
by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Jan 30, 2018 | Colonialism & Conquest
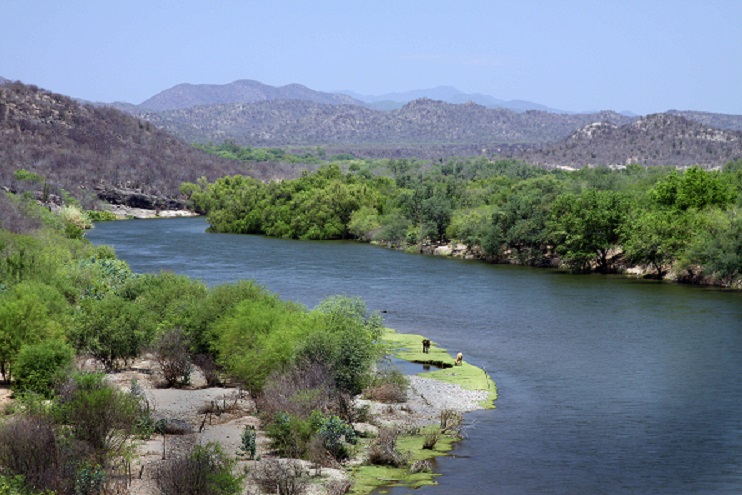
Featured image: The Aguaprieta pipeline crosses the Yaqui River (Río Yaqui), the water source for the Yaqui, an indigenous tribe residing in the Yaqui Valley in Sonora, Mexico. Photo: Tomas Castelazo (CC). As far as one Yaqui community is concerned, the pipeline will never be completed.
by Gabriella Rutherford / Intercontinental Cry
In 2013, Enrique Peña Nieto’s government deregulated Mexico’s energy sector, opening it up to foreign investors for the first time 75 years. In what he called an “historic opportunity”, the Mexican President proclaimed “This profound reform can lift the standards of living for all Mexicans.”
But not everyone stands to see their quality of life materially improve from the deregulated sector. Such is the case for the Yaquí Peoples in Sonora state, Mexico, whose territory is currently home to an 84-kilometre stretch of natural gas pipeline.
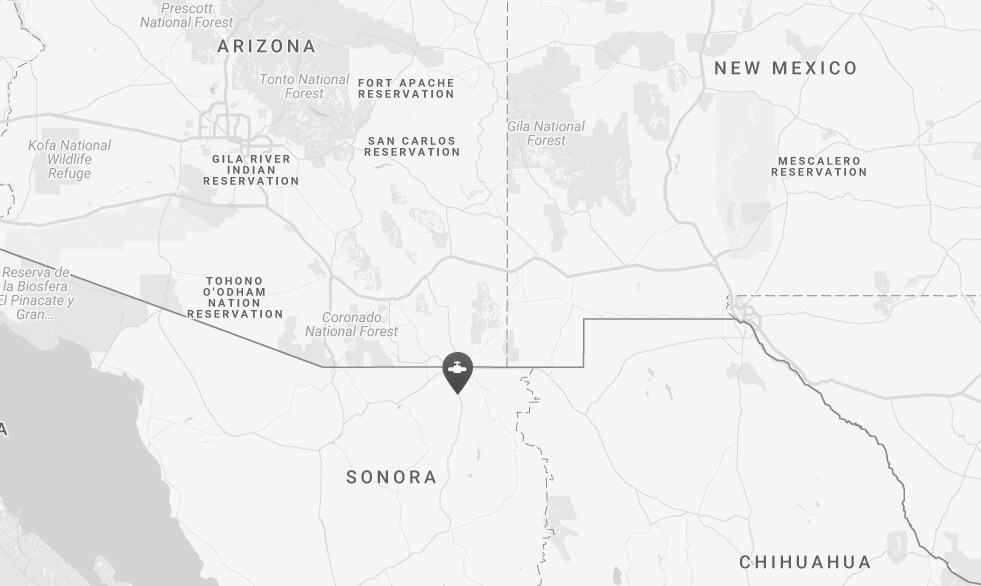
The Aguaprieta (Agua Prieta) pipeline starts out in Arizona and stretches down 833km to Agua Prieta, in the northeastern corner of the Mexican state of Sonora—cutting through Yaqui territory along the way.
Once completed, the pipeline would also cross Yaqui River (Río Yaqui), the Yaqui’s main source of water.
More than a few Yaqui are adamant that they will see no benefits from the project. “The gas pipeline doesn’t help us, it only benefits businessmen, factory owners, but not the Yaqui” said Francisca Vásquez Molina, a Yaquí from the Loma de Bacúm community.
As with Keystone XL and Dakota Access pipelines, the Aguaprieta project comes with its own share of risks.
In addition to the considerable environmental impact that stems from the pipeline’s construction, the high methane content of natural gas could bring on disaster. Rodrigo Gonzalez, natural resources and environmental impact expert, maintains that in the event of a gas explosion all human, plant and animal life within a one-kilometre radius surrounding the explosion would be lost. Anyone within the second kilometre would risk second and third-degree burns.
In the community of Loma de Bacúm, the gas pipeline is just 700 m from houses. In nearby Estación Oroz, it is 591m from a primary school.
Gonzalez has pointed out that another viable route for the pipeline was initially considered by the company that could have avoided Yaqui territory altogether. He suggests this route was ultimately rejected to save costs. “At the beginning of the project, two routes were mooted. That which didn’t cross indigenous territory cost 400 million pesos whilst that which puts Yaquí lives at risk costs 100 million pesos.”
IEnova, the company behind the pipeline, has repeatedly made assurances that all due safety procedures have been followed in construction and that the risk of accidents is minimal but this has not been enough to assuage the fear or anger of everyone opposing the gas pipeline.
In a public statement last year, the group Solidaridad Tribu Yaquí said, “This is a people that say no to a megaproject of death, dispossession and destruction[…]These rich men don’t care about the life of one, two, or three people, much less if they are indigenous… [they] don’t care if the Yaqui culture is exterminated. What is important to these rich men is to conclude the work and pocket all the profits to be brought about by the appropriation of the Yaqui territory.”
Not all Yaquí communities are united in rejecting the gas pipeline, however. Indeed, of the eight Yaquí communities consulted, only the Loma de Bacúm community refused to give their consent to the project. The other seven communities chose to accept the compensation offered. This decision has sadly resulted in tensions between Loma de Bacúm and the other communities. Things reached a critical point in October 2016 where one Yaquí member died and thirty injured in a confrontation involving different Yaquí communities.
Seemingly alone in their struggle, the Loma de Bacúm Yaquí have consistently resisted the Aguaprieta pipeline. In April 2016, they successfully fought to be granted a moratorium on its construction. When, in 2017, it became clear that IEnova, would carry on regardless and that neither federal nor state or authorities could be counted on for support, the Loma de Bacúm community resorted to more drastic measures. On May 21, community members removed cables which had been laid down in the preliminary stages of the gas pipeline construction. Then, after another court ruling that IEnova should remove all infrastructure within 24 hours fell on deaf ears, on August 22 the community went ahead and cut a 25-foot section out of the live gas pipeline, despite the grave risks they ran in doing so. As a result of the community’s actions in August, IEnova was forced to cut off the gas flow in the area and it has remained out of service ever since.
The community has been accused of sabotage and vandalism to IEnova property but the community maintains that IEnova, a company owned by US-based Sempra Energy, is trespassing on their land and holds them responsible for all damage brought on by the construction of a pipeline to which they never consented.
In a video shared on Facebook, one community member explained “If you want to have us killed, there’s no problem. We’re not scared of that… We’re not scared of this company nor this project…All that the Yaquí tribe is asking for is that the law is upheld and that federal and state government respect it. If you want to have us killed, go ahead there’s no problem but we’ll defend our land and that is our right.”
In September 2017, a judge once again found in favour of the Yaquí community ruling that IEnova did not have the right to enter Yaquí territory to repair the gas pipeline. Whether this latest ruling will carry more weight with both local and state authorities than the previous ones remains to be seen.
For the time-being, the stand-off looks set to continue. Loma de Bacúm has made it clear it will not back down until the pipeline is removed or rerouted. “If they want to build a pipeline. that’s fine”, said community spokesperson Guadalupe Flores, “but it will not pass through here.” At the same time, IEnova refuses to accept that one small community can curtail their plan to use Yaquí territory in order to provide electricity to the Comisión Federal de Electricidad (CFE), the country’s largest electric utility. Nor does it seem willing to brazenly defy the court’s latest ruling, at least for the time-being.
The struggle in Loma de Bacúm echoes loudly among all Indigenous Peoples who are grappling to make sure the resource sector cannot run roughshod over human rights and environmental concerns; but it is perhaps loudest in Mexico. Since the new energy policy went into effect, four other pipeline projects have been suspended. Looking ahead, a “shale offensive” is now set to begin later this year should the PRI retain power in July, leading to a proliferation of similar conflicts.

by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Jan 3, 2018 | Lobbying
Featured image: Yaqui community gathering Credit: Andrea Arzaba, CC BY–SA 4.0
by Steve Horn / DeSmog
Since Mexico privatized its oil and gas resources in 2013, border-crossing pipelines including those owned by Sempra Energy and TransCanada have come under intense scrutiny and legal challenges, particularly from Indigenous peoples.
Opening up the spigot for U.S. companies to sell oil and gas into Mexico was a top priority for the Obama State Department under Hillary Clinton.
Mexico is now facing its own Standing Rock-like moment as the Yaqui Tribe challenges Sempra Energy’s Agua Prieta pipeline between Arizona and the Mexican state of Senora. The Yaquis in the village of Loma de Bacum claim that the Mexican government has failed to consult with them adequately, as required by Mexican law.
Indigenous Consultations
Under Mexico’s new legal approach to energy, pipeline project permits require consultations with Indigenous peoples living along pipeline routes. (In addition, Mexico supported the adoption of the United Nations Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples, which includes the principle of “free, prior and informed consent” from Indigenous peoples on projects affecting them — something Canada currently is grappling with as well.)
It was a similar lack of indigenous consultation which the Standing Rock Sioux Tribe said was the impetus for lawsuits and the months-long uprising against the Dakota Access pipeline near the tribe’s reservation in Cannon Ball, North Dakota, in late 2016. Now, according to Bloomberg and Mexican reporter Gema Villela Valenzuela for the Spanish language publication Cimacnoticias, history is repeating itself in the village of Loma de Bacum in northwest Mexico.
Agua Prieta, slated to cross the Yaqui River, was given the OK by seven of eight Yaqui tribal communities. But the Yaquis based in Loma de Bacum have come out against the pipeline passing through their land, even going as far as chopping out a 25 foot section of pipe built across it.
“The Yaquis of Loma de Bacum say they were asked by community authorities in 2015 if they wanted a 9-mile tract of the pipeline running through their farmland — and said no. Construction went ahead anyway,” Bloomberg reported in a December 2017 story. “The project is now in a legal limbo. Ienova, the Sempra unit that operates the pipeline, is awaiting a judicial ruling that could allow them to go in and repair it — or require a costlier re-route.”
As the legal case plays out in the Supreme Court of Justice in Mexico, disagreements over the pipeline and its construction in Loma de Bacum have torn the community apart and even led to violence, according to Cimacnoticias.
Construction of the pipeline “has generated violence ranging from clashes between the community members themselves, to threats to Yaqui leaders and women of the same ethnic group, defenders of the Human Rights of indigenous peoples and of the land,” reported Cimacnoticias, according to a Spanish-to-English translation of its October 2016 story.
“They explained that there have been car fires and fights that have ended in homicide. Some women in the community have had to stay in places they consider safe, on the recommendation of the Yaquis authorities of the town of Bácum, because they have received threats after opposing signing the collective permit for the construction of the pipeline.”
TransCanada’s Troubles Cross Another Border
While best known for the Canada-to-U.S. Keystone XL pipeline and the years-long fight to build that proposed tar sands line, the Alberta-based TransCanada has also faced permitting issues in Mexico for its proposed U.S.-to-Mexico gas pipelines.
According to a December 2017 story published in Natural Gas Intelligence, TransCanada’s proposed Tuxpan-Tula pipeline is facing opposition from the indigenous Otomi community living in the Mexican state of Puebla. With Tuxpan-Tula, TransCanada hopes to send natural gas from Texas to Mexico via an underwater pipeline named the Sur de Texas-Tuxpan pipeline into the western part of the country.
The Otomi community recently won a successful bid in Mexican district court to stop construction of Tuxpan-Tula.
“At a recent hearing on an indoor soccer court at the foot of Cerro del Brujo, or Shaman’s Hill, in the southern Mexican state of Puebla, a district judge sided with an indigenous community and ordered construction” of the pipeline to halt, Natural Gas Intelligence reported. “[T]he court made the order in response to pleas from the local Otomi indigenous community, which claims that the construction would disturb sacred ground.”
Energy sector privatization in Mexico, decried by the country’s left-wing political parties and leading 2018 presidential contender Andrés Manuel López Obrador, has actually opened up the sort of legal opportunities that the Otomi have pursued in court.
“What is new in Mexico is the requirement that indigenous communities should be consulted,” Ramses Pech, CEO of the energy analysis group Caraiva y Asociados, told Natural Gas Intelligence. “That kind of consultation has long been a part of any project in the U.S. and other countries, but not so here. It was obviously needed in Mexico, too, but it has added to the complexities of the Mexican legal system in areas such as land and rights of way.”
In the U.S., the tribal consultation process is governed by the National Historic Preservation Act’s Section 106. That law gave the Standing Rock Sioux Tribe standing to sue U.S. government agencies, though ultimately unsuccessfully, for what the tribe alleged were violations which took place during the inter-agency permitting process.

by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Dec 28, 2017 | Direct Action
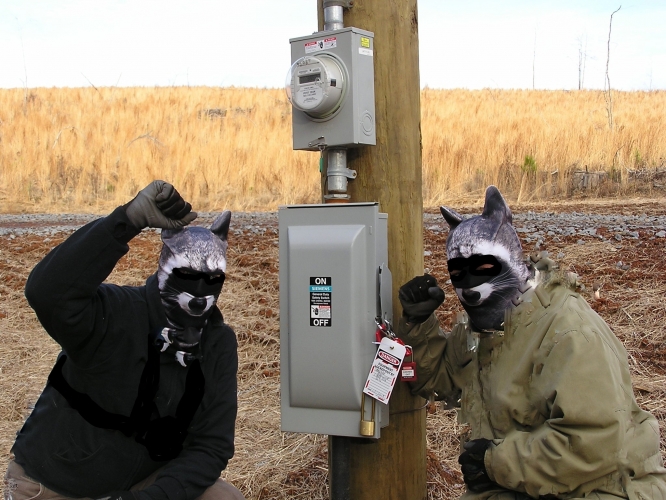
Featured image: Water Protectors from the Raccoon Rebellion-Arkansas Chapter conduct a safety lock-out/tag-out of a Main Operating Valve on the Diamond Pipeline as a Christmas gift to the Natural State.
Editor’s note: This news illustrates how simple, relatively safe, and cost-effective small actions can be. They simply put locks on a pipeline valve control box. The company only needs to send an employee out with bolt cutters to undo the action, but it’s a good example of how easy it is to access such equipment, and how easy it would be to cause more lasting effects.
by Jacques Rogiers / Indybay
On Christmas, with help and assistance from Santa Claus, his reindeer, and mischievous elves, some raccoons from the Arkansas Chapter of the national “Raccoon Rebellion” conducted a safety lockout tag-out on Diamond Pipeline Main Operating Valve (MOV) #2021 east of Jerusalem, Arkansas in accordance with common industrial safety procedures. The Lockout/Tagout devices were placed to prevent access and operation of this hazardous inter-state tool of the extractive, exploitative fossil fuel industry.
Using an eminent domain provision of the State Constitution – created in the last century, the Diamond Pipeline has been drilled, dug, and blasted across the Natural State. Chairman and CEO Greg “Scrooge” Armstrong of Plains-All American (PAA) used every loophole on the books to avoid common sense review, mediation, and mitigation while misrepresenting those that opposed the threat to their water as terrorists.14 Counties, 13 major rivers and creeks, 11 drinking water watersheds, 4 Arkansas NRC Priority Watersheds, 10 Critically Endangered Species, 2 Nuclear reactors as well as major portions of the Arkansas and Mississippi River, 5 Heritage crossing sites, and countless homes, farms and property owners are affected. Any moment now the imported steel from the lowest bidder could break and the ghost of Mayflower past will coil like a black evil spirit – with no emergency plan in place.
This pipeline is unsafe. The continued construction and operation of new fossil fuel infrastructure projects like this and so many others is the TRUE CRIME. We know this from years of extensive monitoring, study, and observation supported with hard evidence–photos, federal regulation, and personal observations by experts. The flora and fauna of the Natural State admire and support the efforts of so many organizations and people that have used every available means to have an open and meaningful dialogue and review. However, we can wait no longer.
Future interventions in the interest of common public safety must occur. In solidarity with the “Rabbit Ridge Resistance” we echo the demands they made before the line went into limited operation.
We demand that Governor Asa Hutchinson:
– Invoke executive authority to halt operation of the Diamond Pipeline for the protection of the people, lands, and wildlife of Arkansas.
– Conduct a complete review of all the information concerning pipeline safety and construction irregularities and hold public meeting in every county affected.
– Conduct complete review of use of law enforcement and security groups in the suppression of lawful 1st Amendment activities associated with protest and opposition to oil and gas industries.
– Invoke a complete moratorium on any OTHER use of eminent domain laws by private utility companies until effective procedures are in place to assess and provide public input to ANY use of those laws.
– Create a bonded, insurance fund to cover ANY potential damage caused by the leak, explosion, or faulty construction by any oil and gas infrastructure project.
–Raccoon Rebellion – Arkansas Chapter

by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Nov 20, 2017 | Obstruction & Occupation
by Makwa Initiative Line 3 Front Line Resistance
Early Wednesday morning water protectors from Camp Makwa stormed an Enbridge construction site, and delayed progress on the last unfinished Wisconsin segment of their proposed line 3 pipeline project. One individual from the Diné Nation descended into the muddy trench, climbed onto the pipe, and locked himself to welding equipment. A Leech Lake Tribal member then climbed atop an excavator and attached himself to a hydraulic arm. Construction was halted for approximately six hours, costing the company thousands of dollars, as the individuals put their bodies on the line to protect the water and the futures of their children.
See the video here
Later in the day two more water protectors were arrested, while standing on the side of the public road. They were both tackled to the ground by Sergeant Kirchhoff of the Superior Police Department. For one of the arrests, when asked on what grounds he was acting, officer Kirchhoff cited a warrant that he could not produce. Later investigation found that the warrant he cited was unsigned and improperly filed. Last Week Sergeant Kirchhoff received media attention for tackling a woman to the ground without warning at a similar protest. The woman’s charges were later dropped.
The Enbridge Line 3 Replacement Project is estimated to carry almost one million barrels of tar sands oil from Alberta, Canada to Superior, Wisconsin; Enbridge has received approval in Wisconsin, but has not received approval in Minnesota, which would be the largest segment of the proposed project. The non-violent direct action came after a week of evidentiary hearings in Minnesota, where Enbridge revealed that it had already paid for 100% of the pipe for the project. The same day as the action it was discovered that before her time in public office Judge Ann C O’Reilly, the individual in charge of holding public hearings on the Line 3 Project, worked for a firm that represented oil companies on multiple occasions.
One water protector stated “Enbridge doesn’t have their permits for Minnesota and they have already started chopping trees down for their easement and filling its pipe storage yards. We went to the public hearings and found them full to the brim with Enbridge employees who were paid to be there. We fought again and again just to have 3 minutes to speak. Now we watch as truck after truck come into our communities carrying pipes and out of state pipeline workers. We made our comments, but they didn’t listen. The project is already bringing violence to our land and our women and children. We know that with these man camps comes increased levels of drugs, rape, and missing and murdered indigenous women. Enbridge will not take no for an answer so we have to stop them. We want to make clear in no uncertain terms, Enbridge is not welcome in Minnesota.”
Donate to Camp Makwa-
Camp Supplies: youcaring.com/makwacampsupplies
Legal Fund: youcaring.com/makwalegal

by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Oct 24, 2017 | Lobbying
Washington, D.C.– Two and half years after asking the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) to reverse its decision to permit construction of the “Algonquin” Pipeline Expansion, residents are finally getting their day in court. Ellen Weininger from Westchester County, New York made the trip to DC Circuit Court for oral arguments Thursday. “From its inception Spectra’s massive Algonquin pipeline expansion violated federal law to avoid a full review of its cumulative impacts. While the courts finally hear oral arguments on the case today in D.C., tens of millions of people in New York and across New England, living and working in the pipeline’s path, continue to remain in harm’s way.”
FERC approved the first phase of Spectra Energy’s massive pipeline expansion in March of 2015. The project, dubbed the “Algonquin” Incremental Market Expansion (AIM) was just the first of a three part expansion designed to increase the volume of fracked gas carried by the “Algonquin” system to facilitate export of ‘natural’ gas overseas. From April of 2015 until January 2016 a “Tolling Order” issued by FERC blocked residents from proceeding with legal action to challenge the approval. Since then, residents from New York to Massachusetts have been waiting for their day in court. Today, lawyers representing grassroots organizations, including SAPE, the non-profit organization Riverkeeper, the City of Boston, and the Town of Dedham, MA will present oral arguments in the case.
In the intervening two and a half years much has happened. The AIM segment of the expansion was built despite being fraught with delays and violations of environmental law, plagued by whistleblower accusations of cutting corners to speed up construction. Spectra, parent company of “Algonquin” Transmission was purchased by Canadian oil and gas giant Enbridge, a partner in the Dakota Access Pipeline. The second segment of the expansion, dubbed Atlantic Bridge because it will serve as a “bridge” to carry fracked gas through New England to Canada, was approved by FERC, and just last week, despite missing numerous permits in Massachusetts, Spectra began work in New York and asked FERC to put certain portions into operation. The third segment of the pipeline expansion, Access Northeast, was halted due to an unconstitutional attempt to pass construction costs onto electric ratepayers in Massachusetts.
Despite all of this, residents and environmental groups persisted in their fight to stop Spectra on the grounds that the approval of the AIM project violated the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) and endangered millions living around Indian Point Nuclear Power Plant in Buchanan, NY. “Every day we live with the risk of this pipeline next to the elementary school, the nuclear power plant, the church, and before we can even get our day in court, FERC gives Spectra permission to pick up where they left off with AIM by just changing the project name to Atlantic Bridge. Same pipe, same place, same project,” said Courtney Williams, a resident of Peekskill, NY.
NEPA requires that FERC consider the cumulative environmental impacts of the projects it considers. Challengers contend that the AIM project was merely the first step in a massive expansion of the pipeline, arbitrarily broken into the parts to avoid a full accounting of the impacts it would have. Indeed marketing materials for the projects show they follow-on one another in time and location like pieces of a puzzle, clearly interconnected.
There is precedent for this kind of wrong-doing being overturned in the District Court. In 2015 Delaware Riverkeeper challenged FERC’s approval of the Northeast Upgrade project on the Tennessee Gas Pipeline on the grounds that it didn’t consider the cumulative environmental impacts of other expansion projects being considered at the time. In the case of the “Algonquin” expansion, while the tolling order was in place on the AIM project, Atlantic Bridge was under consideration and Access Northeast was in ‘pre-filing’ with FERC. “All three projects had FERC docket numbers simultaneously. FERC can’t pretend they didn’t know that Spectra intended to enlarge the entire length of the ‘Algonquin’ Pipeline,” said Williams, a scientist and member of SAPE from Peekskill.
The other major concern of New York residents involved in the legal challenge is the proximity of the pipeline to Indian Point Nuclear Power Plant. The new segment of the “Algonquin” Pipeline runs underneath the Indian Point property and passes only 105 feet from critical safety infrastructure at the plant. “The approval of the Spectra AIM project was based on a faulty analysis by the Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) of the co-location of the gas pipeline and the Indian Point Nuclear Power Plant. FERC ignored Richard Kuprewicz, the nationally recognized pipeline safety expert’s conclusion that the risk of a pipeline rupture could cause a catastrophic release of radiation,” said Susan Van Dolsen, a co-founder of SAPE. New York State Governor Andrew Cuomo agreed, ordering an as yet unreleased risk assessment be conducted by state agencies and asking FERC to halt construction. FERC refused, and the risk assessment, ordered in February 2016 has still not been released by the Governor.
Residents say they are not surprised that these critical legal and safety issues were overlooked. They cite extensive reporting by investigative journalist Itai Vardi at DeSmog Blog which has revealed numerous conflicts of interest, with FERC commissioners having vested financial interests in the pipeline companies or those hired to conduct environmental reviews.
Nancy Vann, whose Reynolds Hills community had property taken by “Algonquin” by eminent domain drove home the need for reforming the system that approved this project, “We are finally getting our day in court (actually just 20 minutes) after four long years of struggling to bring FERC’s attention to the unconscionable danger posed by this unnecessary project. We must not let our rights to a clean and safe environment be further eroded for the profits of a handful of fossil fuel company executives. We need elected officials who will stand up for us on every level of government to stop the slide toward nuclear catastrophe, irreversible climate change and planetary devastation. The world is watching us.”






