by DGR News Service | Sep 2, 2022 | NEWS
Editor’s note: Activists and environmentalists in the Philippines take extreme risks by speaking out to protect land and water. The Philippines has consistently been ranked as the most dangerous country in the world for environmental defenders. This story includes reference to 68-year-old environmental defender Daisy Macapanpan, who was arrested on what appear to be trumped-up charges for resisting the Ahunan pumped hydroelectric dam. This repression is merely the beginning.
Deep Green Resistance has collaborated with grassroots activists in the Philippines for many years. Some of our allies are involved in this fight, and are raising funds to print educational materials, hold events, and support community activism against the Ahunan hydro project by providing expertise, assisting in connections with lawyers, help getting international media coverage, and more. You can donate to these community organizers via PayPal to this email address.  This story has not previously been reported in the international press.
This story has not previously been reported in the international press.
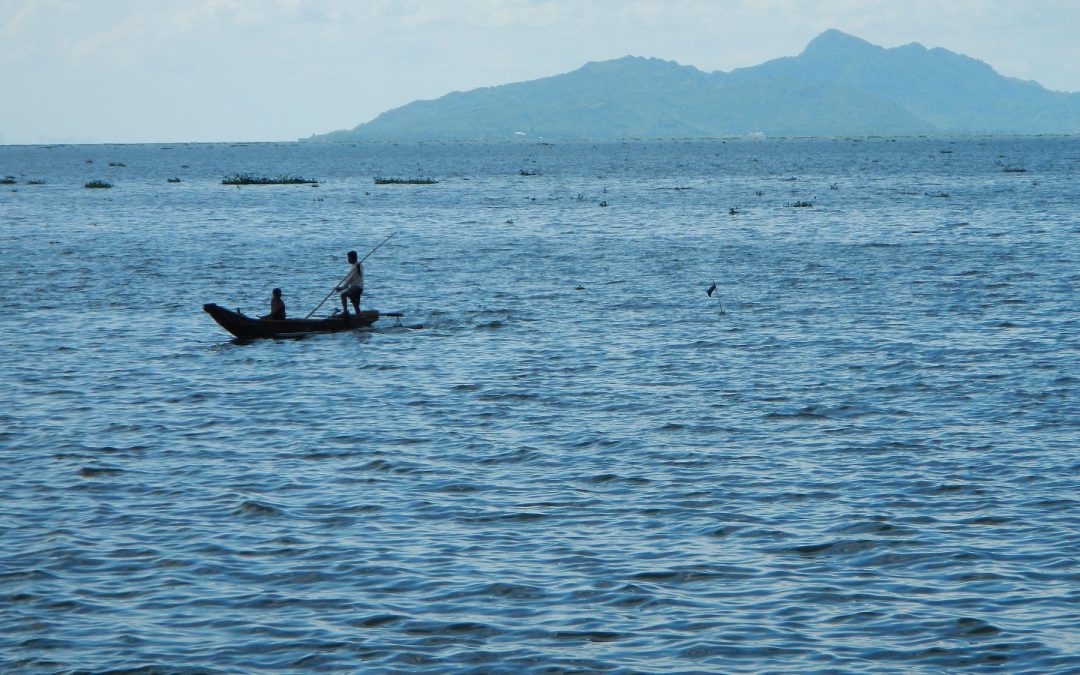
MANILA — Casino billionaire Enrique Razon, one of the richest men in the Philippines, is planning a $1.1 billion hydropower dam which threatens Laguna De Bay, the largest lake in the nation and one of the largest in Southeast Asia, as well as the community of Pakil and rainforests on the flanks of the Sierra Madre mountains on the lake’s east bank.
Prime Infrastructure Capital corporation’s Ahunan Pumped-Storage Hydropower Project would destroy nearly 300 hectares of rainforest, leach toxic chemicals into Laguna De Bay, and could jeopardize the water supply for more than 20,000 residents of the area.
Local residents fear that the project could worsen typhoon flooding and lead to landslides, will destroy natural pools that are used in religious practices, and that the region’s frequent earthquakes could damage the dam and reservoir — which is planned to be built on Mt. Inumpong which rises above their community and that is riven by three major fault lines — leading to catastrophic failure.
Despite widespread community opposition, the project is set to break ground in 2023. Community organizers allege that illegal drilling is already taking place and that the Philippe army is guarding the site.
On June 11th, 68-year-old environmental defender Daisy Macapanpan, one of the leaders of the community opposition, was arrested in her home for “rebellion” after delivering a speech against the project. allegedly by 40 police officers with no warrant. She was released on August 10th on bail. Illegal detentions and arrests of environmentalists are common in the Philippines, which has also been ranked as the deadliest country for environmental defenders.
On August 8th, following extensive pressure from the communities and allegations of illegal conduct, the Municipal Councils and Chieftains of four directly impacted communities revoked a previous “no objection” resolution in favor of the project that had been in place since September 2021.
On August 23rd, the Department of Energy and Natural Resources Environmental Management Bureau and the community of Pakil dispatched representatives to investigate allegations on ongoing illegal construction.

Community organizers gathered in Pakil in August 2022 to resist the Ahunan hydroelectric dam project.
Pumped-storage hydropower is unlike regular hydropower dams, which block a river’s flow to produce electricity. Instead, pumped hydro storage (PHS) is an energy storage method. It depends on finding (or engineering) a site where two sizable reservoirs or natural water bodies at significantly different elevations can be connected by pipes. To store energy, operators pump water from the lower to the upper reservoir, and to use the stored energy, let it run back down through electrical power generation turbines.
According to the book Bright Green Lies: How the Environmental Movement Lost Its Way and What we Can Do About It, pumped-storage hydropower dams kill fish, distribute invasive species, destroy riparian vegetation and harm wetlands, decrease water quality, block aquatic migration, and contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions. The book also states that “these facilities lead to more fossil fuels being burnt” because of inefficiencies in the process.
The Ahunan Pumped-Storage Hydropower Project would produce 1,400 MW of electricity at full flow, none of which would go to the local community. Prime Infrastructure Capital corporation and the Philippines Department of Energy call the project “clean energy.”
The fish who live in Laguna De Bay are an important source of food for the 8.4 million people living in the surrounding communities. A petition to halt the project has been signed by more than 6,000 of the 15,000 voting-age residents closest to the proposed project.
The World Commission on Dams estimates that at least 40 million to 80 million people have been displaced by dams.
Featured image by Ramon FVelasquez. This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license.

by DGR News Service | Jul 29, 2022 | Climate Change, NEWS
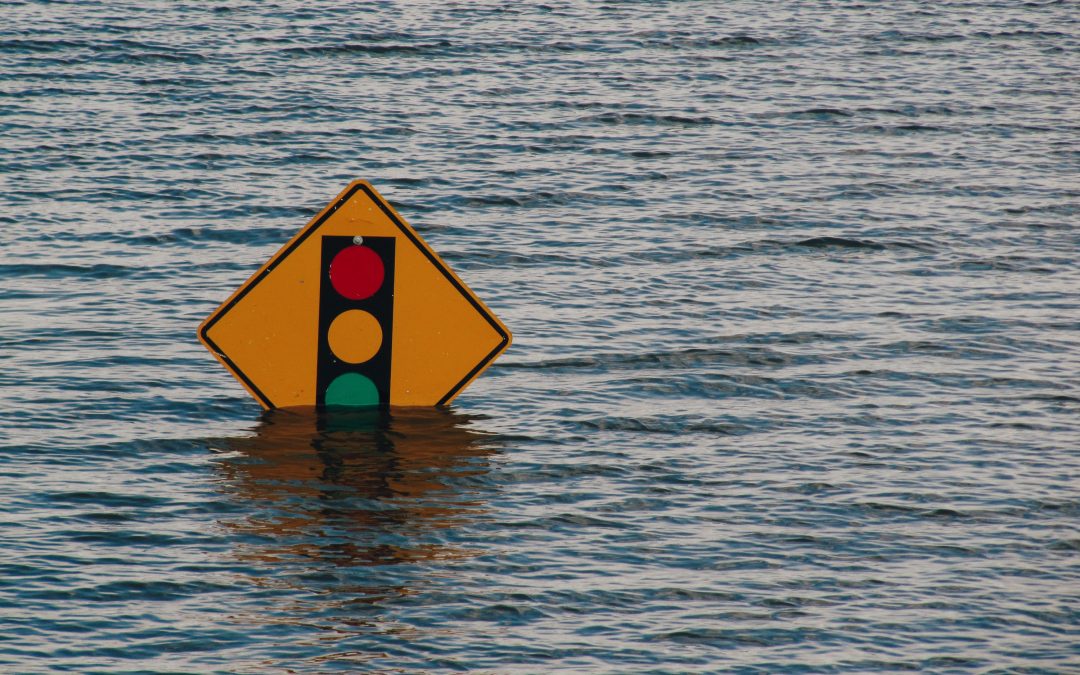
Editor’s note: As the climate crisis accelerates, extreme weather is causing crop failures and other disasters. Today’s article shares a grim projection: the world may see more than 1 billion climate refugees by 2050.
This problem is not new. Throughout the last 10,000 years, many civilizations have grown powerful, destroyed their land and water, and collapsed. Our situation today is only different because of scale. Modern civilization is global, and so the problems are worse.
Industrial civilization is a failed experiment. Wealthy consumer societies have been built by vast quantities of fossil energy and harvesting the natural world. Reversing this crisis will require a basic restructuring of our entire society. The economics of growth are obsolete. Destructive industries must be dismantled. Population must be stabilized and then reduced. Consumerism must be abandoned. Wild nature must be protected and allowed to expand and repair itself. And as centralized systems for food production and other necessities fail, new grassroots structures will need to be created.
“The media report on these crises as though they are all separate issues. They are not. They are inextricably entangled with each other and with the culture that causes them…
These problems are urgent, severe, and worsening… [they] are not hypothetical, projected, or “merely possible” like Y2K, asteroid impacts, nuclear war, or supervolcanoes. These crises are not “possible” or “impending”—they are well underway and will continue to worsen. The only uncertainty is how fast, and thus how long our window of action is.”
– From the book Deep Green Resistance: Strategy to Save the Planet
NB: This report is anthropocentric and focused purely on government aid programs which have limited ability to solve systemic issues.
From The Institute for Economics and Peace / September 9, 2020
Today marks the launch of the inaugural Ecological Threat Register (ETR), that measures the ecological threats countries are currently facing and provides projections to 2050. The report uniquely combines measures of resilience with the most comprehensive ecological data available, to shed light on the countries least likely to cope with extreme ecological shocks. The report is released by leading international think-tank the Institute for Economics & Peace (IEP), which produces indexes such as the Global Peace Index and Global Terrorism Index.
Key Results
- 19 countries with the highest number of ecological threats are among the world’s 40 least peaceful countries including Afghanistan, Syria, Iraq, Chad, India and Pakistan.
- Over one billion people live in 31 countries where the country’s resilience is unlikely to sufficiently withstand the impact of ecological events by 2050, contributing to mass population displacement.
- Sub-Saharan Africa, South Asia, the Middle East and North Africa are the regions facing the largest number of ecological threats.
- 3.5 billion people could suffer from food insecurity by 2050; which is an increase of 1.5 billion people from today.
- The lack of resilience in countries covered in the ETR will lead to worsening food insecurity and competition over resources, increasing civil unrest and mass displacement, exposing developed countries to increased influxes of refugees.The Ecological Threat Register analyses risk from population growth, water stress, food insecurity, droughts, floods, cyclones, rising temperatures and sea levels. Over the next 30 years, the report finds that 141 countries are exposed to at least one ecological threat by 2050. The 19 countries with the highest number of threats have a combined population of 2.1 billion people, which is around 25 per cent of the world’s total population.The ETR analyses the levels of societal resilience within countries to determine whether they have the necessary coping capacities to deal with future ecological shocks. The report finds that more than one billion people live in countries that are unlikely to have the ability to mitigate and adapt to new ecological threats, creating conditions for mass displacement by 2050. The country with the largest number of people at risk of mass displacements is Pakistan, followed by Ethiopia and Iran. Haiti faces the highest threat in Central America. In these countries, even small ecological threats and natural disasters could result in mass population displacement, affecting regional and global security.
Regions that have high resilience, such as Europe and North America, will not be immune from the wider impact of ecological threats, such as a significant number of refugees. The European refugee crisis in the wake of wars in Syria and Iraq in 2015 saw two million people flee to Europe and highlights the link between rapid population shifts with political turbulence and social unrest.
However, Europe, the US and other developed countries are facing fewer ecological threats and also have higher levels of resilience to deal with these risks. Developed countries which are facing no threats include Sweden, Norway, Ireland, and Iceland. In total there are 16 countries facing no threats.
Steve Killelea, Founder & Executive Chairman of the Institute for Economics and Peace, said:
“Ecological threats and climate change pose serious challenges to global peacefulness. Over the next 30 years lack of access to food and water will only increase without urgent global cooperation. In the absence of action civil unrest, riots and conflict will most likely increase. COVID-19 is already exposing gaps in the global food chain”.
Many of the countries most at risk from ecological threats are also predicted to experience significant population increases, such as Nigeria, Angola, Burkina Faso and Uganda. These countries already struggle to address ecological issues. They already suffer from resource scarcity, low levels of peacefulness and high poverty rates.
Steve Killelea, said:
“This will have huge social and political impacts, not just in the developing world, but also in the developed, as mass displacement will lead to larger refugee flows to the most developed countries. Ecological change is the next big global threat to our planet and people’s lives, and we must unlock the power of business and government action to build resilience for the places most at risk.“
Food Insecurity
The global demand for food is projected to increase by 50 per cent by 2050, meaning that without a substantial increase in supply, many more people will be at risk of hunger. Currently, more than two billion people globally face uncertain access to sufficient food. This number is expected to increase to 3.5 billion people by 2050 which is likely to affect global resilience.
The five most food insecure countries are Sierra Leone, Liberia, Niger, Malawi and Lesotho, where more than half of the population experience uncertainty in access to sufficient food to be healthy. COVID-19 has exacerbated levels of food insecurity and given rise to substantial price increases, highlighting potential volatility caused by future ecological change.
In high income countries, the prevalence of undernourishment is still high at 2.7 per cent, or one in 37 people do not have sufficient food to function normally. Undernourishment in developed countries is a byproduct of poverty; Colombia, Slovakia and Mexico have the highest undernourishment rates of OECD countries.
Water Stress
Over the past decade, the number of recorded water-related conflict and violent incidents increased by 270 per cent worldwide. Since 2000, most incidents have taken place in Yemen and Iraq, which highlights the interplay between extreme water stress, resilience and peacefulness, as they are among the least peaceful countries as measured by the Global Peace Index 2020.
Today, 2.6 billion people experience high or extreme water stress – by 2040, this will increase to 5.4 billion people. The majority of these countries are located in South Asia, Middle East, North Africa (MENA), South-Western Europe, and Asia Pacific. Some of the worst affected countries by
2040 will be Lebanon, Singapore, Israel and Iraq, while China and India are also likely to be impacted. Given the past increases in water-related conflict this is likely to drive further tension and reduce global resilience.
Natural Disasters
Changes in climate, especially the warming of global temperatures, increases the likelihood of weather-related natural disasters such as droughts, as well as increasing the intensity of storms and creating wetter monsoons. If natural disasters occur at the same rate seen in the last few decades, 1.2 billion people could be displaced globally by 2050. Asia Pacific has had the most deaths from natural disasters with over 581,000 recorded since 1990. Earthquakes have claimed the most lives in the region, with a death toll exceeding 319,000, followed by storms at 191,000.
Flooding has been the most common natural disaster since 1990, representing 42 per cent of recorded natural disasters. China’s largest event were the 2010 floods and landslides, which led to 15.2 million displaced people. Flooding is also the most common natural disaster in Europe, accounting for 35 per cent of recorded disasters in the region and is expected to rise.
19 countries included in the ETR are at risk of rising sea levels, where at least 10 per cent of each country’s population could be affected. This will have significant consequences for low-lying coastal areas in China, Bangladesh, India, Vietnam, Indonesia and Thailand over the next three decades – as well as cities with large populations like Alexandria in Egypt, the Hague in the Netherlands, and Osaka in Japan.
The Institute for Economics and Peace is an international and independent think tank dedicated to shifting the world’s focus to peace as a positive, achievable and tangible measure of human well-being and progress. It has offices in Sydney, Brussels, New York, The Hague, Mexico City and Harare.
Photo illustration of climate refugees by Kelly Sikkema on Unsplash.

by DGR News Service | Oct 12, 2021 | Education, Movement Building & Support, Strategy & Analysis
This article is from the blog buildingarevolutionarymovement.
This post looks at what is social change, causes of social change, what is historical change, and theories of social and historical change. This final section of the post includes something on Marxist theories of history.
I looked at theories of change at the social movement and institutional level in previous posts: part 1, part 2, part 3.
What is social change?
Social change is the changes to the social structure and social relationships of society. There is also cultural change. Social changes include changes in age distribution, birth rates, changes in the relationship between workers and employers when there is more union activity. Cultural changes include the invention and popularisation of new technology, new words added to a language, changing concepts of morality, new forms of music and art. They overlap and all important changes include both social and cultural changes. In sociology, ‘sociocultural change’ is used to describe changes of both forms. [1]
The main characteristics of social change include:
- social change is universal to all societies
- social change happen across a whole community or society, not small groups of individuals
- the speed of social change is not uniform within a society
- the speed of social change is different in each age or period, it is faster than in the past
- social change is an essential law of nature
- definite prediction of social change is not possible
- social change shows a chain-reaction sequence – on change leads to the next
- social change results from the interaction of several factors
- social changes generally result in modification or replacement [2]
Causes of social change
There are several causes of social change:
- Natural factors such as storms, earthquakes, floods, drought and disease
- geographical factors such as availability or national resources and levels of urbanisation
- demographic factors such as birth and death rate
- socio-economic factors such as levels of industrialisation, market capitalism and bureaucratisation
- cultural factors as describes in the section above
- science and technology factors
- conflict and competition factors such as war and popular movements for change
- political and legal power factors such as redistribution of wealth or corporate power
- ideas and ideology factors such as religious beliefs, political and economic ideology
- diffusion factors which is the rate that populations adopt new goods and services
- acculturation which is the modification of the culture of a group due to contact with a different culture [3]
What is historical change?
This is gradual and fast (rupture) transformation change in society. The transition from feudalism to capitalism was a historical, transformation change. So is a transition from capitalism to an alternative – socialism, communism.
Theories of social and historical change
There are four broad theories of social change: evolutionary, cyclical, functionalist, and conflict. And several other theories of historical change.
Evolutionary theories
These are based on the assumption that societies gradually change from simple or basic to more complex. There are three forms.
Linear or unilinear evolution describes the change to be progress to something better, more positive and beneficial to reach higher levels of civilisation. This theory was developed by the early theorists of human society in the 19th century. They believed that each society would pass through a “fixed and limited number of stages in a given sequence.”
Universal evolution is similar to the previous theory but does not view each society going through the same fixed stages of development.
Multilinear evolution has been developed by modern anthropologists. They see the process of social change as flexible, open-ended and not a universal law. They still see societies developing from small-scale to large-scale and complex. These theorists state that change takes place in many different ways and does not follow the same direction in every society. They do not believe that ‘change’ means ‘progress.’ [4]
Cyclical theory
This is also known as process theory and natural cycles. This describes how civilisations go through a process of birth, growth, maturity, decline and death in the same ways as living beings. Then the process is repeated with a new civilisation. [5]
Functionalist theories
These theories focus on social order and stability so some argue this limits their ability to explain social change. These theories ask what function different aspects of society play in maintaining social order. Examples include religion, education, economic institutions and the family. Some see society as at equilibrium and change results in a new equilibrium forming. Changes can come from other societies outside the society or from inside. [6]
Conflict theories
These can be seen as a response to the functionalist theories, that were seen to not have a place for change so could not explain social change. Conflict theorists argue that institutions and practices were maintained by powerful groups. Conflict theorists do not believe that societies evolve to a better place but that conflict is necessary for change and groups must struggle to ensure progress. Conflict theories are influenced by Karl Marx. [7]
Great man theory of history
This is a 19th-century idea that states that history is driven by great men or heroes, who are “highly influential and unique individuals who, due to their natural attributes, such as superior intellect, heroic courage, extraordinary leadership abilities or divine inspiration, have a decisive historical effect.”[8] Recently this concept has been ‘de-gendered’, replacing ‘Great Man’ with ‘Big Beasts’ [9]
Marxist theories of history
Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels wrote about and inspired several Marxist theories of historical and social change. See a previous post on Marx’s Marxism.
The materialist conception of history (or Historical materialism), Marx argued that the material conditions of a society’s mode of production (productive force and relations of production) that determine a society’s organisation and development and not ideas or consciousness. ‘Material conditions’ mean the ability for humans to collectively reproduce the necessities of life. [10]
Dialectical materialism can be understood as Marx’s framework for history:
“History develops dialectically, that is to say, by a succession of opposing theses and antitheses followed by their synthesis, which contains part of each original thesis. For Marx, this dialectical process would necessarily be a material one; developments in the substructure of economic life, such as those in production, the division of labor, and technology, all have enormous impact on the superstructure of the political, legal, social, cultural, psychological, and religious dimensions of human society.” [11]
Marx and Engels’ “stages of economic development, or modes of production, build on one another in succession, each brought about by a development in technology and social arrangement” They argued that societies pass through various stages with their own social-economic system – slavery, feudalism, capitalism, communism. Each stage develops because of conflict with the previous one. [12]
Economic determinism states the economic relationships such as being a business owner or worker, are the foundation on which political and societal arrangements in society are based. Societies are therefore divided into conflicting economic classes (class struggle) whose political power is determined by the makeup for the economic system. There is some controversy over Marx and Engel’s exact position on this concept. [13]
There is a Marxist gravediggers thesis (also known as gravediggers argument/dialectic or Marxist teleological theory of history). This is based on the quote from the Communist Manifesto “What the Bourgeoisie therefore produces, above all, are its own grave diggers.” That the internal contradictions of capitalism will result in its inevitable destruction. As capitalism continues the class antagonism between the bourgeoisie and the proletariat will increase and push more and more people into the proletariat. [14] There is some controversy about this theory among Marxists and this post does a good job arguing that the end of capitalism is not inevitable.
Technological theories
Technology refers to the use of knowledge to make tools and utilise natural resources. Changes in technology result in changes in social relations. For Marx, “the stage of technological development determines the mode of production and the relationships and the institutions that constitute the economic system. This set of relationships is in turn the chief determinant of the whole social order.” [15]
Multiple causation theory of history
This states that historical change is complex and likely due to multiple causes related to political, economic, social, cultural and environmental events, as well as the significant individuals. [16] Max Weber supported this perspective “historical events are a matter of the coming together of independent causal chains which have previously developed without connection or direct import for one another” [17]
World-systems theory
This is a large scale approach to world history and social change, with the focus of social analysis on the world-system over the nation-state. The ‘world-system’ refers to the inter-regional and international division of labour, which divides the world into ‘core countries’, ‘semi-periphery countries’ and ‘periphery countries’. Core countries focus on ‘higher skilled capital-intensive production’, with the rest of the world focusing on ‘low-skilled, labour-intensive production’ and extraction of raw materials. Immanuel Wallerstein’s World-systems theory describes the shift from feudalism to capitalism; and then during the modern era, the centre of the core has moved from the Netherlands in the 17th century, Britain in the 19th century and the US after World War I. [18]
Endnotes
- https://www.masscommunicationtalk.com/different-theories-of-social-change.html
- https://www.sociologydiscussion.com/sociology/theories-of-social-change-meaning-nature-and-processes/2364
- http://people.uncw.edu/pricej/teaching/socialchange/causes%20of%20social%20change.htm, https://ourfuture.org/20080514/why-change-happens-ten-theories, https://www.shareyouressays.com/knowledge/7-main-factors-which-affect-the-social-change-in-every-society/112456)
- https://www.masscommunicationtalk.com/different-theories-of-social-change.html, https://www.sociologydiscussion.com/sociology/theories-of-social-change-meaning-nature-and-processes/2364, https://www.yourarticlelibrary.com/sociology/top-5-theories-of-social-change-explained/35124, https://guide2socialwork.com/theories-of-social-change/, https://www.academia.edu/25227760/Theories_of_Social_Change, https://www.shareyouressays.com/knowledge/6-most-important-theories-of-social-change-2/112462, https://article1000.com/theories-social-change/
- https://www.masscommunicationtalk.com/different-theories-of-social-change.html, https://www.sociologydiscussion.com/sociology/theories-of-social-change-meaning-nature-and-processes/2364, https://science.jrank.org/pages/8918/Cycles-Twentieth-Century.html, https://www.yourarticlelibrary.com/sociology/top-5-theories-of-social-change-explained/35124, https://guide2socialwork.com/theories-of-social-change/, https://www.shareyouressays.com/knowledge/6-most-important-theories-of-social-change-2/112462, https://article1000.com/theories-social-change/
- https://www.masscommunicationtalk.com/different-theories-of-social-change.html, https://www.yourarticlelibrary.com/sociology/top-5-theories-of-social-change-explained/35124, https://guide2socialwork.com/theories-of-social-change/, https://www.shareyouressays.com/knowledge/6-most-important-theories-of-social-change-2/112462, https://article1000.com/theories-social-change/
- https://www.masscommunicationtalk.com/different-theories-of-social-change.html, https://www.yourarticlelibrary.com/sociology/top-5-theories-of-social-change-explained/35124, https://guide2socialwork.com/theories-of-social-change/, https://article1000.com/theories-social-change/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Great_man_theory
- https://www.historytoday.com/archive/head-head/there-still-value-%E2%80%98great-man%E2%80%99-history, https://www.andrewbernstein.net/2020/01/the-great-man-theory-of-history/, https://www.visiontemenos.com/blog/the-great-man-theory-of-1840-leadership-history, https://www.communicationtheory.org/great-man-theory/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Historical_materialism
- Dialectical Materialism and Economic Determinism: Freedom of the Will and the Interpretation of Behavior, Estelio Iglesias http://www.fau.edu/athenenoctua/pdfs/Estelio%20Iglesias.pdf
- Dialectical Materialism and Economic Determinism: Freedom of the Will and the Interpretation of Behavior
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Economic_determinism
- https://www.enotes.com/homework-help/explain-quote-what-bourgeoisie-therefore-produces-99615
- https://www.yourarticlelibrary.com/sociology/top-5-theories-of-social-change-explained/35124, https://www.yourarticlelibrary.com/sociology/top-5-theories-of-social-change-explained/35124, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/William_Fielding_Ogburn
- https://aeon.co/ideas/we-must-recognise-that-single-events-have-multiple-causes
- Perspectives in Sociology, E.C. Cuff, 2006, page 46
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/World-systems_theory#The_interpretation_of_world_history

by DGR News Service | Jan 9, 2021 | Climate Change
Facing The Truth
by Elisabeth Robson
“In order to maintain our way of living, we must tell lies to each other, and especially to ourselves.” — Derrick Jensen
On November 6, 2020, I allowed myself one breath out, a breath of relief that a despicable administration and its despicable leader have been voted out of office. With my next breath in, I reminded myself that the administration that will replace it will be just as despicable, only in different ways. Its leaders may be more humane—perhaps they will no longer separate children from their parents at the border, and perhaps they will offer sincere sympathies to the families of those who have died of COVID-19—but they will not usher in a voluntary transition to a more sane and sustainable way of living. They may not lie about their tax returns or the size of their inauguration crowd, but they will certainly lie about many other things. More dangerously, they will lie about those things while believing they are righteous, and in so doing will convince many others to believe they are righteous, too.
One lie the Biden-Harris administration is telling that I am most immediately concerned with is the lies that the words “clean energy” and “net zero” mean something real. This lie is rooted in a fundamental denial of physical reality.
Clean Energy and Net Zero
The first and primary goal of the Biden-Harris climate plan is to
“Ensure the U.S. achieves a 100% clean energy economy and reaches net-zero emissions no later than 2050.”
Most people will, at this point, be familiar with the term “clean energy”. This usually means renewables, including wind, solar, hydropower, hydrogen, geothermal, and nuclear. These technologies are considered “clean” because the generated energy does not emit CO2 at generation time.
However, many will be less familiar with the term “net zero”. It’s understandable why so many in climate change circles, including Joe Biden and the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), would rely on the concept of “net zero” given the decline in CO2 emissions required to meet the IPCC’s stated goals of keeping global warming to “well below +2C” if we actually wanted to get our emissions to zero:
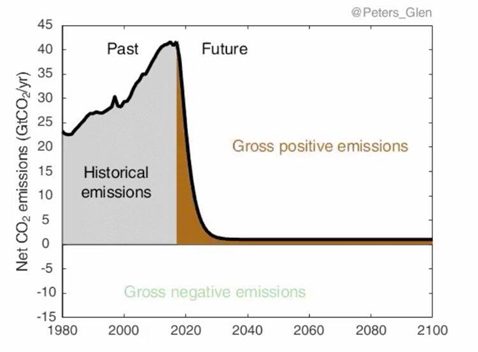
SOURCE: @Peters_Glen
The delusion of “clean energy” and “net zero” allows policy makers world wide to instead produce a graph that looks more like this:
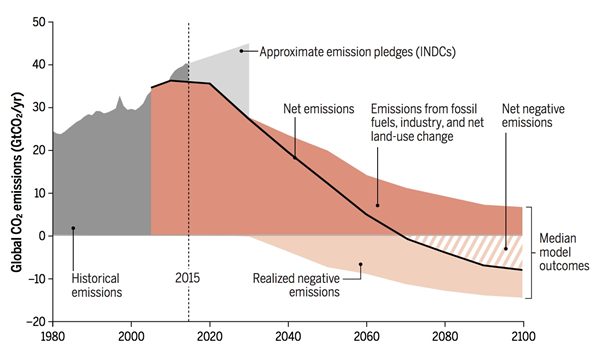
SOURCE: Science, Vol 354, Issue 6309 14 October, 2016
This second graph is a lot more reassuring than the first. It means that we can continue to emit CO2 as long as we count on something—technology? forests? soil?—to pull extra CO2 out of the atmosphere (called carbon dioxide removal, or CDR) so we can say our CO2 emissions are “net zero” instead of zero. As long as the amount of CO2 we continue to emit is less than or equal to the CO2 we are pulling out of the atmosphere at the same time, we’re good.
We imagine that instead of facing the cliff-like drop-off in CO2 emissions in graph 1, we can follow graph 2, by gradually replacing the electricity grid with renewables producing “clean energy”, replace all 1.2 billion cars in the world with EVs, somehow figure out how to make concrete without massive amounts of fossil fuels, invent a substitute for steel that doesn’t require massive amounts of fossil fuels, replace industrial agriculture with regenerative agriculture world wide while still feeding 8 billion people, and do all this at a slower pace than within the decade or two required to get to zero emissions to avoid climate catastrophe. And, if the CDR works well enough, perhaps we imagine that we can continue to burn small amounts of fossil fuels for the foreseeable future, putting CO2 into the atmosphere and pulling it out in equal measure.
Clean energy and net zero go hand in hand, and not just in the Biden-Harris climate plan. Indeed, net zero is required for a clean energy plan to work. To see why, think about what’s required for clean energy.
Wind and Solar
To build, install, and maintain wind and solar requires not just a whole lot of mining and refining of the materials (metals and minerals) to manufacture the component parts of wind turbines and solar panels; it also requires installing the turbines and the panels in giant farms, most often on public lands where plants and animals live until they are scraped away and killed for these farms. Installing the giant turbines and panels is a fairly energy intensive process. It also requires maintaining these farms for their lifespan, which is about 25-30 years, and then dismantling and disposing of the waste at the end of that lifespan (most often in landfills) and replacing them with new wind turbines and solar panels.
It also requires building massive energy storage plants, either from batteries, which require their own energy intensive resources to make, or in energy storage schemes like pumped hydro, which requires building dams (see below). It also requires building additional grid lines to the solar and wind farms and their associated energy storage, which requires vast amounts of copper, steel, and concrete. None of this is easy to do, and all of it currently requires a whole lot of minerals and metals, which must be mined out of the ground, and energy, which is usually in the form of fossil fuels. Hmmm. That means these clean energy solutions are still emitting a lot of CO2.
Dams
To build dams requires immense amounts of concrete, and concrete is still one of the world’s most energy-intensive substances to make. It requires large, heavy machinery, running on fossil fuels, and high heat, provided by fossil fuels. And the reservoirs behind the dams often become methane producers, and methane is a greenhouse gas with 20 times the atmosphere heating qualities of CO2. The water energy must be turned into electricity, which must be transported for use or storage, requiring grid lines. Hmmm. That means that this clean energy solution is still emitting greenhouse gases, both CO2 and methane. Oh, and dams kill rivers, but that doesn’t seem to matter to clean energy advocates.
Hydrogen
Hydrogen fuel is clean when burned (meaning it produces only water at burn time), but currently requires a lot of energy to make. It is usually made from natural gas (a fossil fuel), but sometimes biomass (i.e. plants and trees). Mining natural gas emits quite a bit of methane, and cutting trees and harvesting plants emits CO2. The energy required to convert natural gas or biomass to hydrogen fuel could come from renewable sources but as we’ve seen those renewable sources are not clean. Hmmm. That means this clean energy solution is still emitting greenhouse gases into the atmosphere.
Geothermal
Geothermal might be the least bad of these bad solutions, but geothermal still requires that we build infrastructure (from steel) and power plants (to convert steam heat into electricity) and grid infrastructure to get the electricity from the source to where the electricity is used. Hmmm. All of those steps require metals, minerals, concrete, and other resources, so it would seem this clean energy solution is still emitting greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, too.
Nuclear
Everyone already knows the main downside to nuclear energy: we’ve seen these downsides first hand at Fukushima and Chernobyl and Three Mile Island. Aside from the energy required to mine uranium, build nuclear power plants, and deal with the nuclear waste (all of which requires fossil fuels), the devastating long term impacts of nuclear waste on the natural environment mean that it is perhaps the epitome of delusion to consider nuclear energy clean in any way.
So, even if we were somehow to run our “clean energy economy” on electricity from renewables alone, we’d still be far from zero CO2 emissions. Which is why we need “net zero”. We need a way to offset the CO2 and other greenhouse gas emissions that will happen in the energy sector even if we were to somehow replace fossil fuels with renewables world wide. This accounting also does not include the emissions from other sectors producing greenhouse gas emissions, such as industrial agriculture, transportation, and industry (even if industry is run on renewables for its energy, large amounts of greenhouse gases are released during manufacturing from chemical reactions, as an example).
Negative Emissions Technologies
So what is the future something that we will rely on to pull CO2 from the air so we can get to net zero emissions? It’s a suite of technologies known as negative emissions technologies.
In a 2018 report on negative emissions technologies, the United Nations Framework on Climate Change Convention (UNFCCC, with 197 countries participating) includes the following technologies: reforestation and afforestation, land management, enhanced weathering, ocean fertilization, bioenergy with carbon capture and storage (BECCS), direct air capture and carbon storage (DACCS), and carbon capture and storage (CCS).
Nature-based NETs
Reforestation and afforestation means planting a whole lot of trees. It means reforesting the areas we’ve deforested, and it means planting trees in areas that were not previously forested. The thinking is that trees pull CO2 from the air as they grow. Of course, before industrial civilization, there were a whole lot more trees, and those trees were part of the normal carbon cycle of the Earth, pulling CO2 out of the air in balance with the amount of CO2 emitted by normal processes that are part of life and death on this planet. So to get more CO2 pulled from the atmosphere to offset the industrial emissions from fossil fuels and other man-made sources of greenhouse gases, we’d have to plant a whole lot more trees.
This at a time when deforestation continues apace for mining, development, and industrial agriculture, and at a time when population continues to grow and land is regularly cleared of forest in order to produce the vast quantities of food to feed that growing population. Unfortunately, many tree planting schemes concocted for carbon offsets tend to be mono-crops of trees, rather than forests, and so don’t contribute to increasing viable habitat for wildlife at the same time. In addition, if trees are planted in the wrong place, this can often do more harm than good. It is hard to argue against planting more trees (if done well, and in the right places), but given we continue to deforest more than reforest, it seems unlikely this solution is viable.
Increasing carbon storage in soil through land management:
including regenerative agriculture and biochar, could store up to 0.7 gigatons of carbon (GtC) a year from the atmosphere, according to the UNFCC, and perhaps more if the depth of carbon storage is increased significantly with deeper soils. Keep in mind, that the total GtC released into the atmosphere from fossil fuels is about 10 GtC a year, and that carbon capture in soil would require completely overhauling global industrial agriculture at a time when industrial agriculture is rapidly expanding to feed the world’s growing population.
Enhanced weathering
Enhanced weathering is a technique to increase the rate of CO2 absorption in slow natural mechanisms that remove CO2 from the air, such as rock weathering, by applying chemicals to rocks, or by spreading finely ground rock over large areas of land. This is a purely speculative NET since no studies have been done at scale on the process.
Ocean fertilization
Ocean fertilization is the process of adding fertilizer, typically iron, to the ocean to increase the uptake of CO2 by plankton algae. Only small tests have been done with ocean fertilization, including one rogue fisherman who dumped 100 tons of iron dust in the waters off Canada. As the UNFCCC states in its report, ocean fertilization is “associated with very high levels of uncertainty and ecological risks for relatively small sequestration potential.”
My conclusion is that manipulating nature to reduce atmospheric CO2 has limited potential at best, and the risk of damaging the natural ecology of the Earth at worst.
Technology NETs
That leaves technology. The technologies included in the UNFCCC report are carbon capture and storage (CCS), bioenergy with CCS, and direct air CCS. CCS is really just a catch all name for BECCS and DACCS, as well as the ecosystem manipulation techniques described above.
BECCS requires replacing the fossil fuels burned in power plants world wide with biomass fuels, and adding technology that can capture the CO2 emitted when burning the biomass. Estimates of the amount of land required to grow the biomass to replace electricity at current levels of demand are about twice the size of India. Needless to say this would be problematic not just for food production, but also the reforestation and afforestation plans mentioned above. Another major problem with BECCS is that capturing CO2 in power plants is still highly speculative, has been demonstrated in only a few power plants, and the captured CO2 is most often used for “enhanced oil recovery”—i.e. getting more oil out of the ground—rather than stored. As of 2012 there were 62,500 power plants operating around the world, and 18 of them can now capture carbon. I’ll leave you to do the math.
If we add CO2 capture to all existing, non-biomass burning power plants, this will reduce the CO2 emitted from fossil fuels at burn time, but will do nothing to stop the destructive mining to get the fossil fuels from the ground. Existing coal power plants that have been converted to biomass typically burn wood pellets, some of which come from forests cut down to provide that wood, which seems counterproductive given the first NET discussed above, requiring that we plant more trees, not cut more of them down. In addition, it takes more wood to produce the same energy as you’d get from burning coal, so more CO2 is emitted, and because of the long lag time in tree regrowth and associated carbon sequestration, it quickly becomes clear that burning biomass will add more CO2 to the atmosphere during the critical near-term time period we need to be rapidly decarbonizing.
This is a well-known loophole in CO2 accounting schemes, and yet biomass burning has been enthusiastically embraced by power plants as an easy way to reuse current technology without having to account for the CO2 emitted.
DACCS is another speculative technology that uses giant fans to bring air into reactors made with plastic and potassium hydroxide to bind with CO2 and remove it from the air.
The CO2 is then purified and processed with “chemicals” (I’m not sure which chemicals, it seems to be proprietary information)—a process that requires energy, of course—and the resulting pure CO2 can then be stored to keep it out of the atmosphere. However, to pay for the technology and energy required to capture CO2, rather than being stored, the captured CO2 is typically used for enhanced oil recovery, which would seem to make the entire process moot. Indeed, one of the most well known of the DACCS companies operating today, Carbon Engineering, partnered with Chevron in 2019 in order to use the captured CO2 to pump more oil and gas.
If the captured CO2 from both BECCS and DACCS is to be stored, which is necessary to prevent it from heating the atmosphere, the CO2 must be stored forever. So far the most promising technique for storing CO2 long-term is to mix it with water and inject it into basalt (volcanic) rock, where it reacts with the rock and remineralizes. This technique has been demonstrated in only a small number of experiments. If one imagines power plants and direct capture infrastructure capturing CO2 all around the world, this also begs the question of how to get the captured CO2 to locations where it can be stored into rock, remembering that the world currently emits about 40 GtCO2 a year, which is a huge amount of CO2. Would we use pipelines? And if so, how do we build the pipelines without a whole lot of steel and fossil fuels? Other techniques for storing CO2 are to put it in old salt mines or to replace oil extracted from the ground, but both of these storage techniques have limitations in a world with regular earthquakes, seepy rock, and human error.
In sum, none of the negative emissions technologies discussed in the UNFCCC report sound particularly hopeful, and even the UNFCCC admits in its own report that
“these technologies offer only limited realistic potential to remove carbon from the atmosphere.”
Policy Delusions
Despite this, the IPCC states in a post dated July 31, 2020, that
“global emissions need to be reduced to net-zero within the next few decades to avoid a dangerous increase in global temperatures”
and that
“the good news is we already have affordable, reliable technologies that can put the peak in global emissions behind us and start the drive down to net zero.”
They continue,
“Deployed quickly and on a major scale, the clean energy technologies we have at our disposal right now can bring about the kind of decline in energy-related emissions that would put the world on track for our longer-term climate goals.”
Governments around the world, including the United States, look to the IPCC for guidance on making policy related to climate change and yet this guidance is clearly delusional.
The list of lies one must tell oneself in order to believe this rhetoric is long:
- renewable energy and associated technologies (e.g. electric vehicles) is “clean”;
- deploying renewable energy world wide in time to avoid climate catastrophe is possible or even desirable;
- mining and refining the metals and minerals required to build that renewable energy is an acceptable further destruction to the natural world at a time when scientists are telling us habitat loss and biodiversity loss and extinction are crises just as important as climate change;
- that it’s okay for us to target “net zero” emissions rather than zero emissions because we have faith we’ll have the technology we need to pull CO2 from the air,
- that we can deploy these technologies globally in time to prevent catastrophic climate change;
- and perhaps worst of all, that any of this can be called “environmental justice” for those most impacted—the land, rivers, lakes, plants, and human and non-human animals whose homes and lives are lost to mining, industry, and technology.
Nowhere does the Biden-Harris plan for the future make mention of de-growth, reducing industry or the military, or reducing consumption. Nowhere. In fact we see the opposite: the catch phrase for the Biden-Harris administration is “build back better”. Build back to what? The unsustainable lifestyle to which we have become accustomed? A life of jumping on planes to the nearest tourist destination, where we buy crap we don’t need and throw away six months later? A life of building more houses, more roads, and bigger and more productive corporations with the municipal and industrial waste that goes with that? A life with a military that is the worst polluter in the United States and requires a constant supply of fossil fuels, metals, and minerals mined from the ground? Biden claims he wants to “build prosperity”. Does he understand that true prosperity is created by healthy ecosystems, because without healthy, flourishing, fecund ecosystems, there is no life on Earth? We live in a world where eight people have more wealth that most of the rest of the world combined. How is that prosperity helping the natural world? How is that prosperity being used to stop the destruction? The answer is obvious: it isn’t.
These are just a few of the lies we must tell to each other, and especially ourselves, if we wish to go along quietly with the policies outlined in the Biden-Harris plan for the next four years.
However, if you cannot lie to yourself or your loved ones, speak up. Tell the truth. Face ecological reality. This is no time for delusion, unless we are ready to ignore the suffering around us and give up on this beautiful planet we call home.

![]() This story has not previously been reported in the international press.
This story has not previously been reported in the international press.