay attention to the village protests and the district administration remained silent for months. This led the villagers to stage a mass protest which turned into the worst tragedy in the history of coal in Bangladesh. The government of Bangaldesh announced on April 9 that work at the $2.4 billion power plant would be suspended for 15 days, while it carries out an assessment of the plant’s environmental impact, led by Bangladeshi and foreign scientists.
The plans for coal mine join a laundry list of other planned coal projects being pursued by the government of Bangladesh and foreign investors, despite huge opposition from communities, international coalitions, human rights experts, and environmentalists. Phulbari coal project, in Northeastern Bangladesh, is one infamous case that has lead to massive protests over the 8 years since it was first proposed by GCM resources, a British-based company. Ongoing mobilizations by communities on the ground have been successful in preventing the licensing of the coal mine, and resulted in plummeting financial loss for GCM, who failed to conduct adequate social and environmental impact studies and gain the free, prior, informed consent of the communities at various stages of the project’s life.
As a rapidly developing country, Bangaldesh has a strong demand for electricity, but communities are not willing to accept development at the cost of losing their lands and livelihoods.
In an op-ed in the Dhaka Tribune, Professor Muhammed argued, “Tension and resistance will be certainties if a so-called development projects like this are implemented forcefully and through fraudulent activities and corruption. People will not accept any project that goes against the locals’ interests or may harm the national interests or is taken up without maintaining transparency.”
Bangladesh has made plans to ramp up its coal production, with the goal of setting up 25 coal-fired power plants by 2022. However this lies in conflict with its goals to curb carbon emissions in line with the climate treaty negotiations agreed to in Paris in 2015 known was the COP 21 agreement, to limit global temperature rise to 2 degrees Celsius.
An analysis by the Climate Action Tracker presented at the COP 21 found that attempts to keep global warming to 2 degrees will be wildly off course if existing plans for coal-fire plants are carried out, as coal is the world’s single biggest contributor to global warming. Just by allowing the 2,440 coal-fired power stations that are currently planned would cause emissions rates four times higher than the 2-degree target by 2030. Without a single new coal plant, allowing existing coal plants to continue operating would lead to emissions rates 150 percent higher than what is consistent with a 2-degree target.
Bangladesh was part of a coalition of developing countries who argued for rich countries, who carry more responsibility for climate change, to carry more of the financial burden that developing countries would incur in order to leapfrog past dirty fossil fuels like coal.
Read more: After the COP21: How Bangladesh Can Move Past Coal and Why Rich Countries Must Help

by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Apr 22, 2016 | Colonialism & Conquest
By Intercontinental CryBangkukuk: The Indigenous Rama Speak Out Bangkukuk: The Indigenous Rama Speak Out Against Nicaragua’s Interoceanic Grand CanalAgainst Nicaragua’s Interoceanic Grand Canal
The Rama people have lived on the Atlantic Coast of Nicaragua for thousands of years, long before the existence of the nation state. Nicaragua’s Law 445 recognizes indigenous ownership of traditional lands and natural resources; but for decades, settlers from the Pacific have taken vast amounts of Rama territory causing massive deforestation and threatening the Rama way of life.
In 2013 the Nicaraguan government passed Law 840 allowing the Chinese investment firm Hong Kong Nicaragua Development to construct an interoceanic canal without any public consultation or debate. Though the government hails the project as the means to lift the nation out of poverty, hundreds of thousands of Nicaraguans would be forced from their land and the environmental impact could devastate the country’s rich ecosystem of lakes, rivers, and forests. Almost half of the 160 mile canal would cut through the Southern Atlantic Autonomous Region which is home to the Rama.
In 2014 it was announced that the proposed canal route would cut directly through the Rama village of Bangkukuk, removing the community from their land and way of life. Since then, government officials have been pressuring community members to sign land concessions without legal consultation. In response, community leaders and local officials have partnered with indigenous rights groups to combat this land grab by bringing their case to the Inter-American Court.
The film Bangkukuk is a collaboration between Art of Solidarity and village leaders aimed at sharing their story with the international community. This short trailer is just a glimpse into an upcoming feature-length documentary film that will give voice to the many communities, organizations, and activists at the front lines of the indigenous rights and anti-canal movements in Nicaragua.

by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Apr 18, 2016 | Alienation & Mental Health, Indigenous Autonomy
Featured image: An indigenous youth from Kwalikum First Nation sings. Photo: VIUDeepBay @flickr. Some Rights Reserved.
By Courtney Parker and John Ahni Schertow / Intercontinental Cry
The spiraling rate of suicide among Canada’s First Nations became a state of crisis in Attawapiskat this week after 11 people in the northern Ontario community attempted to take their own lives in one night.
The First Nation was so completely overwhelmed by the spike in suicide attempts that leaders declared a state of emergency. Crisis teams were soon deployed by various agencies to help the community cope with the horror. Meanwhile, as news coverage of the shocking situation spread, activists occupied the Toronto office of Indigenous and Northern Affairs to demand the federal government provide immediate and long-term support to properly address the situation in Attawapiskat.
At least 100 people from the small Cree community have attempted suicide since September. This alarming number—5 per cent of Attawapiskat’s population—is symptomatic of a larger and more pervasive problem in Canada.
While cancer and heart disease are the leading causes of death for the average Canadian, for First Nations youth and adults up to 44 years of age the leading cause of death is suicide and self-inflicted injuries.
According to Health Canada, the suicide rate for First Nations male youth (age 15-24) is 126 per 100,000 compared to 24 per 100,000 for non-indigenous male youth. For First Nations women, the suicide rate is 35 per 100,000 compared to 5 per 100,000 for non-indigenous women.
Handling this situation through a lens of crisis management simply will not do.
In order to bring an end to this long-standing crisis, there are systemic, cyclical and multi-generational issues that must first be addressed, with special attention given to ongoing disruptions in individual and cultural identity.
Historical impacts of colonization, compounded by Canada’s ongoing policies of forced assimilation, are pulling today’s First Nation youth further and further away from their core cultural identities. These identities and cultures have the power to protect and sustain all First Nation youth, and provide them with the resilience they need to overcome whatever individual factors may place them at risk for suicide.
Noting that the Pimicikamak Cree Nation in central Manitoba also responded to the epidemic by declaring their own state of emergency in March, national chief of the Assembly of First Nations, Perry Bellegarde recently proclaimed:
“We need a sustained commitment to address longstanding issues that lead to hopelessness among our peoples, particularly the youth.”
Bellegarde further lamented the lack of specially trained community health workers. He also cited Attawapiskat First Nation’s need for a mental health worker, a youth worker, and proper fiscal support to train workers in the community to respond.
Mainstream media has its own role to play.
Research has shown that merely talking about the devastating indigenous suicide epidemic can have unspeakably damaging consequences.
In 2007, a Canadian research team compiled a comprehensive report entitled, “Suicide Among Aboriginal People in Canada.” The text goes into great detail about how the media should—and should not—handle this extremely delicate subject matter.
“Mass media—in the form of television, Internet, magazines, and music—play an important role in the lives of most contemporary young people. Mass media may influence the rate and pattern of suicide in the general population (Pirkis and Blood, 2001; Stack, 2003; 2005). The media representation of suicides may contribute to suicide clusters. Suicide commands public and government attention and is often perceived as a powerful issue to use in political debates. This focus, however, can inadvertently legitimize suicide as a form of political protest and thus increase its prevalence. Research has shown that reports on youth suicide in newspapers or entertainment media have been associated with increased levels of suicidal behaviour among exposed persons (Phillips and Cartensen, 1986; Phillips, Lesyna,and Paight, 1992; Pirkis and Blood, 2001). The intensity of this effect may depend on how strongly vulnerable individuals identify with the suicides portrayed.
Phillips and colleagues (1992) offer explicit recommendations on the media handling of suicides to reduce this contagion effect. The emphasis is on limiting the degree of coverage of suicides, avoiding romanticizing the action, and presenting alternatives. There is some evidence that this may actually reduce suicides that follow in the wake of media reporting (Stack, 2003). Many Canadian newspaper editors have adopted policies to minimize the reporting of suicide to reduce their negative impact (Pell and Watters, 1982). Suicide prevention materials can also be disseminated through the media. The media can also contribute to mental health promotion more broadly by presenting positive images of Aboriginal cultures and examples of successful coping and community development.”
Even greater than the need for more socially responsible media, is the need for more proactive and community-specific solutions on the ground.
There is a growing body of evidence demonstrating the value of taking protective measures to prevent suicide by preserving and promoting the regular use of traditional indigenous languages.
In 2008, researchers Chandler and Lalonde published a report entitled, “Cultural Continuity as a Protective Factor Against Suicide in First Nations Youth.” In their review, they touched on an inherent risk in raising the conversation on the indigenous suicide epidemic to the international level – though it is particularly severe in Canada, it is indeed global – describing how it may obstruct community-based and community-specific solutions from emerging. Findings also confirmed that individual and community markers of cultural continuity – such as language retention – can form a protective barrier against the staggering incidence rates of suicide ravaging First Nations like Attawapiskat and the Pimicikamak Cree Nation.
Chandler and Lalonde conclude that:
“First Nations communities that succeed in taking steps to preserve their heritage culture, and that work to control their own destinies, are dramatically more successful in insulating their youth against the risks of suicide.”
In 1998, the same research team—Chandler and Lalonde—published a preliminary report detailing some of the most salient markers of cultural continuity among First Nations. Noted protective factors included: land claims; self-governance; autonomy in education; autonomy in police and fire services; autonomy in health services; and the presence of cultural facilities.
Interestingly, indigenous self-governance was discovered to be the strongest protective factor of all. Lower levels of suicide rates were also measured in communities exhibiting greater control over education, and in communities engaged in collective struggles for land rights—or, as they often call it Latin America: ‘La Lucha’!
In 2009, another research team that included Art Napoleon, Cree language speaker, language and culture preservationist and faith-keeper, issued a call for more research on the association between native language retention and reduced rates of indigenous youth suicide. They also called for more inter-tribal dialogues and community based, culturally tailored, strategy building. Their report detailed a host of other significant protective factors such as: honoring the connection between land and health; recognizing traditional medicine; spirituality as a protective factor; maintaining traditional foods; and, maintaining traditional activities.
Yet, perhaps the most compelling evidence to date connecting cultural continuity—and specifically, language retention—with reductions in First Nation suicide rates came in 2007, from research team, Hallett, Chandler and Lalonde. Their analyses demonstrated that rates of language retention among First Nations had the strongest predictive power over youth suicide rates, even when held amongst other influential constructs of cultural continuity. Their conclusions hold shocking implications about the dire importance of native language preservation and retention efforts and interventions.
“The data reported above indicate that, at least in the case of BC, those bands in which a majority of members reported a conversational knowledge of an Aboriginal language also experienced low to absent youth suicide rates. By contrast, those bands in which less than half of the members reported conversational knowledge suicide rates were six times greater.”
It is important to drive this point home. In the First Nation communities where native language retention was above 50 per cent (with at least half of the community retaining or acquiring conversational fluency) suicide rates were virtually null, zero. Yet in the bands where less than half of community members demonstrated conversational fluency in their native tongue, suicide rates spiked upwards of 6 times the rates of surrounding settler communities.
It is also worth noting how overall spikes in suicide prevalence found in Indigenous communities around the world indicate a strong correlation with the socio-political marginalization brought on by colonization. In other words, the suicide epidemic—which is at heart a crisis of mental health—is directly related to, if not directly caused by, the loss of culture and identity set in motion by colonialism.
Cultural continuity—and perhaps most specifically, native language preservation and retention—plays a crucial role in overcoming the ongoing native suicide epidemic—and indeed near universal barriers to indigenous mental health—once and for all First Nations, on a community by community basis.
by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Apr 17, 2016 | Mining & Drilling, Toxification
By Lierre Keith / Deep Green Resistance
Editor’s note: This first appeared in Mother Earth News on July 28, 2010. We are republishing it on the sixth anniversary of the Deepwater Horizon oil spill in the Gulf of Mexico.
Everything that’s wrong with this culture is in the story now pouring out of a broken oil rig 40 miles off the Louisiana coast. I don’t mean story as in fictitious. I mean it as a narrative, the account of successive events that builds into a history. That history is now washing up on the shore as oil-drenched corpses; nothing more than a quick, bracing glance is needed to know how those birds suffered. It’s also a history that’s waiting to turn cells toward the fierce hunger of cancer, settling into the lungs of children, erupting into blisters on the skin “so deep they’re leaving scars.”
We could find our beginning point, our once upon a time, in the first written story of this culture, the Epic of Gilgamesh, which chronicled the deforestation of Mesopotamia. The story hasn’t changed in four thousand years — it’s just quickened with the accelerant of fossil fuel. The pattern is basic to civilization, a feedback loop of overshoot, militarization, slavery, and biotic devastation, a loop that has tightened into a noose. That noose is planet-wide, encircling the earth in a siege beyond the wildest dreams of ambitious Caesars of the past. Nothing is safe, not the South Pole, not the strata 30,000 feet below the earth’s surface, not even the moon, which the power-mad had to “punch” last year. Ownership and entitlement have distilled into a sense of control so pure — and so rancid — that life itself is now being ransomed to the demands of the sociopaths at the top of a very steep, very brutal pyramid.
Where do we stand in that pyramid? Not where we were born — because anyone reading this is one of the globally wealthy — but where do we stand? That’s the question, baring the noblest values of which humans are capable: courage, moral agency, the loyalty that can slow-bloom into solidarity. Are we willing to face how corporations, on the steroids of fossil fuel, have gutted our democracy, our communities, our planet? That insight doesn’t require much intellectually, but it does require courage.
The loyalty will require letting our hearts open to break, as we watch the crabs trying vainly to escape the toxified water of their home and dolphins hemorrhaging. Include them in the clan of you and yours because they are already there; but we will have to fight for them once they become visible, real, a part of the circle called “us” that can’t be broken. Know, too, that two out of three animal breaths are of oxygen made by plankton: if the oceans go down, we go down with them.
Erased into nonexistence by the corporate storytellers are other “resources” as well. These resources dare to insist that they are human, humans with rights against the Kings no less. Most of the clean-up workers of the Exxon Valdez disaster are dead — their average life expectancy was around fifty. This is what it has always meant to be indentured, owned. The powerful get to use you until they discard you as worthless. But each human is priceless: our society is supposed to have learned that somewhere between the Emancipation Proclamation and the Universal Declaration of Human Rights. Besides the visible signs of trauma from losing their coast, their culture, and their livelihoods, there is an inchoate, bewildered grief in the faces of Gulf residents, a grief over the loss of their basic safety and hence their dignity: we are human, we have a right to our lives, how can it be that anyone is allowed to fill our lungs with poison? And the poison keeps coming, as the dispersant Corexit is dropped from planes “like Agent Orange in Viet Nam.”
Here’s my version of the story. A tiny group of wealthy people, backed by the legal system, the government, and, as always, armed force, is allowed to gut an entire ecosystem. When the people organize a nonviolent resistance movement, the leaders are arrested, put through an absurd trial, and then hanged by the military. The outrage of the international community can’t stop the smug sadism of power.
It’s a true story. The group was called MOSOP (the Movement for the Survival of the Ogoni People), and the most famous of the murdered leaders was poet Ken Saro-Wiwa. It has a sequel, too: MEND, the Movement for the Emancipation of the Niger Delta. MEND has said to the oil industry, “Leave our land or you will die in it.” Like the Gulf, the Niger Delta is knee-deep in oil sludge, and the once self-sufficient people are now impoverished, sick, and desperate. Think what you will of MEND’s direct tactics: they’ve reduced oil output by 30 percent and some of the oil companies are considering pulling out. That’s what happens when people resist: sometimes it works, happily ever after.
We need to break the spell of the corporate storytellers, the court magicians with their enticing tricks called CNN and MTV, what Chris Hedges — one of our last, true public intellectuals — calls the Empire of Illusion. In his words, they have us “clamoring for our own enslavement.” But all the fantasies and shiny toys in the world won’t help us when the planet is six degrees too hot for all creatures great and small, from brown pelicans to bacteria. This is being done for the benefit of essentially 1,400 people, the wealthy who control the world economy through the legal structure of the limited liability corporation. Yes, they have mostly destroyed our — that’s “our” as in “us, globally” — our ability to provide for ourselves, addicted us to their mass-produced culture of petulant cruelty, and won the rights that are supposed to adhere to human beings, not business entities. As Rikki Ott, Rachel Carson by any other name, makes clear, “Our government is beholden to oil and cannot imagine a future without oil. We the people have got to imagine this. We have to.”
And that’s where you come in, readers. It’s not just imagination for you: you’re already living another story, human-scale and woven into a living community like roots through soil. Your story is about patience and permanence, connection and commitment. It’s about people as participants in the world — in the carbon cycle, the water cycle, the physical, sacred cycle of life and death — not dominators. These are the values of animals who intend to live in their home for a long, long time. They are values that stand in direct opposition to the corporate masters. They are also the values that a real resistance needs.
A conquered people calls for a boycott. A sovereign people would shred BP’s corporate charter, seize their assets, and put the money of the world’s fourth largest corporation toward restoring the Gulf: the land, the people, the community. There are efforts to do exactly that. More, there are efforts to strike to the heart of corporate power: an amendment to the constitution that would strip them of the rights they have claimed: the Fourteenth Amendment, the Fourth Amendment, the Sixth, the Fifth… rumor has it they have their sights on the Second. They’ve staged a coup and won, and they’ve done what conquerors do: gutted the colony. And it’s not just the earth they’ve scorched, but the oceans and sky as well as the lungs of children and the livers of dolphins.
Call it what it is: a war. It’s not a mistake. It’s not even a set of loopholes that some naughty boys in a bad corporate culture exploited. Whether the oil gushed or was pumped and then burned, the result would have been the same: a planet destroyed — pelican by penguin by Ogoni child — for the benefit of a wealthy few.
It’s time to remember the animals — brave and hungry and loyal — that we are. So with your front paws, turn off all the corporate media flooding our culture and our children with moral stupidity and go dig in the dirt. It’s your dirt, our dirt, the collective home of a tribe called carbon. It’s our place, our people, an indivisible part of the story of us.
As for your hind feet, stand up on them and fight.















