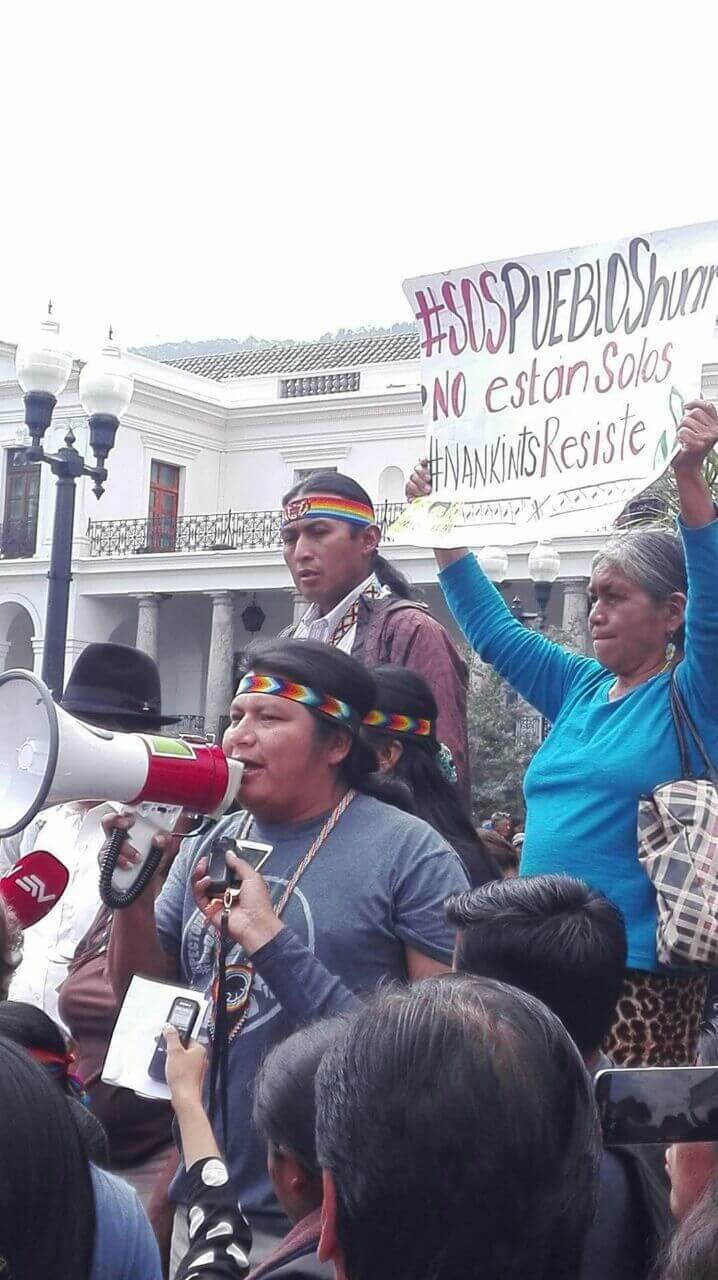By Blood and Fire: Mining and Militarization in the Ecuadorian Amazon
by Jake Ling / Intercontinental Cry
Before dawn on December 21, 2016, dozens of police raided the headquarters of the Shuar Federation (FISCH) in the Ecuadorian Amazon and arbitrarily detained its president, Agustin Wachapá. The indigenous leader was thrown to the ground and repeatedly stamped on and ridiculed beneath the boots of police in front of his wife. The police then razed the Shuar Federation’s office—turning over furniture and carrying away computers. According to the indigenous leader’s wife, her husband was taken away without any kind of explanation. An arrest warrant for Wachapá was never presented.
Agustin Wachapá has since been accused of publicly calling for the mobilization and violent resistance of the Shuar communities against state security forces in San Juan Bosco, where the indigenous community in Nankints was evicted and had their homes demolished against their will to make way for the Chinese Explorcobres S.A. (EXSA) open-cut copper mine. In the two months since the forced eviction, members of the communities surrounding Nankints have twice attempted to retake the land that was confiscated from them. On Dec. 14, the second attempt to storm the mine resulted in the death of a policeman and wounded seven other members of the state security forces.
The Ecuadorian government also declared a State of Emergency suspending basic rights such as freedom of assembly, freedom of movement, and due process under law, as well as granting the military the exceptional power to enter private residences and arbitrarily detain people without warrants or evidence.
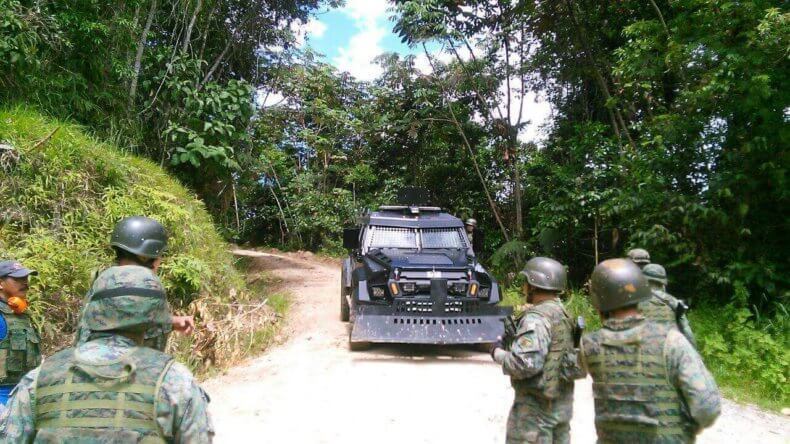
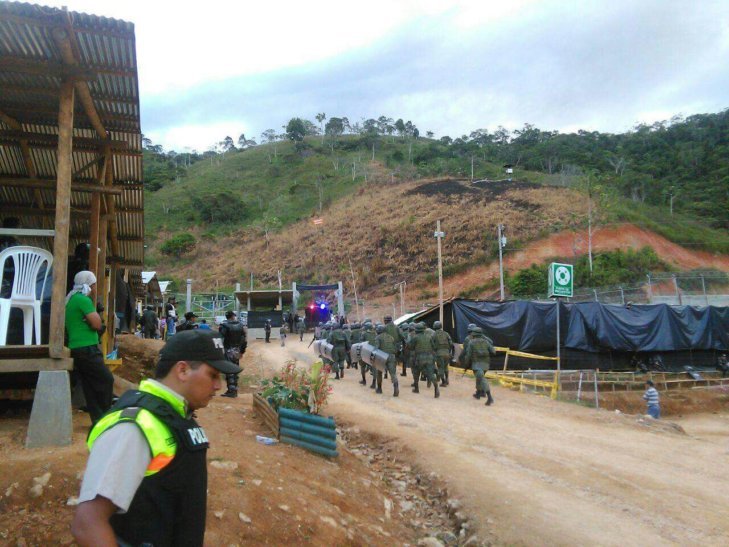
An overwhelming military presence was then deployed across the Amazonian province to bolster security around the Chinese mine and quell all dissent, prompting Domingo Ankuash, the historical leader of the Shuar to call upon the United Nations and other international human rights organizations to monitor the militarization of his people’s ancestral lands, in which he estimates 8,000 high-ranking members of the military—marine, air and land troops—as well as 4 war-tanks, surveillance drones, aerostatic balloons, mobile satellites, and helicopter gunships, have been deployed.
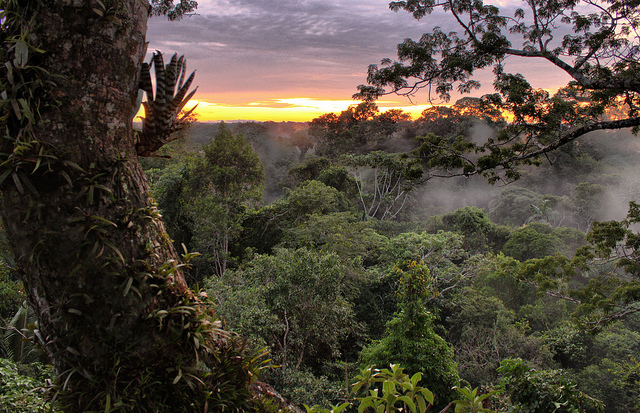
The region—known as the Cordillera of the Condor—is where the cloud forests on the eastern slopes of the Andes drops off into the vast rainforests of the Amazon basin. It contains some of the most richly biodiverse ecosystems in the world. Once operational, the Explorcobres S.A. (EXSA) mine—a joint venture of Tongling and China Railway Construction—will be the second largest copper mine on the planet. It will make an estimated $1.2bn in annual royalties for the Ecuadorian government. It will also consume 41,769 hectares of rainforest and rural agricultural land, much of it belonging to the Shuar Peoples.
Now, almost a month after his arbitrary detention, Agustin Wachupá is being kept in a maximum security prison on the other side of the country near the capital Quito, despite a call from Amnesty International to respect his judicial rights. The State of Emergency within Morona Santiago has been extended for another 30 days, and a media blackout has been imposed, forcing 15 community radio stations to broadcast the state-run Radio Publico.
Meanwhile, the government stepped up its manhunt for the “illegal armed group” involved in the violent incursions onto Explorcobres S.A., but community leaders are claiming a witch-hunt has begun in order to capture and detain people of influence such as teachers or leaders who belong to local committees opposed to the mine, as well as the heads of households whose homes were bulldozed in Nankints. All of these people have one thing in common: they are predominantly indigenous males of military age.
“The government of Rafael Correa is pushing the Armed Forces to play a role that we have never seen before, not even in times of dictatorship,” said Jorge Herrera, an indigenous leader of the Kichwa Peoples from the neighbouring Andes highlands. As president of the Confederation of Indigenous Nationalities of Ecuador (CONAIE), Herrera has expressed his increasing alarm at the military buildup inside of the Condor Cordillera on behalf of the 14 other indigenous nations of Ecuador that belong to the confederation. “The military is not defending the security of the population, but rather the transnational corporations that have purchased licenses [to exploit] large hectares of Ecuadorian territory as private property.”
From Dayuma to Sarayuku, President Correa’s government has deployed its overwhelming military might against rural and indigenous communities that oppose the nation’s booming mining industry before; but the current mobilization of state security forces inside Morona Santiago is unprecedented in terms of scale and scope in the country’s modern history. Not since 1995, during the Cenepa War between Ecuador and Peru, has their been such a massive build-up of armed forces along the Peruvian border on the western ridges of the Condor Cordillera, but back in 1995, in a complete reversal of roles, former president Sixto Duran commended the Shuar for working with the military to defend the Ecuadorian homeland from an invading foreign army.
“We will not yield a millimetre more”
The War of the Cenepa was the third military confrontation between Ecuador and Peru since 1941, and Ecuador had already suffered two embarrassing military defeats in both its previous battles with Peru along with the annexation of almost a third of the country’s former territory—hundreds of thousands of kilometres of oil and mineral rich land in the Amazon rainforest. Until its resolution in 1998, the border dispute between the two nation states had become the longest-running international armed conflict in the Western Hemisphere—and back in 1995, when the Amazon rainforest had turned into a theatre of modern warfare—this ancient people known as the Shuar were joining the Ecuadorian military en-masse.
A military anthem called “We will not yield a millimetre more” was being broadcast into television sets across the country to recruit men in their prime to join the Ecuadorian army and defend the nation’s borders against the Peruvians. The televised anthem featured clips of patriotic crowds waving Ecuadorian flags, coffins of the fallen being carried from army-helicopters, as well as soldiers in motorized canoes with mounted machine guns, scanning the thick vegetation on the river banks for Peruvian invaders. The speech of former-President Sixto Durán invokes patriotic fervour, uniting the Ecuadorian people to defend the motherland against a common enemy. The chorus, “Heroes of the Cenepa, we are all heroes” is chanted as an indigenous leader speaks to the Ecuadorian media, his traditional feather-headress proudly flashed across the screen.
The Shuar have always been a proud and fierce nation of warriors—long-feared for their practice of shrinking and mummifying the heads of enemies killed in combat in the days before contact—and they were respected and admired by their military comrades. In the Cenepa War, they were charged with transporting food and munitions over inhospitable jungle terrain, running reconnaissance missions around enemy camps and fighting on the Amazonian frontline—a mineral-rich basin by the river Cenepa within the mountainous Condor Cordillera. While the ancient tradition of head-hunting is no longer practiced by the Shuar, the feats on the Amazonian battlefield of an elite unit of Special Forces made up indigenous Shuar, and their ethnic cousins the Achuar, had captured the imagination of the Ecuadorian people. They were known as the Arútam Brigade, or the Iwia—the Demons of the Jungle—and they had become the pride of the nation. They were the Heroes of the Cenepa.
As night fell over the Condor Cordillera, legend goes that when possessed by the sacred spirit of Arútam, these indigenous commandos could enter the enemy camp with the stealth of the jaguar and the cunning of the anaconda, and then, disappear into the night as silently as they came without alerting the lookouts. When the Peruvian military woke at dawn the next day they discovered evidence of the incursion when members of their regiment would not move—they were still sleeping, lifeless without heads.
These mythical war-stories of the Arútam Brigade on the Amazonian battlefield not only canonized the Shuar as defenders of the motherland at a time when the Ecuadorian people’s confidence in their own military had been shaken by their two previous military defeats—they struck fear into the heart of the invading Peruvian army. The Shuar Peoples helped the Ecuadorian government and its military win the War of the Cenepa. Ecuador did not yield a millimeter more of its territory to its much larger neighbor Peru—and the Shuar were proud to have served for their military and for their country in a time of need.
Ecuador’s Presidential Elections and Backlash to the Mining Boom
The conflict in Nankints could not have come at a worse time for President Correa and his ruling party Alianza Pais. As the incumbent government closes ranks around Correa’s anointed successor—former Vice-President Lenin Moreno—in the upcoming February presidential elections, the Shuar uprising in the Condor Cordillera has again illuminated the dark underbelly of President Correa’s so-called socialist “Citizens Revolution”. The outgoing president has spent unprecedented sums of money on infrastructure projects and social programs on his ambitious socialist agenda, but a perfect storm of plummeting oil prices, economic mismanagement, and numerous corruption scandals, have almost bankrupted the country.
It took multiple billion-dollar loans from China to artificially prop up the Ecuadorian economy – and with it President Correa’s popularity. It will take generations for Ecuador to pay back this debt, and in the last few years the cash-strapped administration of President Correa has sold mining concessions to the Chinese that span a third of the country’s vast Amazon rainforest, as well as opened up large sections of pristine Andes wetlands and cloud-forests for mining in fragile ecosystems such as Intag and Quimsacocha.
These mines have become even more invasive and destructive to Ecuador’s richly biodiverse ecosystems and rural communities, exposing President Correa’s brand of socialism for what it is: militarized neoliberalism where anyone who is unfortunate enough to live above an oil or mineral deposit is stripped of their rights at the point of a gun.
As the leader of the Shuar federation Agustin Wachupa sits in prison, his thoughts have no doubt called upon the memory of Jose Isidro Tendetza Antun – another Shuar leader who fought against another open-cut copper mine along the Condor Cordillera. El Mirador was the first open-cut mine in the country and was widely viewed as establishing a precedent for the nation’s booming mining industry. For years, Tendetza had organized community opposition to the mine, protesting the contamination of the region’s rivers as well as the eviction of rural and indigenous people who lived on the lands now being consumed by El Mirador.
For his opposition against the mine, the late Shuar leader received constant harassment and death threats against him—including in 2012, when his house and crops were set on fire by men his family claimed were employees of the Chinese mine. Tendetza filed a complaint with the Inter-American Commission on Human Rights. In 2014, as the Shuar leader prepared to leave for Lima, Peru, to give a speech at the 2014 Climate Change Conference, he went missing. After a tip-off, the son of Tendetza found his father in a grave marked “no name”. There were strangulation marks around his father’s throat, as well as broken bones and other signs of torture that marked the Shuar leaders body. His arms and legs were also trussed with a blue rope.
Tendetza was the third Shuar leader to be violently murdered for opposing the mining industry since Bosco Wisum in 2009 and Freddy Taish in 2013.
As is the case with many other large scale mining projects across Ecuador, a process of Free and Informed Prior Consent and Consultation was not carried out with the Shuar community over the exploration and exploitation of the minerals beneath the land in Nankints. This means Explorcobres S.A. (EXSA) is now in direct violation of Section 7 Article 57 of the Ecuadorian Constitution, as well as the rights enshrined in Articles 6 and 15.2 of Convention 169 of the ILO, and Article 19 of the U.N. Declaration of Rights of Indigenous Peoples.
“Our territory is not only Nankints,” the Shuar Peoples stated in a letter. “In fact, more than 38 percent of our territory has been concessioned to large-scale mining. All the riverbanks of the Zamora and Santiago basins have been concessioned to small-scale mining. A gigantic hydroelectric dam is about to be built. So our question is: where do they want us to live?”

“The invasion of oil and mining companies, now Chinese and Canadian and others, are accomplices with this regime and their military police and followers,” said Domingo Ankuash, the historic leader of the Shuar. “The constitution, conventions and international declarations of human rights as well as the United Nations are worthless with no coercive power to stop this aggression. The Shuar Peoples are suffering at this time.”