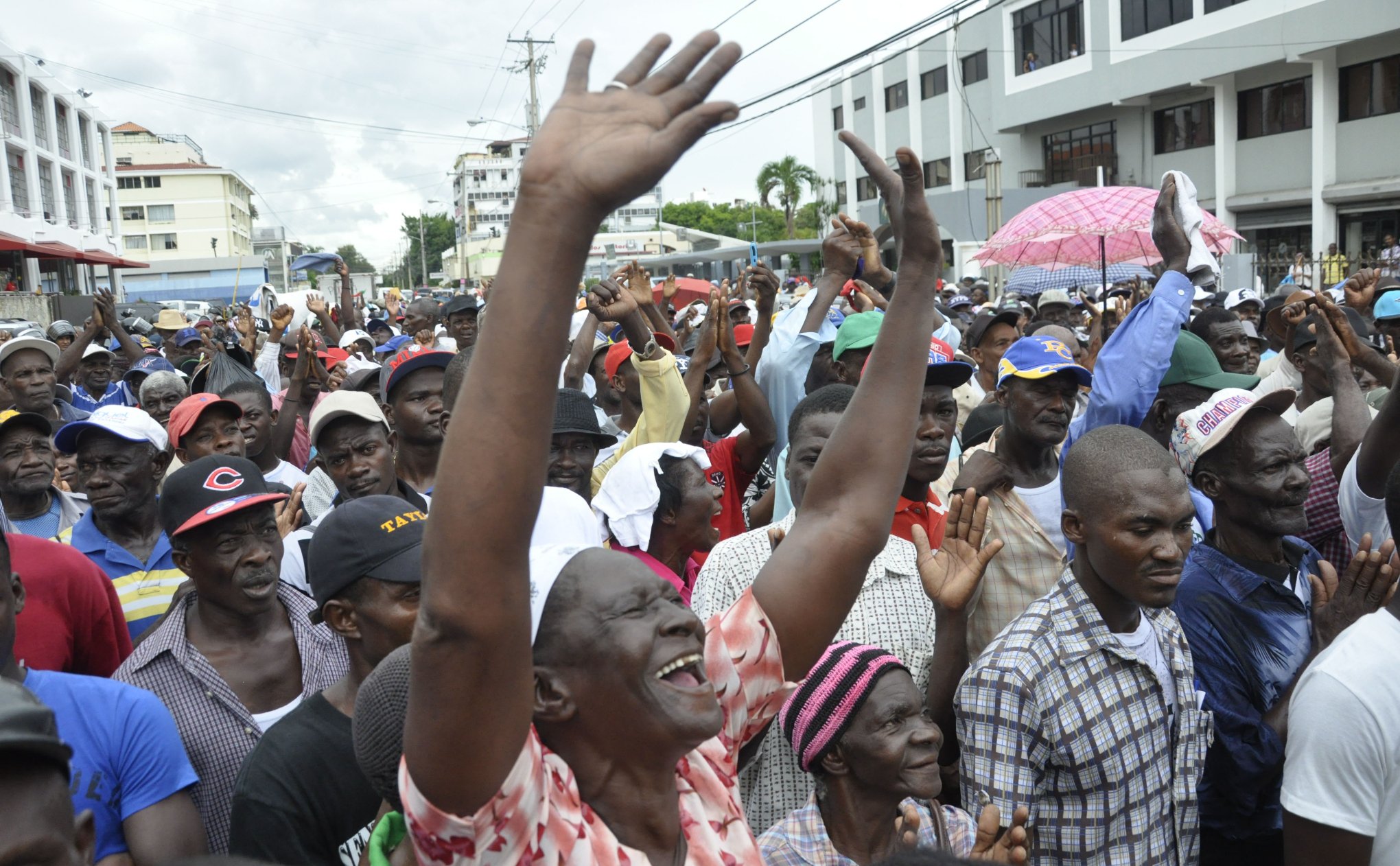By One Struggle
On what I earn, I can’t afford shoes… We are poor, poor, poor. There are days we go to bed without food. – Batey worker from the film, “The Price of Sugar”
In the sugar plantations or bateyes of Dominican Republic, cane cutters often work barefoot. They can’t afford shoes. They can barely afford food, for that matter, despite the fact that they often work a minimum of 12 hours a day, doing the back-breaking work of cutting sugar cane by hand.
On the other side of the border that divides Hispaniola, Haitian garment workers in Port Au Prince recently blockaded a Korean factory because of bounced paychecks. For years, Haitian garment workers have been fighting wage theft and to be paid the inadequate legal minimum wage – still not enough to live off of.
Whatever the product is – the pair of pants, the t-shirt – we are the ones producing it. We labor hard, and don’t get paid. – Haitian garment worker of SOTA in Port Au Prince
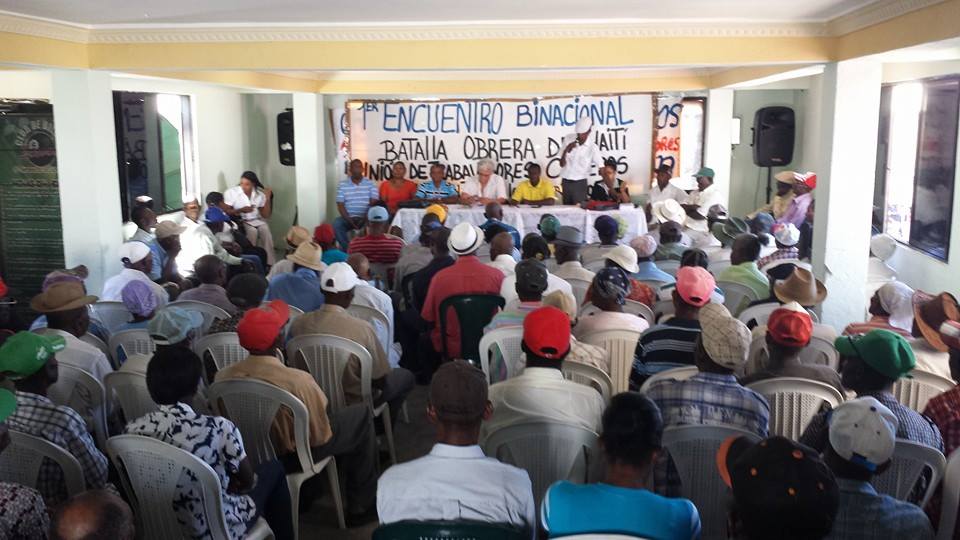
This week Unión De Trabajadores Cañeros De Los Bateyes (Union of the Bateyes of Sugarcane Workers) and Sendika Ouvriye Takstil ak Abiman (SOTA) (Union of Textile and Garment Workers) will meet to discuss their common struggles against exploitation.
Specifically, they are meeting about recent actions of the DR government to strip people of Haitian descent of their citizenship. This has mostly affected the poor – cane cutters, street vendors, and service laborers. In bringing attention and their perspective to this struggle, the groups’ intentions are to put down false divisions of racism and nationalism, with the goal of working together against their common enemy – the Haitian and Dominican ruling classes.
SOTA is affiliated with the autonomous workers’ organization, Batay Ouvriye (BO) (Workers Fight), which will host a series of meetings, a press conference, and direct action in Port Au Prince.
According to one of the event organizers, “They will be three Haitian cane workers, one Dominican cane worker and the coordinator of the union. The presence of the Dominican cane worker is to deny the nationalist option and to put the class situation in concrete relief, in contrast to the bourgeois organizations here who pretend to defend their ‘compatriots.’”
There is a long history of animosity between Haiti and Dominican Republic. Both nationalism and racism are deep rooted. The DR won its independence, not from European colonialists, but from Haiti. Since then, Haitians living in the DR have faced discrimination, and thousands of Haitians and Dominicans of Haitian descent were massacred under Dominican dictator, Rafael Trujillo.
In 2013, the Dominican Supreme Court retroactively withdrew citizenship from anyone born in the DR to undocumented immigrants, with the provision that persons who submitted the proper documentation could apply for legal residency. The deadline for this application was summer 2015. However, many who submitted this paperwork, along with hundreds of dollars in fees, never received any notice or proper documentation from the government. Thousands of Haitians and Dominicans of Haitian descent left the DR, or were rounded up and dropped at the Haitian/Dominican border, often without being able to gather their belongings or to alert their families.
So now, there are hundreds of thousands of people rendered stateless, living in temporary shanty-towns along the border. They’ve been told that if they get documentation proving their country of origin from the Haitian government, then they can apply for Dominican citizenship or work visas. In fact, the Haitian government was paid by the Dominican government to facilitate this process, but Haitians living in limbo on the border have seen no results from this transaction.
Another issue affecting cane workers and low-wage laborers is that for years many paid into social security in the DR. Once they stopped working, they apply for their pensions, submitting the required paperwork to DR government and received nothing. Or, if they’ve been deported, they have no means of claiming their pension either.
This situation is not just about racism or nationalism. It is an issue of the ruling classes of both countries exploiting and stealing from the poor and working class. This summer, many demonstrations were held, especially in New York and Miami, with calls for travel boycotts against the DR and urgent appeals to avert a humanitarian crisis. Most of these demands have been voiced from people outside of the DR/Haiti, or removed from the exploitation of the bateyes and the temporary shanty-towns.
The aim with this series of meetings between workers from both countries is to bring attention to calls and demands led by the workers and people directly affected by these struggles. These are the people whose demands should be amplified, and calls for action should be followed.
Here in the U.S. we use Dominican sugar in our coffee every day. Our clothing is made in sweatshops, often sewn in Haiti (thanks to HELP and HOPE Acts). Capitalism and imperialism give us no choice, no say in how goods are produced. Our sugar and our clothing are the results of wage theft and a politic of misery for the working class in dominated countries. Boycotts and conscious consumerism pretend that with our purchasing, exploitation can be ameliorated. In reality, it is merely shifted to another part of the world. We need to understand the dynamics of capitalism/imperialism, its inherent exploitation, and we must address these issues from the interests of the working class. Who better to lead this effort than the workers themselves?
Read more at One Struggle