by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Jul 26, 2012 | Colonialism & Conquest, Mining & Drilling
By Rhett Butler / Mongabay
A directive signed Monday by Brazil’s Solicitor-General could hamper the efforts of indigenous tribes to win government recognition of their traditional lands, reports Survival International, a human rights group focused on native peoples.
The directive “opens up all indigenous areas to mineral, dams, roads, military bases and other developments of ‘national interest’ without the need to consult with or address concerns of indigenous peoples”, according to an expert familiar with the directive who asked to remain anonymous. It also restricts demarcation of new indigenous territories.
Survival International called the move “disastrous” citing the plight of the Guarani tribe, some members of which are waiting “in roadside camps or overcrowded reserves” for their ancestral lands to be mapped and allocated.
“This directive puts our survival in extreme danger,” Survival International quoted a Guarani spokesman as saying. “We are being ignored as human beings, as the first occupants of this land. It is the start of the extermination of indigenous people.”
According to the indigenous lands expert reached by mongabay.com, the directive was originally intended to overcome issues in implementing the Raposa/Serra do Sol indigenous area in the northern Brazilian state of Roraima, but the powerful ruralista bloc in Congress pushed to apply the directive to all indigenous areas. The ruralistas also successfully pushed for a weakening of the country’s Forest Code, which mandates how much forest landowners are required to protect, earlier this year. (The final version of the Forest Code is pending).However outcry over the directive on Wednesday led Brazil’s Public Prosecutors’ Office to suspend the measure pending a court ruling on the issue. Survival International and several Brazilian indigenous organizations have called for the directive to be revoked entirely.
The directive was passed only a month after an association of more than 1,200 tropical scientists convening at the annual meeting of the Association for Tropical Biology and Conservation sounded the alarm on the potential development.
Indigenous territories cover roughly 22 percent of the legal Brazilian Amazon. Areas managed by indigenous groups have lower deforestation rates than unprotected forests.
by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Jul 25, 2012 | Defensive Violence, Indigenous Autonomy
By Amazon Watch
Three engineers employed by Norte Energia, S.A (NESA), the company building the Belo Monte Dam on Brazil’s Xingu river, were detained Tuesday by Juruna and Arara tribal authorities in the remote village of Muratu after the company failed to live up to promised mitigation measures aimed at reducing the dam’s devastating impacts on local communities.
The incident occurred yesterday as Norte Energia sought to reach agreement with tribal leaders over measures to allegedly mitigate adverse impacts stemming from construction of earthen cofferdams on the Xingu river. The authorities report that the engineers are being prohibited from leaving the village but there is no use of force or violence. The dams are blocking navigation of small boats used by indigenous peoples and other local communities, especially to reach the town of Altamira, an important center for accessing markets, basic health care, education and other services.
In Tuesday’s meeting, Norte Energia representatives presented a proposal for a system for transportation of indigenous vessels around the site where cofferdams are blocking boat traffic. Tribal leaders interrupted the meeting, arguing that the proposal was ludicrous, and that such discussions would not proceed while a long list of legally required actions to mitigate and compensate the adverse impacts of Belo Monte continues to be ignored by NESA. A first phase of the earthen dams has already had negative consequences for indigenous peoples, especially on water quality and devastation of fisheries.
“Nobody understood anything that the technicians said, and they didn’t have any answers to our questions,” explained Giliarde Juruna, a leader of the Juruna tribe from the Paquiçamba territory immediately downstream from the dam. “They didn’t know how to respond when we asked them how we would bathe or how we would navigate on the river, or even how the project had changed since they presented it to us last year. In the end, the engineers agreed that our complaints were justified.”
“There was a climate of total disbelief on behalf of the tribes, since Norte Energia recognized it had yet to implement the vast majority of the legally-required measures to minimize the impacts of the project on their lands,” explained Thais Santi of the Federal Public Prosecutor’s Office in Altamira, who was an observer at the meeting. “At a certain level, even the engineers recognized that the dam is an absurdity, that the consultation was a sham, and that the mitigation projects presented by the company’s technical team didn’t make any sense,” noted Santi.
According to tribal leaders, the engineers will remain under detention until Norte Energia and government agencies have fully carried out promises to mitigate and compensate adverse impacts of Belo Monte, not only in relation to boat traffic, but also in terms of water quality, sanitation, and protection of their territories and natural resources.
On Monday, the Federal Public Prosecutors’ Office filed a lawsuit calling for the immediate suspension of the construction license for Belo Monte, granted in June 2011 by the federal environmental agency, IBAMA. Citing an abundance of evidence, including reports produced by IBAMA and municipal governments and well-documented complaints files by local indigenous leaders and NGOs, the lawsuit demands that project construction at Belo Monte be immediately halted, given the chronic non-compliance of Norte Energia with legally-required mitigation and compensation measures.
“It’s an outrage that Norte Energia has been allowed to continue construction for over a year while ignoring basic measures they are obliged to carry out in order to avoid or minimize impacts on affected communities. The developer is ignoring the impacts the project is already having on indigenous people, and in the process, running roughshod over their rights,” said Brent Millikan of International Rivers.
Last month, over 300 indigenous people from 9 tribes occupied the Belo Monte Dam construction site on the final day of the United Nations Rio+20 conference, maintaining the occupation for 21 days until Norte Energia stated it had reached an agreement with the occupiers. The tribal leaders involved in yesterday’s action claim that an agreement was never reached, and that the developer has instead created divisions among the communities.
Norte Energia consortium, while technically a “private” enterprise, is dominated by the Brazilian state-owned energy conglomerate Eletrobras. Major investments come from the public employee pension funds of Petrobras, Banco do Brasil and Caixa Econômica Federal, all entities under government control. The mining giant Vale, privatized in the mid-1990s but still highly influenced by the Brazilian government, recently purchased a 9% stake in the NESA consortium. Eighty percent of project financing for Belo Monte’s mushrooming budget, currently estimated at US$12 billion, comes from BNDES, the government-controlled development bank, financed by worker taxes and Brazilian treasury bonds.
From Amazon Watch: http://amazonwatch.org/news/2012/0725-amidst-broken-promises-indigenous-authorities-detain-belo-monte-dam-engineers
by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Jul 25, 2012 | Climate Change
By Suzanne Goldberg / The Guardian
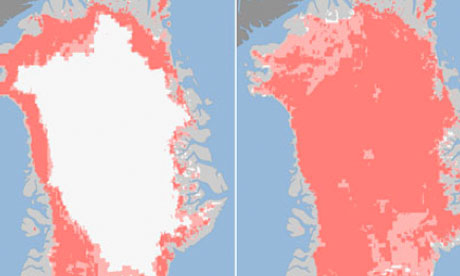
The Greenland ice sheet melted at a faster rate this month than at any other time in recorded history, with virtually the entire ice sheet showing signs of thaw.
The rapid melting over just four days was captured by three satellites. It has stunned and alarmed scientists, and deepened fears about the pace and future consequences of climate change.
In a statement posted on Nasa’s website on Tuesday, scientists admitted the satellite data was so striking they thought at first there had to be a mistake.
“This was so extraordinary that at first I questioned the result: was this real or was it due to a data error?” Son Nghiem of Nasa’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena said in the release.
He consulted with several colleagues, who confirmed his findings. Dorothy Hall, who studies the surface temperature of Greenland at Nasa’s space flight centre in Greenbelt, Maryland, confirmed that the area experienced unusually high temperatures in mid-July, and that there was widespread melting over the surface of the ice sheet.
Climatologists Thomas Mote, at the University of Georgia, and Marco Tedesco, of the City University of New York, also confirmed the melt recorded by the satellites.
However, scientists were still coming to grips with the shocking images on Tuesday. “I think it’s fair to say that this is unprecedented,” Jay Zwally, a glaciologist at Nasa’s Goddard Space Flight Center, told the Guardian.
The set of images released by Nasa on Tuesday show a rapid thaw between 8 July and 12 July. Within that four-day period, measurements from three satellites showed a swift expansion of the area of melting ice, from about 40% of the ice sheet surface to 97%.
Zwally, who has made almost yearly trips to the Greenland ice sheet for more than three decades, said he had never seen such a rapid melt.
About half of Greenland’s surface ice sheet melts during a typical summer, but Zwally said he and other scientists had been recording an acceleration of that melting process over the last few decades. This year his team had to rebuild their camp, at Swiss Station, when the snow and ice supports melted.
He said he was most surprised to see indications in the images of melting even around the area of Summit Station, which is about two miles above sea level.
It was the second unusual event in Greenland in a matter of days, after an iceberg the size of Manhattan broke off from the Petermann Glacier. But the rapid melt was viewed as more serious.
“If you look at the 8 July image that might be the maximum extent of warming you would see in the summer,” Zwally noted. “There have been periods when melting might have occurred at higher elevations briefly – maybe for a day or so – but to have it cover the whole of Greenland like this is unknown, certainly in the time of satellite records.”
Read more from The Guardian: http://www.guardian.co.uk/environment/2012/jul/24/greenland-ice-sheet-thaw-nasa

by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Jul 24, 2012 | Mining & Drilling
By Andreea Campeanu / Agence France-Presse
Knee-deep in muddy water, a 10-year-old child and a woman with braided hair lean over a large sieve, washing earth and rocks, their eyes clenched against the filthy splashing water.
They are among the thousands of panners hoping to strike it rich on a recently discovered seam of sapphires, running through Madagascar’s newest national park created to protect the island’s famed lemurs and dozens of other rare species.
The 381,000 hectares (941,000 acres) of virgin rainforest of the Ankeniheny-Zahamena corridor officially became a protected area late last year. Then in April, sapphires were found.
“We had an invasion of illegal miners in this park, which is our most recent protected area”, says Angelo Francois Randriambeloson from the ministry of environment.
The park has 2,043 identified species of plants; 85 percent are found no where else in the world. There’s also 15 species of lemurs, 30 other mammals, 89 types of birds and 129 kinds of amphibians. And that’s just what’s been discovered so far.
But now among the park’s tall trees, a one-kilometre (half-mile) stretch of river valley has turned into a mudpit as thousands of Madagascar’s desperately poor people have thrown up makeshift homes of branches and plastic sheets, beaten by near-daily rains.
The vast Indian Ocean island is one of the poorest countries in the world, with 81 percent of the population living on less than $1.25 a day, according to the World Bank.
Sapphires present an irresistible lure of quick riches for the lucky, who say they don’t have to dig more than three metres (10 feet) to find large stones.
Madagascar is one of the world’s biggest sapphire producers, selling most to Sri Lanka and Thailand for cutting and polishing.
Reaching the mine takes two days of hard walking from the small town of Didy, the closest place reachable by bush taxi. Even getting to Didi is tough. It’s 300 kilometres from the capital, and less than a third of the distance is on paved roads.
The last 10 hours of the walk is through beautiful rain forest, climbing precipitous hills on barely perceptive boggy paths.
Morris, a 40-year-old aspiring miner, walked barefoot, carrying a heavy sack of rice so he would have food at the mine.
Most people spend just a few weeks here until they find one or more larger sapphires or rubies, some up to 10 grams.
“Here there are only two: blue sapphires and rubies. But there are more large ones,” said Dudu, a 35-year-old buyer.
But the government wants miners to leave the park.
“We are now forming a commission and we are trying to plan a way to send the people away from the mine,” said Randriambeloson. “As it’s a protected park, its soil also belongs to the Malagasy state.”
But people still go every day, in groups, to and from the mine. Some have nothing but the clothes they are wearing. Others carry bags of rice, noodles, powdered milk or even generators.
Water for washing is now hard to find, since the river is extremely dirty. There is no drinking water and not a lot of food. Informal eateries surrounded by mud and fallen branches are expensive.
“The place has changed, there are more people around. But there are no security problems, only sanitation ones,” Didy’s deputy mayor said.
The authorities in the capital Antananarivo sent in police to discourage people from mining, to little result so far.
“Once the miners are out, we will restore the damage done,” Randriambeloson vowed.
From Google News:
by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Jul 23, 2012 | Worker Exploitation
By Heather Stewart / The Observer
The world’s super-rich have taken advantage of lax tax rules to siphon off at least $21 trillion, and possibly as much as $32tn, from their home countries and hide it abroad – a sum larger than the entire American economy.
James Henry, a former chief economist at consultancy McKinsey and an expert on tax havens, has conducted groundbreaking new research for the Tax Justice Network campaign group – sifting through data from the Bank for International Settlements (BIS), the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and private sector analysts to construct an alarming picture that shows capital flooding out of countries across the world and disappearing into the cracks in the financial system.
Comedian Jimmy Carr became the public face of tax-dodging in the UK earlier this year when it emerged that he had made use of a Cayman Islands-based trust to slash his income tax bill.
But the kind of scheme Carr took part in is the tip of the iceberg, according to Henry’s report, entitled The Price of Offshore Revisited. Despite the professed determination of the G20 group of leading economies to tackle tax secrecy, investors in scores of countries – including the US and the UK – are still able to hide some or all of their assets from the taxman.
“This offshore economy is large enough to have a major impact on estimates of inequality of wealth and income; on estimates of national income and debt ratios; and – most importantly – to have very significant negative impacts on the domestic tax bases of ‘source’ countries,” Henry says.
Using the BIS’s measure of “offshore deposits” – cash held outside the depositor’s home country – and scaling it up according to the proportion of their portfolio large investors usually hold in cash, he estimates that between $21tn (£13tn) and $32tn (£20tn) in financial assets has been hidden from the world’s tax authorities.
“These estimates reveal a staggering failure,” says John Christensen of the Tax Justice Network. “Inequality is much, much worse than official statistics show, but politicians are still relying on trickle-down to transfer wealth to poorer people.
“This new data shows the exact opposite has happened: for three decades extraordinary wealth has been cascading into the offshore accounts of a tiny number of super-rich.”
Read more from The Guardian: http://www.guardian.co.uk/business/2012/jul/21/offshore-wealth-global-economy-tax-havens


