by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Jan 8, 2018 | Colonialism & Conquest
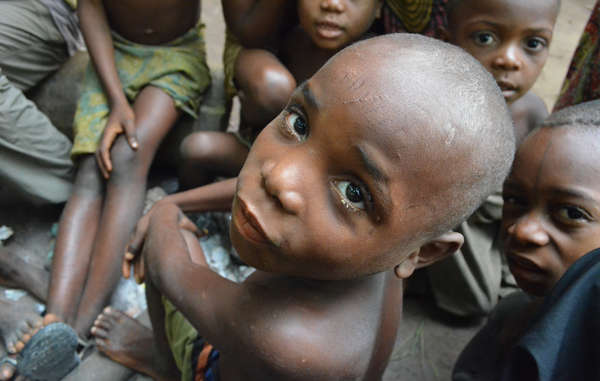
Featured image: A recent epidemic in the Republic of Congo is said to have been aggravated by the loss of indigenous peoples’ resources due to conservation and logging projects. © C. Fornellino Romero/Survival International
by Survival International
A Congolese organization has recently raised concerns that conservation contributed to the deaths of several dozen children, mostly Bayaka “Pygmies,” during an epidemic in 2016 in the Republic of Congo – the latest in a long line of related reports.
The deaths have been attributed by a medical expert to malaria, pneumonia and dysentery, aggravated by severe malnutrition.
Conservation-related malnutrition among Bayaka children in this region has been reported since 2005 at least, as the Bayaka are prevented from hunting and gathering on their lands by wildlife guards through violence and intimidation.
These guards are funded and equipped by the Wildlife Conservation Society (WCS), one of the world’s largest conservation organizations, and the logging company it has partnered with, CIB. Both organizations have failed to take effective action to prevent abuse.
“The wildlife guards abuse us. They don’t want us to go into the forest. How can we feed our children?” a Bayaka man from Mbandza, the site of the epidemic, told Survival in 2016.
These guards have been accused of abusing Bayaka and stealing their food for over 13 years. One such attack that took place in Mbandza in early 2016 left one man hospitalized.

The Baka and Bayaka’s consent is required by law for any major project on their lands, but this is ignored by WWF and WCS. © Survival International
In this way, the Bayaka are being illegally evicted from their ancestral homelands by threat of violence. As one Bayaka woman explained: “If we go into the forest we eat well there compared to the village. We eat wild yams and honey. We want to go into the forest but they forbid us to. It frightens us. It frightens us.”
Critics have noted that the guards have also failed to protect the wildlife the Bayaka depend on for food, since they have difficulty tackling corruption and the creation of logging roads, the two main drivers of poaching.
Plummeting health has been reported among Bayaka living in the Dzanga-Sangha Protected Areas in the Central African Republic – one of the World Wildlife Fund’s (WWF) flagship projects – since 2006. Conditions encountered among older women “would be considered a public health crisis by international health agencies,” according to research published in 2016.
Increased malnutrition and mortality have been reported among Baka “Pygmies” in Cameroon, where WWF also operates, and among Batwa “Pygmies” in another of WCS’s project sites in east Democratic Republic of Congo.
“Now we are afraid of the anti-poaching squads. Before when a woman gave birth we took her to the forest to help her regain her strength and weight, now we can’t do this. We would take our children to the forest to avoid epidemics. Now we know illnesses we never knew before,” one Baka woman in Cameroon told Survival.
Watch Baka describe the abuse they face as a result of WWF’s conservation projects
Baka health plummets due to conservation
In the Congo Basin, the Baka, Bayaka and dozens of other rainforest peoples are being illegally evicted from their ancestral homelands in the name of conservation. Their health is plummeting as a result.
The big conservation organizations that support these conservation projects, like the World Wildlife Fund (WWF), refuse to abide by basic international standards and secure their consent.
Neither WCS nor WWF has attempted to secure the indigenous peoples’ consent, as basic due diligence and their own human rights policies require.
Survival’s Director Stephen Corry said: “Land theft is a serious and deadly crime, as these reports show. Many associate conservation with reason and compassion but, for Baka and Bayaka, it often means mindless violence and plummeting health. When will WWF and WCS finally start complying with their own human rights policies? ”
Timeline
1996: The organization Berggorilla & Regenwald Direkthilfe finds that malnutrition and mortality has increased among Batwa “Pygmies” since they were evicted from Kahuzi-Biega, a national park in east Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) funded by WCS.
1997: WWF observes that the fact that the Bayaka are banned from hunting or gathering inside the Dzanga-Ndoki Park, the park in the Central African Republic (CAR) that WWF helped to create, “punishes [the Bayaka] severely” and is undermining their food security.
2000: A study finds that the Batwa in Kahuzi-Biega, DRC, are suffering from nutritional deficiencies, because they are no longer able to hunt in the forest, and soaring mortality rates. Malnutrition is particularly pronounced among women and children.
2004: A BBC investigation into CIB’s logging concessions in Congo hears from a Bayaka man: “We get so much suffering because of [wildlife] guards. We can’t go and find things in the forest as we used to. All we hear is hunger.”
2004: Bayaka from another community in Congo report to Greenpeace: “Then we met another white man (WCS) who came to tell us to stop hunting and that the wildlife guards would make sure we did. Now we are afraid to go far in the forest in case the wildlife guards catch us so we have to stay in the village. […] Now we are dying of hunger.”
2005: The Congolese Observatory on Human Rights, the organization that reported on the 2016 epidemic, documents three cases of violent abuse against Bayaka by wildlife guards, and warns that some Bayaka “are dying of hunger.”
2005: A news report recounts how Bayaka in one of CIB’s logging concessions describe being targeted by wildlife guards that mistreat and temporarily imprison them, and how this has led to more frequent malnutrition among children and vulnerable adults.
2006: WWF and its partners commission a report that finds that the Bayaka in Dzanga-Sangha, CAR, are struggling to feed themselves. The Bayaka interviewed for the report state that the conservation project has forced them out of some of their richest hunting and gathering grounds. They report that wildlife guards harass or attack them even when they try to use the reduced areas of land they have left, all the while accepting bribes from the real poachers who were emptying the forest of its wildlife. Some Bayaka women are finding it so hard to find food, the investigator hears, that they have been driven to sex work in the nearby town.
2006: An article in The Lancet cautions that “Pygmy peoples’ health risks are changing as the central African forests, which are the basis for their traditional social structure, culture, and hunter-gatherer economy, are being destroyed or expropriated by […] conservation projects:”
2008: UNICEF warns that the Bayaka’s right to gather resources is being “flouted on the most basic level because indigenous people no longer have access to areas rich in game” due to protected areas in Congo.
2012: An anthropologist with 18 years’ experience working with Bayaka in Congo reports increasingly poor nutrition and increased mortality. He attributes this to the removal of forest resources by loggers and to “conservationists’ exclusionary and draconian management practices.”
2013: A researcher at the University of Oxford reports that the combined impact of conservation and logging have led to poorer health and higher levels of drug and alcohol addiction among the Bayaka. He argues that conservation efforts would benefit from gaining people’s consent
2014: A medical study finds that “punitive anti-poaching measures” and dwindling wildlife have caused health to plummet among Bayaka in Dzanga-Sangha, CAR, particularly among women. “It is disheartening to see health decline so closely tied […] to the conservation management policies of the last twenty-five years,” the study’s authors note.
2015: A doctor with extensive experience working in CIB’s logging concessions reports that: “Aside from wounds inflicted by gorillas, buffalo or other wild animals, my colleague and I also see [gun] wounds in people claiming to have been attacked – sometimes without warning – by the protectors of wildlife: the wildlife guards.”
2015: The same doctor tells Survival: “I find this [wildlife guard violence] a very serious problem and in my opinion most wildlife guards have other motives than protecting the animals to work as a wildlife guard.”
2016: A second doctor with extensive experience working in CIB’s logging concessions describes to Survival the seasonal malnutrition she encounters among Bayaka, which she attributes to repressive conservation policies.
“Pygmy” is an umbrella term commonly used to refer to the hunter-gatherer peoples of the Congo Basin and elsewhere in Central Africa. The word is considered pejorative and avoided by some tribespeople, but used by others as a convenient and easily recognized way of describing themselves.
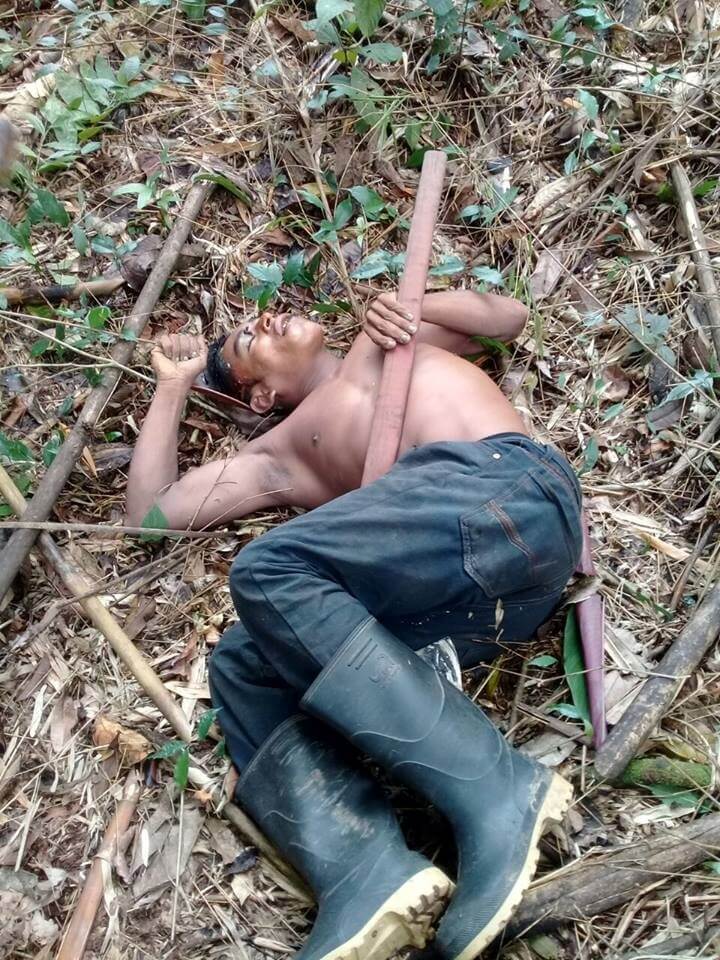

by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Dec 7, 2017 | Colonialism & Conquest
Featured image: Cejudhcan Derechos Humanos
by Courtney Parker / Intercontinental Cry
¡Ya Basta! A phrase known for its political and revolutionary connotations throughout much of the Spanish-speaking world, translates roughly into English as, ‘Enough is Enough!’
It is a statement of finality; a concrete call to action; a heightened call for awareness; and an official call of duty to end cultures of violence and impunity against Indigenous Peoples.
His name was Felipe Perez Gamboa. He was 24 years old.
According to Mark Rivas, who has aided in representing the Moskito Council of Elders at the United Nations, Gamboa was a leader of much distinction among the young people of the community of La Esperanza on the traditional Indigenous frontier region of Moskitia – located on the northern Caribbean coast of colonial Nicaragua and home to the largest tropical rainforest, second only to the Amazon, in the western world.
For his part, Rivas credited Cejudhcan Derechos Humanos – a local NGO whose founder, lawyer Lottie Cunningham, and staff, have been on the receiving end of death threats for their ongoing human rights work in the region – with originally disseminating and confirming the tragedy to the larger community.
The traditional Indigenous frontier regions of Moskitia have been terrorized by mounting acts of deadly colonial violence, stemming from the expanding agricultural frontier and the rigidly nationalist agenda, since 2015.
IC first began reporting on the escalating tragedies in the traditional Indigenous regions in June of 2016.
Readers may refer to previous analyses here and in other outlets concerning the role of the Ortega government, neoliberalism, and the fraudulent banner of ‘Christian Socialism’ the fallen Sandinista leader still attempts to hang over his tenuous authoritarian rule.
As of right now, we can do no more than reach out to the Indigenous rights community in the rest of Latin America, and across the world, with the simple message, made famous by the Zapatsista, that ‘Enough IS Enough’.
It’s time to end this culture of impunity surrounding deadly violence against Indigenous Peoples – in this instance, those who are protecting the last bastions of a biodiverse, climate mitigating rainforest.
¡Ya basta!
¡YA BASTA!
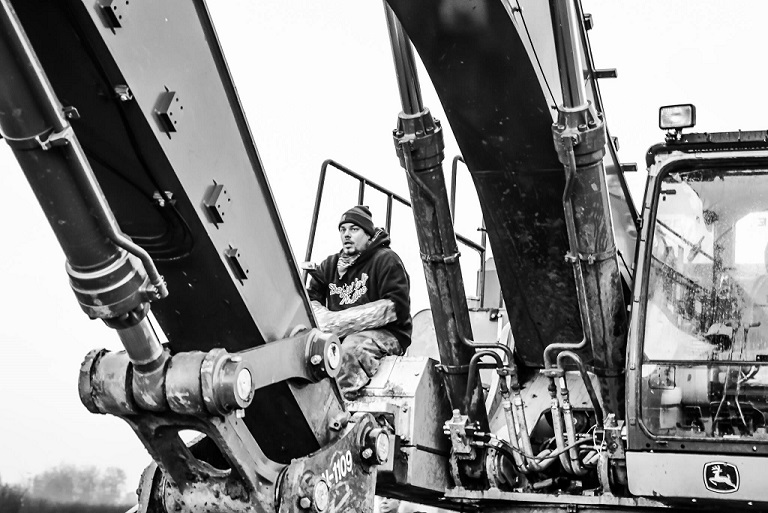

by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Nov 20, 2017 | Obstruction & Occupation
by Makwa Initiative Line 3 Front Line Resistance
Early Wednesday morning water protectors from Camp Makwa stormed an Enbridge construction site, and delayed progress on the last unfinished Wisconsin segment of their proposed line 3 pipeline project. One individual from the Diné Nation descended into the muddy trench, climbed onto the pipe, and locked himself to welding equipment. A Leech Lake Tribal member then climbed atop an excavator and attached himself to a hydraulic arm. Construction was halted for approximately six hours, costing the company thousands of dollars, as the individuals put their bodies on the line to protect the water and the futures of their children.
See the video here
Later in the day two more water protectors were arrested, while standing on the side of the public road. They were both tackled to the ground by Sergeant Kirchhoff of the Superior Police Department. For one of the arrests, when asked on what grounds he was acting, officer Kirchhoff cited a warrant that he could not produce. Later investigation found that the warrant he cited was unsigned and improperly filed. Last Week Sergeant Kirchhoff received media attention for tackling a woman to the ground without warning at a similar protest. The woman’s charges were later dropped.
The Enbridge Line 3 Replacement Project is estimated to carry almost one million barrels of tar sands oil from Alberta, Canada to Superior, Wisconsin; Enbridge has received approval in Wisconsin, but has not received approval in Minnesota, which would be the largest segment of the proposed project. The non-violent direct action came after a week of evidentiary hearings in Minnesota, where Enbridge revealed that it had already paid for 100% of the pipe for the project. The same day as the action it was discovered that before her time in public office Judge Ann C O’Reilly, the individual in charge of holding public hearings on the Line 3 Project, worked for a firm that represented oil companies on multiple occasions.
One water protector stated “Enbridge doesn’t have their permits for Minnesota and they have already started chopping trees down for their easement and filling its pipe storage yards. We went to the public hearings and found them full to the brim with Enbridge employees who were paid to be there. We fought again and again just to have 3 minutes to speak. Now we watch as truck after truck come into our communities carrying pipes and out of state pipeline workers. We made our comments, but they didn’t listen. The project is already bringing violence to our land and our women and children. We know that with these man camps comes increased levels of drugs, rape, and missing and murdered indigenous women. Enbridge will not take no for an answer so we have to stop them. We want to make clear in no uncertain terms, Enbridge is not welcome in Minnesota.”
Donate to Camp Makwa-
Camp Supplies: youcaring.com/makwacampsupplies
Legal Fund: youcaring.com/makwalegal
by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Sep 25, 2017 | Colonialism & Conquest
Featured image: World Wildlife Fund (WWF) has been working in the Congo Basin for decades – supporting squads who have committed violent abuse against tribal people. © WWF
by Survival International
A new Survival International report details widespread and systematic human rights abuses in the Congo Basin, by wildlife guards funded by the World Wildlife Fund (WWF) and other big conservation organizations.
The report documents serious instances of abuse between 1989 and the present day in Cameroon, the Republic of Congo, and the Central African Republic (CAR) by guards funded and equipped by WWF and the Wildlife Conservation Society (WCS), the parent organization of New York’s Bronx zoo.
It lists more than 200 instances of abuse since 1989, including pouring hot wax onto exposed skin, beating, and maiming with red-hot machetes. These incidents are likely just a tiny fraction of the full picture of systematic and ongoing violence, beatings, torture and even death.
As well as these especially cruel incidents, the report also documents the forms of harassment that have become part of everyday life for many people, including threats, and the destruction of food, tools and personal belongings.
Read the full report here.

WWF funded guards in Gabon. © WWF
As well as Survival, over the past three decades, numerous independent experts and NGOs have raised concerns about these abuses. These have included NGOs like Greenpeace, Oxfam, UNICEF, Global Witness, Forest Peoples Programme, and research specialists from University College London, the University of Oxford, Durham University, and Kent University.
WWF and WCS have even partnered with several logging companies, despite evidence that their activities are unsustainable, and have not had the consent of tribal peoples as required by international law and their own stated policies.
One Bayaka man said: “A wildlife guard asked me to kneel down. I said: “Never, I could never do that.” He said: “If you don’t get down on your knees I’m going to beat you.”
A Baka woman said: “They took me to the middle of the road and tied my hands with rubber cord. They forced my hands behind my back and cut me with their machete.”

Survival has documented hundreds of instances of abuse, and collected testimonies from many “Pygmy” people. © Survival International
A Bayaka woman said: “They started kicking me all over my body… I had my baby with me. The child had just been born three days before.”
Tribal peoples have been dependent on and managed their environments for millennia. Their lands are not wilderness. Evidence proves that tribal peoples are better at looking after their environment than anyone else.
But big conservation organizations like WWF are partnering with industry and tourism and destroying the environment’s best allies. Now tribal people are accused of “poaching” because they hunt to feed their families. And they face arrest and beatings, torture and death, while big game trophy hunters are encouraged.
Survival’s Director Stephen Corry said: “This shocking report lays out, in detail, the abuse and persecution that “conservation” has brought the indigenous and tribal peoples of the Congo Basin. These are just the cases that have been documented, it’s impossible to imagine there aren’t a lot more which remain hidden.
“The big conservation organizations should admit that their activities in the region have been catastrophic, both for the environment and for the tribal peoples who guarded these forests for so long.
“WWF and WCS supporters might ask these organizations how they could have let this situation carry on for so long – and what they’re going to do now to make sure it stops.”
“Pygmy” is an umbrella term commonly used to refer to the hunter-gatherer peoples of the Congo Basin and elsewhere in Central Africa. The word is considered pejorative and avoided by some tribespeople, but used by others as a convenient and easily recognized way of describing themselves.
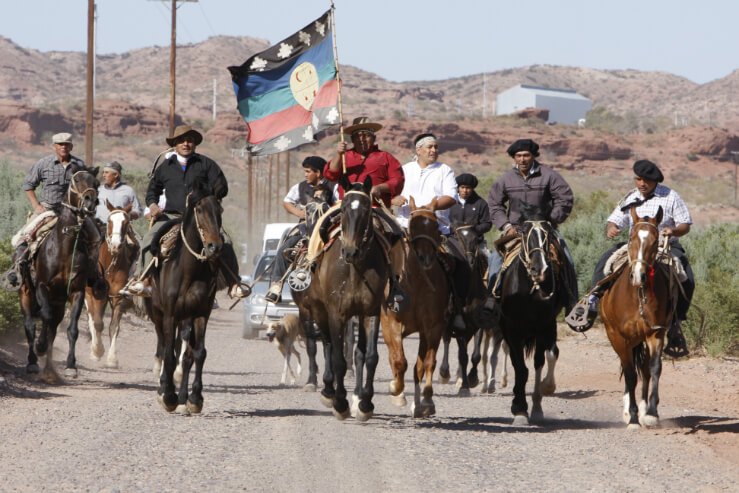

by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Sep 15, 2017 | Indigenous Autonomy
Featured image: James Anaya (former UN Special Rapporteur) visits Mapuche land in Argentina. Credit: Alejandro Parellada IWGIA
by Pamela Leiva Jacquelín, International Work Group for Indigenous Affairs (IWGIA) / Intercontinental Cry
Imagine that your survival depended on defending your right to live where you are standing right now.
Any day, the government could decide to start extracting oil or constructing a highway, exactly where your family goes to sleep every night, without consulting you. Just picture the mine or highway polluting the water you drink and poisoning the soil so completely that crops can’t even grow. On top of this, every day you are pushed to speak a foreign language in a country that endangers your culture and way of life.
This scenario is not fictitious. It is a reality for many of the 370 million people worldwide who identify as Indigenous Peoples. If there could be a simple way to define them, we can agree that they are the living descendants of the pre-colonized inhabitants of lands now dominated by others.
It was only 10 years ago, when Indigenous Peoples around the globe achieved the most substantial victory in a century of demands: the United Nations Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples (UNDRIP).
The adoption of this declaration has been a breaking point, given the fact that 144 countries reaffirmed that Indigenous Peoples are entitled without discrimination to all human rights recognized in international law. Since 2007, the UNDRIP has guided global efforts to overcome and repair the historical denial of their most fundamental rights, including the most basic right to self-determination.
UNDRIP brought the concept of collective rights to the table. This means that as a group, Indigenous Peoples possess rights that are indispensable for their existence, well-being and integral development as a distinct society. This is perhaps the reason why many find it difficult to relate to their struggles, since dominant societies base policy making and development actions on the protection of individual rights, such as the right to property or privacy.

Maya Weavers holding a proposal for the recognition of collective intellectual property, February 2017. Photo: AFEDES
Representing 5 percent of the world’s population, today many Indigenous Peoples are still excluded from society and deprived of their rights as equal citizens of a state. Living in 70 countries and speaking more than 4,000 native languages, they have gained increasing visibility for raising their voices on aggressive development policies that threaten the world’s remaining ecosystems and the biodiversity that depends on them.
As the world moves fast to explore and exploit these ecosystems to meet increasing consumption, Indigenous Peoples are at the top list of those murdered for defending their land.
Almost 130 environmental activists have been killed so far in 2017. Another four are expected to be killed in the next week.
This global trend is not a coincidence. Indigenous territories are the richest in biodiversity and today more than ever they are becoming the new battleground for human rights and the environment.
“Even though violence against Indigenous Peoples is increasing, the Declaration should be celebrated. Without this Declaration, Indigenous Peoples wouldn’t have a chance to fight”, describes Julie Koch, Director of International Work Group for Indigenous Affairs (IWGIA).
The main driving force for the global assault on indigenous land is that state governments have largely failed to establish constitutional rights and protections for Indigenous Peoples. UNDRIP provides states with a legal framework to establish these rights and protections.
The increasing rates of criminalization of indigenous leaders and the murder of environmental defenders shows us just how much work states have to do for the Indigenous Peoples of the world. It is also a strong reminder that the world’s Indigenous Peoples are key to saving our planet.
The global trend of attacks on Indigenous Peoples takes different shapes on different continents. Let’s go through some of it.
Latin America: Where the Extractive Agenda Threatens Indigenous Victories
Even though Latin America has a favourable legal framework to rely on, it is often reported as the most dangerous continent for environmentalists. Many of the reported killings were of people trying to combat illegal logging in the Amazon.
It only takes a quick look into Brazil to understand what the fight is all about. Here is where the highest number of environmental defenders have died on Earth. Since 2013, 900 indigenous leaders have been killed for defending their lands, despite legally owning 12.2 percent of the country’s territory and living peacefully in 704 collective territories.
Another eye-opening case is Venezuela, where actually the land demarcation process has only met 13 percent of the cases in the last 17 years, neglecting the urgent call to action stated in the Constitution. Just to make things more complicated, the government recently approved the creation of the AMO (Orinoco Mining Arc) region, a mega mining project that will give 150 companies from 35 countries access to 12 percent of the national territory. Once again, national policies seem to forget how illegal mining has already driven aggressions and threats towards the Yabarana, Hoti and Panare peoples close to the border with Brazil.
The race for water is also affecting Guatemala, where hydroelectric projects are quickly on the rise. Groundwater recharge areas are located on indigenous land and indigenous communities have constantly denounced the theft of river water. Various companies and private landowners illegally divert rivers to sugar cane, banana and palm oil plantations and cattle ranches during dry seasons.
Surprisingly, Bolivia does not escape from this pattern. With a controversial political decision, Evo Morales gave the green light to construct a highway on indigenous land. This development project has for several years been opposed by environmentalists and the indigenous movement since it cuts through Isiboro Sécure National Park and Indigenous Territory (well-known as TIPNIS). The construction of this highway is part of a bigger plan. The highway aims to extend the existing Brazilian-led effort commonly known as IIRSA (Initiative for the Regional Integration of South America). This entails a network of 531 mega-projects that include hydroelectric dams, highways, bridges, and electrical power systems that seek to ease the flow of transportation of soybeans and coca across the region. But the impacts are not only economic. The highway will considerably affect the traditional way of life of three indigenous groups: the Tsimanes, Yuracarés and Mojeño-Trinitarios.
But the fight back seems promising. Indigenous autonomous governments are representing much more than a trend in the region. Self-governance is one of the most significant claims made by Indigenous Peoples in this part of the world and it seems to be on its peak of realization with the two first indigenous governments settled in Peru and Bolivia. The Wampís Nation’s Parliament and the Charagua government took office last year and made their goals clear: they aim to control how to administer the future of their ways of life within the territory they inhabit.

Wampis Nation mapping territory in Peru. Credits Jacob Balzani Lööv
Asia: Where Discrimination Pairs with Militarization
Asia is home to 260 million Indigenous Peoples, making it the most culturally diverse region in the world. The land dispute pattern in this region is significantly worse due to heavy assimilation pressure and violent repression by state security forces. As Indigenous Peoples in other countries, they face the routine denial of self-determination, loss of control over their land and extreme discrimination.
One of the most clear examples of the lack of respect for indigenous land rights is the conflict in the Chittagong Hill Tracts (CHT) region in Bangladesh, where approximately 600,000 Indigenous Peoples live. Ever since the creation of Bangladesh, the elected representatives of the CHT have demanded regional autonomy. Being trapped between demilitarization and displacement, gross human rights have been committed and documented over the last 10 years. The most affected by the conflict are indigenous women. Being under the review of the UN Convention on the Elimination of all Forms of Discrimination Against Women (CEDAW), several reports highlight cases of gender-based violence against indigenous women connected with land grabbing.
Indigenous Peoples and minority populations in the Philippines are also hit by militarization. The “war on drugs” and the fight against Maoist rebels now led by President Duterte has led to many political extrajudicial killings in their communities. Indigenous Peoples are also cornered by the aggressive expansion of monocrop plantations, especially oil palm plantations in Mindanao. Community members from the municipalities of Bataraza and Española in Palawan have reported how their rights had been violated by several companies that continue to expand on community lands with the complicity of government officials.
The situation in Nepal follows the course of aggressive development. During 2016, many protests against road expansion and electricity transmission lines intensified. The common picture that local indigenous communities paint is that bulldozers enter their land to ensure infrastructure developments go according the plan.
Perhaps the most illustrative situation of discrimination comes from Japan. The huge gap in public awareness shows the long lasting effects of systematic discrimination. A national survey released by the government in 2016 showed that 72.1 percent of Ainu people agreed that “discrimination against the Ainu people exist”, meanwhile 50.7 percent of the general public stated that “discrimination does not exist”.
Africa: Where Evictions are Driven by Conservation and Agribusiness
Laws protecting Indigenous Peoples are weak or nonexistent throughout continental Africa. With very little political support and space for critical NGOs and media that can effectively report on human rights violations, conservationist and agribusiness agendas frequently push Indigenous Peoples from their homelands.
In Loliondo village in Tanzania, indigenous communities suffer from a systematic attack that aims to reduce their number of livestock, which is vital for their survival. Increasing tensions and clashes with farmers and ranchers are usually driven by recurrent drought. Another common tactic used by the military is to burn houses, which speeds up illegal evictions.
Just last month, Serengeti National Park and Ngorongoro Conservation Area Authority rangers, with the support of Loliondo police, burned down about 185 Maasai bomas (homesteads). The evictions left approximately 6,800 people homeless, with most of their property destroyed.
Evictions are also a current challenge for Indigenous Peoples in Kenya, where the definition of community lands is not in place to allow the urgent need to formalize land ownership. Earlier this year, drought caused traditional herdsmen to steal pasture from landowners, burning down tourist lodges and grabbing the attention of the world media in the process. Laikipia, meanwhile, has experienced unprecedented grazing pressure and the Maasai have been forced to endure limited access to water. This is not the first time that climate shock has systematically triggered violence over land rights in Northern Kenya. The chain of events is pretty straightforward: when there is no water, no grass grows and pastoralists’ cattle starve to death.
The other side of the coin is that Indigenous Peoples are gaining recognition in the courts. Against all odds, we saw an historic land ruling in Kenya this year in the hands of the Ogiek. The African Court on Human and Peoples’ Rights set a vital precedent, recognizing that as Indigenous Peoples the Ogiek have the right to reparations from the Kenyan government for the suffering they have endured from forced evictions.
We Are All Fighting the Same Fight
If Indigenous Peoples remain unprotected, it will continue to have a direct impact on the shape of our planet and its capacity to sustain life. Many would think this gap has nothing to do with protecting the environment, but it absolutely does.
The fight for indigenous land rights is not just about rights, but about securing a sustainable future for everyone.
If states and corporations fail to protect those who are putting their lives on the line to defend the diversity we depend on, it may only be a matter of time before resource scarcity leads them to turn on everyone else.
Indigenous Peoples have pursued environmental justice since long before climate change became a mainstream issue. Ten years after their biggest victory, it is time we take indigenous land rights seriously to ensure we all continue to have water to drink, air to breathe, and even land to call home.









