
by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Jul 1, 2018 | Strategy & Analysis
Editor’s note: The following is from the chapter “A Taxonomy of Action” of the book Deep Green Resistance: A Strategy to Save the Planet. This book is now available for free online.
by Aric McBay
As we’ve made clear, acts of omission are not going to bring down civilization. Let’s talk about action with more potential. We can split all acts of commission into six branches:
- lobbying;
- protests and symbolic acts;
- education and awareness raising;
- support work and building alternatives;
- capacity building and logistics;
- and direct confrontation and conflict.
The illustration “Taxonomy of Action” groups them by directness. The most indirect tactics are on the left, and become progressively more direct when moving from left to right. More direct tactics involve more personal risk. (The main collective risk is failing to save the planet.) Direct acts require fewer people.
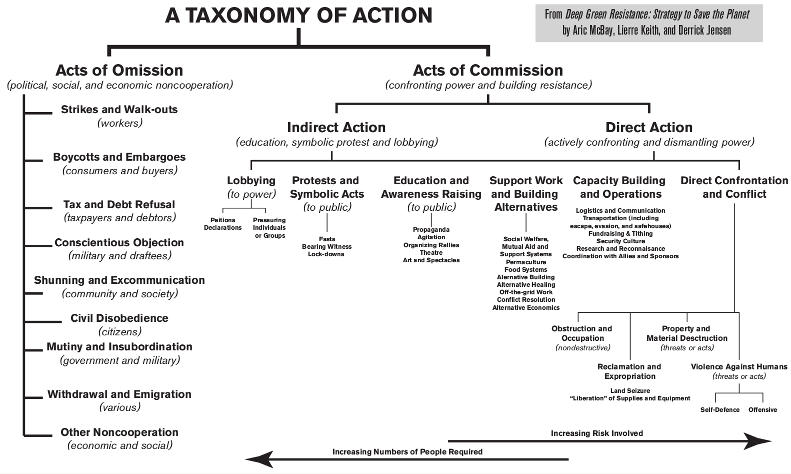
Figure 6-1. Click for larger image.
Lobbying seems attractive because if you have enough resources (i.e., money), you can get government to do things for you, magnifying your actions. Success is possible when many people push for minor change, and unlikely when few people push for major change. But lobbying is too indirect—it requires us to try to convince someone to convince other people to make a decision or pass a law, which will then hopefully be enacted by other people, and enforced by yet a further group.
Lobbying via persuasion is a dead end, not just in terms of taking down civilization, but in virtually every radical endeavor. It assumes that those in power are essentially moral and can be convinced to change their behavior. But let’s be blunt: if they wanted to do the right thing, we wouldn’t be where we are now. Or to put it another way, their moral sense (if present) is so profoundly distorted they are almost all unreachable by persuasion.
And what if they could be persuaded? Capitalists employ vast armies of professional lobbyists to manipulate government. Our ability to lobby those in power (which includes heads of governments and corporations) is vastly outmatched by their ability to lobby each other. Convincing those in power to change would require huge numbers of people. If we had those people, those in power wouldn’t be convinced—they would be replaced. Convincing them to mend their ways would be irrelevant, because we could undertake much more effective action.
Lobbying is simply not a priority in taking down civilization. This is not to diminish or insult lobbying victories like the Clean Water Act and the Wildlife Act, which have bought us valuable time. It is merely to point out that lobbying will not work to topple a system as vast as civilization.
When effective, demonstrations are part of a broader movement and go beyond the symbolic. There have been effective protests, such as the civil rights actions in Birmingham, but they were not symbolic; they were physical obstructions of business and politics. This disruption is usually illegal. Still, symbolic protests can get attention. Protests are most effective at “getting a message out” when they focus on one issue. Modern media coverage is so superficial and sensational that nuances get lost. But a critique of civilization can’t be expressed in sound bytes, so protests can’t publicize it. And civilization is so large and so ubiquitous that there is no one place to protest it. Some resistance movements have employed protests, to show strength and attract recruits, but the majority of people will never be on our side; our strategy needs to be based on effectiveness, not just numbers.
For public education to work, several conditions must be met. The resistance education and propaganda must be able to outcompete the mass media. The general public must be able and willing to unravel the prevailing falsehoods, even if doing that contravenes their own social, psychological, and economic self-interest. They must have accessible ways to change their actions, and they must choose morally preferable actions over convenient ones. Unfortunately, none of these conditions are in place right now.
Another drawback of education is its built-in delay; it may take years before a given person translates new information into action. But as we know, the planet is being murdered, and the window for effective action is small. For deep green resisters, skills training and agitation may be more effective than public education.
Education won’t directly take down civilization, but it may help to radicalize and recruit people by providing a critical interpretation of their experiences. And as civilization continues to collapse, education may encourage people to question the underlying reasons for a declining economy, food crises, and so on.
These support structures directly enable resistance. The Quakers’ Society of Friends developed a sturdy ethic of support for the families of Quakers who were arrested under draconian conditions of religious persecution (see Chapter 4: “Loyalty, Material Support, & Leadership”). People can take riskier (and more effective) action if they know that they and their families will be supported.
Building alternatives won’t directly bring down civilization, but as industrial civilization unravels, alternatives have two special roles. First, they can bolster resistance in times of crisis; resisters are more able to fight if they aren’t preoccupied with getting food, water, and shelter. Second, alternative communities can act as an escape hatch for regular people, so that their day-to-day work and efforts go to autonomous societies rather than authoritarian ones.
To serve either role, people building alternatives must be part of a culture of resistance—or better yet, part of a resistance movement. If the “alternative” people are aligned with civilization, their actions will prolong the destructiveness of the dominant culture. Let’s not forget that Hitler’s V2 rockets were powered by biofuel fermented from potatoes. The US military has built windmills at Guantanamo Bay, and is conducting research on hybrid and fuel-cell vehicles. Renewable energy is a necessity for a sustainable and equitable society, but not a guarantee of one. Militants and builders of alternatives are actually natural allies. As I wrote in What We Leave Behind, “If this monstrosity is not stopped, the carefully tended permaculture gardens and groves of lifeboat ecovillages will be nothing more than after-dinner snacks for civilization.” Organized militants can help such communities from being consumed.
In addition, even the most carefully designed ecovillage will not be sustainable if neighboring communities are not sustainable. As neighbors deplete their landbases, they have to look further afield for more resources, and a nearby ecovillage will surely be at the top of their list of targets for expansion. An ecovillage either has to ensure that its neighbors are sustainable or be able to repel their future efforts at expansion.
In many cultures, what might be considered an “alternative” by some people today is simply a traditional way of life—perhaps the traditional way of life. Peoples struggling with displacement from their lands and dealing with attempts at assimilation and genocide may be mostly concerned with their own survival and the survival of their way of life. And for many indigenous groups, expressing their traditional lifestyle and culture may be in itself a direct confrontation with power. This is a very different situation from people whose lives and lifestyles are not under immediate threat.
Of course, even people primarily concerned with the perpetuation of their traditional cultures and lifestyles are living with the fact that civilization has to come down for any of us to survive. People born into civilization, and those who have benefitted from its privilege, have a much greater responsibility to bring it down. Despite this, indigenous peoples are mostly fighting much harder against civilization than those born inside of it.
Every successful historical resistance movement has rested upon a subsistence base of some kind. Establishing that base is a necessary step, but that alone is not sufficient to stop the world from being destroyed.
Capacity Building and Logistics
Capacity building and logistics are the backbone of any successful resistance movement. Although direct confrontation and conflict may get the glory, no sustained campaign of direct action is possible without a healthy logistical and operational core. That includes the following:
Resistance movements of all kinds must be able to screen recruits or volunteers to assess their suitability and to exclude infiltrators. Members of the group must share certain essential viewpoints and values (either assured through screening or teaching) in order to maintain the group’s cohesion and focus.
Resisters need to be able to communicate securely and rapidly with one another to share information and coordinate plans. They may also need to communicate with a wider audience, for propaganda or agitation. Many resistance groups have been defeated because of inadequate communications or poor communications security.
Resistance requires funding, whether for offices and equipment, legal costs and bail, or underground activities. In aboveground resistance, procurement is mostly a subset of fund raising, since people can buy the items or materials they need. In underground resistance, procurement may mean getting specialized equipment without gathering attention or simply getting items the resistance otherwise would be unable to get.
Of course, fund raising isn’t just a way to get materials, but also a way to support mutual aid and social welfare activities, support arrestees and casualties or their families, and allow core actionists to focus on resistance efforts rather than on “making a living.”
People and equipment need access to transportation in order to reach other resisters and facilitate distribution of materials. Conventional means of transportation may be impaired by collapse, poverty, or social or political repression, but there are other ways. The Underground Railroad was a solid resistance transportation network. The Montgomery bus boycott was enabled by backup transportation systems (especially walking and carpooling) coordinated by civil rights organizers who scheduled carpools and even replaced worn-out shoes.
Security is necessary for any group big enough to make a splash and become a target for state intelligence gathering and repression. Infiltration is definitely a concern, but so is ubiquitous surveillance. This does not apply solely to people or groups considering illegal action. Nonviolent, law-abiding groups have been and are surveilled and disrupted by COINTELPRO-like entities. Many times it is the aboveground resisters who are more at risk as working aboveground means being identifiable.
Research and reconnaissance are equally important logistical tools. To be effective, any strategy requires critical information about potential targets. This is true whether a group is planning to boycott a corporation, blockade a factory, or take out a dam.
Imagine how foolish you’d feel if you organized a huge boycott against some military contractor, only to find that they’d recently converted to making school buses. Resistance researchers can help develop a strategy and identify potential targets and weaknesses, as well as tactics likely to be useful against them. Research is also needed to gain an understanding of the strategy and tactics of those in power.
There are certain essential services and care that keep a resistance movement running smoothly. These include services like the repair of equipment, clothing, and so on. Health care skills and equipment can be extremely valuable, and resistance groups should have at least basic health care capabilities, including first aid and rudimentary emergency medicine, wound care, and preventative medicine.
Coordination with allies and sponsors is often a logistical concern. Many historical guerilla and insurgent groups have been “sponsored” by other established revolutionary regimes or by states hoping to foment revolution and undermine unfriendly foreign governments. For example, in 1965 Che Guevera left postrevolutionary Cuba to help organize and train Congolese guerillas, and Cuba itself had the backing of Soviet Russia. Both Russia and the United States spent much of the Cold War “sponsoring” various resistance groups by training and arming them, partly as a method of trying to put “friendly” governments in power, and partly as a means of waging proxy wars against each other.
Resistance groups can also have sponsors and allies who are genuinely interested in supporting them, rather than attempting to manipulate them. Resistance in WWII Europe is a good example. State-sponsored armed partisan groups and other partisan and underground groups supported resistance fighters such as those in the Warsaw Ghetto.
Direct Conflict and Confrontation
Ultimately, success requires direct confrontation and conflict with power; you can’t win on the defensive. But direct confrontation doesn’t always mean overt confrontation. Disrupting and dismantling systems of power doesn’t require advertising who you are, when and where you are planning to act, or what means you will use.
Back in the heyday of the summit-hopping “antiglobalization” movement, I enjoyed seeing the Black Bloc in action. But I was discomfited when I saw them smash the windows of a Gap storefront, a Starbucks, or even a military recruiting office during a protest. I was not opposed to seeing those windows smashed, just surprised that those in the Black Bloc had deliberately waited until the one day their targets were surrounded by thousands of heavily armed riot police, with countless additional cameras recording their every move and dozens of police buses idling on the corner waiting to take them to jail. It seemed to be the worst possible time and place to act if their objective was to smash windows and escape to smash another day.
Of course, their real aim wasn’t to smash windows—if you wanted to destroy corporate property there are much more effective ways of doing it—but to fight. If they wanted to smash windows, they could have gone out in the middle of the night a few days before the protest and smashed every corporate franchise on the block without anyone stopping them. They wanted to fight power, and they wanted people to see them doing it. But we need to fight to win, and that means fighting smart. Sometimes that means being more covert or oblique, especially if effective resistance is going to trigger a punitive response.
That said, actions can be both effective and draw attention. Anarchist theorist and Russian revolutionary Mikhail Bakunin argued that “we must spread our principles, not with words but with deeds, for this is the most popular, the most potent, and the most irresistible form of propaganda.”30 The intent of the deed is not to commit a symbolic act to get attention, but to carry out a genuinely meaningful action that will serve as an example to others.

by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Jun 2, 2018 | Strategy & Analysis
Editor’s note: The following is from the chapter “A Taxonomy of Action” of the book Deep Green Resistance: A Strategy to Save the Planet. This book is now available for free online.
by Aric McBay
All acts of omission require very large numbers of people to be permanently effective on a large scale. There are plenty of examples of strikes shutting down factories temporarily, but what if you don’t ever want that factory to run again? What if you work at a cruise missile factory or a factory that manufactures nuclear warheads? Is everyone working there willing to go on strike indefinitely? The large pool of unemployed or underpaid working poor means that there are always people willing to step in to work for a wage, even a relatively low one. Failing that, the company in question could just move the factory overseas, as so many have. All of this is especially true in a time when capitalism falters, and attempting to bring down civilization would definitely make capitalism falter.
The same problems apply to economic boycotts. You and I could stop buying anything produced by a given company. Or we could stop buying anything that had been sold through the global capitalist economy. We probably willsee widespread acts of economic omission, but only when large numbers of people get too poor to buy mass-produced consumer luxuries. But because of globalization and automation, these acts of omission will be less effective than they were in the past.
Which isn’t to say we shouldn’t undertake such acts when appropriate. Acts of omission are commonly part of resistance movements; they may be implicit rather than explicit. Pre-Civil War abolitionists would not have owned slaves. But this was an implicit result of their morality and political philosophy rather than a means of change. Few abolitionists would have suggested that by refraining from personally owning slaves they were posing a serious or fundamental threat to the institution of slavery.
An effective resistance movement based on acts of omission might need 10 percent, or 50 percent, or 90 percent of the population to win. One in a thousand people withdrawing from the global economy would have negligible impact. Acts of commission are a different story. What if one out of a thousand people joined a campaign of direct action to bring down civilization? Seven million brave and smart people could ensure the survival of our planet.

If we are going to talk about survival—or about courage, for that matter—we should talk about Sobibór. Sobibór was a Nazi concentration camp built in a remote part of Poland near the German border. Brought into operation in April 1943, Sobibór received regular train loads of prisoners, almost all Jewish. Like other Nazi concentration camps, Sobibór was also a work camp, both for prisoners skilled in certain trades and for unskilled labor, such as body removal. Sobibór was not the largest concentration camp, but it ran with murderous efficiency. Records show that by October 1944 a quarter of a million people had been murdered there, and some argue the casualties were significantly higher.26
Sobibór presented two distinct faces. Upon arrival to the camp, those selected to be killed received a polite welcoming speech from the Nazis (sometimes dressed in lab coats to project expertise and authority), and heard classical music played over loudspeakers. The door to the extermination “showers” was decorated with flowers and a Star of David. Touches like these encouraged them to go quietly and calmly to what some surely realized was their death. In contrast, those who were selected for work were shown a more overtly violent face, suffering arbitrary beatings and sometimes killed for even the smallest failure in cooperation. As at other concentration camps, if individual prisoners even attempted to escape, other prisoners would be killed as a reprisal. (At Auschwitz it was common practice for the SS to kill ten random prisoners for each escapee.)
Sobibór is a lesson for us because it became the site of the most successful—and also the most audacious—concentration camp uprising during the entire Holocaust. A small number of prisoners recognized that it was only a matter of time until they, too, were murdered, and decided that it was worth the risk to escape. However, they knew that those left behind would suffer the consequences of their act. So they hatched a bold plan to allow everyone in the camp to escape.
This was not an easy task. The camp was surrounded by multiple razor wire fences and a minefield, beyond which was forest. In addition to the SS, the camp had SS-trained guards of various Eastern European nationalities, guards who had themselves been brought in from POW camps. The perimeter of the camp had bright lighting systems and numerous machine gun towers.
A breakthrough came with the arrival of a group of Jewish-Russian POWs, with whom the long-time prisoners joined together and devised an escape plan. But to avoid being discovered, they had to keep the plan secret from all but a small group, meaning that the majority of the prisoners would be expected to escape at a moment’s notice without preparation. A Russian POW leader, Alexander “Sasha” Aronowicz Pechersky, understood the benefits. “As a military man, I was aware that a surprise attack is worth a division of solders. If we can maintain secrecy until the last minute of the outbreak, the revolt is 80 percent accomplished. The biggest danger was deconspiration.”27 In preparation for the escape, the conspirators used their trade skills to make or steal knives and axes small enough to conceal in their clothes.
At four o’clock on the day of the escape, they sprang into action. Carefully but quickly, they began to lure SS guards into private locations one by one, under various false pretexts. Then, small groups of prepared prisoners would quickly and quietly kill the SS men by striking them on the head with an axe, or by covering their mouths and stabbing them to death. Within an hour they had killed eleven SS men, half of the SS guards present at the time, and concealed the bodies. At five o’clock they came together for evening roll call, but they arrived slightly early, before the remaining SS men had gathered. Their plan was to avoid the minefield by simply marching as a group to the front gate, as though they were on their way to a work detail. Upon reaching the gate, they hoped to shoot the two Ukrainian guards present and then rush out the front way.
Though they had been lucky so far, one of the bodies was discovered at the last moment, before they could make for the front gate. The Russian Sasha made a very brief “every man for himself” speech and encouraged everyone to escape immediately. The camp then burst into chaos, with some proceeding to the front gate, and others breaking their way through the fence and taking their chances with the mine field. All had to deal with machine gun fire from the guard towers.
Of the roughly 550 prisoners, 150 were unwilling or unable to escape. Some were separated in a different subcamp and were out of communication, and others simply refused to run. Anyone unable or unwilling to fight or run was shot by the SS. About eighty of those who did run were killed by the mines or by hostile fire. Still, more than 300 people (mostly with no preparation) managed to escape the camp into the surrounding woodlands.
Tragically, close to half of these people were captured and executed over the following weeks because of a German dragnet. But since they would have been killed by the SS regardless, the escape was still a remarkable success. Better yet, within days of the uprising, humiliated SS boss Heinrich Himmler ordered the camp shut down, dismantled, and replanted with trees. (See, they don’t always rebuild.)28 And a number of the escapees joined friendly partisan groups in the area and continued to fight the Nazis (including Sasha, who later returned to the Red Army and was sent to a gulag by Stalin for “allowing” himself to be captured in the first place).
The survivors would spend decades mulling over the escape. In many ways, they could hardly have hoped for better luck. If their actions had been discovered any earlier, it’s very possible that everyone in the camp would have been executed. Furthermore, it’s simply amazing that half of the group—very few of whom had any weapons, survival, or escape and evasion training—managed to avoid capture by the Nazis.
They certainly would have benefitted from further training or preparation, although in this case that was at odds with their priority of security. Another issue identified by survivors was that almost all of the firearms went to the Russian POWs, meaning that most escapees were defenseless. They also lacked prearranged cells or affinity groups, and many people who did know each other became separated during the escape. A further problem was the fact that the prisoners did not have contact with Allies or resistance groups who could have helped to arrange further escape or provide supplies or weapons. In the end, a large number of escaped prisoners ended up being killed by anti-Semitic Polish nationals, including some Polish partisans.
Despite these issues, we can learn a lot from this story. The prisoners made remarkable use of their limited resources to escape. The very fact that they attempted escape is inspiring, especially when literally millions of others went to their deaths without fighting back. Indeed, considering that so many of them lacked specific combat and evasion skills and equipment, it was solely the courage to fight back that saved many lives.
No withdrawal or refusal would help them—their lives were won only by audacious acts of commission.

by Deep Green Resistance News Service | May 19, 2018 | Strategy & Analysis
Editor’s note: The following is from the chapter “A Taxonomy of Action” of the book Deep Green Resistance: A Strategy to Save the Planet. This book is now available for free online.
by Aric McBay
The word strike comes from eighteenth-century English sailors, who struck (removed) their ship’s sails and refused to go to sea, but the concept of a workers’ strike dates back to ancient Egypt.3 It became a popular tactic during the industrial revolution, parallel to the rise of labor unions and the proliferation of crowded and dangerous factories.
Historical strikes were not solely acts of omission. Capitalists went to great lengths to violently prevent or end strikes that cost them money, so they became more than pickets or marches; they were often pitched battles, with strikers on one side, police and hired goons on the other. This should be no surprise; any effective action against those in power will trigger a forceful, and likely violent, response. Hence, historical strikers often had a pragmatic attitude toward the use of violence. Even if opposed to violence, historical strikers planned to defend themselves out of necessity.
The May 1968 student protests and general strike in France—which rallied ten million people, two-thirds of the French workforce—forced the government to dissolve and call elections, (as well as triggering extensive police brutality). The 1980 Gdansk Shipyard strike in Poland sparked a series of strikes across the country and contributed to the fall of Communism in Eastern Europe; strike leader Lech Walesa won the Nobel Peace Prize and was later elected president of Poland. General strikes were common in Spain in the early twentieth century, especially in the years leading up to the civil war and anarchist revolution.
The practice of boycotting predates the name itself. Captain Charles Boycott was the agent of an absentee landlord in Ireland in 1880. Captain Boycott evicted tenants who had demanded rent reductions, so the community fought back by socially and economically isolating him. People refused to work for him, sell things to him, or trade with him—the postman even refused to deliver his mail. The British government was forced to bring in fifty outside workers to undertake the harvest, and protected the workers with one thousand police. This show of force meant that it cost over ₤10,000 to harvest ₤350 of potatoes.4 Boycott fled to England, and his name entered the lexicon.
As we have discussed, consumer spending is a small lever for resistance movements, since most spending is done by corporations, governments, and other institutions. If we ignore the obligatory food, housing, and health care, Americans spend around $2.7 trillion dollars per year on their clothing, insurance, transportation, and other expenses.5 Government spending might be $4.4 trillion, with corporations spending $1 trillion on marketing alone.6Discretionary consumer spending is small, and even if a boycott were effective against a corporation, the state would bail out that corporation with tax money, as they’ve made clear.
But there’s no question that boycotts can be very effective in specific situations. The original example of Captain Boycott shows some conditions that lead to successful action: the participation of an entire community, the use of additional force beyond economic measures, and the context of a geographically limited social and economic realm. Such actions helped lead to what Irish labor agitator and politician Michael Davitt called “the fall of feudalism in Ireland.”7
Of course there are exceptional circumstances. When the winter’s load of chicken feed arrived on the farm today, the mayor was driving the delivery truck, nosing carefully through a herd of curious cattle. But most people don’t take deliveries from their elected officials, and—with apologies to Mayor Jim—the mayors of tiny islands don’t wield much power on a global scale.
Indeed, corporate globalization has wrought a much different situation than the old rural arrangement. There is no single community that can be unified to offer a solid front of resistance. When corporations encounter trouble from labor or simply want to pay lower wages, they move their operations elsewhere. And those in power are so segregated from the rest of us socially, economically, culturally, and physically that enforcing social shaming or shunning is almost impossible.
Even if we want to be optimistic and say that a large number of people could decide to engage in a boycott of the biggest ten corporations, it’s completely reasonable to expect that if a boycott seriously threatened the interests of those in power, they would simply make the boycott illegal.
In fact, the United States already has several antiboycott laws on the books, dating from the 1970s. The US Bureau of Industry and Security’s Office of Antiboycott Compliance explains that these laws were meant “to encourage, and in specified cases, require US firms to refuse to participate in foreign boycotts that the United States does not sanction.” The laws prohibit businesses from participating in boycotts, and from sharing information which can aid boycotters. In addition, inquiries must be reported to the government. For example, the Kansas City Star reports that a company based in Kansas City was fined $6,000 for answering a customer’s question about whether their product contained materials made in Israel (which it did not) and for failing to report that inquiry to the Bureau of Industry and Security.8 American law allows the bureau to fine businesses “up to $50,000, or five times the value” of the products in question. The laws don’t just apply to corporations, but are intended “to counteract the participation of US citizens” in boycotts and embargoes “which run counter to US policy.”9
Certainly, large numbers of committed people can use boycotts to exert major pressure on governments or corporations that can result in policy changes. But boycotts alone are unlikely to result in major structural overhauls to capitalism or civilization at large, and will certainly not result in their overthrow.
The success of tax refusal is usually low, partly because people already try to avoid taxes for nonpolitical reasons. In the US, 41 percent of adults do not pay federal income tax to begin with, so it’s reasonable to conclude that the government could absorb (or compensate for) even high levels of tax refusal.12
Even though tax refusal will not bring down civilization, there are times when it could be especially decisive. Regional or local governments on the verge of bankruptcy may be forced to close prisons or stop funding new infrastructure in order to save costs, and organized tax resistance could help drive such trends while diverting money to grassroots social or ecological programs.
Although conscientious objection has certainly saved people from having to kill, it doesn’t always save people from dying or the risk of death, since the punishments or alternative jobs like mining or bomb disposal are also inherently dangerous. It’s unlikely that conscientious objection has ever ended a war or even caused significant troop shortages. Governments short of troops usually enact or increase conscription to fill out the ranks. Where alternative service programs have existed, the conscientious objectors have usually done traditional masculine work, like farming and logging, thus freeing up other men to go to war. Conscientious objection alone is unlikely to be an effective form of resistance against war or governments.
Since individual insubordination may result in severe punishment, military personnel sometimes join together to mutiny. But large-scale refusal of orders is almost unheard of because of the culture, indoctrination, and threat of punishment in the military (there are notable exceptions, like the mutiny on the Russian battleship Potemkin or the mass mutinies of Russian soldiers during the February Revolution). Perhaps a greater cause for hope is the potential that military personnel, who often have very useful skill sets, will join more active resistance groups.
Shunning requires a majority to be effective, so it’s not a tool that can be used to bring down civilization, although it can still be used to discourage wrongdoing within communities, including activist communities.
The Birmingham campaign used many different tactics, which gave it flexibility and strength. It began with a series of economic boycotts against businesses that promoted or tolerated segregation. Starting in 1962, these boycotts targeted downtown businesses and decreased sales by as much as 40 percent.15 Black organizers patrolled for people breaking the boycott. When they found black people shopping in a target store, they confronted them publically and shamed them into participating in the boycott, even destroying purchased merchandise. When several businesses took down their segregation signs, Commissioner Connor threatened to revoke their business licenses.16
The next step in the civil disobedience campaign was “Project C,” the systematic violation of segregation laws. Organizers timed walking distances between the campaign headquarters and various targets, and conducted reconnaissance of segregated lunch counters, all-white churches, stores, federal buildings, and so on.17 The campaign participants then staged sit-ins at the various buildings, libraries, and lunch counters (or, in the case of the white churches, kneel-ins). Businesses mostly refused to serve the protesters, some of whom were spat on by white customers, and hundreds of the protesters were arrested. Some observers, black and white, considered Project C to be an extremist approach, and criticized King and the protesters for not simply sticking to negotiation. “Wasteful and worthless,” proclaimed the city’s black newspaper.18 A statement by eight white clergymen called the demonstrations “unwise and untimely,” and wrote that such protests “incite to hatred and violence” when black people should focus on “working peacefully.”19 (Of course, they blamed the victim. Of course, they cautioned that an action like sitting down in a deli and ordering a sandwich is only “technically peaceful” and warned against such “extreme measures.” And, of course, it’s never the right time, is it?)
The city promptly obtained an injunction against the protests and quadrupled the bail for arrestees to $1,200 per person (more than $8,000 in 2010 currency).20 But the protests continued, and two days later fifty people were arrested, including Martin Luther King Jr. Instead of paying bail for King, the organizers allowed the police to keep him in prison to draw attention to the struggle. National attention meant the expansion of boycotts; national retail chains started to suffer, and their bosses put pressure on the White House to deal with the situation.
Despite the attention, the campaign began to run out of protesters willing to risk arrest. So they used a controversial plan called the “Children’s Crusade,” recruiting young students to join in the protests.21Organizers held workshops to show films of other protests and to help the young people deal with their fear of jail and police dogs. On May 2, 1963, more than a thousand students skipped school to join the protest, some scaling the walls around their school after a principal attempted to lock them in.22 Six hundred of them, some as young as eight, were arrested.
Firehoses and police dogs were used against the marching students. The now-iconic images of this violence drew immense sympathy for the protesters and galvanized the black community in Birmingham. The situation came to a head on May 7, 1963, when thousands of protestors flooded the streets and all business ceased; the city was essentially defeated.23 Business leaders were the first to support the protestors’ demands, and soon the politicians (under pressure from President Kennedy) had no choice but to capitulate and agree to a compromise with King and the other organizers.
But no resistance comes without reprisals. Martin Luther King Jr.’s house was bombed. So was a hotel he was staying at. His brother’s house was bombed. Protest leader Fred Shuttlesworth’s house was bombed. The home of an NAACP attorney was bombed.24 Some blamed the KKK, but no one was caught. A few months later the KKK bombed a Baptist church, killing four girls.25
And the compromise was controversial. Some felt that King had made a deal too soon, that the terms were less than even the moderate demands. In any case, the victorious campaign in Birmingham is widely regarded as a watershed for the civil rights movement, and a model for success.
Let’s compare the goals of Birmingham with our goals in this book. The Birmingham success was achieved because the black protestors wanted to participate in economy and government. Indeed, that was the crux of the struggle, to be able to participate more actively and equally in the economy, in government, and in civil society. Because they were so numerous (they made up about one-third of the city’s population) and because they were so driven, their threat of selective withdrawal from the economy was very powerful (I almost wrote “persuasive,” but the point is that they stopped relying on persuasion alone).
But what if you don’t want to participate in capitalism or in the US government? What if you don’t even want those things to exist? Boycotts aren’t very persuasive to business leaders if the boycotts are intended to be permanent. The Birmingham civil rights activists forced those in power to change the law by penalizing their behavior, by increasing the cost of business as usual to the point where it became easier and more economically viable for government to accede to their demands.
There’s no doubt that we can try to apply the same approach in our situation. We can apply penalties to bad behavior, both on community and global scales. But the dominant culture functions by taking more than it gives back, by being unsustainable. In order to get people to change, we would have to apply a penalty proportionally massive. To try to persuade those in power to make serious change is folly; it’s effectively impossible to make truly sustainable decisions within the framework of the dominant system. And persuasion can only work on people, whereas we are dealing with massive social machines like corporations, which are functionally sociopathic.
In any case, what we call civil disobedience perhaps is the prototypical act of omission, and a requirement for more than a few acts of commission. Refusing to follow an unjust law is one step on the way to working more actively against it.
by Deep Green Resistance News Service | May 13, 2018 | Strategy & Analysis
Editor’s note: The following is from the chapter “A Taxonomy of Action” of the book Deep Green Resistance: A Strategy to Save the Planet. This book is now available for free online.
by Aric McBay
And here yet another temptation asserts itself. Why not wait until our cause becomes vivid and urgent enough, and our side numerous enough, to vote our opponents out of office? Why not be patient? My own answer is that while we are being patient, more mountains, forests, and streams, more people’s homes and lives, will be destroyed in the Appalachian coal fields. Are 400,000 acres of devastated land, and 1,200 miles of obliterated streams not enough? This needs to be stopped. It does not need to be “regulated.” As both federal and state governments have amply shown, you cannot regulate an abomination. You have got to stop it.
—Wendell Berry, author and farmer
We got further smashing windows than we ever got letting them smash our heads.
—Christabel Pankhurst, suffragist
What is at stake? Whippoorwills, the female so loyal to her young she won’t leave her nest unless stepped on, the male piping his mating song of pure liturgy. They are 97 percent gone from their eastern range.
What is at stake? Mycorrhizal fungi, feeding their chosen plant companions and helping to create soil, with miles of filament in a teaspoon of earth. Bluefin tuna, warm-blooded and shimmering with speed. The eldritch beauty of amanita mushrooms. The mission blue butterfly, a fairy creature if there ever was one. A hundred miles of river turned silver with fish. A thousand autumn wings urging home. A million tiny radicles anchoring into earth, each with a dream of leaves, a lace of miracles, each thread both fierce and fragile, holding the others in place.
If you love this planet, it’s time to put away the distractions that have no potential to stop this destruction: lifestyle adjustments, consumer choices, moral purity. And it’s time to put away the diversion of hope, the last, useless weapon of the desperate.
We have better weapons. If you love this planet, it’s time to put them all on the table and make some decisions.
What do we want? We want global warming to stop. We want to end the globalized exploitation of the poor. We want to stop the planet from being devoured alive. And we want the planet to recover and rejuvenate.
We want, in no uncertain terms, to bring down civilization.
As Derrick succinctly wrote in Endgame, “Bringing down civilization means depriving the rich of their ability to steal from the poor, and it means depriving the powerful of their ability to destroy the planet.” It means thoroughly destroying the political, social, physical, and technological infrastructure that not only permits the rich to steal and the powerful to destroy, but rewards them for doing so.

The strategies and tactics we choose must be part of a grander strategy. This is not the same as movement-building; taking down civilization does not require a majority or a single coherent movement. A grand strategy is necessarily diverse and decentralized, and will include many kinds of actionists. If those in power seek Full-Spectrum Dominance, then we need Full-Spectrum Resistance.1
Effective action often requires a high degree of risk or personal sacrifice, so the absence of a plausible grand strategy discourages many genuinely radical people from acting. Why should I take risks with my own safety for symbolic or useless acts? One purpose of this book is to identify plausible strategies for winning.
If we want to win, we must learn the lessons of history. Let’s take a closer look at what has made past resistance movements effective. Are there general criteria to judge effectiveness? Can we tell whether tactics or strategies from historical examples will work for us? Is there a general model—a kind of catalog or taxonomy of action—from which resistance groups can pick and choose?
The answer to each of these questions is yes.
To learn from historical groups we need four specific types of information: their goals, strategies, tactics, and organization.
Goals can tell us what a certain movement aimed to accomplish and whether it was ultimately successful on its own terms. Did they do what they said they wanted to?
Strategies and tactics are two different things. Strategies are long-term, large-scale plans to reach goals. Historian Liddell Hart called military strategy “the art of distributing and applying military means to fulfill the ends of policy.”2 The Allied bombing of German infrastructure during WWII is an example of one successful strategy. Others include the civil rights boycotts of prosegregation businesses and suffragist strategies of petitioning and pressuring political candidates directly and indirectly through acts that included property destruction and arson.
Tactics, on the other hand, are short-term, smaller-scale actions; they are particular acts which put strategies into effect. If the strategy is systematic bombing, the tactic might be an Allied bombing flight to target a particular factory. The civil rights boycott strategy employed tactics such as pickets and protests at particular stores. The suffragists met their strategic goal by planning small-scale arson attacks on particular buildings. Successful tactics are tailored to fit particular situations, and they match the people and resources available.
Organization is the way in which a group composes itself to carry out acts of resistance. Resistance movements can vary in size from atomized individuals to large, centrally run bureaucracies, and how a group organizes itself determines what strategies and tactics it is capable of undertaking. Is the group centralized or decentralized? Does it have rank and hierarchy or is it explicitly anarchist in nature? Is the group heavily organized with codes of conduct and policies or is it an improvisational “ad hocracy?” Who is a member, and how are members recruited? And so on.
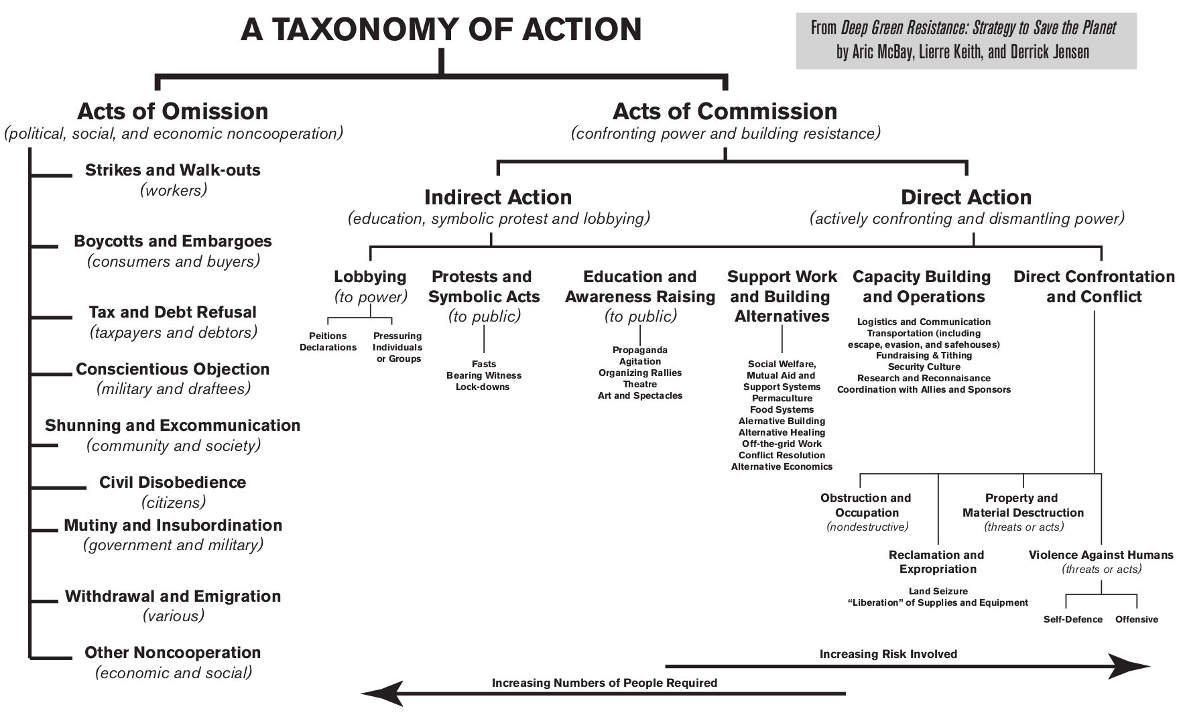
Figure 6-1. Click for larger image.
We’ve all seen biological taxonomies, which categorize living organisms by kingdom and phylum down to genus and species. Though there are tens of millions of living species of vastly different shapes, sizes, and habitats, we can use a taxonomy to quickly zero in on a tiny group.
When we seek effective strategies and tactics, we have to sort through millions of past and potential actions, most of which are either historical failures or dead ends. We can save ourselves a lot of time and a lot of anguish with a quick and dirty resistance taxonomy. By looking over whole branches of action at once we can quickly judge which tactics are actually appropriate and effective for saving the planet (and for many specific kinds of social and ecological justice activism). A taxonomy of action can also suggest tactics we might otherwise overlook.
Broadly speaking, we can divide all of our tactics and projects either into acts of omission or acts of commission. Of course, sometimes these categories overlap. A protest can be a means to lobby a government, a way of raising public awareness, a targeted tactic of economic disruption, or all three, depending on the intent and organization. And sometimes one tactic can support another; an act of omission like a labor strike is much more likely to be effective when combined with propagandizing and protest.
In a moment we’ll do a quick tour of our taxonomic options for resistance. But first, a warning. Learning the lessons of history will offer us many gifts, but these gifts aren’t free. They come with a burden. Yes, the stories of those who fight back are full of courage, brilliance, and drama. And yes, we can find insight and inspiration in both their triumphs and their tragedies. But the burden of history is this: there is no easy way out.
In Star Trek, every problem can be solved in the final scene by reversing the polarity of the deflector array. But that isn’t reality, and that isn’t our future. Every resistance victory has been won by blood and tears, with anguish and sacrifice. Our burden is the knowledge that there are only so many ways to resist, that these ways have already been invented, and they all involve profound and dangerous struggle. When resisters win, it is because they fight harder than they thought possible.
And this is the second part of our burden. Once we learn the stories of those who fight back—once we really learn them, once we cry over them, once we inscribe them in our hearts, once we carry them in our bodies like a war veteran carries aching shrapnel—we have no choice but to fight back ourselves. Only by doing that can we hope to live up to their example. People have fought back under the most adverse and awful conditions imaginable; those people are our kin in the struggle for justice and for a livable future. And we find those people—our courageous kin—not just in history, but now. We find them among not just humans, but all those who fight back.
We must fight back because if we don’t we will die. This is certainly true in the physical sense, but it is also true on another level. Once you really know the self-sacrifice and tirelessness and bravery that our kin have shown in the darkest times, you must either act or die as a person. We must fight back not only to win, but to show that we are both alive and worthy of that life.

by Deep Green Resistance News Service | May 4, 2018 | Strategy & Analysis
by Boris Forkel / Deep Green Resistance Germany
Capitalism reaches fulfillment when it sells communism as a commodity. Communism as a commodity spells the end of revolution.
—Byung-Chul Han
I’m a permaculturalist. And I became a permie in the first place because I wanted to break free from this culture.
To me, permaculture was and still is highly political. “Permaculture is revolution disguised as gardening” is one of my favorite Bill Mollison quotes.
After all, what freedom can we have without subsistence, without having control over our most basic resources, our own food? “There is no sovereignty without food sovereignty,” said Native American activist John Mohawk.
I’ve been so ardent and naive. I thought that the permaculture-approach is so ingenious that it would become a mass-movement, indeed a quiet and peaceful revolution. It would free us from being dependent on the digital food they sell us in grocery stores nowadays, and from the wage economy at the same time, because we would build small, local food cooperatives that would all be sharing the surplus.
Unfortunately, time and experience shows that it’s not that easy.
One of my permaculture teachers, who taught me the concept of the food forest, often said: “I don’t understand what’s the problem for all these critical people. Nowadays, we have all the freedoms we want.” He also articulated a very strange notion about the future: “Once we have reached the number of 10 billion, human population growth will come to a halt. Thanks to Internet technology, humans will then all be connected and serve as the consciousness of planet earth.” Attendants hung on his lips when he said that, and while everybody else was amazed by this perspective of a golden future, I sat quietly, stunned.
I knew in my heart that he was wrong, but couldn’t articulate a sufficient answer to his statements back then.
It made me angry. How can one say that “we have all the freedoms we want,” while the air we need to breathe is being polluted, the greatest mass extinction in planetary history is happening, the climate is being destroyed, the oceans are vacuumed and filled with toxic garbage? In short: when the most basic functions of our planet to support life are being destroyed?
What about the freedom of having breathable air? What about the freedom of having a livable planet? What about the freedom of having a future?
I’ve given a lot of thought to his statements ever since, because they seem so appealing to many people. The Earth never supported more than 2 billion humans until Fritz Haber and Robert Bosch indeed broke the planetary boundaries with the invention of the Haber-Bosch process. Nowadays, we are hopelessly overpopulated. So the number of 10 billion is purely random and nothing but magical thinking. The notion of Internet technology and humans as the consciousness of the planet is nothing more than a new fashion of the good old ideology of humans as the crown of creation. What about nature in this fantasy? With 10 billion (industrial) humans, there will hardly be anything left.
Everybody with a sane mind and a little understanding—especially a permie—should know that the trees, the fungi, the soil, the air, the water, the animals and so on, in short what we call nature, indeed is the consciousness of planet earth. Apparently, the manifest destiny of the technocrats is to eradicate what they perceive as primitive, raw, red in tooth and claw, wild and uncontrollable, and to replace nature with a “better” system of human technology.
Deconstructing that was the easy part. The hard part is his statement about freedom. With all this in mind, the primary question is: what does freedom mean for someone like him?
A friend of mine, who was lucky enough to hear Noam Chomsky speak live, told me that in the discussion after somebody asked the usual question: “What can we do about it?” Chomsky responded that he thinks this is a strange question. People from so-called developing countries would never ask such a question, only westerners, he stated. Apparently, third-world-people still have a clearer sense for suppression and cultures of resistance. “We should rather ask what we can’t do,” Chomsky said.
When I attended a talk by Rainer Mausfeld, of course someone asked the very same question. Mausfeld stated that this question shows how well the soft power techniques he’d been describing work. We can’t even imagine any form of resistance.
For more than a century, the political left’s analysis has been very clear: The suppression and exploitation of the poor (working class) by the rich (owning class), that is the very basis of capitalism, can only be solved by organized class struggle to come from the working class. This concept isn’t hard to understand. It is classic Marxism. But somehow, the ruling class has managed to completely eradicate it from the proletarian minds.
I’ve come across a lot more of what I like to call liberal lifestyle-activists. I understood that most permies chose permaculture not because they want a revolution (like I did), but because they want a more sustainable lifestyle for themselves. They believe that they are free, because they perceive their individualism and their freedom of choice as the greatest freedom, the greatest achievement of modernity. Being part of any group, class or movement is perceived as regressive. The notion of class struggle is so yesterday.
At the same time, they’re usually educated people, and they know that a lot of things are going badly wrong. But as liberals who are taking power out of the equation, and individualists lacking any concept of social group our class, they must take it all on themselves. “It is all of us who are causing the destruction,” they’d say.
As a result, the only thinkable form of political action are personal consumer choices. Buy organic soap and feel better.
A great example of this are vegans. No doubt that factory farming is horrible and has to stop. But as a lifestyle-activist, all you can do about it is to stop consuming meat. In your worldview, the problem can only be solved by everybody stopping eating meat.
For liberal lifestyle-activists, “having all the freedoms we want” can only mean the freedom to consume (or not consume) whatever we want, whenever we want, in any quality and quantity we want. This is the kind of “freedom” with which capitalism has hijacked us. If we can afford it, of course. But within neoliberal capitalist ideology, there is no such thing as a suppressed class. The poor are poor because they don’t work hard enough, or they are simply to stupid to sell themselves well enough.
“Neoliberalism turns the oppressed worker into a free contractor, an entrepreneur of the self. Today, everyone is a self-exploiting worker in their own enterprise. Every individual is master and slave in one. This also means that class struggle has become an internal struggle with oneself. Today, anyone who fails to succeed blames themselves and feels ashamed. People see themselves, not society, as the problem.”
Byung-Chul Han
For radicals, the question remains: Without the possibility of mass movements, how do we stop the destruction of the planet that is our only home?
For a new generation of serious activists who are tired of all that shit and ready to take action, DGR has the Decisive Ecological Warfare strategy.

by DGR News Service | Apr 28, 2018 | Strategy & Analysis
Featured image: Activists March Against Nestlé On Bridge of The Gods
Land defense and social justice work are necessary for healthy human and non-human communities, but any victories will be irrelevant if industrial civilization makes the planet literally unlivable. The system must be stopped before it triggers irreversible runaway climate change and ecological collapse, and only strategic underground attacks against critical infrastructure will stop it. There are many hard working activists in the aboveground struggle, though we can always use more. Unfortunately, as far as we can tell, vanishingly few people are carrying out the necessary attacks against industrial bottlenecks and weak points in infrastructure. Underground promotion remains the most important work for those of us in the aboveground.
To help us better understand the barriers to formation of an underground, we’re surveying those who have committed to aboveground work. If you’ve joined a radical aboveground group, publicly stated your support of ecosabotage, engaged in environmental civil disobedience, or otherwise drawn attention to your strong enviro-political beliefs, we want to learn the reasons behind your decision.
Please take a few minutes to let us know why you chose an aboveground path, rather than underground work. You can fill out the short anonymous survey below, email us, or leave a comment. Thanks!








