Book Excerpt: Spirituality and Cultural Appropriation
Editor’s note: The following is from the chapter “Culture of Resistance” of the book Deep Green Resistance: A Strategy to Save the Planet. This book is now available for free online.
by Lierre Keith / Deep Green Resistance
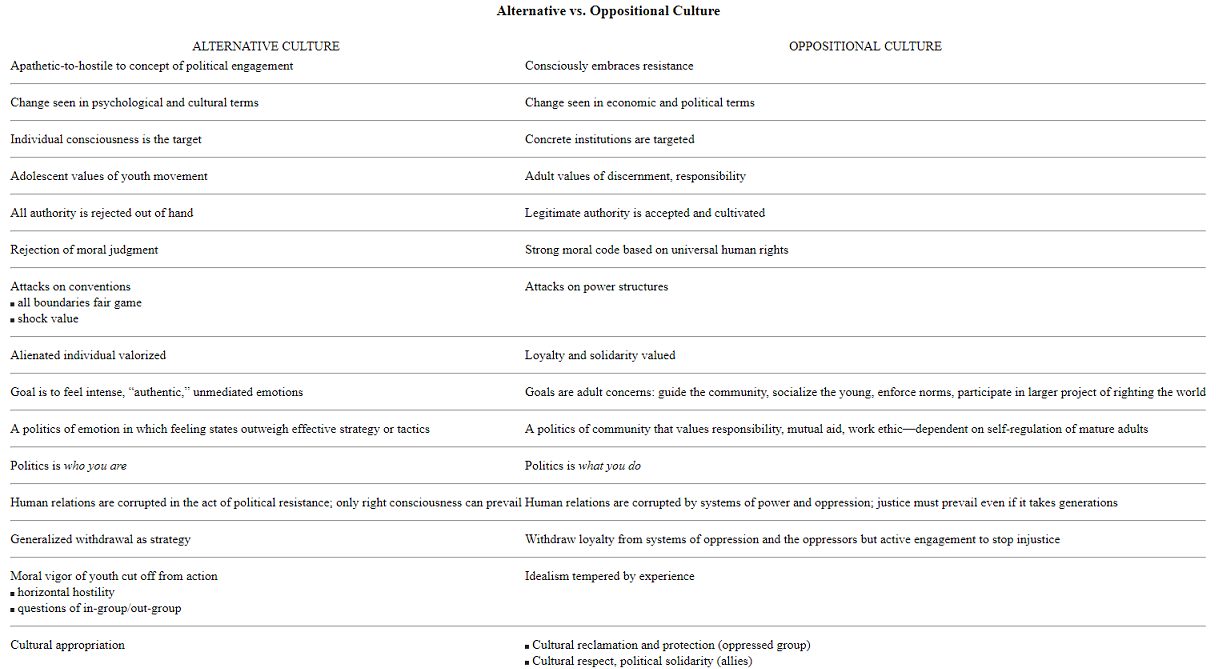
The final difference between the alternative culture and a culture of resistance is the issue of spirituality. Remember that the Romantic Movement, arising as it did in opposition to industrialization, upheld Nature as an ideal and mourned a lost “state of nature” for humans. Emotions were privileged as unmediated and authentic. Nonindustrialized peoples were cast as living in that pure state of nature. The Wandervogel idealized medieval peasants, developing a penchant for tunics, folk music, and castles. Writes Keith Melville,
Predictably, this attraction to the peasantry never developed into a firm alliance. For all their vague notions of solidarity with the folk, the German youths did not remain for long among the peasants, nor did they take up political issues on their behalf. What the peasants provided was both an example and a symbol which sharpened the German Youth Movement’s dissent against the mainstream society, against modernity, the industrialized city, and “progress.”86
When the subculture was transplanted to the US, there were no peasants on which the new Nature Boys could model themselves. Peasant blouses and folkwear patterns found a role, but the real exploitation was saved for Native Americans and African Americans. Primitivism, an offshoot of Romanticism, constructs an image of indigenous people as timeless and ahistoric. As I discussed in the beginning of the chapter, this stance denies the indigenous their humanity by ignoring that they, too, make culture. Primitivism sees the indigenous as childlike, sexually unfettered, and at one with the natural world. The indigenous could be either naturally peaceful or uninhibited in their violence, depending on the proclivities of the white viewer. Hence, Jack Kerouac could write:
At lilac evening I walked with every muscle aching among the lights of 27th and Welton in the Denver colored section, wishing I were a Negro, feeling that the best the white world had offered was not enough ecstasy for me, not enough life, joy, kicks, darkness, music, not enough music, not enough night.87
He’d rather be black? Really? Would he rather have a better chance of going to jail than going to college? Would he rather have only one thirty-eighth the wealth of whites? Would he really want to face fire hoses and lynching for daring to struggle for the right to vote? This is Romanticism at its most offensive, a complete erasure of the painful realities that an oppressed community must endure in favor of the projections of the entitled. And depressingly, it’s all too common across the alternative culture.
The appropriation of Native American religious practices has become so widespread that in 1993 elders issued a statement, “The Declaration of War Against Exploiters of Lakota Spirituality.” The Declaration was unanimously passed by 500 representatives from forty Lakota tribes and bands. The statement could not be clearer: white people helping themselves to Native American religious practices is destructive enough to be called genocide by the Lakotas. The elders have spoken loud and clear and, indeed, even reaffirmed their statement. We should have learned this in kindergarten: don’t take what’s not yours. Other people’s cultures are not a shopping mall from which the privileged get to pick and choose.
Americans are living on stolen land. The land belongs to people who are still, right now, trying to survive an ongoing genocide. Those people are not relics of some far distant, mythic natural state before history. They live here, and they are very much under assault. Native Americans have the highest alcoholism rate, highest suicide rate, poorest housing, and lowest life expectancy in the United States. From every direction, they’re being pulled apart.
Let’s learn from the mistakes of the Wandervogel. Their interest in peasants had nothing to do with the actual conditions of peasants, nor with the solidarity and loyalty that the rural poor could have used; it had everything to do with their own privileged desires. Judging from my many years of experience with the current alternative culture, nothing has changed. The people who adopt the sacred symbols or religious forms of Native Americans—the pipe ceremony, inipi—do it to fulfill their own perceived needs, even over the Native Americans’ clear protests. These Euro-Americans may sometimes go a step further and try to claim their actions are somehow antiracist, a stunning reversal of reality. It doesn’t matter how much people feel drawn to their own version of Native American spirituality or how much a sweat lodge (in all probability led by a plastic shaman) means to them. No perceived need outweighs the wishes of the culture’s owners. They have said no. Respect starts in hearing no—in fact, it cannot exist without it. Just because something moves you deeply, or even speaks to a painful absence in your life, does not give you permission. As with the Wandervogel, the current alternative culture’s approach is never a call for solidarity and political work with Native Americans. Instead, it’s always about what white people want and feel they have a right to take. They want to have a sweat lodge “experience.” They don’t want to do the hard, often boring, work of reparation and justice. If, in doing that work, the elders invite you to participate in their religion, that’s their call.
Many people have longings for a spiritual practice and a spiritual community. There aren’t any obvious, honorable answers for Euro-Americans. The majority of radicals are repulsed by the authoritarian, militaristic misogyny of the Abrahmic religions. The leftist edges of those religions are where the radicals often congregate, and that’s one option; you don’t have to check your brain at the door, and you usually get a functioning community. But for many of us, the framework is still too alienating, and feels frankly unreformable. These religions have had centuries to prove what kind of culture they can create, and the results don’t inspire confidence.
Next up are the pagans and the Goddess people. Unlike the Abrahmists, they often offer a vision of the cosmos that’s a better fit for radicals. Some of them believe in a pantheon of supernaturals, and show an almost alarming degree of interest in the minutia of the believers’ lives. Other pagans believe in an animist life force: everything is alive, sentient, and sacred. But if the theology is a better fit, the practice is where these religions often fall apart. They may be based on ancient images, but the spiritual practices of paganism are new, created by urban people in a modern context. The rituals often feel awkward, and even embarrassing. We shouldn’t give up on the project; ultimately, we need a new cosmic story and religious practices that will keep people linked to it. But new practices don’t have the depth of tradition or the functioning communities that develop over time.
In order to understand where the pagans have gone astray, it may be helpful to discuss the function of a spiritual tradition. Three elements that seem central are a connection to the divine, communal bonding, and reinforcement of the culture’s ethic. What forms of the sacred are sought by the subculture, and by what paths does it intend to reach them? Obviously a community broad enough to encompass everything from crystal healing to “Celtic Wicca” will have a multitude of specific answers. But taken as a whole, the spiritual impulse has been rerouted to the realm of the psychological—the exact opposite of a religious experience.
By whatever name you wish to call it, the sacred is a realm beyond human description, what William James rightly describes as “ineffable.” The religious experience is one of “overcoming all the usual barriers between the individual and the Absolute … In mystic states we both become one with the Absolute and we become aware of our oneness.”88 He describes this experience as one of “enlargement, union, and emancipation.”89 James offers a startlingly accurate description of that ineffable experience. But spiritual enlargement, union, and emancipation do not emerge from a focus on our psychology. We experience them when we leave the prisons of our personal pains and joys by connecting to that mystery that animates everything. The arrow—the spiritual journey—leads out, not in. But like everything else that might lend our lives strength and meaning, spiritual life—and the communities it both needs and creates—has been destroyed by the dictates of capitalism. The single-pointed focus on ourselves as some kind of project is not just predictably narcissistic, but at odds with every religion worth the name. The whole point of a spiritual practice is to experience something beyond our own needs, pains, and desires.
Ten years ago, I attended a weekend workshop called “The Great Goddess Returns.” I was already leery of these events back then, but there was one scholar I wanted to hear. The description, in so many words, offered what many people long to find: support, community, empowerment, relief from pain and isolation, and connection to ourselves, each other, the cosmos. These are valid longings and I don’t mean to dismiss anyone’s struggle with loneliness, alienation, or trauma. My criticism is directed instead at the standard form of the faux solutions into which neopaganism has fallen.
Drumming from a CD thumped softly through the darkened room. A hundred people were told to shut their eyes and imagine a journey back through time to an ancient foremother in a cave. I wasn’t actually sure what the point was, but I didn’t want to cultivate a spiritual Attitude Problem so early in the day, so I visualized. We were then handed a small piece of clay. No talking was allowed to break the sacrosanct if technological drumming. We were told to make something with the clay. Okay. It being March, and I being a gardener, I formed a peapod. Time ticked on. The drumming was more baffling than meaningful. And how long could it take people to mold a brownie size bit of clay? I kept waiting, the drumming kept drumming. Finally we were told to crumble up what we had made. All right. I smooshed up my peapod, and went back to waiting and my internal struggle against the demons of attitude. Boredom is annoying. It’s also really boring. I didn’t want to look around—everyone was hunched over with a gravitas that left me bewildered—but I was starting to feel confused on top of bored. Had I missed the part where they said, “Destroy your sculpture one mote at a time”? Finally, the rapture descended: further instructions. “Make your sculpture again,” came the hushed voice. What? Why? I hadn’t particularly wanted the first peapod. Did I have to make another one? Meanwhile, the drums banged on and on, emphasizing my growing ennui, and again, heads all around me bent to the work of clay like it was Day Six in the Garden. I reformed my peapod, which took about sixty seconds, then waited another eternity. I was ready to have a Serious Talk with whoever invented the drum.
Then the lights were slowly raised, a dawn to this long night of the bored soul. We were quietly divided into groups of ten and given the following instructions: “Talk about what you just experienced.”
Talk about … what? I made a pea pod. I crushed a pea pod. I remade a pea pod. For dramatic tension, I tried not to get bored.
Luckily, I was the seventh person in the circle, which gave me time to recognize the pattern and understand the rules. Because everyone else already understood. Being dwellers in the Land of Psychological Ritual, they knew too well what was expected. First up was a woman in her fifties. I don’t remember what she made with her clay. I do remember what she said. Crumbling up her sculpture brought her back to the worst loss of life, the death of her infant daughter. She cried over her clay, and she cried again while telling us, a group of complete strangers.
The next one up said it was her divorce, that crumbling the clay was the end of marriage. She cried, too.
For the third, the destruction of her clay was the destruction of her child-self when her brother raped her when she was five. She trembled, but didn’t cry.
The fourth woman’s clay was her struggle with cancer.
I had to stop paying attention right about then because I had to figure out what I was going to say.90 But I was also reaching overload. Not because of the pain in these stories—after years as an activist against male violence, I have the emotional skills to handle secondary trauma—but because the pain in their stories deserved respect that this workshop culture actively destroyed. This was a performance of pain, a cheapening of grief and loss that I found repulsive. How authentic to their experiences could these women have been when their response was almost Pavlovian, with tears instead of saliva? Smoosh clay, feel grief. Not knowing the expectation—not having trained myself to produce emotion on demand—I felt very little, beyond annoyance, during the exercise, and a mixture of unease, pity, and repugnance during the “sharing circle.” I had no business hearing such stories. We were strangers. I did not ask for their vulnerability nor did I deserve it. To be told the worst griefs of their lives was a violation both of the dignity such pain deserves and of the natural bonds of human community. This was not a factual disclosure—“I lost my first child when she was an infant”—but a full monty of grief. And it was wrong.
A true intimacy with ourselves and with others will die beneath that exposure. Intimacy requires a slow, cumulative build of safety between people who agree to a relationship, an ongoing connection of care and concern. The performance of pain is essentially a form of bonding over trauma, and people can get addicted to their endorphins. But whatever else it is, it’s not a spiritual practice. It’s not even good psychotherapy, divorced as it is from reflection and guidance. If you’re going to explore the shaping of your past and its impact on the present, that’s what friends are for, and probably what licensed professionals are for.
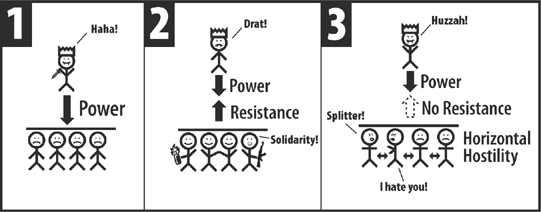
This “ritual” was, once more, a product of the adolescent brain and the alterna-culture of the ’60s, which imprinted itself unbroken across the self-help workshop culture it stimulated. No amount of background drumming will turn self-obsession and emotional intensity into an experience of what Rudolph Otto named “the numinous.” It will not build a functioning community. “Instant community” is a contradictory as “fast food,” and about as nourishing.
I have done grocery shopping after someone’s surgery, picked up a 2:00 am call to help keep a friend’s first, bottomless drink at bay, and taken friends into my home to die. I’ve also celebrated everything from weddings to Harry Potter releases. True community requires time, respect, and participation; it means, most simply, caring for the people to whom we are committed. A performative ethic is ultimately about self-narration and narcissism, which are the opposite of a communal ethic, and its scripted intensity is an emotional sugar rush. Why would anyone try to make this a religious practice?
I have way too many examples of this ethos to leave me with much hope. Some of the worst instances still make me cringe (white people got invited to an inipi and all I got was this lousy embarrassment?). I’ve been included in indigenous rituals and watched the white neopagans and other alterna-culturites behave abominably. Pretend you got invited to a Catholic Mass: would you start rolling on the floor screaming for your mother as the Catholics approached the rail for communion? And would you later defend this behavior as a self-evidently necessary “catharsis,” “discharge,” or “release of power”? When did pop psychology get elevated to a universal component of religious practice? Meanwhile, do I even need to say, the traditional people would never behave that way either at their own or anyone else’s sacred ceremonies. And they’d rather die than do it naked. Their dignity, the long stretches of quiet, the humility before the mystery, all build toward an active receptivity to the spiritual realm and whatever dwells there. The performative endorphin rush is a grasping at empty intensity that will never lead out of the self and into the all. Nor will it strengthen interpersonal bonds or reinforce the community’s ethics, unless those ethics are a self-indulgent and increasingly pornified hedonism, in which case it’s doomed to failure anyway.
So we’re stuck with some primary human needs and, as yet, no way to fill them. Many of us have traveled a continuum of spiritual communities and practices and found that none of them fit. My attempts to name cultural appropriation in the alternative culture have been largely met with hostility. For me, grief has given way to acceptance. The forces misdirecting attempts to “indigenize” Euro-Americans and other settlers/immigrants have been in motion since the Wandervogel. I will not be able to find or create an authentic and honorable spiritual practice or community in my lifetime. All I can do is lay out the problems as I see them and perhaps some guidelines and hope that, over time, something better emerges. It will take generations, but it’s not a project we can abandon.
Humans are hard-wired for spiritual ecstasy. We are hungry animals who need to be taught how to participate, respectfully and humbly, in the cycles of death and rebirth on which our lives depend. We’re social creatures who need behavioral norms to form and guide us if our cultures are to be decent places to live. We’re suffering individuals, faced with the human condition of loss and mortality, who will look for solace and grace. We also look for beauty. Soaring music produces an endorphin release in most people. And you don’t even need to believe in anything beyond the physical plane to agree with most of the above.
Some white people say they want to “reindigenize,” that they want a spiritual connection to the land where they live. That requires building a relationship to that place. That place is actually millions of creatures, the vast majority too small for us to see, all working together to create more life. Some of them create oxygen; many more create soil; some create habitat, like beavers making wetlands. To indigenize means offering friendship to all of them. That means getting to know them, their histories, their needs, their joys and sorrows. It means respecting their boundaries and committing to their care. It means learning to listen, which requires turning off the chatter and static of the self. Maybe then they will speak to you or even offer you help. All of them are under assault right now: every biome, each living community is being pulled to pieces, 200 species at a time. It’s a thirty-year mystery to me how the neopagans can claim to worship the earth and, with few exceptions, be indifferent to fighting for it. There’s a vague liberalism but no clarion call to action. That needs to change if this fledgling religion wants to make any reasonable claim to a moral framework that sacrilizes the earth. If the sacred doesn’t deserve defense, then what ever will?