
by DGR News Service | Nov 2, 2021 | Climate Change, Education, Human Supremacy, Indirect Action, The Problem: Civilization, The Solution: Resistance
This is an excerpt from the book Bright Green Lies, P. 20 ff
By Derrick Jensen, Lierre Keith and Max Wilbert
What this adds up to should be clear enough, yet many people who should know better choose not to see it. This is business-as- usual: the expansive, colonizing, progressive human narrative, shorn only of the carbon. It is the latest phase of our careless, self-absorbed, ambition-addled destruction of the wild, the unpolluted, and the nonhuman. It is the mass destruction of the world’s remaining wild places in order to feed the human economy. And without any sense of irony, people are calling this “environmentalism.”1 —PAUL KINGSNORTH
Once upon a time, environmentalism was about saving wild beings and wild places from destruction. “The beauty of the living world I was trying to save has always been uppermost in my mind,” Rachel Carson wrote to a friend as she finished the manuscript that would become Silent Spring. “That, and anger at the senseless, brutish things that were being done.”2 She wrote with unapologetic reverence of “the oak and maple and birch” in autumn, the foxes in the morning mist, the cool streams and the shady ponds, and, of course, the birds: “In the mornings, which had once throbbed with the dawn chorus of robins, catbirds, doves, jays, and wrens, and scores of other bird voices, there was now no sound; only silence lay over the fields and woods and marshes.”3 Her editor noted that Silent Spring required a “sense of almost religious dedication” as well as “extraordinary courage.”4 Carson knew the chemical industry would come after her, and come it did, in attacks as “bitter and unscrupulous as anything of the sort since the publication of Charles Darwin’s Origin of Species a century before.”5 Seriously ill with the cancer that would kill her, Carson fought back in defense of the living world, testifying with calm fortitude before President John F. Kennedy’s Science Advisory Committee and the U.S. Senate. She did these things because she had to. “There would be no peace for me,” she wrote to a friend, “if I kept silent.”6
Carson’s work inspired the grassroots environmental movement; the creation of the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA); and the passage of the Clean Air Act, the Clean Water Act, and the Endangered Species Act. Silent Spring was more than a critique of pesticides—it was a clarion call against “the basic irresponsibility of an industrialized, technological society toward the natural world.”7 Today’s environmental movement stands upon the shoulders of giants, but something has gone terribly wrong with it. Carson didn’t save the birds from DDT so that her legatees could blithely offer them up to wind turbines. We are writing this book because we want our environmental movement back.
Mainstream environmentalists now overwhelmingly prioritize saving industrial civilization over saving life on the planet. The how and the why of this institutional capture is the subject for another book, but the capture is near total. For example, Lester Brown, founder of the Worldwatch Institute and Earth Policy Institute—someone who has been labeled as “one of the world’s most influential thinkers” and “the guru of the environmental movement”8—routinely makes comments like, “We talk about saving the planet.… But the planet’s going to be around for a while. The question is, can we save civilization? That’s what’s at stake now, and I don’t think we’ve yet realized it.” Brown wrote this in an article entitled “The Race to Save Civilization.”9
The world is being killed because of civilization, yet what Brown says is at stake, and what he’s racing to save, is precisely the social structure causing the harm: civilization. Not saving salmon. Not monarch butterflies. Not oceans. Not the planet. Saving civilization. Brown is not alone. Peter Kareiva, chief scientist for The Nature Conservancy, more or less constantly pushes the line that “Instead of pursuing the protection of biodiversity for biodiversity’s sake, a new conservation should seek to enhance those natural systems that benefit the widest number of [human] people…. Conservation will measure its achievement in large part by its relevance to [human] people.”10 Bill McKibben, who works tirelessly and selflessly to raise awareness about global warming, and who has been called “probably America’s most important environmentalist,” constantly stresses his work is about saving civilization, with articles like “Civilization’s Last Chance,”11 or with quotes like, “We’re losing the fight, badly and quickly—losing it because, most of all, we remain in denial about the peril that human civilization is in.”12
We’ll bet you that polar bears, walruses, and glaciers would have preferred that sentence ended a different way.
In 2014 the Environmental Laureates’ Declaration on Climate Change was signed by “160 leading environmentalists from 44 countries” who were “calling on the world’s foundations and philanthropies to take a stand against global warming.” Why did they take this stand? Because global warming “threatens to cause the very fabric of civilization to crash.” The declaration con- cludes: “We, 160 winners of the world’s environmental prizes, call on foundations and philanthropists everywhere to deploy their endowments urgently in the effort to save civilization.”13
Coral reefs, emperor penguins, and Joshua trees probably wish that sentence would have ended differently. The entire declaration, signed by “160 winners of the world’s environmental prizes,” never once mentions harm to the natural world. In fact, it never mentions the natural world at all.
Are leatherback turtles, American pikas, and flying foxes “abstract ecological issues,” or are they our kin, each imbued with their own “wild and precious life”?14 Wes Stephenson, yet another climate activist, has this to say: “I’m not an environmentalist. Most of the people in the climate movement that I know are not environmentalists. They are young people who didn’t necessarily come up through the environmental movement, so they don’t think of themselves as environmentalists. They think of themselves as climate activists and as human rights activists. The terms ‘environment’ and ‘environmentalism’ carry baggage historically and culturally. It has been more about protecting the natural world, protecting other species, and conservation of wild places than it has been about the welfare of human beings. I come at from the opposite direction. It’s first and foremost about human beings.”15
Note that Stephenson calls “protecting the natural world, protecting other species, and conservation of wild places” baggage. Naomi Klein states explicitly in the film This Changes Everything: “I’ve been to more climate rallies than I can count, but the polar bears? They still don’t do it for me. I wish them well, but if there’s one thing I’ve learned, it’s that stopping climate change isn’t really about them, it’s about us.”
And finally, Kumi Naidoo, former head of Greenpeace International, says: “The struggle has never been about saving the planet. The planet does not need saving.”16 When Naidoo said that, in December 2015, it was 50 degrees Fahrenheit at the North Pole, much warmer than normal, far above freezing in the middle of winter.
1 Paul Kingsnorth, “Confessions of a recovering environmentalist,” Orion Magazine, December 23, 2011.
2 Rachel Carson, Silent Spring (Greenwich, CT: Fawcett Publishing, 1962), 9.
3 Ibid, 10.
4 Ibid, 8.
5 Ibid, 8.
6 Ibid, 8.
7 Ibid, 8.
8 “Biography of Lester Brown,” Earth Policy Institute.
9 Lester Brown, “The Race to Save Civilization,” Tikkun, September/October 2010, 25(5): 58.
10 Peter Kareiva, Michelle Marvier, and Robert Lalasz, “Conservation in the Anthropocene: Beyond Solitude and Fragility,” Breakthrough Journal, Winter 2012.
11 Bill McKibben, “Civilization’s Last Chance,” Los Angeles Times, May 11, 2008.
12 Bill McKibben, “Global Warming’s Terrifying New Math,” Rolling Stone, August 2, 2012.
13 “Environmental Laureates’ Declaration on Climate Change,” European Environment Foundation, September 15, 2014. It shouldn’t surprise us that the person behind this declaration is a solar energy entrepreneur. It probably also shouldn’t surprise us that he’s begging for money.
14 “Wild and precious life” is from Mary Oliver’s poem “The Summer Day.” House of Light (Boston, MA: Beacon Press, 1992).
15 Gabrielle Gurley, “From journalist to climate crusader: Wen Stephenson moves to the front lines of climate movement,” Commonwealth: Politics, Ideas & Civic Life in Massachusetts, November 10, 2015.
16 Emma Howard and John Vidal, “Kumi Naidoo: The Struggle Has Never Been About Saving the Planet,” The Guardian, December 30, 2015.

by DGR News Service | Oct 2, 2021 | Climate Change, Human Supremacy, Women & Radical Feminism
This article originally appeared in Common Dreams.
“This is the time to unite together to build the healthy and just future we know is possible for each other and the Earth.”
By JULIA CONLEY
As world leaders gathered in New York for the United Nations General Assembly Thursday and amid preparations for a global climate conference coming up in November, women leading more than 120 international organizations delivered a call to action demanding “a transformation of how we relate to the natural world and to one another”—one that will enable far-reaching action to save the planet.
“As the world prepares for one of the most important climate talks since the Paris Agreement, we know solutions exist to mitigate the worst impacts, and that women are leading the way.” —Osprey Orielle Lake, WECAN International
Led by Women’s Earth & Climate Action Network (WECAN) International, the organizations called on governments and financial institutions to commit to policies that prioritize “social, racial, and economic justice for all” as they work to keep the heating of the planet below 1.5C.
“We must rapidly halt the extraction of oil, gas, and coal and end all deforestation while building a new economy predicated on community-led solutions,” reads the call to action, which was signed by groups including MADRE, CodePink, and Women’s Earth Alliance.
“As we herald in sustainable, democratic, and equitable governance paradigms, we need to prioritize the leadership and well-being of women, gender non-conforming people, Black and Brown communities, and Indigenous peoples who are disproportionately impacted by climate change, but also lead the frontlines of systemic solutions,” the groups said.
The organizations also plan to present their demands at the 2021 U.N. Climate Change Conference (COP 26) in November, where leaders from nearly 200 countries will be under pressure to increase their ambitions to reduce emissions and uphold their existing obligations to frontline communities across the globe, particularly in the Global South.
“We are at a choice point for humanity,” said Osprey Orielle Lake, executive director of WECAN International. “Every day, we can see for ourselves forest fires burning all over the world, massive flooding, extreme droughts, people losing their livelihoods and lives—we are in a climate emergency. As the world prepares for one of the most important climate talks since the Paris Agreement, we know solutions exist to mitigate the worst impacts, and that women are leading the way.”
The call to action includes a number of steps recommended for governments as well as financial institutions, including:
- End fossil fuel expansion and rapidly accelerate a just transition to 100% renewable and regenerative energy;
- Promote women’s leadership and gender equity;
- Protect the rights of Indigenous people by upholding all treaties, and follow Indigenous communities’ traditional ecological knowledge;
- Protect forests and biodiversity with a global moratorium on logging and a phase-out of agricultural practices that cause soil erosion and depletion;
- Preserve oceans and freshwater;
- Promote food security and food sovereignty;
- Protect the rights of nature; and
- Halt the financing of all fossil fuel projects.
The call to action comes ahead of a six-day virtual forum organized by WECAN.
At the Global Women’s Assembly for Climate Justice, which begins Saturday, speakers will include scientist and conservationist Dr. Jane Goodall; Casey Camp-Horinek of the Ponca Nation, a WECAN board member and environmental ambassador; Ruth Nyambura of the African Ecofeminist Collective in Kenya; and Sônia Bone Guajajara of the Articulation of Indigenous Peoples of Brazil.
“As a Matriarch of the Ponca Nation, I am honored to have the responsibility of caring for the generations to come by ensuring the health and welfare of Mother Earth, Father Sky, and Relatives in every form,” said Camp-Horinek. “Life itself hangs in the balance, and we women are coming together to say that we must make the correct choices for our collective future now.”
Events at the six-day forum will include discussions about protecting the planet’s forests, rejecting “greenwashing” by corporations, and supporting feminist frameworks for climate justice.
“We can act now and we must act now, which is why WECAN is hosting the Global Women’s Assembly for Climate Justice to uplift women, gender-diverse and community-led solutions, strategies, policies, and frameworks to address the climate crisis,” said Lake. “It is code red and we are drawing a red line to say no more sacrifice people and no more sacrifice zones. This is the time to unite together to build the healthy and just future we know is possible for each other and the Earth.”

by DGR News Service | Nov 6, 2020 | Listening to the Land
This piece, by Paul Feather, explores what it means to be a citizen of system ruled by the machine, placing it in context of the recent elections that offers no real choice to the voters.
I voted today, even though I think it’s a crock of shit.
It’s easy enough and doesn’t hurt anything. At least not as far as I can tell. I took the sticker that proclaims, “I secured my vote,” from the smiling lady by the exit, but I didn’t post a selfie with the sticker to let everyone else know how easy that was, or how civic minded I am, or to remind them of their duty to democracy. Don’t get me wrong. I hope all y’all vote. Go team.
I won’t say that voting doesn’t matter. I’m sure it does. If nothing else, votes are expensive. In the 2016 presidential election, Trump and Clinton spent a combined 1.8 billion dollars on their campaigns with Clinton outspending Trump by nearly two to one. Since there were about 129 million votes cast for these two candidates, this comes to about $14/vote, (with Clinton paying $19/vote and Trump paying a little less than $10). Gary Johnson, the Libertarian candidate, got about 4.5 million votes and only paid about $2.60/apiece for them, but he didn’t scrape up too many at that price, and his campaign spending was literally pennies to Trump and Clinton’s dollars. I’m sure there’s more to it than money, but not terribly much more. Votes are expensive, and the more of them you need the more they cost. Roughly speaking, I figure my vote for president’s worth about 15 bucks.
So by all means, go spend your vote, but can we stop pretending that it’s worth much more than dinner for two at a cheap Mexican joint? (Throw in the value of the down-ticket votes and you’ve earned a Miller Lite with your chile relleno.) Can we stop pretending that this is the most important election of our lifetimes? Can we stop pretending that we’ve got to “vote like our democracy and freedom are on the line?” I hear people saying things like this, and I don’t even know what it means. How do you vote like your freedom’s on the line? You vote or you don’t. You can’t do it extra hard so it counts double. Damn straight our democracy’s on the line, but it ain’t the line outside the precinct. Vote, but can we stop pretending?
I feel like this election is something out of the Salem witch trials…
when Puritan settlers would throw a woman in the lake to see if she sank or swam; if she didn’t drown, they burned her. Poor Lady Liberty’s on trial for devil worship. The blue team will drown her, the red team will burn her, and there’s no way out of this one. Go team.
It’s not really a fair metaphor, I know. I’m comparing Lady Liberty to some poor woman that the Puritans probably killed for a heinous crime like midwifery, herbalism, or refusing to suck the parson’s cock. Lady Liberty is not that blameless lass, and if we’re equally lost when we sink or swim, maybe we should admit to some dealings with the devil. Not you, of course. Nor me either, but the whole body politic of the USA—who will ostensibly choose a president next week—has sold its soul for sure.
That’s why we can’t tell what’s true anymore.
Nobody ever asked me if I wanted to be a citizen of the USA, and maybe I’m glad for that because I’m not sure how I’d choose. There are some obvious benefits. It’s possible to live off reasonably well in this country of what other people throw away. That—or rather the general opulence it implies—is a very big deal. But there are costs as well. Perhaps I lean too heavily on metaphor when I say we have sold our collective soul, but the food we eat is grown on land that was stolen from people who now go hungry. I don’t drink the water that was poisoned in the manufacture of the computer I use to write these words, but other people do. To be a citizen of the USA means that other people in other places will bear the material cost of our consumption, our decisions, and our lives.
We can imagine that the food we eat, our energy, our clothing, every need or whim that we fulfill finds provenance in a sort of materialist soul.
Without that food, we die. Without that warmth or clothing, we can’t survive. But we don’t fulfill these needs alone. The days of rugged self-sufficiency are over. We fulfill these needs as participants in the body politic. We will not eat without the functioning of a whole production and distribution system involving untold numbers of people—and very often sitting at the bottom on stolen land. What is the word for the totality of these systems that keep us alive both individually and collectively? This is literally the source of our being; it existed before we were born; and so I will call it our soul.
This soul of ours is not nice to look at, so mostly we don’t. We’d rather pretend we don’t have a soul, or that the source of our existence is abstract and ethereal. Fast for a week and get back to me on that one. I think when our soul is ugly—when the material systems that form the source of our existence are exploitative, unjust, and criminal—then we tend to turn away from that. We cover our soul up with distractions and stories we’d rather hear, but in doing this we deny the source of our existence. In the end—and this is starting to look like an ending—we lose our bearings. We can’t tell what’s true anymore.
When this happens, I suspect there is no way out. We will sink, or we will burn.
If, by chance, an individual attempts to come to terms with her soul, she may find the drama of presidential elections to be less exciting. Not because their outcomes don’t directly affect quality of life for a great many people. I’m sure they do, so go vote. But if one places her full attention upon our soul—again speaking of the whole and material systems that are the source of our lives—she will be disappointed to find that no one else is talking about this. She will not be able to play with either team.
The other thing this individual will notice (if she hadn’t already) is that neither side is willing to look at the truth about who we are and how we got here, and so both sides are locked inside of a strange simulacrum of the world that has no soul. In that world, the only thing that matters is power, and the only way to get votes is to buy them.
The soul functions as a bedrock of reality…
for without it we are dead—and in its absence nothing is real, nothing is sacred; we find ourselves in a post-truth world where the only thing that matters is power.
A soulful vision perceives our electoral process to be a sham, not only because that vision is entirely unrepresented, but because the process itself isn’t sacred. There is no integrity, no trust; it’s not even possible to cheat, because the only real rule—the only sacred thing—is power. It’s not cheating as long as you win, and deep down everyone knows this. We may be close to the breaking point—where the absence of any inviolable law forces one or both contenders to claim the presidency on terms of power alone. We won’t be able to pretend anymore, and I don’t expect that’ll be pretty.
I suspect the only way out is this: to turn the consciousness of the body politic to the real and material systems that support our lives. To illuminate the soul. We can fight about two healthcare systems that are equally devoid of connection to the source of our medicine, or we can bring people to that source. We can vote for one or another plan to keep anonymously packaged food on indistinguishable grocery shelves, or we can anchor our souls in the black dirt of home. This collective shift may not be wholly possible until our souls become so hollow that they collapse and people die—it may be that this is already happening—but incremental shifts toward soulful connection are possible and even inevitable.
You may (and certainly should) attempt to recover your soul on your own, but I’ll warn you that this attempt will be only partially successful. There may once have been a time when there were enough commons left that one could escape into them and live on chestnuts and game, but the commons are now fenced, and the chestnuts are gone. You will continue to live alongside and even inside the soulless simulacrum that we have co-created.
If this election has stirred up a brief moment of civic-mindedness, I hope to leverage that moment not to remind you to #vote, but to question our concept of citizenship. Materially, what are we citizens of except of this massive machine that keeps us alive—that moves bananas and timber and textiles from wherever they’re produced to wherever someone needs them to live? And although most of our consumption goes far beyond mere survival, the conditions of our survival must be met. It is the machine that meets them. You and I are citizens of the machine. Look at it. Look at it squarely. Do not flinch. That machine is your soul. That machine is your center.
Let us stop pretending.
Note: Editor’s introduction to the piece has been edited.

by DGR News Service | Sep 25, 2020 | Culture of Resistance
As the book Deep Green Resistance reminds us, there are certain aspects of collapse that are positive (declining oil demand, for example) and others that are negative (e.g., rising patriarchal, racist elements). This piece from Vince Emanuele argues that individualist survivalism is often an anti-social response to the social problems we are facing, and that we must organize as communities to survive.
Guns, Land, and Chickens Won’t Save You
by Vincent Emanuele / Counterpunch
“We are condemned to be modern. We can’t escape the facts of our history or of living in an age dominated by instrumental rationality, even as we look for ways out of it… But it has become our historic responsibility to acknowledge the continuing importance of myth, at a level beyond science, in realizing a more organic, holistic relation to the world. A future social ecology would transcend both anti-Enlightenment reaction and [a] reified Enlightenment counter-reaction, which remain only fragmented polarities within bourgeois modernity.”
– David Watson, Beyond Bookchin: Preface for a Future Social Ecology
Following the Great Recession of 2008, many of my friends started talking about “living off the land.” At the time, I didn’t give their words much thought. After all, Obama was in the White House; Neoliberalism was on the rise; imperial wars raged abroad, and the antiwar movement was falling apart.
During those dark and tumultuous years, my primary focus was building the sort of left institutions that could prevent the situation in which we now find ourselves: a nation on the brink of collapse, civil war, or some combination of the two. Sometime around 2010, I started reading about the connections between climate change and the U.S. empire and militarism, which led me to research and learn more about ecological devastation and biodiversity loss.
The global picture was much grimmer than I had imagined.
Not only was capitalism and empire destroying human life, but it was also destroying the planet. At that point, I began to better understand my friends’ urge to “move to the countryside,” but I didn’t agree with their vision. To me, it seemed like a uniquely white and middle to upper-middle-class thing to do. It also seemed like the easy way out.
I remember thinking, “I don’t know too many black or Hispanic people who are starting small farms.” And I still don’t. That’s not because they’re not interested in doing so. Black and Hispanic Americans simply don’t have the material resources to start small farms, which require land (money), equipment (money), time (money), specialized skills (access), and various other resources (money and access).
Plus, I don’t know too many black or Hispanic people who are champing at the bit to live in Southern Indiana, northern Wisconsin, or rural Montana, whereas many of my white friends wouldn’t blink an eye moving to those regions. And I sure as hell don’t know of any poor people who have the resources to do any of the above. They’re happy if they can go out to eat at a sit-down restaurant once a month.
If we’re genuinely interested in building multiracial coalitions of working-class people who are capable of combating capital, the military-industrial complex, corporate power, state repression, and rightwing nationalism, we can’t do it from the isolated countryside. We can’t do it from the safety of a family farm, totally detached from the day-to-day realities facing the very people, disproportionately black and Hispanic, but also poor whites, we need to build relationships with if we hope to win.
Urban communities, churches, schools, workplaces, bars, social and sporting clubs, recreational centers, community centers, and neighborhoods provide fertile organizing terrain for leftists. According to the U.S. Census Bureau, roughly 80% of Americans live in urban areas. By 2050, studies suggest that 66% of the global population will live in cities. Those numbers will only grow with time.
If you live in rural Iowa, you depend on people in New York City, Mexico City, and Tokyo.
You’re not some sort of lone-ranger-cowboy-farmer: you’re wholly dependent upon petroleum-based products, including everything from fertilizers and fuel to equipment and cleaning products. Multinational corporations produce those goods. International banks finance production. All of this requires international agreements, governments, legal apparatuses, and the like. Global supply chains provide your equipment. And the fuel that runs your equipment is extracted, refined, shipped, and distributed on a global scale. You’re not living a ‘sustainable life’ — you’re just as part of the global economic system as anyone else, hell, even more so than low-wage workers who live in cities.
Whoever controls the cities and, to some degree, the suburbs, will control the nation. Cities are the lifeblood of capitalism. Capital dwells in cities, not rural areas. Lockheed Martin depends on Wall Street. BP depends on Lockheed Martin. Corporate headquarters, executives, and lenders are located in cities. The bulk of their customers reside in cities. The economic activity that takes place in cities supports the flow of capital which facilitates capitalism.
Our enemies, both visible (corporations, governments, militarized police) and invisible (capital) reside in cities, not the countryside.
Furthermore, think about the past 20 years of social movements and political uprisings: the ‘Battle For Seattle’ (urban environment); the antiwar movement (largely based in urban environments); Occupy Wall Street (cities), the pro-union occupation in Madison, Wisconsin, (urban environment/college town), Black Lives Matter uprising in Ferguson, Missouri, (urban/suburban environment), and the current wave of Black Lives Matter uprisings, occupations, marches, and the like (yes, throughout the country, but primarily based in urban environments). The only notable exception is Standing Rock. Even the teachers’ strikes that swept the nation a few years ago were based in cities and suburban school districts. The same is true of insurgent socialist electoral campaigns.
At some point, I realized that many of the people, including my friends, who’ve moved to the countryside to start small farms aren’t interested in building political movements, fighting back against corporate and government power, or creating a better world. They’re interested in survival, yet they know nothing about survival. They didn’t grow up in the woods. They don’t live off the land. They use power tools. They use cars, and fuel, and technology, and all the rest. To the degree they’re able to “live off the land,” it’s only because modernity has allowed them to do so with minimal risk.
They believe, näively, that they can survive as a small family unit in a world of 7.8 billion people. They can’t even organize their family members or close friends to get on the same page, let alone function as a tribe or small community, yet they believe they’re going to live in some sort of self-sustainable fantasy land of yesteryear? It’s a joke, but it’s also dangerous.
The ‘back-to-the-land’ movement in the U.S. has a long history.
For the sake of time and courtesy, I won’t bore you by revisiting its history. In today’s context, however, the ‘back-to-the-land’ movement operates comfortably within the framework of Neoliberal ideology. Hyper-individualism is the religious dogma that fuels the ‘back-to-the-land’ movement. Only someone totally detached from the broader global community would be able to convince themselves that they can survive in this world with minimal social cooperation.
The same people who talk about ‘living off the land’ are the same people who say things like, “I’ve gotta look out for mine,” or “My family is the only thing that matters.” This parochial worldview is not uncommon in the U.S., especially since the Reagan Revolution. The Cult of Individuality infects virtually every aspect of modern U.S. culture, from politics and economics to sports, film, art, and social relations. This is evident when I see pictures of my friends hiding out in their quasi-secluded countryside homes, tending to chickens and growing tomatoes, while the country and world collapse in real-time.
Speaking of collapse, the people who think they’re going to hide out in relative safety as the world crumbles around them are so detached from reality that it’s hard to seriously consider where they’re coming from, but I’ll try.
Let’s say you live 60-120 miles outside a major city (this would apply to many of my friends in Northwest Indiana or Southwest Michigan who own property). If the economy collapses (due to any number of factors), or if the country devolves into a civil war, perhaps even a revolution, or a nuclear war, or a cataclysmic ecological disaster, you’re fucked. If cities become unlivable, you’re fucked. If suburbs become unlivable, you’re fucked.
You and the family are going to hunker down at the homestead, and the hundreds of thousands or millions of people who live within a week’s walk aren’t gonna discover your property? Oh, you have guns? So what? Have you ever used them in a combat situation? How often do you and your family drill? How often do you shoot? How big is your family? Big enough to fend off hoards of people traversing the countryside in search of food, shelter, and safety?
What are you going to do if we can’t stop governments (U.S., Israel, Pakistan, India) from triggering a nuclear conflict? As one Wired headline put it, “Even a Small Nuclear War Could Trigger a Global Apocalypse.’ You can’t stop nuclear wars from your chicken coup. You can’t stop nuclear wars with your daddy’s shotgun. You can’t stop nuclear wars with organic produce. And you can’t stop nuclear wars with gluten-free home-cooked bread.
Only internationally coordinated political campaigns and movements can stop a potential nuclear war.
What are you and your family going to do when tens of millions of Americans are migrating across the U.S. as a result of runaway climate change and rapidly changing weather patterns, ecologies, and natural landscapes? What’s your plan? To mow down thousands of people fleeing natural disasters? Is that how you want to live? Do you think they’re not going to shoot back? Do you think your property won’t, at some point, also become uninhabitable due to climate disaster?
My advice to people who think they’re going to survive a collapsing society? Take a flight to Libya, Somalia, Pakistan, Iraq, Afghanistan, Syria, or Yemen, then tell me about your absurd and childlike ‘collapse’ fantasies. Nothing is inspiring, humane, or decent about living in a fractured and crumbling society. The glorification of violence, destruction, and death in U.S. culture is, to say the least, quite disturbing. There’s nothing cool or sexy about banditry, religious mobs, sectarian violence, terrorism, torture, or wanton violence. Americans (mostly white people who grew up in the suburbs) hoping for collapse should spend more time in places that have experienced collapse. It’s not like the movies (or your imagination).
In the end, there’s no hiding from what’s coming.
Climate change is a global problem. Capitalism, the primary driver of climate change, is a global economic system. Each of us lives within its grips, unfortunately. The only way to stop or mitigate what’s coming is through collective action on a massive global scale. Either we make it out of this mess together, or none of us make it out alive. It’s that simple. Our collective challenges require national and international solidarity. We must build relationships, bonds, trust, and networks across geographical, ethnic, racial, and religious boundaries.
Regional or local solutions won’t suffice. Regional and local solutions will contribute, but we need an international vision to address 21st-century challenges. And that international vision won’t be cultivated by those living ‘off the grid.’ Any international vision worth considering must prioritize large-scale (global) projects. Large-scale solutions can only be developed democratically and equitably through collective decision-making processes that incorporate diverse political movements from around the globe.
I became a leftist because Marx’s and Engels’s writings, particularly those in the Communist Manifesto, resonated with me on a very deep level. Their writings didn’t encourage me to run away to the countryside and relive some sort of 18th-century ‘back-to-the-land’ fantasy. Their writings inspired me to build relationships and organize with working-class people around the globe in the hope that, someday, we will overthrow this terrible system (capitalism).
Today, we need a vision that’s inspiring, complex, and flexible (always willing to adapt to changing circumstances), but also principled.
Without a principled vision of how to proceed, we’ll continue to spin our tails resisting the latest excesses of capitalism, empire, or racism, without accomplishing much. People joined socialist and communist movements because those movements inspired poor and working-class people through ideology and action.
If our vision doesn’t include those who don’t have the means to escape ‘back-to-the-land,’ what sort of vision is it? The left should seek to include, not exclude, people. I’m not interested in building more walls (visible or invisible), internal borders, or tribal social relationships. The right does a fine job of inciting reactionary worldviews.
The left’s vision should be about more than simply surviving the coming storm. We need a vision that inspires and motivates people from around the world to join our movements, campaigns, and organizations. That can’t happen in seclusion. It can only happen through intentionally building broad, deep, and sustained social relationships with people from around the globe.
Vincent Emanuele writes for teleSUR English and lives in Michigan City, Indiana. He can be reached at vincent.emanuele333@gmail.com.
This article was originally published in Counter Punch on September 11, 2020. You can read the article here:
Guns, Land, and Chickens Won’t Save You
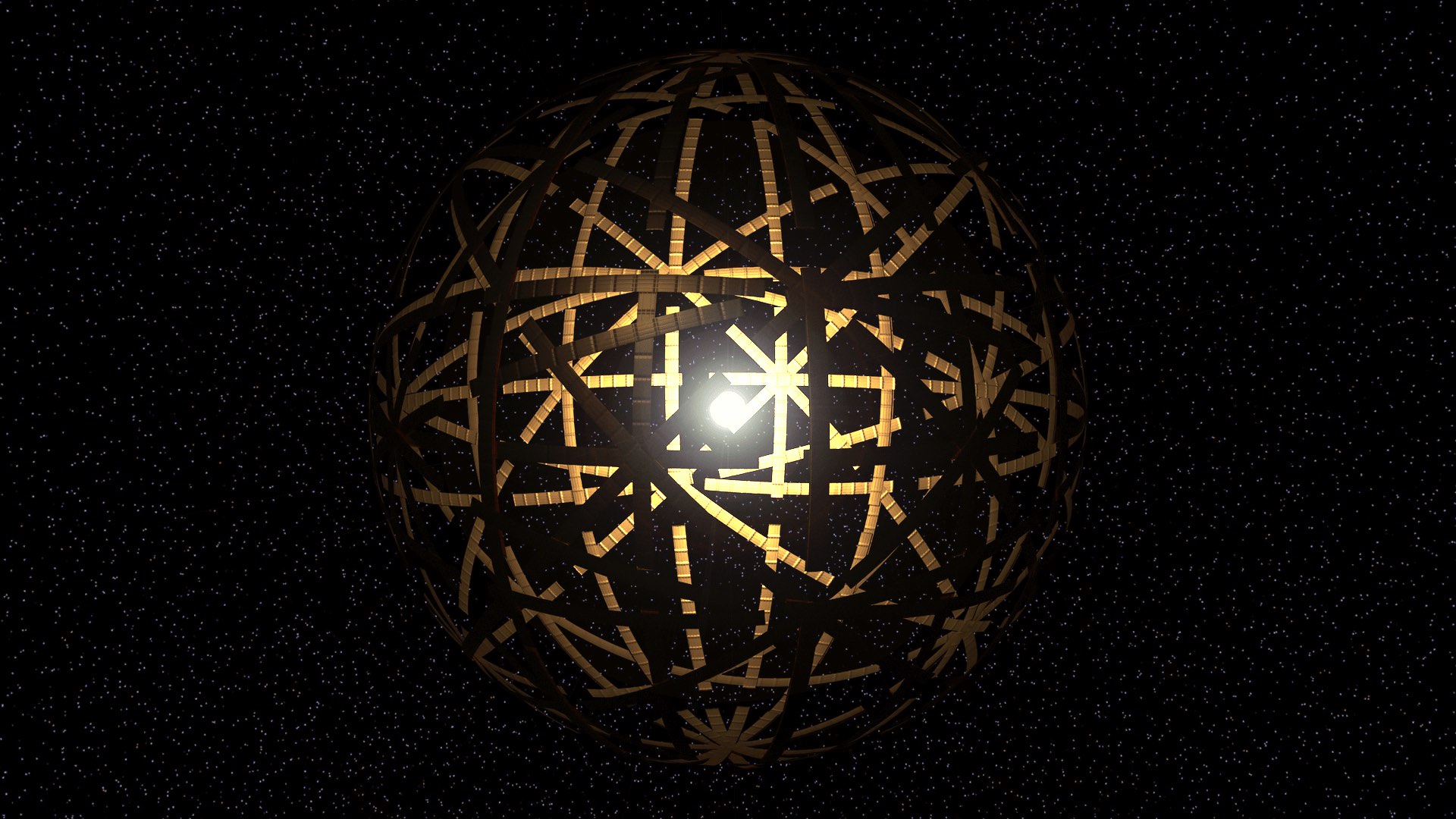
by DGR News Service | Aug 29, 2020 | Human Supremacy
This is the second in a series of articles reflecting on a recent study which predicts collapse of industrial society within a few decades. In the first essay, Max Wilbert discusses how in the long-run, collapse will benefit both humans and nature alike. This second essay in the series explores a “solution” proposed by the original authors of the study—a “Dyson sphere”—and why it will not save us from a collapse.
By Salonika / DGR Asia-Pacific
A Dyson sphere is a theoretical energy harvesting, a metal sphere that completely encompasses a star, and harnesses 100% of the solar energy. The solar panels that form its membranes would capture and transmit energy to Earth’s surface through microwave or laser. A concept that originated from a science fiction, it has been considered to be the ultimate “solution” to an industrial civilization’s ever increasing demand for energy.
There are a lot of problems with this theoretical solution. The authors of the study themselves are skeptical about the possibility of building a Dyson sphere by the time of their predicted collapse. We are going to deal with this issue in later parts of this series. In this piece, I will explore the improbable scenario that a Dyson sphere is built to fulfill the fantastical visions of the technocrats and whether that could prevent the ensuing collapse.
Is energy crisis the only crisis we are facing?
The obsession of the current environmental movement with renewable energy could easily confuse anyone regarding the scale of the ecological crisis that we are facing. We now witness a mass delusion that the energy crisis is, in fact, the only crisis that civilization is facing. In reality, the energy crisis represents just a facet of the ecological crisis.
Let’s consider global deforestation, which was used in the model for the study. The authors assert that once the Dyson sphere is used to “solve” our energy problems, the global deforestation would halt, ensuring the longevity of human civilization on Earth. This assertion is based on an unstated assumption that forests are being cleared primarily for fuel. As a matter of fact, fuel is only one driver of deforestation. Forests are also cleared for agriculture, cattle ranching, human settlements, buildings, mining, and roads. Unlimited energy does not “solve” or remove these pressures.
The same is true for all other forms of ecocide. Ninety percent of large fish in the oceans are gone, not to exploit their bodies for fuel, but due to overconsumption of fish as food. Bees colonies are collapsing, not for fuel, but, scientists estimate, due to pesticides, malnutrition, electromagnetic radiation, and genetically modified crops. Two hundred species are disappearing every day. That’s one every six minutes. That’s a result of habitat destruction, climate change, overexploitation, and toxification, not the need for energy.
A Dyson sphere (if it is ever created) could solve only the so-called energy crisis. All the other crises – habitat destruction, toxic environmental pollution, land clearing for agriculture, mining, overexploitation of species, and so on – would still continue. Indeed, the very existence of a Dyson sphere could increase the exploitation of the environment.
How is a Dyson sphere created?
First, a Dyson sphere would bemore massive than Earth itself. It would demands an astronomical (pun intended!) amount of raw materials, particularly metals. Procurement of these raw materials would require resource extraction on an unprecedented scale. Resource extraction (like mining) is one of the primary causes of environmental degradation, including global deforestation. Proponents advocate mitigating this harm by mining asteroids rather than planet Earth, but developing and building the fleet of spacecraft necessary for such an endeavor would necessarily begin on Earth, and would be incredibly harmful. In a single launch, a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket emits 1352 tonnes of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. (That’s nearly 300 times what an average car emits every year.)
Once created, a Dyson sphere would also need to be maintained. On average, a solar panel lasts about 25-30 years, after which the amount of energy produced will decline by a significant amount. It means that in every thirty years, the entire Dyson sphere would have to be rebuilt again. Let’s assume that the solar panels of the Dyson sphere would be more durable than the ones we use now. Even so, they will be subjected to different risks, like damage from asteroids or comets. A Dyson sphere would create a perpetual demand for (and, inevitably, overconsumption of) nonrenewable materials.
Additionally, the Dyson sphere could not function on its own. A new set of infrastructures would need to be built in order to utilize the energy harnessed. These include laser beam or microwave transmitters for wireless energy transmission from space to earth, additional photovoltaic cells in Earth to receive the transmitted solar energy, transmission wires (and poles) to supply the energy to industrial areas, and batteries to store the energy for when clouds block microwave transmission.
These building blocks come with additional costs. Wireless transmission of such vast quantities of energy can potentially cause eye and skin damage and other harm to human health, change the weather, and are potential culprits behind bees colony collapse. And what about birds? Traditional transmission lines are a prime cause of deforestation. Photo-voltaic cells usually end up in landfills or are sent to a developing country with lax environmental laws. Creating, maintaining, and disposing of solar panels pollutes the environment at every step.
An Authoritarian Technic
Lewis Mumford distinguishes between authoritarian technics and democratic technics based on whether a piece of technology requires a large-scale hierarchical structure, and whether it reinforces this structure. The Dyson sphere can be considered an authoritarian technic based on both of these criteria. The Dyson sphere requires a massive hierarchical infrastructure to exist in the first place: only specific group of individuals – those who have access and control over these infrastructures – can control its creation. Once created, it will be used to perpetuate the very hierarchical structure that created the conditions for its existence.
A Dyson sphere could exist only in an explicitly human supremacist, and implicitly colonial and patriarchal, culture. It will require resource extraction (primarily mining), on a scale much larger than what we have seen before. Extraction is inherently an ecocidal practice based on forced labor. It has been responsible for the destruction of numerous biospheres, and displacement of both humans and nonhuman communities.
The beneficiaries of this so-called technological “innovation” would be those who are already on the upper rungs of the hierarchical structure. Those on the bottom, on the other hand, would face the consequences. The same is true for other forms of technological innovations that we use every day. Consider a cell phone, for example. For the “haves” of the industrialized society, cell phones are little short of a basic necessity of life, the cost of which are covered by the “have-nots” through perpetual conflicts over resources, forced labor in modern day sweatshops, or even their lives.
The Root of the Problem: Overconsumption
Most importantly, the Dyson sphere does not address the core cause of the civilization’s impending collapse: overconsumption. Despite the claims that technology contributes to efficiency of resource consumption, technology seems to have very little (or even adverse) effect on the global energy consumption. With the exception of 2009 (the year of the global economic recession), consumption has only increased each year since 1990. When the demand for a product is constantly rising, no matter how efficient the production process gets, it will lead to greater consumption of resources.
On the contrary, the authors present a Dyson sphere as a solution to their predicted population collapse. They assume that, the perpetual energy source would lead to a lowered consumption of natural resources, allowing a sustained human population of 10 billion. Even if the culture’s energy demands are met by the perpetual source, in face of a growing (industrialized) human population, we can only presume, the need for more food, more land, more “progress,” and – inevitably – more deforestation.
Furthermore, an implicit (yet obvious) motive for creation of a Dyson sphere is to facilitate our increasing levels of consumption. It will promote an energy intensive way of life. The more energy intensive a way of life is, the more it is based on (over)consumption. In fact, the very existence of a Dyson sphere would demand an exploitation of resources.
A Dyson sphere would not halt deforestation; neither would it stop the acidification of oceans. We’re facing an emergency: an imminent collapse. Many nonhumans have already faced its brutal reality (think about the last member of the species that died while you were reading this article). Now is not the time to indulge in fantasies of a non-existent technology that will salvage the civilization: it is the time to stop whatever is causing the collapse (hint: it’s overconsumption).
Salonika is a member of Deep Green Resistance Asia-Pacific. She believes that the needs of the natural world should trump the wants of the extractive culture.
Featured image: rendering of Dyson swarm by Kevin M. Gill, cc-by-2.0.





