In an effort to make way for new investment projects, the Brazilian government and transnational corporations have been taking over ancestral indigenous lands, triggering a rise in murders of indigenous people in Brazil.
According to the report, “Violence Against Indigenous People in Brazil,” recently published by the Indigenous Missionary Council (CIMI by its Portuguese initials), the number of indigenous people killed in the country grew 42 percent from 2013 to 2014; 138 cases were officially registered. The majority of the murders were carried out by hit men hired by those with economic interests in the territories.
The states of Mato Grosso del Sur, Amazonas and Bahía figure heavily in the statistics. An emblematic case was the brutal killing of the indigenous woman Marinalva Kaiowá, in November of 2014. She lived in recovered territories, land that for over 40 years has been claimed by the Guaraní people as the land of their ancestors. Marinalva was assassinated – stabbed 35 times – two weeks after attending a protest with other indigenous leaders at the Federal Supreme Court in the Federal District of Brasilia. The group was protesting a court ruling that annulled the demarcation process in the indigenous territory of the Guyraroká.
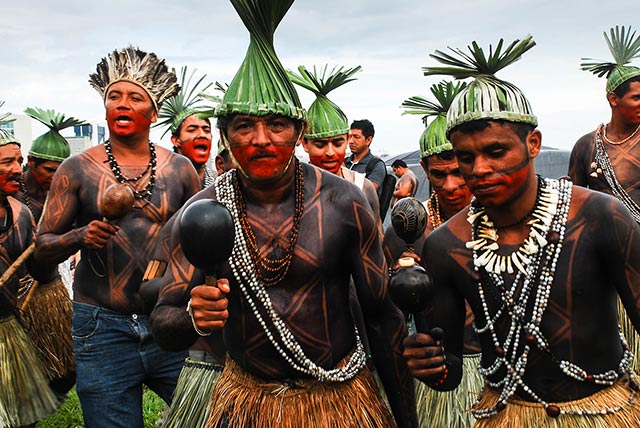
 For four days and three nights, more than 1,500 indigenous individuals filled one of the gardens in front of the National Congress with colors, music and rituals. (Photo: Santiago Navarro F.)
For four days and three nights, more than 1,500 indigenous individuals filled one of the gardens in front of the National Congress with colors, music and rituals. (Photo: Santiago Navarro F.)
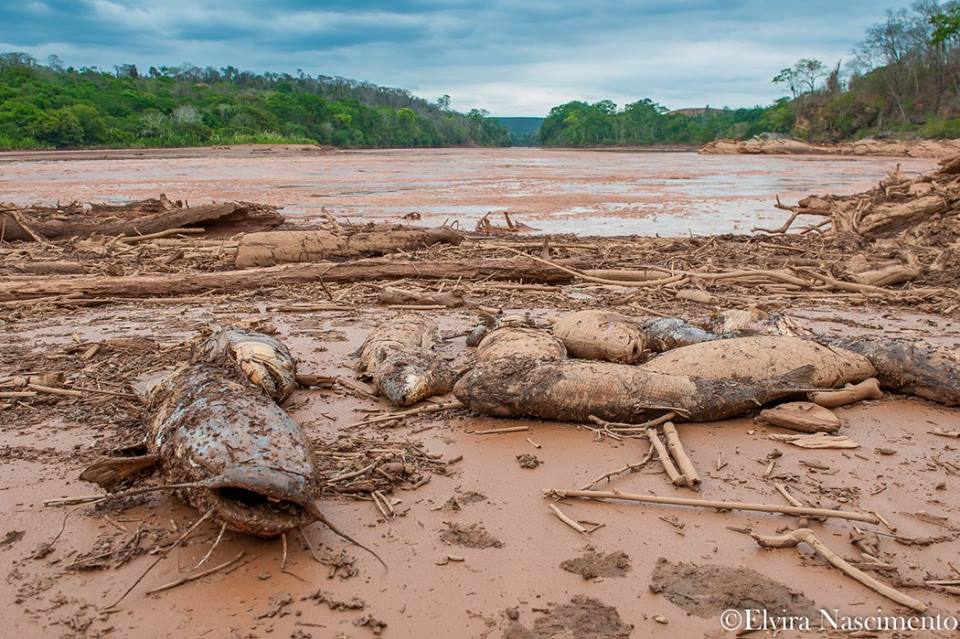
In addition to this, there has been a steady flow of people forced to move to small territories after being displaced by economic development projects, as in the case of the state of Mato Grosso do Sul, where the majority of the population – over 40,000 people – live concentrated on small reservations. These are communities that are exposed to assassinations by hired hit men, lack education and basic necessities, and endure deplorable health conditions. Infant mortality rates in the community are high and rising: According to official statistics, last year 785 children between the ages of 0 and 5 died.
“We, the Guaraní, principally from Mato Grosso do Sul, have been the greatest victims of massacres and violence,” the Guaraní Kaiowá indigenous leader Araqueraju told Truthout. “They have killed many of our leaders, they have spilled much blood because we are fighting for the respect for and demarcation of what is left of our territories that the government does not want to recognize.”
 Indigenous women leaders were also present for the taking of congress to denounce violations of human rights suffered by indigenous people. (Photo: Santiago Navarro F.)
Indigenous women leaders were also present for the taking of congress to denounce violations of human rights suffered by indigenous people. (Photo: Santiago Navarro F.)
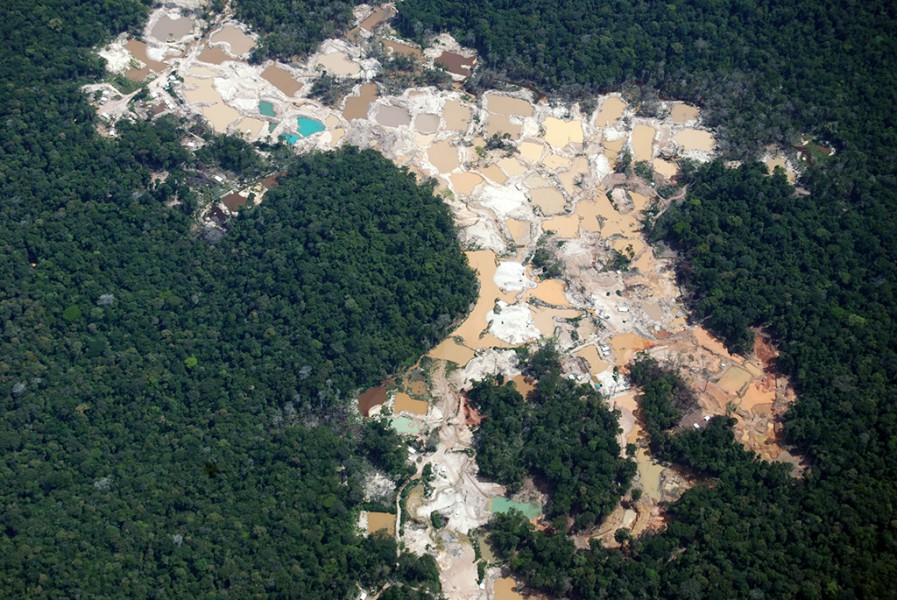
The rise in the rate of violence is related in large part to the development policies of the Brazilian government – policies that have been denounced by the Indigenous Missionary Council. Another report, titled “Projects that impact indigenous lands,” released by CIMI in 2014, revealed that at least 519 projects have impacted 437 ancestral territories, directly affecting 204 indigenous groups.
The energy sector has most deeply affected indigenous people; of the 519 documented projects, 267 are energy-related. In second place is infrastructure, with 196 projects. Mining is third, with 21 projects, and in fourth place, with 19 expansive projects, is agribusiness. Ecotourism comes next with 9 projects.
“In the Amazon region, the region of the Tapajos River, we are being fenced in,” João Tapajó – a member of the Arimun indigenous group – told Truthout. “The Teles waterway is being constructed and the BR163 highway widened. This is being done to transport the transnational corporations’ grain and minerals,” added Tapajó, who is part of one of the groups that make up the Indigenous Movement of the region Bajo Tapajós, in the state of Pará. “We live under constant threat from agribusinesses and lumber companies. There is a construction project to build five hydroelectric dams on the same river. To top it off, our region is suffering from a process of prospecting for the exploitation of minerals, by the companies Alcoa y Vale do Rio Doce.”
 The military police were constantly present, protecting the headquarters of Brazil’s three branches of government from the indigenous protesters. (Photo: Santiago Navarro F.)
The military police were constantly present, protecting the headquarters of Brazil’s three branches of government from the indigenous protesters. (Photo: Santiago Navarro F.)
Similarly, a report produced by the Federal Public Ministry, based on its own evaluations and carried out by anthropologists María Fernanda Paranhos and Deborah Stucchi, shows that the processes of social change generated by these projects principally affect those who live in rural contexts. This includes many groups living collectively who are relatively invisible in the sociopolitical context of Brazil.
“The evaluations provide evidence that the intense social changes, the possibility of the breaking up of productive circuits, the disappearance of small-scale agriculture, fishing, and forested areas, a reduction in jobs, and the impoverishment and degradation of material and immaterial conditions of life … have led to strong reactions and an avalanche of social conflict,” according to the ministry’s report.
 Indigenous people of ethnic Pataxo struggle to return their lands. In October 2014, they closed the highway to pressure the government. (Photo: Santiago Navarro F.)
Indigenous people of ethnic Pataxo struggle to return their lands. In October 2014, they closed the highway to pressure the government. (Photo: Santiago Navarro F.)
Hydroelectric Dams in the Brazilian Amazon
The government’s Ten-Year Plan for energy expansion – 2023, which projects for the period of 2014 to 2023 an expansion of over 28,000 megawatts of energy generation by way of hydroelectric dams, claims that none of the 30 hydroelectric dams projected for construction in this country during this period will have any direct effect on indigenous lands.
Data from the Institute of Socioeconomic Studies, through an initiative called Investments and Rights in the Amazon, tells a different story. According to research carried out by Ricardo Verdum, a PhD in social anthropology and member of the Center for the Study of Indigenous Populations at the Federal University in the state of Santa Catarina, of the 23 hydroelectric dams that will be built in the Amazon, at least 16 will have negative social and environmental effects on indigenous territories. They will destroy the environmental conditions that these indigenous groups depend on to live and maintain their way of life.
“The difference in results is due to the way the idea of ‘impact’ or ‘interference’ is defined conceptually and materially,” Verdum told Truthout. “According to current legislation, interference in indigenous lands occurs when a parcel of land is directly affected by the dam itself or the reservoir. The territorial and environmental criteria do not consider the human and social aspects of the interference, or influence of the project on the population.”
 The atmosphere grew tense as Federal Police came in, although this was no surprise to the Pataxo. They have been long been rejected by cattle farmers, businessmen and people living in cities close to Monte Pascoal – one of the richest areas in terms of flora and fauna in the world. (Photo: Santiago Navarro F.)
The atmosphere grew tense as Federal Police came in, although this was no surprise to the Pataxo. They have been long been rejected by cattle farmers, businessmen and people living in cities close to Monte Pascoal – one of the richest areas in terms of flora and fauna in the world. (Photo: Santiago Navarro F.)
A Militaristic Approach to the Economy
Brazil’s development model – a model adopted by most countries in Latin America within the old international division of labor – leads the country to specialize in the export of raw materials or basic products at a low cost in relation to the import of final products that return to Brazil at elevated prices. This is a logic that is based on the colonial model, according to Clovis Brighenti, a professor of history at the Federal University of Latin American Integration. “It is an entry into the globalized world by way of intense exploitation of the environment with few results,” Brighenti told Truthout. “What’s more, these results are in exchange for high investment costs, made with public resources and subsidized interest rates, concentrated in a tiny group of beneficiaries. It is a dried-up model but in its death throes, it causes irreversible damage to the environment and for the people that depend on these ecosystems.”
The design of this development model, according to Brighenti, is connected to the modern myth that an economy needs to grow rapidly and continuously to satisfy the material necessities of society. “However, behind this myth, is hidden the essence of the capitalist system: the need to guarantee a logic that is based on consumerism, and in this way, guarantee the accumulation and the benefit of the elites and the privileged sectors of society.”
In Brazil, the belief is that material happiness is connected to the search for new spaces for development expansion. “In other words, it is searching for constant advancement into ‘new’ territories, where there is still a natural environment to be explored and appropriated,” Brighenti said. “Thus, capital’s interests revolve around indigenous and traditional territories, as ideal spaces for the execution of these projects.”
He added that in Brazil there is a continuity of a militaristic mentality, due to the fact that the country was shaped by a military dictatorship from 1964 to 1985. During that time, the United States was involved through a program called Operation Brother Sam.
The objective was to remove peasants and indigenous people from their lands to concentrate territories in the hands of businesses that currently produce soy, sugar cane and eucalyptus. These companies include Monsanto, ADM, Cargill, Bunge, Louis Dreyfus Commodities, Coca-Cola, Nestlé and Ford. In this sense, current governments did not inherit just the military structure but also a business platform that dominates production and the raw materials market. “The principal similarity between the military government and what we are currently living is the development perspective, which means thinking about natural resources as infinite and readily available. In order to make a country grow economically, the amount of territory that is occupied for economic projects must increase,” Brighenti said.
Another similarity is the relationship that they establish with communities. “It could be said that there is no dialogue,” Brighenti said. “The government makes a decision and all that is left for the communities to do is to hand over their territories in the name of these initiatives. Trying to keep indigenous communities quiet is a recurring action in the sense that these populations are seen as barriers to the establishment of these projects … thus, the continuance of a militaristic mentality is explicit – proceed with development and stop the protests of those who are affected.”
An essential point that sets the period of the dictatorship apart from progressive governments is the source of financing for the projects. “Today the works are financed with public resources, through the National Economic and Social Development Bank, which is the principal funder of these megaprojects, while under the military dictatorship they were financed by the World Bank and the Inter-American Development Bank,” he said.
In 2013, the Brazilian government published an order that allowed the intervention of the Armed Forces in protests against development projects. That same year, the military police in southern Brazil killed an indigenous Terena man and wounded others in the fulfillment of an order to re-take the land that the Terena had reclaimed as part of their ancestral territories. This was disputed by Ricardo Bacha, a former congressman from the Brazilian Social Democratic Party, who said that the lands had belonged to his family since 1927.
Similarly, at the request of the ex-governor of Bahia, Jaques Wagner, who is the current defense minister of Brazil, President Dilma Rousseff signed in 2014 an authorization by the federal government to dispatch close to 500 military personnel to the Tupinambá territory, alleging that his objective was the “guarantee of law and order” and to “pacify” the region. To this very day, the Tupinambá region continues to be militarized.
 Since 2010, indigenous people have intensified the re-taking of their lands in a process of self-demarcation. (Photo: Santiago Navarro F.)
Since 2010, indigenous people have intensified the re-taking of their lands in a process of self-demarcation. (Photo: Santiago Navarro F.)
Institutional Violence Against Indigenous Communities
The assassinations are just the tip of the iceberg. Among the constitutional amendments that are being debated in Brazil’s Congress is PEC-215, which transfers the power to decide the demarcation of indigenous territories to the legislative branch, when it has historically been in the hands of the executive branch. The amendment would leave indigenous people in the hands of Congress and the Senate, which are primarily made up of the family members of large businessmen and the owners of huge extensions of land.
“These proposed constitutional amendments favor a group of 264 parliamentarians of Brazil’s Congress, who have received campaign financing from multinational corporations, such as Monsanto, Cargill, Bunge and Syngenta. PEC-215 favors the expansion of big agriculture, using the discourse of food production, but Brazil’s food is produced by small-scale producers,” Lindomar, of the Terena people, told Truthout.
The principal cause of the conflicts, according to the Indigenous Missionary Council, is the negation on the part of the Brazilian government to recognize and demarcate indigenous territories. In 2014, of the almost 600 indigenous territories currently claimed by different groups, only two were recognized (Xeta Herarekã, in the state of Paraná, and Xakriabá, in the state of Minas Gerais) and one was approved (Paquicamba, in the state of Pará). The current government of the Workers Party, led by Dilma Rousseff, is that which has demarcated the fewest indigenous lands since the end of the military dictatorship in Brazil.
In the state of Mato Grosso do Sul, the state with the highest rates of violence against indigenous people, communities live on the edges of highways, in precarious living conditions. The recognition of indigenous territories was outlined in an agreement that was signed in 2007 by the National Indigenous Foundation, a government agency, which later broke the agreement. Even if the demarcation had gone into effect, indigenous people would only occupy 2 percent of the state, in one of the regions of Brazil where the largest number of indigenous people reside.
Resisting the Old Development Model
According to Brighenti, since the start of the Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva (Lula) administration, indigenous people have expressed to the government that they wanted to share their knowledge and practices with the new administration. “But the government ignored them, and what’s worse, Lula declared that Brazil needed to overcome three great obstacles to development, including indigenous groups, environmental laws and the Federal Public Ministry,” he said. “Thus, since the beginning, he made it clear that for the indigenous movement and its allies, the government had chosen a different model and aligned himself with other sectors that are unfortunately at odds with indigenous groups, big agro-industry.”
Indigenous people realized that they needed to come together to avoid losing their rights. “Few social and union movements supported them. Each social movement defined its relationship with the government and indigenous people were many times criticized for their radicalness,” Brighenti added.
Indigenous lands in Brazil, as recognized by the federal government, are property of the government. Indigenous people can possess and use the land, with the exception of the subsoil and water resources. “It is necessary to advance in the sense of constructing autonomous communities, which does not mean independence, but the freedom to decide their own future,” Brighenti said.
Even with the demarcation of indigenous territories, there is no assurance against intervention in indigenous lands, since the law allows for the intervention of the federal government at any time because the lands are considered property of the government.
“All the government projects are threatening to us and the entire Amazon,” María Leus, an indigenous Munduruku woman, told Truthout. “We do not accept any negotiation with the government, because we cannot make negotiations regarding our mother and because we do not accept any of these projects that are going to affect us. We have always been here: These are the lands of our ancestors, and today we continuing fighting for the respect for our way of life, because governments have never respected how we live, and today they are devastating what is left of our lands in order to continue with their projects.”


 Some resources in Portuguese to learn more and get active:
Some resources in Portuguese to learn more and get active:







 For four days and three nights, more than 1,500 indigenous individuals filled one of the gardens in front of the National Congress with colors, music and rituals. (Photo: Santiago Navarro F.)
For four days and three nights, more than 1,500 indigenous individuals filled one of the gardens in front of the National Congress with colors, music and rituals. (Photo: Santiago Navarro F.) Indigenous women leaders were also present for the taking of congress to denounce violations of human rights suffered by indigenous people. (Photo: Santiago Navarro F.)
Indigenous women leaders were also present for the taking of congress to denounce violations of human rights suffered by indigenous people. (Photo: Santiago Navarro F.) The military police were constantly present, protecting the headquarters of Brazil’s three branches of government from the indigenous protesters. (Photo: Santiago Navarro F.)
The military police were constantly present, protecting the headquarters of Brazil’s three branches of government from the indigenous protesters. (Photo: Santiago Navarro F.) Indigenous people of ethnic Pataxo struggle to return their lands. In October 2014, they closed the highway to pressure the government. (Photo: Santiago Navarro F.)
Indigenous people of ethnic Pataxo struggle to return their lands. In October 2014, they closed the highway to pressure the government. (Photo: Santiago Navarro F.) The atmosphere grew tense as Federal Police came in, although this was no surprise to the Pataxo. They have been long been rejected by cattle farmers, businessmen and people living in cities close to Monte Pascoal – one of the richest areas in terms of flora and fauna in the world. (Photo: Santiago Navarro F.)
The atmosphere grew tense as Federal Police came in, although this was no surprise to the Pataxo. They have been long been rejected by cattle farmers, businessmen and people living in cities close to Monte Pascoal – one of the richest areas in terms of flora and fauna in the world. (Photo: Santiago Navarro F.) Since 2010, indigenous people have intensified the re-taking of their lands in a process of self-demarcation. (Photo: Santiago Navarro F.)
Since 2010, indigenous people have intensified the re-taking of their lands in a process of self-demarcation. (Photo: Santiago Navarro F.)