
by DGR News Service | Jul 12, 2024 | ACTION, Culture of Resistance
Editor’s note: When we engage in any form of activism, building leadership capacity helps people become more confident and proactive. It means the leader of the group doesn’t have to be responsible for every task and can delegate other important tasks to members. In this case, the author talks about climate change, we at DGR think that climate change is one of many problems and stems from our destructive industrial culture. But you can exchange the word for any other that would describe a dire situation today – the strategy of leadership capacity still applies. DGR disagrees with 350.org’s belief that electrifying everything will “solve” climate change. It is, in fact, impossible, and attempts to do so will only make matters worse.
By 350.org, Daniel Hunter
Learn how organisers recruit and build the leadership capacity of others with the Ladder of Engagement.
This article has been sourced from Daniel Hunter’s book published by 350.org called The Climate Resistance Handbook. Daniel explains the Ladder of Engagement with a story from South Africa about an environmental justice group. Read below or see Chapter 3 on Growth and pages 40 – 46. The images have been added by the Commons Library.
The Ladder of Leadership
Growing groups face a challenge. Organisers are often the ones doing much of the work of the group — and they get tired of doing everything…One option for the organisers getting tired is they keep sacrificing more and more. They give up sleep. They sacrifice school and work. They stop social activities — it always becomes about the activism.
For most people, that’s just not sustainable. So what’s the alternative?
Getting new people to step into leadership!
A story from Ferrial Adam in South Africa provides us an example. She was part of an environmental justice organisation working with folks at the grassroots. Led largely by women, they were challenging a government policy called “Free Basic Electricity.” That policy guarantees the government will pay for a certain amount of electricity to poorer households (currently 50 kWh, about 5% of what the average US home uses).
This is a major issue, as the lack of access to energy often dooms whole districts to poverty. For example, those lacking electricity often rely on carbon-intensive paraffin, candles, or cutting down trees. This leads to a host of negative environmental and health effects.
Building relationships is key
This policy was widely credited as a successful social justice policy. But those who were most impacted by this policy weren’t part of the debate. So Ferrial began a research study to learn more about the actual impacts this had for households, which meant going to the poor districts in the city of Johannesburg.
She started where the people were. Her first step was finding a group of women who were keen and already working on energy struggles. It was important to start by explaining the intention and need for the work. She started by getting people to monitor their use of electricity. She spent time building relationships with mostly women, who ran the households. It took many months of weekly workshops to teach people to calculate the energy consumption of different household items.
Increased confidence
Her report was done. And she could have been the person presenting the report in front of national bodies. But when public hearings were planned to increase costs, the people Ferrial had been working with wanted more. She asked the women if they would testify on their own behalf. They jumped at the chance. Ferrial says, “It was so amazing and powerful watching people go to a hearing and speak as a collective on why the government should not raise the price of electricity.”
“They became part of the organisation and took their own leadership. Ferrial wasn’t calculating people’s consumption for them and writing the report and talking before the national bodies. She was organising. She wasn’t doing things that people could do for themselves.”
The women were supported through steps of engagement over the months. This way, they gained expertise about their own electricity usage and education on national policy and the impacts of climate change. Each step gave them increased confidence to not only testify but be strong community activists.
This concept is called the “ladder of engagement.”
The women wouldn’t have been ready to testify as their first step. Instead, they needed to learn more about their own situation. Then they needed to connect to others’ stories and see they weren’t alone. The ladder helps us think about what to do when people say, “What you’re doing is great, how can I help?”
“In our minds, we have our to-do list and things we need done. But that’s not where to start. We have to think from the perspective of that person.”
That probably means our first response is, “Let’s talk about what you’re up for doing.” And we find out what kinds of tasks they might be willing to help us with — ones that match their interest and involvement (not our long to-do list).
“This isn’t a science, and each person is different. Some people have absolute terror making phone calls but would happily risk civil disobedience. So chatting with people about their interests is important.”
Thinking about newer activists in our group with the ladder of engagement in mind helps us think about the next step for them.
And as Ferrial did, we can offer steps to keep increasing their level of commitment and involvement. This cultivates relationships and helps people move up the ladder of engagement, which is how you, too, will increase your group’s involvement.
Recruit People Outside your Circle
“Of course, to get more people into leadership, you have to have lots of conversations with them — about the goals of the campaign and the work you’re doing. You have to build trust. And you have to find them!”
Sometimes it’s hard to recruit new people, because we get used to talking the same way about an issue. You may have some ways you talk about climate change that you’re used to.
But someone you want to recruit may not talk about it that way. They may not care about climate change, but they may care about cats. You can tell them that climate change is increasing the habitat for fleas, ticks and mosquitoes. That’s bad news for pets. It exposes them to new diseases, like West Nile, Lyme disease and heartworm. Or maybe they care about football. Climate change isn’t going to end football soon, but it will change the game. With more erratic climactic events, you will see more games like the snowy 2013 World Cup qualifying match between USA and Costa Rica. It was a disaster. Or, since the spread of Zika (and other diseases) increase with the rise of temperatures, Brazil’s warmer temperatures threatened to derail the Rio 2016 Olympics.
How to organize?
Or maybe they just don’t like being angry! A study on climate and conflict showed that warmer temperatures increase people’s personal conflicts (by 2% amongst friends, and by 11% outside their social circle). So hot temperatures can cause more anger.
But even when we get more flexible in talking about climate change, many groups often mistakenly believe they’ve tapped all the people who are passionate about their issue. “Nobody in my school cares about climate change.” The problem is often not that we have exhausted the possibilities in our city or small town — it’s how we are organising.
Building leadership capacity
When it comes to recruitment, many of us think of people just as individuals. We imagine there is a scattering of people out there from whom to recruit.
The reality is different. Most people are not attracted to groups simply as individuals. Ask around, and you’ll find that very few people get involved in a cause because they receive a flyer, get sent an e-mail, see a poster, or see a Facebook post.
Most people join a group or get involved because someone they know personally invited them.
That’s because society is better understood as clusters of “social circles”. Social circles may be organised as formal or informal groups — religious communities, gangs, tight-knit neighborhoods, etc. Social media can show you the number of people who are friends of friends many times over.
The quickest way to build a group is to ask people in your net works of friends or family. Those people are the most likely to say yes to you. But a group stops growing when it reaches its maximum potential of people from its members’ initial social circle. Continuing to reach out within that circle may not bring in many more people.
The trick is to jump out of your social circle and find people connected with other social circles.
Ways to recruit in social circles
Show up at the events and meetings of people outside your circle. This is a great chance to meet others, see how they work, and find out where their values overlap with your campaign.
- Stop doing the tactics you’ve always been doing, and try new ones that might appeal to different audiences. If your tactics are marches, strikes, and massive, disruptive direct actions, and it’s not working, then it’s time to adapt. Ritualising our actions makes us predictable and boring. People want to join fresh and interesting groups.
- Notice when other groups make overtures toward your movement, and follow up with them. For example, if we are seeing reluctant corporate and government allies taking steps towards us, maybe with some of them there are relationships we can build to keep them moving faster.
- Do lots of one-on-one meet-ups with leaders from other movements and groups. Meet with different people — not to recruit them, but to learn from them.
- What are their values?
- What interests them?
- What strategies recruit people like them?
- Do direct service. Gandhi was a big fan of what he called the “constructive program,” which means not only campaigning against what we don’t want, but also building the alternative that we do want. Climate disasters provide large-scale and small-scale chances for us to be part of that. Direct service to disaster survivors and other community-based projects put us shoulder to shoulder with others who want to make things better. Who better to hear a pitch about joining your campaign?
Growing outside of your social circle takes time, but when it comes to building successful groups, it’s worth the effort.
This article is from the Climate Resistance Handbook which brings together a wealth of learnings from the climate justice movement. It starts with breaking social myths about how social movements win. Then dives into campaign tools and frameworks you can use. It closes with how to grow your group and use creative, impactful actions and tactics. This book is full of stories of climate warriors from around the globe and historical movements. It’s filled with practical wisdom and inspiration to make you more effective, more active, and ready for what’s next.
Derivative of graphic by parasoley/Getty Images Signature via Canva.com

by DGR News Service | Dec 12, 2022 | ANALYSIS, Education, Movement Building & Support
Editor’s note: Less than five years ago in Ireland, a woman getting an abortion could get a longer sentence than her rapist. That changed with a referendum in 2018, where the people of Ireland voted for abortion rights. The following article is written by one of the organizers of the Yes campaign: a campaign that reached out to people leading up to the referendum to get them to vote Yes for abortion rights. IN this piece, Clodagh Schofield describes her experiences with using powerful conversations as a tactic in the campaign.
As social beings, we tend to be reluctant to voice our opinions if we believe that those around us would get uncomfortable because of it. It might be because we think others don’t agree with us, or simply because the topic is an awkward one (like abortion). Voicing our opinions in such situations can be a small, yet powerful, way to start a discussion on a topic. It can lead to an exchange of ideas and people beginning to understand each other’s perspectives. Sometimes, it can also be part of a wider strategy to influence public opinion.
While DGR does not believe that changing public opinion in itself can lead to a cultural shift required to save the world, we do believe it is an important part of our movement. It is also a tactic that you can use with the people around you which requires relatively less time and energy and a higher amount of courage. Let us know if you have started uncomfortable conversations around you, and the effects you observed.
By Clodagh Schofield/Commons Library
Overturning the abortion ban in Ireland meant equipping people to share their stories and spark conversations with their friends and family.
In Ireland on May 25, 2018, the Yes campaign to repeal the nation’s 8th Amendment abortion ban won after receiving nearly two-thirds of the over 2.1 million votes cast.
The victory resulted in part from people across the country having hard conversations about abortion. Let’s take a look at how the campaign helped start and support the tough talks needed to shift perceptions about deeply held values.
In Ireland’s landslide win for abortion rights, a long-silent majority appeared to vote Yes. The Yes vote also won decisively in rural counties thought to be the heartland of the No campaign. Why?
After the vote, 39% of people polled about what changed their minds to Yes cited a conversation with family or friends. Thousands of people with traumatic abortion experiences broke their silence and inspired others to speak up.
But it wasn’t by accident that people across Ireland had these difficult conversations over tea, at sporting events on the weekend, in the car, after school and online. In fact, when polled in January, four and a half months before the vote, over half of voters said they would be too uncomfortable to talk about abortion with people in their lives.
The Yes campaign helped people start and maintain conversations, modeled positive values-based talk that didn’t play into the opposition’s messaging frame and ran a grassroots effort that gave people agency over their conversations.
The campaign also recognised the value of each person. In Ireland, where abortion has been banned since the 8th Amendment was passed in 1983, everyone has a story about abortion. When it comes time to vote, a person needs just one story to change or affirm how they mark the ballot.
I worked on the Yes campaign and see valuable lessons in sparking difficult conversations for campaigners working elsewhere in the world on issues that, like the Ireland abortion referendum, are steeped in centuries-old mixes of institutions, politics and values.
Help people start conversations in diverse ways
It’s not easy to talk about abortion on a personal level. Different people need different prompts and various levels of support.
Groups used a variety of approaches to help people start conversations. Amnesty International partnered with the Minister for Health, Simon Harris, and asked members to pledge to have conversations with those around them on itstime.ie (unfortunately the site is now retired). Local groups of the official Yes campaign held some amazing conversation cafes. My favourite tactic was so simple: the Abortion Rights Campaign produced badges for supporters which read “Talk to me about Repeal.”
At Uplift, we ran a number of different campaigns to encourage people to start conversations. We also equipped people to have effective and meaningful conversations.
Early in the campaign, we ran an online conversations training on Crowdcast. We focused on using stories and values based communication to approach undecided voters. We followed up conversations with a microsite, letstalkrepeal.ie [Link not working 27 April, 2022]. Engagement with these resources was strong. Feedback was also good. The program provided an accessible low bar ask for people who supported Yes and wanted to step up but not into leadership roles.
We launched Mobilisr [link not found 29 April 2022], a peer-to-peer messaging program, in the run up to the vote. People used it to get in touch with their Facebook Messenger, WhatsApp, and Telegram contacts to either start a conversation about abortion care, or ask them to get out and vote. People were slow to start using Mobilisr but activity picked up once users had used the tool at least once.
By 25 May, the app converted extremely well – especially as users could select as many people in their contacts as they chose to send a prefilled but customisable message. Lightweight and adaptable, this tool shows huge promise for starting conversations with users outside of a campaign’s existing reach.
We segmented lists into people who were a Yes vote, people voting No, and undecided voters. Strong pro-choice members were recruited to have conversations with undecided voters. One volunteer trained and supported a team of “e-Repealers” who offered undecided people the opportunity to have a conversation via email using Freshdesk. Though at times a little rough and ready, this program was entirely volunteer run. The program fostered earnest and often complicated discussions between very different people.
Focus on your values and vision, not the opposition’s framing
Campaigning was organised locally but most Yes groups used messaging focused on care, compassion and change.
At Uplift we worked with Anat Shenker-Osorio to develop messaging. We talked about abortion as a part of healthcare and shared stories of individuals instead of speaking of women collectively. We also shared a vision of the society where everyone has the freedom to decide whether and when to become a parent.
The tone of the Yes campaign paved the way for powerful conversations between people on an issue that’s historically untouchable. Even the No campaign acknowledged that Yes campaign messaging grounded the debate and prevented it from becoming as toxic as it could have been.
Empower people with campaign ownership
The Abortion Rights Campaign, one of three partners in the official Yes campaign, is an unashamedly radical organisation with no paid staff and a flat structure. Local groups have a strong sense of campaign ownership built through years of distributed community organising and grassroots fundraising.
But a campaign with few paid staff still needs leaders. The referendum campaign facilitated opportunities for people to step in, learn and take on campaign roles. The challenge was in finding lightweight, scalable and impactful ways to connect and resource them.
A voter only needs one story in mind to vote Yes
In the end, the aim of the Yes campaign was to make space for brave people to talk about their abortion care experiences in a country that banned abortion. We also created a situation in which those stories would have power.
Together4Yes and campaigning NGOs like Uplift and Amnesty International targeted personal story video ads on social media. We gave particular weight to stories of “hard cases.” These included people who were pregnant as a result of incest or sexual assault and cases of fatal foetal abnormality. These stories were so powerful with undecided voters that the No campaign tried to do a double-take in the final week and argue for a compromise that would enable abortion in those cases.
In Her Shoes, a volunteer-run Facebook page, is a great example of how people created a way for others to share personal stories. The format was simple. People sent in their story with a picture of their shoes. Posted anonymously, these stories went viral again and again. It became possible for people to feel surrounded by anonymous women, wearing Vans, sandals, runners and heels, who’ve kept their struggle secret from those around them for years.
By far the most powerful story of the referendum campaign was that of the late Savita Halappanavar. Savita’s parents shared their daughter’s story in one of the most watched videos of the campaign. In it, they called on the people of Ireland to remember their daughter and vote Yes.
Halappanavar had a septic miscarriage and was denied a requested abortion in a hospital when it was determined that her life was not sufficiently threatened. She died shortly thereafter. Eight percent of Yes voters polled by Irish national broadcaster RTE said they voted yes because of Savita.
In the same poll, 43% of Yes voters said people’s personal stories in the media convinced them. 34% cited experiences of people they knew. Creating safe and respectful platforms with reach for these stories was crucial to the success of the Yes campaign, and gave people the tools they needed to talk to those around them.
A people-powered catharsis
As a woman living in Ireland, knowing that this fight was won by the people around me makes me feel that broken trust is now mending. Reflecting on the campaign, many have said that the country is changed forever: stories have come to light that will never be hidden again. In listening, and acting compassionately, we’ve gone through a catharsis.
As an organiser, this campaign taught me that it’s valuable to pick moments when people are passionate and ready to act. As important is providing tools for people to follow through on that passion by connecting with people around them: family, friends and social networks.
People power, properly organised and resourced, can beat a huge budget and Cambridge Analytica style dark ads. More on that later.
The online conversation training by Uplift can be replayed in Crowdcast.
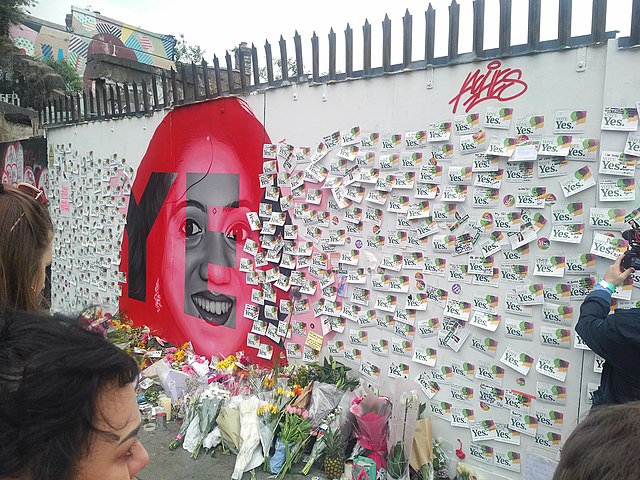
Featured image: A mural outside the Bernard Shaw Pub in Portobello, Dublin depicting Savita Halappanavar by Zcbeaton via Wikimedia Commons (CC BY-SA 4.0)

by DGR News Service | Jun 6, 2022 | ACTION, Culture of Resistance, The Solution: Resistance
How to Become and Activist and Organize Your Life for Resistance
By Max Wilbert
There is a spectrum of involvement in political organizing.
It begins with awareness of the issues. Then, a person may wish to volunteer and contribute to a cause. Eventually, if commitment and experience continues to grow, a person can begin to be a leader and true organizer, bringing other people together and coordinating work that falls into the three categories of resistance efforts [Ed. note: see our next article this Friday for more on these categories].
Ideally, political organizing should be conducted inside an organization. Organizations help us build power by forcing us to clearly define goals, bring people together, create structure and accountability, and evolve over time. Working in a group also requires more of us as individuals; we learn to work better with others, get feedback on our approach, and are exposed to different ways of thinking.
When I first got involved in Deep Green Resistance more than a decade ago, I began to ask myself, “how do I contribute?” First, I found simple ways. I posted to social media, washed dishes at gatherings, and participated in discussions to build community. I shared resources that I found interesting, contributed short articles and blog posts, and donated $5 per month — not much, since I was very poor at the time, but an important symbol of my commitment.
I also worked to educate myself as much as I could, reading books about historical resistance movements, community organizing, fundraising, environmental issues, and of course the Deep Green Resistance book.
Whenever there was an opportunity to step up and volunteer for something, I tried to take it. Over time, I built more experience and confidence, and I started doing more.
Getting started with local and regional organizing
When I moved to a new town, I began by organizing a chapter of DGR there. I talked with leadership, made us a website, and started sharing information about local and regional environmental issues, learning about them as I went along.
I started attending rallies and protests with homemade signs. I met some people who were interested and worked to recruit them into the organization. We held several events, such as meetings, film screenings, and so on. Some were attended by only one or two people. But this experience helped me learn, and eventually I organized a full two-day event including speakers from a half-dozen organizations and regional tribes, which was attended by 30 people. I was learning.
When I head about a radical direct action campaign in the area, I got involved. I started going to meetings, taking notes, doing research, and contributing as much as I could. We visited the site of a proposed fossil fuel project, and got to know the area. I fell in love with the land and started to write essays. As the campaign went on, I had a chance to participate in several direct actions and risked arrest.
Soon, I redirected my energy towards another environmental issue in my region that was less well-known.
This period I’m describing ended about eight years ago. Since then, I haven’t stopped learning. I thought it might be useful to share this story with you all to help you envision yourself going through a similar process.
Here are a few things I’ve tried to keep in mind throughout this time period to deliberately organize my life for resistance.
1. Cultivate passion
The most important thing is to keep the fire burning. I fall in love with the natural world over and over again. And my heart breaks and I get angry over and over again when I see the world being destroyed. This is the foundation of everything.

2. Learn
Effective resistance is a skill, not an innate trait. If I study, practice, and reflect, I will become more skilled over time. I work to gain theoretical (analysis, history, philosophy, writing, etc.), interpersonal (communication, conflict mediation, community organizing, fundraising, etc.), and practical (self-defense, wilderness survival, climbing, navigation, cooking, etc.) skills.
3. Find flexible and stable work
Both poverty and professional-workaholism are weapons of capitalism. Capitalism is set up to keep us locked into the prison of 40-hour work weeks and the nuclear family model. To have maximum time and energy for resistance, I try and find flexible work (self-employed if possible) and minimize my expenses by living an alternative lifestyle.
4. Build a supportive network and focus on your health
I surround myself with people who reflect my values and help me expand my thinking. Cultivating good relationships and personal health gives me vitality and allows my energy to match my passion. I try to distinguish between things that feed my soul and things that are a waste of time so I can prioritize resistance work.
5. Don’t give up
I am always looking for better ways to do things and do not hesitate to self-criticize and change course.
Max Wilbert is an organizer, writer, and wilderness guide. He is the author of two books, most recently: Bright Green Lies: How the Environmental Movement Lost Its Way and What We Can Do About It (Monkfish 2021 — co-authored with Derrick Jensen and Lierre Keith).
by DGR News Service | May 9, 2022 | ACTION, Movement Building & Support
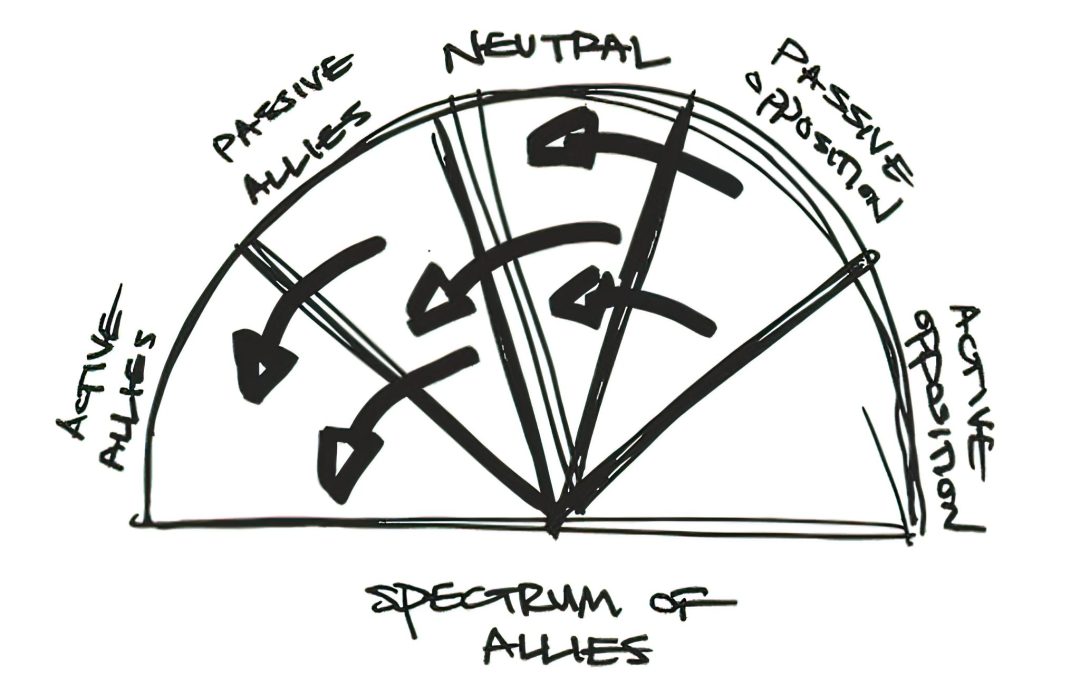
Editor’s note: The following conceptual tool is designed to help community organizers to categorize community groups, businesses, government bodies, and individuals along a “spectrum of allies.” This exercise teaches a fundamental tenet of community organizing: that our goal is not only to find people who agree with us fully, but to gradually shift those who disagree with us into greater political alignment.
We use this tool regularly in Deep Green Resistance training programs and campaigns, and encourage you to do so as well.
By Nadine Bloch
Introduction
Movements seldom win by overpowering the opposition; they win by shifting support out from under it. Use a spectrum-of-allies analysis to identify the social groups (students, workers) that are affected by your issue, and locate those groups along a spectrum, from active opposition to active allies, so you can focus your efforts on shifting those groups closer to your position. Identifying specific stakeholders (e.g. not just students, but students at public colleges; not just workers, but domestic workers) can help you identify the most effective ways of moving different social groups closer to your position, in order to win your campaign.
When mapping out your campaign, it is useful to look at society as a collection of specific communities, blocs, or networks, some of which are institutions (unions, churches, schools), others of which are less visible or cohesive, like youth subcultures or demographic groupings. The more precisely you can identify stakeholders and impacted communities, the better you can prepare to persuade those groups or individuals to move closer to your position. You can then weigh the relative costs and benefits of focusing on different blocs.
Evaluating your spectrum of allies can help you avoid some common pitfalls. Some activist groups, for instance, only concern themselves with their active allies, which runs the risk of “preaching to the choir” — building marginal subcultures that are incomprehensible to everyone else, while ignoring the people you actually need to convince. Others behave as if everyone who disagrees with their position is an active opponent, playing out the “story of the righteous few,” acting as if the whole world is against them. Yet others take a “speak truth to power” approach, figuring that through moral appeal or force of logical argument, they can somehow win over their most entrenched active opponents. All three of these extreme approaches virtually guarantee failure.
Movements and campaigns are won not by overpowering one’s active opposition, but by shifting each group one notch around the spectrum (passive allies into active allies, neutrals into passive allies, and passive opponents into neutrals), thereby increasing people power in favour of change and weakening your opposition.
For example, in 1964 in the U.S., the Student Nonviolent Coordinating Committee (SNCC), a major driver of the African-American civil rights movement in the racially segregated South, realized that in order to win desegregation and voting rights for African Americans, they needed to make active allies of sympathetic white northerners. Many students in the North were sympathetic, but had no entry point into the movement. They didn’t need to be educated or convinced, they needed an invitation to enter the struggle. (Or in the spectrum-of-allies schema, they needed to be moved from passive allies into active allies.) Moreover, these white students had extended communities of white families and friends who were not directly impacted by the struggles of African-American southerners. As the struggle escalated, these groups could be shifted from neutral to passive allies or even active allies.
Based on this analysis, the SNCC made a strategic decision to focus on reaching neutral white communities in the North by engaging sympathetic white students in their Freedom Summer program. Busloads of students travelled to the South to assist with voter registration, and many were deeply radicalized in the process. They witnessed lynchings, violent police abuse, and angry white mobs, all a response to black Southerners simply trying to exercise their right to vote.
Many wrote letters home to their parents, who suddenly had a personal connection to the struggle. This triggered another desired shift: Their families became passive allies, often bringing their workplaces and social networks with them. The students, meanwhile, returned to school in the fall as active allies, and proceeded to organize their campuses — more shifts in the direction of civil rights. The result: a profound transformation of the political landscape.
This cascading shift of support wasn’t spontaneous; it was part of a deliberate movement strategy that, to this day, carries profound lessons for other movements.
How to use
Use this tool to identify the constituencies that could be moved one notch along the spectrum, as well as to assess the relative costs of reaching, educating, or mobilizing each of these constituencies. Do not use this tool to identify your arch enemies and go after them — it’s the people in the middle you’ll most often want to focus on. The groupings or individuals you identify should be as specific as possible: not just unions, for instance, but specific unions. The more specific you can be, the better this tool will serve you.
Here’s how to do a spectrum-of-allies analysis:
1. Set up a “half-pie” drawing (see diagram).
Label the entire drawing with the name of the specific movement or campaign you are discussing, and put yourself on the left side, with your opposition on the right side.
2. Divide the half-pie into five slices:
- active allies, or people who agree with you and are fighting alongside you;
- passive allies, or people who agree with you but aren’t (yet) doing anything about it;
- neutrals, or the unengaged and uninformed;
- passive opposition, or people who disagree with you but aren’t actively trying to stop you; and
- active opposition, or people who not only disagree with you, but are actively organizing against you.
In the appropriate wedges, place different constituencies, organizations, or individuals. Spend a significant amount of time brainstorming the groups and individuals that belong in each of the sections. Be specific: list them with as many identifying characteristics as possible. And make sure to cover every wedge; neglecting sections will limit your strategic planning and your potential effectiveness.
3. Step back and see if you’re being specific enough
For every group or bloc you listed in the diagram, ask yourself whether you could be more specific — are there more adjectives or qualifiers you could add to give more definition to the description? You might be tempted to say “mothers,” but the reality might be that “wealthy mothers who live in gated communities” might belong in one wedge, and “mothers who work as market vendors” would belong in another. The more specific you can be, the better this tool will serve you.
4. Identify what else you need to know.
When you come up against the limits of your knowledge, make sure to start a list of follow-up questions — and commit to doing the research you’ll need to get the answers.
Combine with other tools
The spectrum of allies can also work well in combination with other methodologies:
- First, use pillars of power to map out the biggest forces at play.
- Combine with a SWOT matrix in order to help you identify all key constituencies.
- Follow up with points of intervention in order to identify tactics and actions to engage the key constituencies you’ve identified.
Nadine Bloch is currently Training Director for Beautiful Trouble, as well as an artist, political organizer, direct action trainer, and puppetista. If you have a question for Nadine about this tool you can contact her via the form at the bottom on the Beautiful Uprising Spectrum of Allies article.
This article is published under the Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike CC BY-NC-SA license. Small portions of the original article were omitted for clarity.

by DGR News Service | May 1, 2022 | ACTION
Editor’s note: The ability to work with others who we may disagree is fundamental to organizing in a socially fractured, multi-polar world. But doing so is difficult, distasteful, and increasingly rare in our filter-bubble modern experience, where people we disagree with are purged in service of the creation of ideological echo chambers. Today’s essay speaks to the necessity and challenges of such coalition-building.
Before we begin, we would like to share with you some actionable advice for coalitions. Building principled alliances depends on a series of steps that must be undertaken with intelligence and great care:
1. Movement Building. You cannot build an alliance as an individual. Alliances are built between organizations. We will assume here you have already done the work of identifying the core issues you are trying to address, articulating your core values, and bringing together a team/organization to take action.
2. Objectives. Alliances depend on you clearly understanding what you are trying to achieve. Determine your objectives. Ensure they are SMART and practical. You may also wish to sequence objectives along a timeline towards your broader strategic goals.
3. Understand the Political Context. Conduct a spectrum of allies exercise. Identify communities, individuals, and organizations who are involved in the situation or may be swayed to take part, and how sympathetic they are to your perspective.
4. Determine Potential Allies. Determine which organizations you will focus on for alliance building. Usually, this is not the “easy allies” who will work with you regardless of what you do. Instead, pivotal allies are often found among the ranks of those who are ambivalent or opposed to your organization in some way. Focus on key individuals, usually either formal or informal leaders. Research these people and identify areas of overlap, shared values, and how to effectively communicate with them.
5. Build Relationships and Negotiate. Talk with potential allies. Begin to build a relationship. Do not gloss over disagreements, but focus on areas of mutual benefit and overlapping values. Propose specific ways work together towards shared goals. Keep in mind that collaboration can fall along a spectrum from public to private, that political considerations may prevent certain approaches, and that building trust takes time.
By Jaskiran Dhillon / ROAR Magazine
They called it the heat dome.
The hottest temperatures ever recorded in the US Pacific Northwest and far southwest Canada appeared in the summer of 2021 with the force of an invisible, slow-motion siege. Meteorologists tracking the silently rising tidal wave of heat broadcasted maps painted in shades of crimson, alerting a sleeping public to a summer gone blazing red. The headlines said it all: “This Summer Could Change Our Understanding of Extreme Heat,” “Sweltering Temperatures Expected Across U.S. Due to Heat Dome,” and “Western Canada Burns and Deaths Mount After World’s Most Extreme Heat Wave in Modern History.”
Created through a high pressure system that causes the atmosphere to trap very warm air — and precipitated, in part, through heat emerging from increasingly warming oceans — a heat dome produces extreme temperatures at ground level that can persist for days or even weeks. In British Columbia, Canada, thermometers were registering the air at an alarming 49.6 degrees Celsius, with similar highs in the states of Washington and Oregon, immediately south of the border, exposing US and Canadian residents to the type of extreme weather events countries in the Global South have been experiencing for years. But this kind of heat does not just live in the air that we breathe — it envelopes everything it touches, leaving a trail of death, destruction, and urgent questions about the future.
For climate scientists who have been studying the intensification of heat wavesover the last decade, the results of the heat dome were predictably devastating. The British Columbia Coroners Service identified 569 heat related deaths between June 20 to July 29, and 445 of them occurred during the heat dome. A human body exposed to severe and relentless heat is a body under duress, a body working overtime: when subjected to an elevation in air temperatures, our bodies draw additional blood to the skin to dissipate heat — a natural cooling system designed to maintain optimal body temperature. This process becomes more strained when the temperature continues to rise, without the reprieve of cooling; oxygen consumption and metabolism both escalate, leading to a faster heart rate and rapid breathing. Above 42 degrees Celsius, enzyme and energy production fail and the body is in danger of developing a systemic inflammatory response. Eventually, multi-system failure can occur.
And humans were not the only beings impacted. According to an article published in The Atlantic in July 2021, billions of mussels, clams, oysters, barnacles, sea stars and other intertidal species also died. A number of land-based species also fared badly, buckling in the sweltering and suffocating air, creating a dystopic tale of “desperate and dying wildlife.”
To put it plainly: the physiological stress of extreme heat on living organisms is life threatening — in particular for human beings: baking to death is a real possibility if you do not have access to cooling systems, or if you are one of the millions of people who live in parts of the world where climate change has increased your chances of exposure to extreme heat and comprehensive adaptation strategies have yet to be developed.
Our bodies are not meant to work this hard under these kinds of conditions — and neither is the planet.
A Profound Imbalance of Power
So how did we arrive here? A rapid attribution analysis of the heat dome conducted by a global team of scientists revealed that the occurrence of this kind of heat wave was virtually impossible without human-caused climate change. Their results came with a strong warning: “our rapidly warming climate is bringing us into uncharted territory that has significant consequences for health, well-being and livelihoods. Adaptation and mitigation are urgently needed to prepare societies for a very different future.” The situation is only expected to get more dire — three billion people could live in places as hot as the Sahara by 2070 unless we address climate change with radical action and address it now.
The Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, released in August 2021, mirrors a similarly grave picture of our current climate reality and forecast of what lies ahead. In a bold, oppositional move against national governments who have edited the findings of such assessments in the past, a group of scientists leaked the third part of the report which reveals, in unequivocal terms, how fossil fuel industries propped up by state governments are some of the largest contributors to our current environmental condition and what needs to be done to shift course.
The report reminds us that human influence has warmed the climate at a rate that is unprecedented in at least the last 2000 years with a near-linear relationship between cumulative anthropogenic CO2 emissions and the global warming they cause. This means that we are no longer waiting for the arrival of climate change — it is here. It lives in the stifling hot air we breathe during unanticipated heat waves. It is the reason droughts are becoming more severe and at the same time flooding is driving millions of peoples’ lives into chaos, precariousness, and displacement. It explains why Arctic ice has reached its lowest levels since at least 1850. Ocean acidification exists because of it. And it is the driver behind environmental conditions that are expected to produce 200 million climate migrants over the next 30 years. We do not need more evidence. The science could not be more clear.
Human influence has warmed the climate at a rate that is unprecedented in at least the last 2000 years.
The answer to how we ended up here, however, cannot be collapsed into a homogenized “all of us are to blame” scenario that does little to differentiate how countries like the United States and other western nations have produced the vast majority of the carbon emissions that have led to this point of immense and disastrous planetary change. The US has contributed more to the problem of excess carbon dioxide than any other country on the planet, with the largest carbon footprints made by wealthy communities — the higher the household income, the greater the emissions. In fact, a Scientific American article explains that the United States, with less than 5 percent of the global population, uses about a quarter of the world’s fossil fuel resources — burning up nearly 23 percent of the coal, 25 percent of the oil, 27 percent of the aluminum and 19 percent of the copper.
A recent Oxfam report, Confronting Carbon Inequality, provides staggering revelations about the way correlations between wealth and carbon emissions extend out to the global context: the richest 1 percent on the planet are responsible for more than double the emissions of the poorest half of humanity, and the richest 10 percent in the world are accountable for over half of all emissions. Wealthy individuals and communities, though, are not the only source of dangerous and excessive carbon emissions — global corporations dedicated to the ongoing development and flourishing of fossil fuel energy infrastructure are also a major, if not the largest, part of the problem.
If we zoom in even further, it becomes apparent that the relationship among racial capitalism, colonialism and climate change lies at the center of a critical understanding of the Anthropocene given that colonialism and capitalism together laid the groundwork for the development of carbon intensive economies that have prioritized capitalist accumulation — in all of its destructive forms — at the expense of everything else. As Potawatomi philosopher Kyle Whyte explains, with respect to the specific experiences of Indigenous peoples on Turtle Island, “the colonial invasion that began centuries ago caused anthropogenic environmental changes that rapidly disrupted many Indigenous peoples, including deforestation, pollution, modification of hydrological cycles, and the amplification of soil-use and terraforming for particular types of farming, grazing, transportation, and residential, commercial and government infrastructure.”
These critiques are not new: Indigenous leaders throughout the world have been sounding the alarm about impending ecocide derived from the never-ending cycle of extraction and consumption for as long as settler colonies like the United States have been in existence. They have also reminded us that other kinds of worlds are possible, worlds that are built on care, reciprocity, interdependence and co-existence as opposed to structural violence, dispossession and domination.
Not surprisingly, then, a social, political and economic arrangement of our world that is anchored to colonialism and imperialism has resulted in massive disparities in terms of disproportionate impact — race, class and gender are deeply woven into the experience and violence of climate catastrophe. In the Global South, the crisis has been producing perilous and deadly climate-related events in numerous countries for over a decade, well preceding the notable arrival of the heat dome in the United States and Canada in the summer of 2021.
In Sudan, for example, temperatures are consistently rising, water is becoming more scarce and severe droughts are commonplace, producing major problems with soil fertility and agriculture. Southern Africa is warming at twice the global rate: 2019 alone saw 1200 climate related deaths. Bangladesh, often referred to as “ground zero for climate change” despite having contributed as little as 0.09 percent to global cumulative CO2 emissions, has experienced a major surge in flooding which has resulted in the destruction of millions of homes, created numerous obstacles in crop production, and caused an alarming escalation in food insecurity.
People all over the globe are living on the front lines of a planet-wide crisis that has been produced far outside the boundaries of their own communities. To make matters worse, climate researchers from the Global South face multiple challenges obtaining funding for their projects and getting their research in front of the global community of scientists — largely from Western states — who are driving the agenda of adaptation. COP26 was illustrative of this problem of access — given the uneven distribution of vaccines, many climate organizers and scientists from the Global South, as well as Indigenous leaders, were unable to attend the conference that had been heralded as the “last chance to save humanity.” Perhaps this was one of the reasons that COP26 was such a catastrophic failure. There is a profound power imbalance within the context of the climate crisis which sits alongside vital questions about social inequality and shared responsibility.
A Framework of Internationalism
In the face of such grim and devastating projections, sidestepping into the hopelessness trap seems like the easiest place to land, but millions of people across the globe do not have the luxury of retreat or denial — and if we consider the long game, none of us do. How do those of us who are determined to act on climate change think about what it means to actualize global solidarity and mass mobilization within the context of this historical moment where everything is at stake? What are some of the political guideposts that should lie at the heart of what it means to be a climate organizer?
One thing that immediately comes to mind is that our mobilizations around climate change and environmental justice must be guided by an internationalist framework that is both anti-colonial and anti-capitalist. A consistent focus on the ways that “here is deeply connected to there and there is deeply connected to here” necessitates that we never lose sight of the fact that the vast majority of people in the world who are staring down the devastation of climate change at this moment have not had a hand in producing it.
We can take our cue from youth climate organizers in this regard. In Philadelphia, as a case in point, activists with Youth Climate Strike have been mobilizing protests in the streets while operating with a direct line to internationalism — linking struggles for environmental justice in the neighborhoods in which they live with the devastation of the climate crisis in the Global South. Their organizing transcends geographical boundaries, demanding that those of us in the Global North open our eyes and act on our responsibility to communities locally and to the rest of the world for a climate catastrophe that is, in large part, made in the United States.
A framework of internationalism, however, must also include foregrounding a critical analysis of the ways that racial capitalism continues to wreak havoc on the planet. Indeed, countries like the US function as part of a much larger constellation of imperial projects that produce great suffering, initiate catastrophic death, and remake ecologies and modes of relationship in order to facilitate the movement of capital. The Zapatistas knew this in 1994 when they made their “First Declaration from the Lacandon Jungle.” The Standing Rock Sioux stood in opposition to this when they launched their epic battle against the Dakota Access Pipeline in 2016. And communities in Guyana are pushing back against this as they organize in response to the expansion of Exxon’s oil extraction which expects to send more than two billion metric tons of CO2 into the atmosphere.
A framework of internationalism must also include a critical analysis of the ways that racial capitalism continues to wreak havoc on the planet.
A related reason that an internationalist and anti-colonial framework is so vital in this moment of climate organizing is that imperialism goes hand in hand with environmental destruction. That is to say, imperial projects such as the United States’ 20-year colonial occupation of Afghanistan has not only left countless Afghan citizens in a situation of immense danger and precariousness since the reinstatement of the Taliban, but has also left the country in a state of environmental wreckage. This destruction is evident in rampant deforestation, which proliferated during the turbulence of such a long war, and a rise in toxic air pollutants that were released by US armed forces through trash burning — and other military activities — and are making Afghani people chronically ill because they increase the risk of cancer and other diseases. Defunct military bases also require environmental remediation before the land can be used for life giving instead of life taking purposes.
A recent report from Brown University’s The Cost of War Project confirms that the United States spends more on the military than any other country in the world — substantially more than the combined military spending of Russia and China. The use of military force requires a great deal of energy, and most of it in the form of fossil fuels. As a result of this monstrous commitment to militarization, the US war machine is one of the largest polluters on the planet with this cataclysmic damage extending out to the other colonial projects supported through US tax dollars.
The war-finance nexus ties the United States and Canada to Africa, to the Middle East, to South America, to Asia; in short, to all places where international finance capital moves. The billions of dollars that have gone to support the Israeli military, for example, has enabled immense environmental ruination in Palestine. Bombs and related lethal weaponry are intended to destroy, not to build. And the afterlife of such destruction continues to impact the air, land, water, plants, animals and people who have lived under conditions of war for years, even after a war ostensibly comes to an end or an occupying force ostensibly “withdraws.” This means that a robust climate justice movement must necessarily include demilitarization in order for an internationalist agenda of ecological justice and sustainability to be realized.
Multi-Racial and Anti-Colonial Feminist Coalition Building
In order to make internationalism happen in the spaces and places of climate organizing, however, coalitions must also be part of the answer. Those of us who are the most privileged have a responsibility to do the hard work of building multi-racial and anti-colonial feminist coalitions between different social movements collaborating across political and geographical borders — multi-issue coalitions that foster self-reflexivity and allow us to understand one another better, to decipher the ways that our worlds have become co-constituted through a series of lived experiences and historical material relations.
Racial capitalism, as it is fueled by colonial and imperial projects, works through all of us, it becomes entrenched in even the most seemingly benign social practices and ways of being, it shapes our collective and individual memories about who we are. In essence, it plays with what it means to be human — how we develop relationships to one another and the world around us, how we eat, breath and love — part of the labor we have to commit to doing has to do with understanding how this happens in order to identify the things that bind us together and determine how best to unify in a collective struggle to save the planet.
In this regard, a crucial aspect of the climate justice movement should involve creating platforms where people can engage in debates and dialogues about power and history in their everyday mobilizing efforts. Through these interactions, people can knit together their social positions and experiences of oppression, marginalization and resistance while being attentive to the specificities of particular struggles. This resonates with Afro-Caribbean scholar and activist Jacqui Alexander’s call for feminists of color to become “fluent in each other’s histories” and Black radical feminist Angela Davis’s plea to foster “unlikely coalitions.”
Multi-racial and anti-colonial feminist coalition building of this sort has the ability to speak loudly to a politics of interdependence; to become a powerful counter to political echo chambers. It allows us to set forth a challenge to (re)educate ourselves and confront, head on, blind spots about history and present and to explore how nationality and citizenship status, class, race, gender, sexuality, age, and ability, among other factors, produce social realities and lived experiences that are tied to one another but also very unequal. We can start to see linkages between social issues and communities all over the world that are often positioned as separate and removed from each other and prompt those in the Global North to adjust their organizing efforts, networking, and platform building in a manner that addresses these inequalities in practical ways to begin to shift power dynamics.
Wherever these coalitions come into being, Indigenous leaders must play a fundamental role given global histories of land dispossession and ongoing colonial occupations, and because they offer critical guidance and anti-colonial blueprints for how we can actively shape a decolonizing path moving forward.
Multi-racial and anti-colonial feminist coalition building has the ability to speak loudly to a politics of interdependence.
Put simply: in order to push our politics of solidarity further, we have to refuse the desire to isolate as well as the messiness and limitations of identity politics that will always seek to divide us instead of bringing us together. We need people who are pushing the boundaries of environmental movements to speak across divergent but shared colonial histories, contemporary forms of racial state violence and the ongoing devastation of settler colonialism, colonial gender violence and anti-Black racism in places like the United States. And we also need people who can identify the ways these forms of colonial violence exist as part of a larger imperial web that reaches far beyond national borders. African American composer and activist Bernice Reagan’s oft cited speech, “Coalition Politics: Turning the Century” offers counsel here about why this matters so much: we need coalitions because movements that exist in relation to one another are stronger for it. We need them to ensure survival.
Perhaps what we will gain from multi-racial and anti-colonial feminist coalitions, then, is an emerging architecture of decolonization and practice of solidarity that produces new political ecologies reflective of this historical moment. In turn, this holds the potential to illustrate points of alignment and intersection, thus enabling the identification of common political goals and paving the way for global unification across distinct social and historical geographies. States do their best to carry out projects of colonialism and imperialism, but the people are never conquered. As such, those of us persevering for a better world must also conduct our political organizing around climate change in a way that actively works to bring people together, addressing colonialism at home and abroad.
A Revolutionary Plan of Action
Finally, because organizing against climate change is a future-oriented project, it is one that demands and requires durable and deep relationships. This means that we need to commit to resurrecting the idea and practice of solidarity by pulling it back from the clutches of oversimplification and empty overuse. In the parlance of Palestinian writer Steven Salaita, solidarity requires ethical commitments to function and does not involve appropriation. It is performed in the interest of better human relationships and for a world that allows societies to be organized around justice rather than profit. This is the kind of solidarity we must seek to bring into existence.
We have to ask ourselves, then, to identify the processes and practices that will allow us to build real understanding while centering a common interest of survival that is informed by notions of reciprocity, empathy and humility, reminiscent of the Zapatista’s idea of “caminar preguntando” — asking questions while walking. We have to be able to see one another and to recognize the individual and collective struggles that taken together are threatening the continuation of life itself. We have to be willing to listen and receive a rigorous education and simultaneously be eager to teach, to share, to trust and to invest ourselves in a future that elevates mutual validation and recovers a sense of dignity through resistance. Philosopher Esme Murdock reminds of this (re)alignment so powerfully when she says, “[t]here is a whole, messy, and beautiful place waiting for us where we fuck up and make it right and fuck up and make it right by holding each other responsible in the strength and terror of becoming and making kin.”
A relationality of this type has the power to activate, it moves us towards political organizing and praxis because it reminds us that we are, in fact, capable of crafting relationships with our relatives, human and other-than-human, that are built on mutual respect and interconnection. But to do this, we have to be honest with ourselves about the culpabilities and responsibilities we carry and be open to altering our comprehension of the problems we are facing and in turn, be ready to shift our ideas of “solutions” that will be most effective in the context of a rapidly shrinking timeline. We have to both harness and give up some of our power.
Science alone will not save us, and neither will government policy, UN meetings or climate summits where we expect “world leaders” to stand up and unify around the changes that we so desperately need. We cannot ameliorate this problem by promoting better consumer choices that privilege individual behavioral change or by supporting corporations pedaling “sustainable products.” There is no magical technology that is going to allow things to return to “normal,” the green billionaires do not have the answers, and there is no fantasy island that we can swim to that will offer a climate reset.
We require a revolutionary plan of action that is generated by a global peoples’ movement and guided by a set of shared political commitments and ways of relating to one another that can withstand the immense uncertainty of this moment, a plan that is grounded in the dynamics of the here and now and committed to a just future liberated from the shackles of climate apocalypse. The road forward is not easy, but making the decision to step onto it is perhaps the thing that matters most in this moment because it signals an attachment to the idea that something else is possible, that we have not conceded or given up, that we are willing to keep trying. And in the end, our ability to stand together is one of the greatest weapons of hope and resistance we have.
A version of this article will be included in Jaskiran Dhillon’s latest book Notes on Becoming a Comrade: Solidarity, Relationality, and Future-Making, forthcoming in 2022 with Common Notions Press.
Photo by Markus Spiske on Unsplash.





