
by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Jan 8, 2017 | Lobbying, Strategy & Analysis
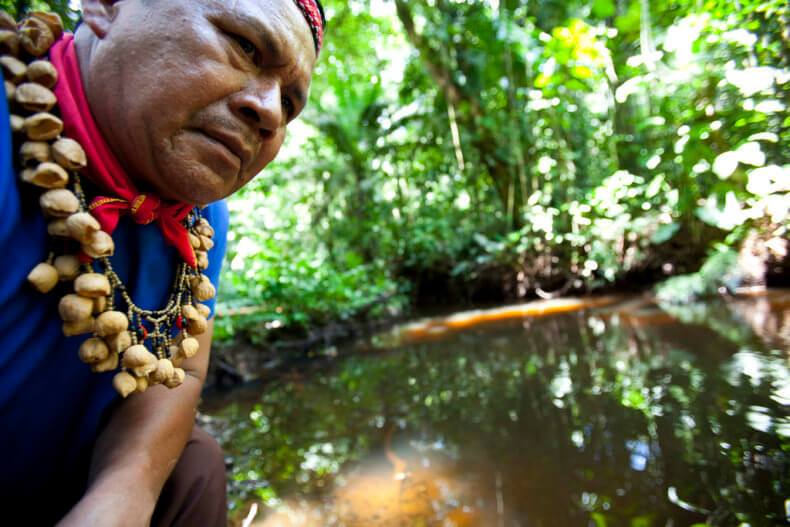
Featured image: Cofan Indigenous leader Emergildo Criollo looks over an oil contaminated river hear his home in northern Ecuador. Photo by Caroline Bennett / Rainforest Action Network (flickr). Some rights reserved.
by Kiana Herold / Intercontinental Cry
Indigenous battles to defend nature have taken to the streets, leading to powerful mobilizations like the gathering at Standing Rock. They have also taken to the courts, through the development of innovative legal ways of protecting nature. In Ecuador, Bolivia and New Zealand, indigenous activism has helped spur the creation of a novel legal phenomenon—the idea that nature itself can have rights.
The 2008 constitution of Ecuador was the first national constitution to establish rights of nature. In this legal paradigm shift, nature changed from being held as property to a rights-bearing entity.
Rights are typically given to actors who can claim them—humans—but they have expanded especially in recent years to non-human entities such as corporations, animals and the natural environment.
The notion that nature has rights is a huge conceptual advance in protecting the Earth. Prior to this framework, an environmental lawsuit could only be filed if a personal human injury was proven in connection to the environment. This can be quite difficult. Under Ecuadorian law, people can now sue on the ecosystem’s behalf, without it being connected to a direct human injury.
The Kichwa notion of “Sumak Kawsay” or “buen vivir” in Spanish translates roughly to good living in English. It expresses the idea of harmonious, balanced living among people and nature. The idea centers on living “well” rather than “better” and thus rejects the capitalist logic of increasing accumulation and material improvement. In that sense, this model provides an alternative to the model of development, by instead prioritizing living sustainably with Pachamama, the Andean goddess of mother earth. Nature is conceived as part of the social fabric of life, rather than a resource to be exploited or as a tool of production.
The Preamble of the Ecuadorian Constitution reads:
“We women and men, the sovereign people of Ecuador recognizing our age-old roots, wrought by women and men from various peoples, Celebrating nature, the Pacha Mama (Mother Earth), of which we are a part and which is vital to our existence…. Hereby decide to build a new form of public coexistence, in diversity and in harmony with nature, to achieve the good way of living, the sumac kawsay.”
The traditional Quechua relation to the natural world is firmly rooted in the Constitution. The interchangeable use of nature and Pacha Mama testifies to the indigenous influence on the Constitution.
The concept and the praxis
In the 1970s, Christopher Stone, an American environmental legal scholar, articulated the legal notion of the rights of nature in his widely read essay Should Trees Have Standing? Stone envisioned a new way of conceptualizing nature through law that broke with the existing paradigm of the commodification of nature, often established through law.
Property rights are a primary example of commodifying the natural world. When treated as property, nature incurs damages that often go unrecognized. Stone writes that an argument for “personifying” nature can best be considered from a welfare economics perspective. Under capitalist economic logic, many externalities that negatively impact the environment are not registered when calculating the cost of an action. Transforming nature legally from mere property to a rights-holding entity would force byproduct environmental effects of production to factor into cost calculations. Under this framework, nature would be better protected.
Incorporating rights of nature into a national constitution is a powerful paradigm shift, but may seem hypocritical and idealistic given states’ continuing dependence on extractive industries. In Ecuador, 14.8 percent of the GDP comes from profits from natural resources as of 2014.
Moreover, under Ecuadorian law, the rights of nature are subject to principles of so-called national development. Article 408 of the constitution stipulates that all natural resources are the property of the state, and that the state can decide to exploit them if deemed to be of national importance, as long as it “consults” the affected communities. However, there is no state obligation to abide to the result of the consultation to these communities– a gaping hole in full protection of these environments and the people living within them.
Nonetheless, Ecuador’s Constitution was a significant step in changing the legal paradigm of rights to one that is inclusive of nature.
Bolivia follows
Bolivia followed in Ecuador’s footsteps. Evo Morales, the first indigenous head of state in Latin America, was elected in 2005 and called for a constitutional reform that ultimately established rights to nature in 2009.
Again, indigenous philosophies were instrumental in the formulation of Bolivia’s new Constitution. The constitution’s preamble states that Bolivia is founded anew “with the strength of our Pachamama,” placing the indigenous understanding of nature as central to the very creation of the revised political state. Like in Ecuador, the Bolivian Constitution allows anyone to legally defend environmental rights.
Bolivia’s government soon instituted the Law of Mother Earth in 2010, later re-coining it as the Framework Law of Mother Earth and Integral Development to Live Well. The law lays out a number of rights for nature, such as the right to life and to exist, to pure water, clean air, to be free from toxic and radioactive pollution, a ban on genetic modification, and freedom from interference by mega-infrastructure and development projects that disturb the balance of ecosystems and local communities.
Part of the rationale behind the law is the hope of helping the environment through reducing causes of climate change, which is directly in Bolivia’s interests. Increasing temperatures in Bolivia pose problems to the nation’s farming sector and water supply.
Again, however, this legal concept does not match economic realities. The rights of nature are directly at odds with extractive industries that are intimately tied to Bolivia’s model of economic development. Despite legal frameworks defending the rights of nature, Bolivia’s profits from natural resources comprise 12.6 percent of the GDP as of 2014.
But there are alternatives to the Andean experience. Across the Pacific, New Zealand has also granted a legal status of personhood to specific rivers and forest, thus enabling the environment itself to have rights.
The New Zealand Take on Rights of Nature
Unlike Ecuador and Bolivia, New Zealand’s rights of nature are not embedded in its constitutional law, but rather protect specific natural entities. Native communities in New Zealand were instrumental in creating new legal frameworks that give legal personhood, and thus rights, to land and rivers.
New Zealand has bestowed legal personhood on the 821-square mile Te Urewara Park, and the Whanganui River, the nation’s third-largest river. This was part of the government’s reparation efforts for the historical injustice at the foundation of New Zealand’s state: colonial conquest of land from native peoples.
The Tuhoe tribe’s ancestral homeland is currently the Te Urewara Park. With the imposition of colonial governance, most of their land was taken from them without consultation, resulting in great spiritual and socio-economic losses. The land was designated a national park in 1954.
The Tuhoe tribe never signed the 1840 Treaty of Waitangi with the British Crown, which stripped the tribe of their sovereign right over their land. They have since contested the British assertion of sovereignty that undergirds the formation of the modern New Zealand state.
Their centuries-long struggle finally yielded results. As part of New Zealand’s reparation process towards Indigenous Peoples, the national government negotiated with the Tuhoe tribe regarding their historic land. In 2012 the Tuhoe tribe accepted the Crown’s offer of financial reparations, a historical account and apology and co-governance of Te Urewera lands. The national government renounced ownership of the land, giving the land its own personhood.
Under this framework, the land is now a legal entity in itself, owned neither by the government nor the Tuhoe tribe. The land is no longer property. It is its own untamed natural presence in and of itself, with, as per native understanding, its own life force and identity.
The land is now co-governed by the Tuhoe people and the New Zealand government.
The 2014 Te Urewara Act declares the park “a place of spiritual value.” The Act acknowledges that it is the sacred home of the Tuhoe people, integral to their “culture, language, customs and identity,” while also being of intrinsic value to all New Zealanders.
In a similar process of granting legal personhood, the local Maori tribe, the Iwi, helped the Whanganui River earn legal personhood status in 2014 after winning a long-fought court case.
This was part of a centuries-long struggle that the Whanganui tribes undertook to protect the river. Since the signing of the Treaty of Waitangi, the river has been subject to gravel extraction, water diversion for hydro-electric plans, and river bed works to better navigability, under protest from local tribes.
The Maori fought to protect the river through a series of court cases beginning in 1938, defending their claim to the management of the river as its rightful guardian. Throughout the court cases, negotiations were undergirded by the native saying “Ko au te awa, ko te awa ko au,” which translates to “I am the river and the river is me.” This reflects native philsophies of reciprocal and equal relations between people and nature.
New Zealand’s attorney general Chris Finlayson was quoted in the New York Times as acknowledging the Maori perspective as formative in the granting of rights to these natural entities, saying “In their worldview, ‘I am the river and the river is me,’” he said. “Their geographic region is part and parcel of who they are.”
Expanding Legal Horizons?
The legal concept of rights of nature signal the influence of Indigenous Peoples as political actors in state-making, fundamentally reimagining law and how the natural world is conceived. These ideas present a revolutionary rupture in the conventional anthropocentric understanding of sovereignty, and a realignment of how the natural world is valued. In fact, they could chart the path forward for a new understanding of mankind’s relation to the natural world, even if they operate within the legal structures that are not conducive to indigenous philosophies.
It is true that the rights of nature as they currently stand have deep limitations, particularly given the ongoing extraction of non-renewable natural resources in Ecuador and Bolivia. Problems of corruption, environmental inequality and economic dependence on extractive industries are major challenges to the full realization of the rights of nature.
Yet small acts can lead to lasting change. This shift in the way we relate to and legally protect nature, however small and plagued by obstacles, could be an incremental step toward a more sustainable relation to the planet that could allow us to preserve the earth for future generations.
by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Dec 25, 2016 | Colonialism & Conquest, Mining & Drilling
Featured image: Domingo Ankuash of the Shuar speaking at the Inter-American Commission in Washington DC. By Daniel Cima.
by Cultural Survival
Cultural Survival condemns the action of the Ecuadorian government in the raiding of the Shuar federation, FICSH (Federación Interprovincial de Centros Shuar), and the arbitrary detention of its president, Agustin Wachapa, on December 20, 2016.
The Shuar have been organizing to defend their ancestral lands from the development of a Chinese copper mine. Under the San Carlos Panantza copper project, the Ecuadorian government conceded 41 thousand hectares of land to the Chinese mining company ECSA for a period of 25 years. The project, currently in the exploration phase, is estimated to deliver around $1200 million USD in annual profits.
To make way for the mine, the Shuar community of Nankints was evicted in August 2016 without their Free, Prior and Informed Consent, in violation of Convention 169 of the International Labor Organization, the Ecuadorian constitution, and the UN Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples.
Since the evictions, violent clashes have broken out between individuals seeking to regain control of their homes and ancestral lands and military and police who are stationed to guard the property and employees of the mine. Now, the government has declared a “state of exception” in the province of Morona Santiago, and militarized the community of Nankints with hundreds of military personnel, tanks, and trucks, and helicopters. The state of exception strips Indigenous residents of the rights to freedom of movement, freedom of association, freedom of assembly and inviolability of the home, among others.
Cultural Survival joins COICA (Coordinadora de la Organizaciones Indígenas de la Cuenca Amazónica) in making the following demands:
- We urge for intervention by neutral third parties in order to find a dialogue that does not deepen and aggravate the existing conflict.
- We call for an immediate demilitarization of the community of Nankints, insuring the continued respect for human rights and collective rights of the Indigenous Shuar people, guaranteed by the Ecuadorian constitution in article 57. 20.
- We demand the immediate release of Shuar leader and human rights and environmental defender Agustin Wachapa, and for him to be treated in accordance with the UN Declaration on Human Rights Defenders.
- We condemn the Ministry of the Environment in Ecuador for their December 20th call to close the grassroots environmental organization Accion Ecologica.
Take Action: Defend Environmental Defenders! Stand with Acción Ecológica and the Shuar!
by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Dec 24, 2016 | Colonialism & Conquest
Featured image: Rosa Andrade was the last female speaker of the Resígaro language. © Alberto Chirif
by Survival International
The last female speaker of the Resígaro language has been murdered in Peru. Her body was found decapitated at her home in the Amazon rainforest.
Rosa Andrade, 67, lived with the Ocaina tribe. Her father was Ocaina and her mother Resígaro.
The Ocaina and Resígaro tribes were victims of the rubber boom, which began at the end of the nineteenth century. Tens of thousands of Indians were enslaved by rubber barons intent on extracting rubber in the Amazon. Many indigenous people died from sheer exhaustion, or were killed by violence and diseases like flu and measles to which they had no immunity.
The Resígaro tribe was eventually wiped out, and Rosa and her brother became the last remaining speakers of the language.
Rosa was also one of the last speakers of Ocaina and was regarded as a pillar of her community. She knew a wide repertoire of songs and stories in both languages and had recently been designated, by the government, to teach children Ocaina
Five thousand of the world’s six thousand languages are indigenous, and it is estimated that an indigenous language dies once every two weeks.
There are over a hundred uncontacted tribes worldwide, and their languages are the most endangered. Survival International is campaigning for the lands of uncontacted tribes to be protected, for where their rights are respected, they continue to thrive.
Rosa’s community suspects that an outsider, known for violent behavior, is responsible for the murder. However, the local prosecutor has declared that there is insufficient evidence to prosecute. The community is calling for a serious investigation to take place to find the culprit.
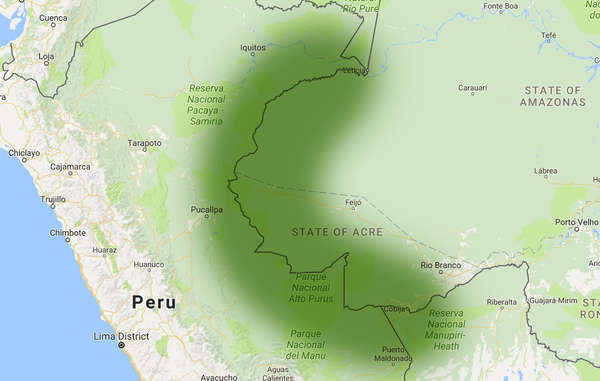
by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Dec 1, 2016 | Colonialism & Conquest
Featured image: The Amazon Uncontacted Frontier, a large area on the Peru-Brazil border that is home to the largest concentration of uncontacted tribes in the world. © Survival International
By Survival International
A new “death road” advocated by a notorious Italian priest is set to cut in two the land of several uncontacted tribes in the heartland of the Amazon Uncontacted Frontier.
The road is expected to be approved by Peru’s congress soon, and will run through 270 km of the Amazon’s most biodiverse and sensitive protected areas.
The project has been supported for years by Father Miguel Piovesan, a Catholic priest who has described the local tribal peoples as “prehistoric,” and slammed international NGOs for raising concerns about the plan.
The road was rejected by Peru’s Congress in 2012. Despite this, work continued illegally for many years, and now the project has been proposed again by Congressman Carlos Tubino.

Fr. Miguel Piovesan, the main backer of the Purus road, alongside former President Ollanta Humala.
© Anon
Uncontacted tribes are the most vulnerable peoples on the planet. There are estimated to be around 15 uncontacted peoples in Peru, many of them in the region where the road will be built.
Survival International has lodged a complaint with the United Nations, citing the catastrophic impact on the uncontacted Indians and urging the Peruvian government to veto the plan.
Of the 3-4,000 people in the area, around 80% are indigenous. Most of them are opposed to the road.
Emilio Montes, president of the indigenous organization FECONAPU, which is based in Puerto Esperanza said: “We flatly reject this road. We indigenous people won’t benefit from it, only the loggers, miners, oil companies and narcotraffickers. It threatens the lives of our isolated relatives, like the Mashco Piro. It will destroy our animals and plants. They should, instead, respect our ancestral territories. We’ve always lived here, and our children must carry on doing so. We need another type of development which looks after our resources sustainably: so that we can live properly, and secure our future.”
Survival’s Director Stephen Corry said: “If this road goes ahead, it will destroy the uncontacted tribes, and their “development” will be terminated for ever. Survival has fought roads in this part of Amazonia for decades. Who are they supposed to help? If Peru has any respect for fundamental human rights and the rule of law, it must stop these plans now.”

Uncontacted Mashco-Piro Indians on a riverbank near the Manú National Park. 2011.
© Jean-Paul Van Belle
Background
- The road will connect Puerto Esperanza to the Inter-Oceanic Highway, which runs through Peru and Brazil. The area is part of the Amazon Uncontacted Frontier, the region along the Peru-Brazil border with the highest concentration of uncontacted tribes in the world.
- Uncontacted peoples who could be wiped out if the road is built include the Mashco Piro, Chitonahua, Mastanahua and Sapanawa, who have all lived nomadically in the region for generations. Outsiders such as missionaries and loggers have forced several groups to make contact in recent years.
- Elsewhere in the Amazon, road “development” projects have allowed an influx of colonists to access remote areas and threaten the lives and lands of uncontacted peoples.
- Several indigenous organizations in Peru have made a statement rejecting the road.
- Fr. Piovesan has repeatedly denied the existence of uncontacted peoples. His parish newsletter stated that: “Isolation is not a natural wish. We can’t prove that isolated people exist. They are dreamt up by those who barely know indigenous people, or base their investigations on unproven theories.”
- Uncontacted Indians have clearly expressed their desire to remain uncontacted. The project cannot be carried out with their consent and will violate their right to determine their own futures.
We know very little about uncontacted tribes. But we do know there are more than a hundred around the world. And we know whole populations are being wiped out by genocidal violence from outsiders who steal their land and resources, and by diseases like flu and measles to which they have no resistance.
Uncontacted tribes are not backward and primitive relics of a remote past. They are our contemporaries and a vitally important part of humankind’s diversity. Where their rights are respected, they continue to thrive.
All uncontacted tribal peoples face catastrophe unless their land is protected. Survival International are doing everything we can to secure their land for them, and to give them the chance to determine their own futures.
by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Nov 17, 2016 | Colonialism & Conquest, Mining & Drilling
by Jen Moore / Canadian Centre for Policy Alternatives
Stories of bloody, degrading violence associated with Canadian mining operations abroad sporadically land on Canadian news pages. HudBay Minerals, Goldcorp, Barrick Gold, Nevsun and Tahoe Resources are some of the bigger corporate names associated with this activity. Sometimes our attention is held for a moment, sometimes at a stretch. It usually depends on what solidarity networks and under-resourced support groups can sustain in their attempts to raise the issues and amplify the voices of those affected by one of Canada’s most globalized industries. But even they only tell us part of the story, as Todd Gordon and Jeffery Webber make painfully clear in their new book, The Blood of Extraction: Canadian Imperialism in Latin America (Fernwood Publishing, November 2016).
“Rather than a series of isolated incidents carried out by a few bad apples,” they write, “the extraordinary violence and social injustice accompanying the activities of Canadian capital in Latin America are systemic features of Canadian imperialism in the twenty-first century.” While not completely focused on mining, The Blood of Extraction examines a considerable range of mining conflicts in Central America and the northern Andes. Together with a careful review of government documents obtained under access to information requests, Gorden and Webber manage to provide a clear account of Canadian foreign policy at work to “ensure the expansion and protection of Canadian capital at the expense of local populations.”
Fortunately, the book is careful, as it must be in a region rich with creative community resistance and social movement organizing, not to present people as mere victims. Rather, by providing important context to the political economy in each country studied, and illustrating the truly vigorous social organization that this destructive development model has awoken, the authors are able to demonstrate the “dialectic of expansion and resistance.” With care, they also show how Canadian tactics become differentiated to capitalize on relations with governing regimes considered friendly to Canadian interests or to try to contain changes taking place in countries where the model of “militarized neoliberalism” is in dispute.
The spectacular expansion of “Canadian interests” in Latin America
We are frequently told Canadian mining investment is necessary to improve living standards in other countries. Gordon and Webber take a moment to spell out which “Canadian interests” are really at stake in Latin America—the principal region for Canadian direct investment abroad (CDIA) in the mining sector—and what it has looked like for at least two decades: “liberalization of capital flows, the rewriting of natural resource and financial sector rules, the privatization of public assets, and so on.”
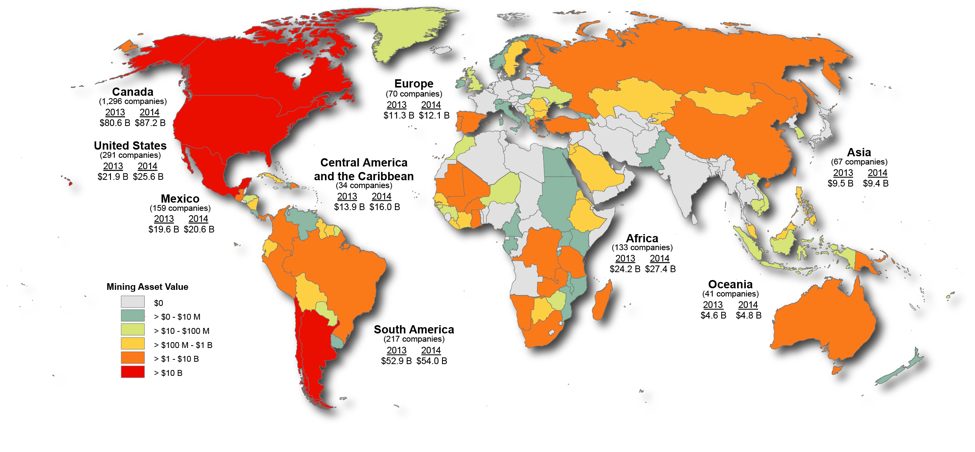
Cumulative CDIA in the region jumped from $2.58 billion in stock in 1990 to $59.4 billion in 2013. These numbers are considerably underestimated, the authors note, since they do not include Canadian capital routed through tax havens. In comparison, U.S. direct investment in the region increased proportionately about a quarter as much over the same period. Despite having an economy one-tenth the size of the U.S., Canadian investment in Latin America and the Caribbean is about a quarter the value of U.S. investment, and most of it is in mining and banking.
Canadian mining investment abroad
To cite a few of the statistics from Gordon and Webber’s book, Latin America and the Caribbean now account for over half of Canadian mining assets abroad (worth $72.4 billion in 2014). Whereas Canadian companies operated two mines in the region in 1990, as of 2012 there were 80, with 48 more in stages of advanced development. In 2014, Northern Miner claimed that 62% of all producing mines in the region were owned by a company headquartered in Canada. This does not take into consideration that 90% of the mining companies listed on Canadian stock exchanges do not actually operate any mine, but rather focus their efforts on speculating on possible mineral finds. This means that, even if a mine is eventually controlled by another source of private capital, Canadian companies are very frequently the first face a community will see in the early stages of a mining project.
The results have been phenomenal “super-profits” for private companies like Barrick Gold, Goldcorp and Yamana, who netted a combined $2.8-billion windfall in 2012 from their operating mines, according to the authors. (Canadian mining companies earned a total of $19.3 billion that year.) Between 1998 and 2013, the authors calculate that these three companies averaged a 45% rate of profit on their operating mines when the Canadian economy’s average rate of profit was 11.8%.
Compare this to Canada’s miserly Latin American development aid expenditures of $187.7 million in in 2012—a good portion of this destined for training, infrastructure and legislative reform programs intended to support the Canadian mining sector. Or consider that the same year $2.8 billion was taken out of Latin America by three Canadian mining firms, remittances back to the region from migrants living in Canada totalled only $798 million (much more than Canadian aid).
Without spelling out the long-term social and environmental costs of these operations—costs that are externalized onto affected communities—or going into the problematic ways that private investment and Canadian aid can be used to condition local support for a mine project, Gordon and Webber posit that “super-profits” may be precisely the “Canadian interests” the government’s foreign policy apparatus is set up to defend—not authentic community development, lasting quality jobs or a reliable macroeconomic model.
State support for “militarized neoliberalism”
The argument that the role of the Canadian state is “to create the best possible conditions for the accumulation of profit” is central to Gordon and Webber’s book. From the Prime Minister’s Office (PMO) down, Canadian agencies and foreign policy have been harnessed to justify “Canadian plunder of the wealth and resources of poorer and weaker countries.” Furthermore, they write, Canada has actively supported the advancement of “militarized neoliberalism” in the region, as country after country has returned to extractive industry, and export-driven and commodity-fuelled economic growth, which comes with high costs for affected-communities and other macroeconomic risks:
The extractive model of capitalism maturing in the Latin American context today does not only involve the imposition of a logic of accumulation by dispossession, pollution of the environment, reassertion of power of the region by multinational capital, and new forms of dependency. It also, necessarily and systematically involved what we call militarized neoliberalism: violence, fraud, corruption, and authoritarian practices on the part of militaries and security forces. In Latin America, this has involved murder, death threats, assaults and arbitrary detention against opponents of resource extraction.
The rapid and widespread granting of mining concessions across large swaths of territory (20% of landmass in some countries), regardless of who lives there or how they might value different lands, water or territory, has provoked hundreds of conflicts and powerful resistance from the community level upward. In reaction, and in order to guarantee foreign investment, in many parts of the region states have intensified the demonization and criminalization of land- and environment-defenders, while state armed forces have increased their powers, and para-state armed forces expanded their territorial control.
Far from being a countervailing force to this trend, the Canadian state has focused its aid, trade and diplomacy on those countries most aligned with its economic interests. It is not unusual to see public gestures of friendship or allegiance toward governments “that share [Canada’s] flexible attitude towards the protection of human rights,” such as Mexico, post-coup Honduras, Guatemala and Colombia. Meanwhile, Canada has used diverse tactics (in Venezuela and Ecuador, for example) to contain resistance and influence even modest reforms.
Canada’s ‘whole-of-government’ approach in Honduras
One of the more detailed examples in Blood of Extraction of Canadian imperialism in Central America covers Canada’s role in Honduras following the military-backed coup in June 2009. Documents obtained from access to information requests provide new revelations and new clarity into how Canadian authorities tried to take advantage of the political opportunities afforded by the coup to push forward measures that favour big business. Once again, though other economic sectors are discussed, mining takes centre stage.
After the terrible experience of affected communities with Goldcorp’s San Martin mine (from the year 2000 onward), Hondurans successfully put a moratorium on all new mining permits pending legal reforms promised by former president José Manuel Zelaya. On the eve of the 2009 coup, a legislative proposal was awaiting debate that would have banned open-pit mining and the use of certain toxic substances in mineral processing, while also making community consent binding on whether or not mining could take place at all. The debate never happened.
Instead, shortly after the coup, and once a president more friendly to “Canadian interests” was in place following a questionable election, the Canadian lobby for a new mining law went into high gear. A key goal for the Canadian government, according to an embassy memo, was “[to facilitate] private sector discussions with the new government in order to promote a comprehensive mining code to give clarity and certainty to our investments.” Another embassy record said that mining executives were happy to assist with the writing of a new mining law that would be “comparable to what is working in other jurisdictions” and developed with a resource person with whom their “ideologies aligned.”
In a highly authoritarian and repressive context, and under the deceptive banner of corporate social responsibility, the Canadian Embassy—with support from Canadian ministerial visits, a Honduran delegation to the annual meeting of the Prospectors & Developers Association of Canada (PDAC), and overseas development aid to pay for technical support—managed to get the desired law passed in early 2013, lifting the moratorium. Then, in June 2014, with full support from Liberals and Conservatives in the House of Commons and the Senate, Canada ratified a free trade agreement with Honduras, effectively declaring that “Honduras, despite its political problems, is a legitimate destination for foreign capital,” write Gordon and Webber.
Contrary to the prevailing theory in Canada that sustaining and increasing economic and political engagement with such a country will lead to improved human rights, the social and economic indicators in Honduras have gotten worse. Since 2010, the authors note, Honduras has the worst income distribution of any country in Latin America (it is the most unequal region in the world). Poverty and extreme poverty rates are up by 13.2% and 26.3%, respectively, after having fallen under Zelaya by 7.7% and 20.9%. Compounding this, Honduras is now the deadliest place to fight for Indigenous autonomy, land, the environment, the rule of law, or just about any other social good.
A strategy of containment in Correa’s Ecuador
In contrast to how Canada has more strongly aligned itself with Latin American regimes openly supportive of militarized neoliberalism, the experience in Ecuador under the administration of President Rafael Correa illustrates how Canada considers “any government that does not conform to the norms of neoliberal policy, and which stretches, however modestly, the narrow structures of liberal democracy…a threat to democracy as such.”
In the chapter on Ecuador, Gordon and Webber provide a detailed account of Canada’s “whole-of-government” approach to containing modest reforms advanced by Correa and undermining the opposition of affected communities and social movements to opening the country to large-scale mining. A critical moment in this process occurred in mid-2008, when a constitutional-level decree was issued in response to local and national mobilizations against mining. The Mining Mandate would have extinguished most or all of the mining concessions that had been granted in the country without prior consultation with affected communities, or that overlapped with water supplies or protected areas, among other criteria. It also set in place a short timeline for the development of a new mining law.
The Canadian embassy immediately went to work. Meetings between Canadian industry and Ecuadorian officials, including the president, were set up to ensure a privileged seat at talks over the new mining law. Gordon and Webber’s review of documents obtained under access to information requests further reveals that the embassy even helped organize pro-mining demonstrations together with industry and the Ecuadorian government. Embassy records describe their intention “to create sympathy and support from the people” as part of a “a pro-image campaign,” which included “an aggressive advertisement campaign, in favour of the development of mining in Ecuador.” Meanwhile, behind closed doors, industry threatened to bring international arbitration against Ecuador under a Canada–Ecuador investor protection agreement (which a couple of investors eventually did).
Ultimately, the authors conclude, Canadian diplomacy “played no small part” in ensuring that the Mining Mandate was never applied to most Canadian-owned projects, and that a relatively acceptable new mining law was passed in early 2009. While embassy documents show the Canadian government considered the law useful enough to “open the sector to commercial mining,” it was still not business-friendly enough, particularly because of the higher rents the state hoped to reap from the sector. As a result, the embassy kept up the pressure, including using the threat of withholding badly needed funds for infrastructure projects until mining company concerns were addressed and dialogue opened up with all Canadian companies.
Not discussed in The Blood of Extraction, we also know the pressure from Canadian industry continued for many more years, eventually achieving reforms, in 2013, that weakened environmental requirements and the tax and royalty regime in Ecuador. Meanwhile, as the door opened to the mining industry, mining-affected communities and supporting organizations were feeling the walls of political and social organizing space cave in, as they faced persistent legal persecution and demonization from the state itself, while the serious negative impacts of the country’s first open-pit copper mine started to be felt.
Canada’s “cruel hypocrisy”
The Blood of Extraction is a helpful portrait of “the drivers behind Canadian foreign policy.” Gordon and Webber lay bear “a systematic, predictable, and repeated pattern of behaviour on the part of Canadian capital and the Canadian state in the region,” along with its systemic and almost predictable harms to the lives, wellbeing and desired futures of Indigenous peoples, communities and even whole populations. They call it Canada’s “cruel hypocrisy.”
The problem is not Goldcorp or HudBay Minerals, Tahoe Resources or Nevsun. These companies are all symptoms of a system on overdrive, fuelling the overexploitation of land, communities, workers and nature to fill the pockets of a small transnational elite based principally in the Global North. If we cannot see how deeply enmeshed Canadian capital is with the Canadian state—how “Canadian interests” are considered met when Canadian-based companies are making super-profits, even through violent destruction—we cannot get a sense of how thoroughly things need to change.
Jen Moore is the Latin America Program Coordinator at Mining Watch Canada, working to support communities, organizations and networks in the region struggling with mining conflicts.
This article was published in the November/December 2016 issue of The Monitor. Click here for more or to download the whole issue.





