by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Mar 2, 2019 | Agriculture
by Fred Iutzi and Robert Jensen / Resilience.org
Propelled by the energy of progressive legislators elected in the 2018 midterms elections, a “Green New Deal” has become part of the political conversation in the United States, culminating in a resolution in the U.S. House with 67 cosponsors and a number of prominent senators lining up to join them. Decades of activism by groups working on climate change and other ecological crises, along with a surge of support in recent years for democratic socialism, has opened up new political opportunities for serious discussion of the intersection of social justice and sustainability.The Green New Deal proposal—which is a resolution, not a bill, that offers only a broad outline of goals and requires more detailed legislative proposals—will not be successful right out of the gate; many centrist Democrats are lukewarm, and most Republicans are hostile. This gives supporters plenty of time to consider crucial questions embedded in the term: (1) how “Green” will we have to get to create a truly sustainable society, and (2) is a “New Deal” a sufficient response to the multiple, cascading economic/ecological crises we face?
In strategic terms: Should a Green New Deal limit itself to a reformist agenda that proposes programs that can be passed as soon as possible, or should it advance a more revolutionary agenda aimed at challenging our economic system? Should those of us concerned about economic justice and ecological sustainability be realistic or radical?
Our answer—yes to all—does not avoid tough choices. The false dichotomies of reform v. revolution and realistic v. radical too often encourage self-marginalizing squabbles among people working for change. Philosophical and strategic differences exist among critics of the existing systems of power, of course, but collaborative work is possible—if all parties can agree not to ignore the potentially catastrophic long-term threats while trying to enact limited policies that are possible in the short term. Reforms can take us beyond a reformist agenda when pursued with revolutionary ideals. Radical proposals are often more realistic than policies crafted out of fear of going to the root of a problem.
Our proposal for an agricultural component for a Green New Deal offers an example of this approach. Humans need a revolutionary new way of producing food, which must go forward with a radical critique of capitalism’s ideology and the industrial worldview. Reforms can begin to bring those revolutionary ideas to life, and realistic proposals can be radical in helping to change worldviews.
We focus here on two proposals for a Green New Deal that are politically viable today but also point us toward the deeper long-term change needed: (1) job training that could help repopulate the countryside and change how farmers work, and (2) research on perennial grain crops that could change how we farm. Two existing organizations, the Land Stewardship Project in Minnesota and The Land Institute in Kansas, offer models for successful work in these areas.
Philosophy and Politics
We begin by foregrounding our critique of capitalism and the industrial worldview. All policy proposals are based on a vision of the future that we seek, and an assessment of the existing systems that create impediments to moving toward that vision. In a politically healthy and intellectually vibrant democracy, policy debates should start with articulations of those visions and assessments. “Pragmatists”—those who appoint themselves as guardians of common sense—are quick to warn against getting bogged down in ideological debates and/or talk of the future, advising that we must focus on what works today within existing systems. But accepting that barely camouflaged defense of the status quo guarantees that people with power today will remain in power, in the same institutions serving the same interests. It is more productive to debate big ideas as we move toward compromise on policy. Compromise without vision is capitulation.
Green New Deal proposals should not only offer a set of specific policy proposals but also articulate a new way of seeing humans and our place in the ecosphere. At the core of our worldview is the belief that:
- People are not merely labor-machines in the production process or customers in a mass-consumption economy. Economic systems must create meaningful work (along with an equitable distribution of wealth) and healthy communities (along with fulfilled individuals).
- The more-than-human world (what we typically call “nature”) cannot be treated as if the planet is nothing more than a mine for extraction and a dump for wastes. Economic systems must make possible a sustainable human presence on the planet.
These two statements of values are a direct challenge to capitalism and the industrial worldview that currently define the global economy. Fueled by the dense energy in coal, oil, and natural gas, industrial capitalism has been the most wildly productive economic system in human history, but it routinely fails to produce meaning in people’s lives and it draws down the ecological capital of the planet at a rate well beyond replacement levels. Most of the contemporary U.S. political establishment assumes these systems will continue in perpetuity, but Green New Deal advocates can challenge that by speaking to how their proposals meet human needs for meaning-in-community and challenge the illusion of infinite growth on a finite planet.
The Countryside
In an urban society and industrial economy dominated by finance, many people do not think of agriculture as either a significant economic sector or a threat to ecological sustainability. With less than two percent of the population employed in agriculture, farming is “out of sight, out of mind” for most of the population. To deal effectively with both economic and ecological crises, a Green New Deal should include agricultural policies that (1) support smaller farms with more farmers, living in viable rural economies and communities, and (2) advance alternatives to annual monoculture industrial farming, which is a major contributor to global warming and the degradation of ecosystems.
These concerns for the declining health of rural communities and ecosystems are connected. Economic and cultural forces have made farming increasingly unprofitable for small family operations and encouraged young people to view education as a vehicle to escape the farm. The command from the industrial worldview was “get big or get out,” and the not-so-subtle hint to young people has been that social status comes with managerial, technical, and intellectual careers in cities. The economic drivers have encouraged increasingly industrialized agriculture, adding to soil erosion and land degradation in the pursuit of short-term yield increases. The dominant culture tells us that markets know best and advanced technology is always better than traditional methods.
Today one hears of how rural America and its people are ignored, but a more accurate term would be exploited—an “economic colonization of rural America.” Agricultural land is exploited, as are below-ground mineral and water resources, typically in ecologically destructive fashion. Meanwhile, recreation areas are “preserved,” largely for use by city people. The damage done to land and people are, in economists’ vocabulary, externalities—rural people, the land, and its creatures pay costs that are not factored into economic transactions. Responding to the crises in rural America is crucial in any program aimed at building a just and sustainable society.
Farmer Training
Much of the discussion about job training/retraining for a Green Economy focuses on technical skills needed for solar-panel installation, weatherizing homes, etc.—important projects that are politically realistic, culturally palatable, and technologically mature today. But a sustainable future with dramatic reductions in fossil-fuel consumption also requires a redesigned agricultural system, which requires more people on the land. We need the appropriate “eyes-to-acres ratio” that makes it possible to farm in an ecologically responsibly manner, according to Wes Jackson, co-founder of The Land Institute and a leader in the sustainable agriculture movement.
A visionary Green New Deal proposal would, as a first step, provide support for programs to expand farming and farm-related occupations in rural areas, part of a long-term project to repopulate the countryside in preparation for the more labor-intensive sustainable agriculture that we would like to see today and will be necessary for a future with “land-conserving communities and healthy regional economies,” to borrow from The Berry Center. The dominant culture equates urban with the progressive and modern, and rural with the unsophisticated and backward, a prejudice that must be challenged not only in the world of ideas but also on the ground.
The Land Stewardship Project offers a template, with three successful training programs. A four-hour Farm Dreams workshop helps people clarify their motivations to farm and begins a process of identifying resources and needs, with help from an experienced farmer. In farmer-led classroom sessions, on-farm tours, and an extensive farmer network, the Farm Beginnings course is a one-year program designed for prospective farmers with some experience who are ready to start a farm, whether or not they currently own land. The two-year Journeyperson course supports people who have been managing their own farm and need guidance to improve or expand their operation for long-term success.
There are, of course, many other farm-training programs from non-profits, governmental agencies, and educational institutions. We highlight LSP, which was founded in 1982, because of its track record and flexibility in responding to political conditions and community needs, particularly its willingness to engage critiques of white supremacy. Support for such programs is not only sensible policy but, in blunt political terms, a signal that progressives backing a Green New Deal recognize the need to revitalize rural areas, where people often feel forgotten by urban legislators and their constituents.
Perennial Polycultures
There has been growing interest in community-supported agriculture, urban farms, and backyard gardening, all of which are components of a healthy food system and healthy communities but do not address the central challenges in the production of the grains (cereals, oilseeds, and pulses) that are the main staples of the human diet. Natural Systems Agriculture research at The Land Institute—which focuses on perennial polycultures (grain crops grown in mixtures of plants) to replace annual monoculture grain farming—offers a model for the long-term commitment to research and outreach necessary for large-scale sustainable agriculture.
Annual plants are alive for only part of the year and are weakly rooted even then, which leads to the loss of precious soil, nutrients, and water that perennial plants do a better job of holding. Monoculture approaches in some ways simplify farming, but those fields have only one kind of root architecture, which exacerbates the problem of wasted nutrients and water. Current industrial farming techniques (use of fossil-fuel based fertilizers, herbicides, and pesticides, with increasingly expensive and complex farm implements) that are dominant in the developed world, and spreading beyond, also are a major source of greenhouse gas emissions. Less disturbance of soil carbon, in tandem with reduced fossil fuel use in production, reduces the contribution of agriculture to global warming.
Founded in 1976, TLI’s long-term research program has developed Kernza, an intermediate wheatgrass now in limited commercial production, and is working on rice, wheat, sorghum, oilseeds, and legumes, in collaborations with people at 16 universities in the United States and in 18 other countries. Through this combination of perennial species in a diverse community of plants, “ecological intensification” can enhance fertility and reduce weeds, pests, and pathogens, supplanting commercial inputs and maintaining food production while reducing environmental impacts of agriculture.
A visionary Green New Deal could fund additional research into perennial polycultures and other projects that come under the heading of agro-ecology, an umbrella term for farming that rejects the reliance on the pesticides, herbicides, and chemical fertilizers that poison ecosystems all over the world.
Revolution in the Air?
Expanding the number of farmers with the skills needed to leave industrial agriculture behind, and developing crops for a low-energy world are crucial if we are to achieve an ecologically sustainable agriculture. But those changes are of little value without land on which those new farmers can raise those new crops. There is no avoiding the question of land ownership and the need for land reform.
We have no expertise in this area and no specific proposals to offer, but we recognize the importance of the question and the challenge it presents to achieving sustainability in the contemporary United States, as well as around the world. Today, land ownership patterns are at odds with our stated commitment to justice and sustainability—too few people own too much of the agricultural land, and women and people of color are particularly vulnerable to what a Food First report described as, “the disastrous effects of widespread land grabbing and land concentration.”
In somewhat tamer language, the USDA-supported Farmland Information Center reports what is common knowledge in the countryside: “Finding affordable land for purchase or long-term lease is often cited by beginning and expanding farmers and ranchers as their most significant challenge.” Adding to the problem is the loss of farmland to development; in a 2018 report, the American Farmland Trust reported that almost 31 million acres of agricultural land was “converted” between 1992 and 2012.
No one expects any bill introduced in today’s Congress to endorse government action to protect agricultural land from development and redistribute that land to prospective farmers who are currently landless—growing support for democratic socialism does not a revolution make. But any serious long-term planning will have to address land reform, for as the agrarian writer Wendell Berry points out, “There’s a fundamental incompatibility between industrial capitalism and both the ecological and the social principles of good agriculture.”
A vision of rural communities based on family farms is often mistakenly dismissed as mere nostalgia for a romanticized past. We can take stock of the past failures not only of the capitalist farm economy but also of farmers—small family farms are no guarantee of good farming, and rural communities do not guarantee social justice—and still realize that repopulating the countryside is an essential part of a sustainable future.
Conclusion
We began with a faith that people with shared values might disagree about strategies yet still work together. People working on a wide variety of other projects—for example, worker/producer/consumer cooperatives and land trusts—can find reasons to support our ideas, just as we support those projects. But we also recognize that real-world proposals have to prioritize, and so we want to be clear about differences.
For example, the Green New Deal resolution calls for “100 percent of the power demand in the United States through clean, renewable, and zero-emission energy sources.” One of the key groups backing the plan, the Sunrise Movement, calls this one of the three pillars of its program. We believe this is unrealistic. No combination of renewable energy sources can power the United States in its current form. To talk about renewable energy as a solution without highlighting the need for a dramatic decrease in consumption in the developed world is disingenuous. Pretending that we can maintain First World affluence and achieve sustainability will lead to failed projects and waste limited resources.
Many advocates of a Green New Deal focus on renewable energy technologies and other technological responses to rapid climate disruption and ecological crises. These technologies are only part of the solution. We should reject the dominant culture’s “technological fundamentalism”—the illusion that high-energy/high-technology can magically produce sustainability at current levels of human population and consumption. A Green New Deal should support technological innovations, but only those that help us move to a low-energy world in which human flourishing is redefined by improving the quality of relationships rather than maintaining the capacity for consumption.
We understand that short-term policy proposals must be “reasonable”—that is, they must connect to people’s concerns and be articulated in terms that can be widely understood. But they also must help move us toward a system that many today find impossible to imagine: An economy that not only (1) transcends capitalism and its wealth inequality but also (2) rejects the industrial worldview and its obsession with production. Today’s policy proposals should advance egalitarian goals for the economy but also embrace an ecological worldview for society, without turning from the difficulty posed by the dramatic changes that lie ahead.

by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Feb 23, 2019 | Colonialism & Conquest
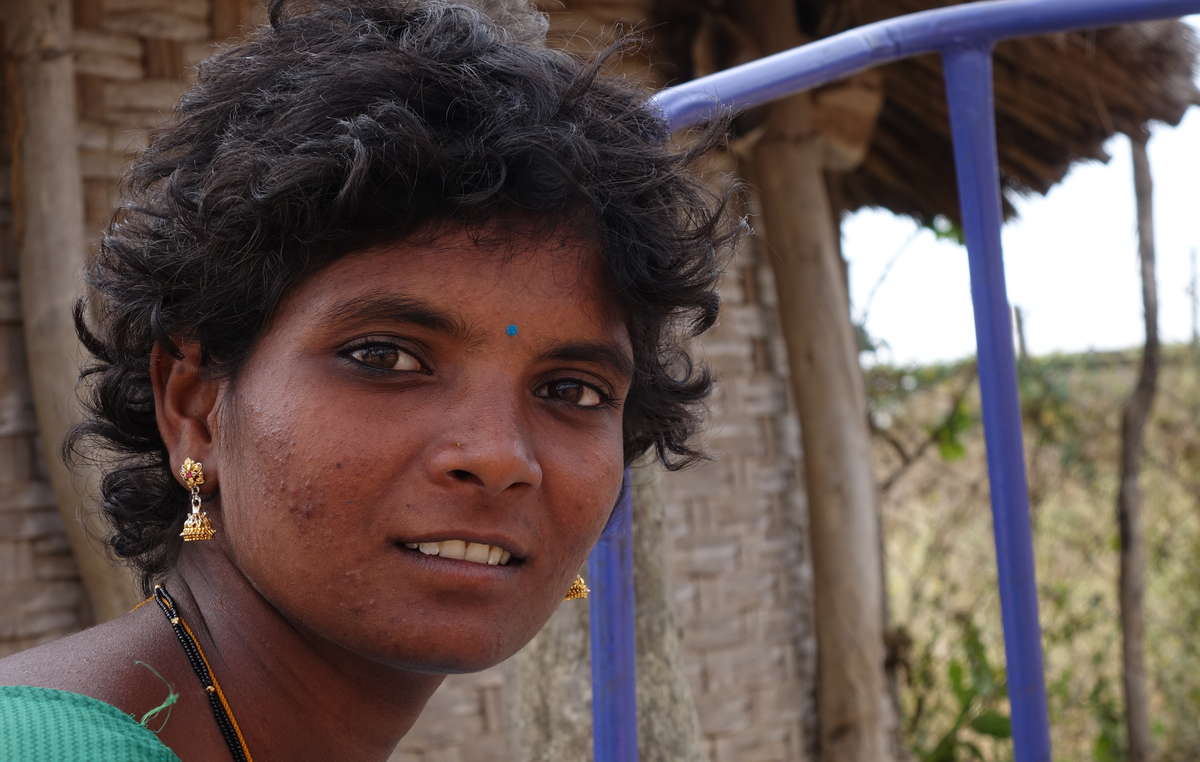
Featured image: Many tribes, like some Chenchu, have already been evicted after their lands were turned into tiger reserves. Now millions more face eviction. © Survival International
by Survival International
India’s Supreme Court has ordered the eviction of up to 8 million tribal and other forest-dwelling people, in what campaigners have described as “an unprecedented disaster,” and “the biggest mass eviction in the name of conservation, ever.”
The ruling is in response to requests by Indian conservation groups to declare invalid the Forest Rights Act, which gives forest-dwelling people rights to their ancestral lands, including in protected areas. The groups had also demanded that where tribespeople had tried and failed to secure their rights under the Act, they should be evicted.
The groups reportedly include Wildlife First, Wildlife Trust of India, the Nature Conservation Society, the Tiger Research and Conservation Trust and the Bombay Natural History Society.
In an extraordinary move, the national government failed to appear in court to defend the tribespeople’s rights, and the Court therefore ruled in favor of the evictions, which it decreed should be completed by July 27.
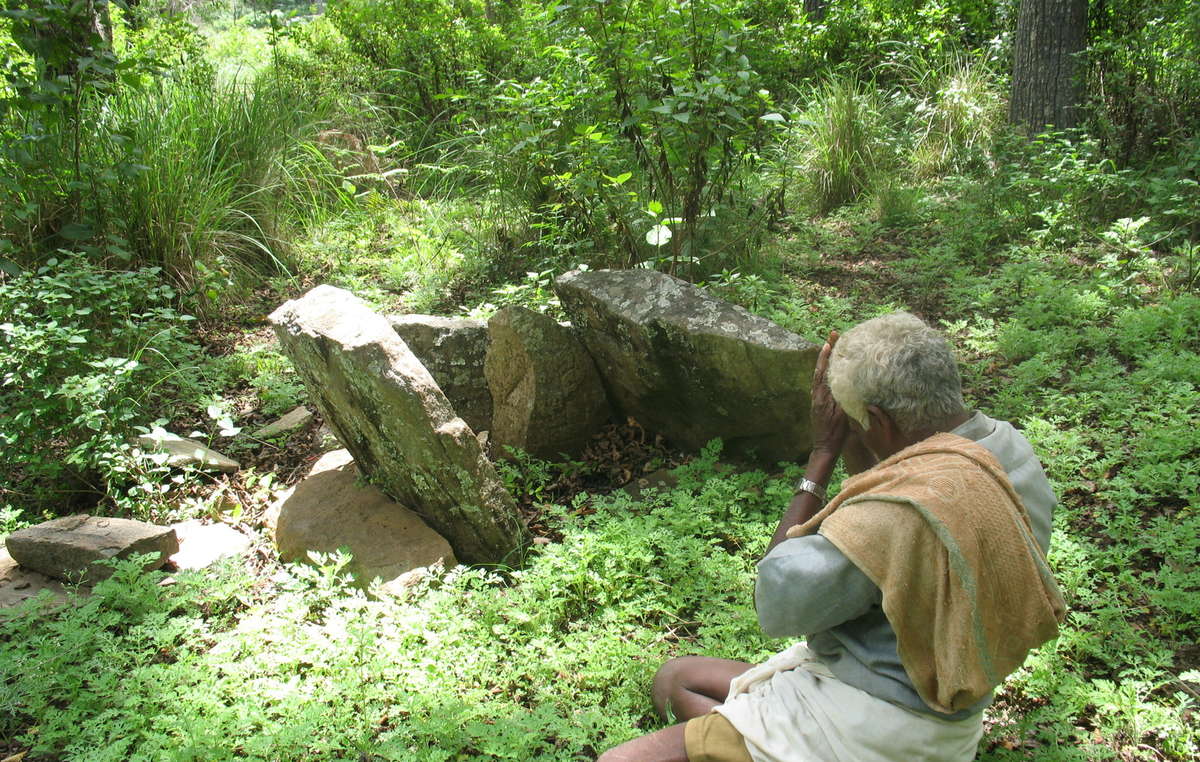

A Soliga man worships at a sacred site, now inside a tiger reserve. © Atree/Survival
The order affects more than 1.1 million households, with experts estimating this could mean more than 8 million individuals will now be evicted – and the number is likely to rise, as some states have not provided details as to how many will be affected.
Survival International’s Director Stephen Corry said today: “This judgement is a death sentence for millions of tribal people in India, land theft on an epic scale, and a monumental injustice.
“It will lead to wholesale misery, impoverishment, disease and death, an urgent humanitarian crisis, and it will do nothing to save the forests which these tribespeople have protected for generations.
“Will the big conservation organizations like WWF and WCS condemn this ruling and pledge to fight it, or will they be complicit in the biggest mass eviction in the name of conservation, ever?”

by DGR News Service | Feb 18, 2019 | The Problem: Civilization
Part 2
This is an excerpt from the book Deep Green Resistance – Strategy to save the planet
by Lierre Keith
Most people, or at least most people with a beating heart, have already done the math, added up the arrogance, sadism, stupidity, and denial, and reached the bottom line: a dead planet. Some of us carry that final sum like the weight of a corpse. For others, that conclusion turns the heart to a smoldering coal. But despair and rage have been declared unevolved and unclean, beneath the “spiritual warriors” who insist they will save the planet by “healing” themselves. How this activity will stop the release of carbon and the felling of forests is never actually explained. The answer lies vaguely between being the change we wish to see and a 100th monkey of hope, a monkey that is frankly more Christmas pony than actual possibility.
Given that the culture of America is founded on individualism and awash in privilege, it’s no surprise that narcissism is the end result. The social upheavals of the ’60s split along fault lines of responsibility and hedonism, of justice and selfishness, of sacrifice and entitlement. What we are left with is an alternative culture, a small, separate world of the converted, content to coexist alongside a virulent mainstream. Here, one can find workshops on “scarcity consciousness,” as if poverty were a state of mind and not a structural support of capitalism. This culture leaves us ill-prepared to face the crisis of planetary biocide that greets us daily with its own grim dawn. The facts are not conducive to an open-hearted state of wonder. To confront the truth as adults, not as faux children, requires an adult fortitude and courage, grounded in our adult responsibilities to the world. It requires those things because the situation is horrific and living with that knowledge will hurt. Meanwhile, I have been to workshops where global warming was treated as an opportunity for personal growth, and no one there but me saw a problem with that.
The word sustainable—the “Praise, Jesus!” of the eco-earnest—serves as an example of the worst tendencies of the alternative culture. It’s a word that perfectly meshes corporate marketers’ carefully calculated upswell of green sentiment with the relentless denial of the privileged. It’s a word I can barely stand to use because it has been so exsanguinated by cheerleaders for a technotopic, consumer kingdom come. To doubt the vague promise now firmly embedded in the word—that we can have our cars, our corporations, our consumption, and our planet, too—is both treason and heresy to the emotional well-being of most progressives. But here’s the question: Do we want to feel better or do we want to be effective? Are we sentimentalists or are we warriors?
For “sustainable” to mean anything, we must embrace and then defend the bare truth: the planet is primary. The life-producing work of a million species is literally the earth, air, and water that we depend on. No human activity—not the vacuous, not the sublime—is worth more than that matrix. Neither, in the end, is any human life. If we use the word “sustainable” and don’t mean that, then we are liars of the worst sort: the kind who let atrocities happen while we stand by and do nothing.
Even if it were possible to reach narcissists, we are out of time. Admitting we have to move forward without them, we step away from the cloying childishness and optimistic white-lite denial of so much of the left and embrace our adult knowledge. With all apologies to Yeats, in knowledge begins responsibilities. It’s to you grown-ups, the grieving and the raging, that we address this book.

The vast majority of the population will do nothing unless they are led, cajoled, or forced. If the structural determinants are in place for people to live their lives without doing damage—for example, if they’re hunter-gatherers with respected elders—then that’s what happens. If, on the other hand, the environment has been arranged for cars, industrial schooling is mandatory, resisting war taxes will land you in jail, food is only available through giant corporate enterprises selling giant corporate degradation, and misogynist pornography is only a click away 24/7—well, welcome to the nightmare. This culture is basically conducting a massive Milgram experiment on us, only the electric shocks aren’t fake—they’re killing off the planet, species by species.
But wherever there is oppression there is resistance. That is true everywhere, and has been forever. The resistance is built body by body from a tiny few, from the stalwart, the brave, the determined, who are willing to stand against both power and social censure. It is our prediction that there will be no mass movement, not in time to save this planet, our home. That tiny percent—Margaret Mead’s small group of thoughtful, committed citizens—has been able to shift both the cultural consciousness and the power structures toward justice in times past. It is valid to long for a mass movement, however, no matter how much we rationally know that we’re wishing on a star. Theoretically, the human race as a whole could face our situation and make some decisions—tough decisions, but fair ones, that include an equitable distribution of both resources and justice, that respect and embrace the limits of our planet. But none of the institutions that govern our lives, from the economic to the religious, are on the side of justice or sustainability. Theoretically, these institutions could be forced to change. The history of every human rights struggle bears witness to how courage and sacrifice can dismantle power and injustice. But again, it takes time. If we had a thousand years, even a hundred years, building a movement to transform the dominant institutions around the globe would be the task before us. But the Western black rhinoceros is out of time. So is the golden toad, the pygmy rabbit. No one is going to save this planet except us.
So what are our options? The usual approach of long, slow institutional change has been foreclosed, and many of us know that. The default setting for environmentalists has become personal lifestyle “choices.” This should have been predictable as it merges perfectly into the demands of capitalism, especially the condensed corporate version mediating our every impulse into their profit. But we can’t consume our way out of environmental collapse; consumption is the problem. We might be forgiven for initially accepting an exhortation to “simple living” as a solution to that consumption, especially as the major environmental organizations and the media have declared lifestyle change our First Commandment. Have you accepted compact fluorescents as your personal savior? But lifestyle change is not a solution as it doesn’t address the root of the problem.
We have believed such ridiculous solutions because our perception has been blunted by some portion of denial and despair. And those are legitimate reactions. I’m not persuading anyone out of them. But do we want to develop a strategy to manage our emotional state or to save the planet?
And we’ve believed in these lifestyle solutions because everyone around us insists they’re workable, a collective repeating mantra of “renewables, recycling” that has dulled us into belief. Like Eichmann, no one has told us that it’s wrong.
Until now. So this is the moment when you will have to decide. Do you want to be part of a serious effort to save this planet? Not a serious effort at collective delusion, not a serious effort to feel better, not a serious effort to save you and yours, but an actual strategy to stop the destruction of everything worth loving. If your answer feels as imperative as instinct, read on.
Image: copyright free via Unsplash
by DGR News Service | Feb 16, 2019 | Climate Change
by Papillon
Today on Facebook I came across an article celebrating the fact that NASA has found that the earth has greened up over the past 20 years thanks to massive tree planting in China and India.
Surely not, I thought. So I googled the phrase “NASA says world greener” and found a slew of articles published over the past 24 hours all trumpeting the news. The first 20 or so all had variations on the same headline praising China and India’s tree planting. So it must be true, right?
Unfortunately no. This is a really good example of bad science reporting, spin and “greenwashing”.
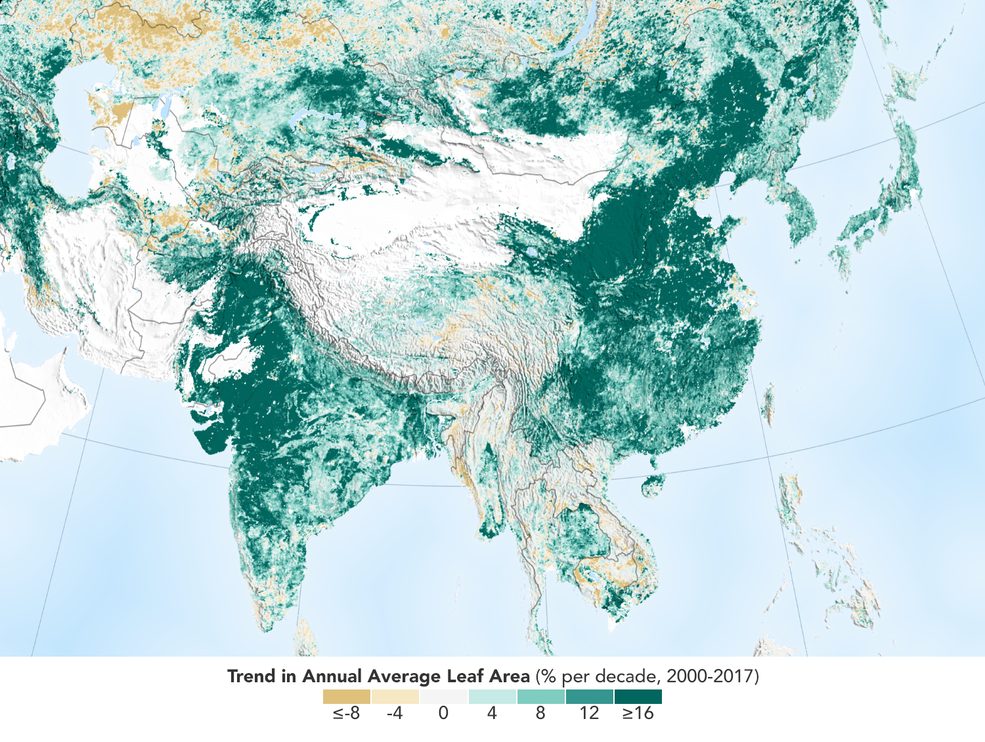
Over the last two decades, the Earth has seen an increase in foliage around the planet, measured in average leaf area per year on plants and trees. Data from NASA satellites shows that China and India are leading the increase in greening on land. The effect stems mainly from ambitious tree planting programs in China and intensive agriculture in both countries.
Credits: NASA Earth Observatory
[Image and caption copied directly from the NASA Ames Research Centre article linked below]
Regrettably, even the NASA web page about the research – which was NOT conducted by NASA at all but merely used publicly available data from NASA’s satellites – is highly misleading. And it’s all in the spin. When you talk about “China and India leading the increase” and China’s “ambitious tree planting programs” as in NASA’s caption above, you can certainly see where the commonly reported headline comes from. While the NASA article isn’t technically incorrect, the wording is very misleading. Unless you have been trained to focus on the precise meaning of every single word (as scientists like me have), you are simply not going to pick it up. But it’s spin. Fake news. Greenwash. Given an aura of legitimacy by the NASA badge.
YES, it’s true, there have been massive tree plantings in China and, to a lesser extent, India. And we should certainly be happy about that.
And YES, scientist Chi Chen and colleagues from Boston University in Massachusetts are reporting a 5% increase in average total leaf area across the entire planet over the period 2000-2017.
But tree plantings in China and India are NOT chiefly responsible for the increase in planetary greenness. What the headline should probably have said is what the scientists actually reported in their paper, namely
“Earth is 5% greener since 2000 due to the Greenhouse Effect”.
But that’s not quite as sexy, is it. Nor is it good news. In fact it’s quite the opposite.
What Chi Chen and colleagues actually found (as reported in Nature Sustainability volume 2, pages 122–129 (2019)) was:
- the earth’s Greenness Index (something detected by sensors on NASA’s MODIS satellites) has increased over the period 2000-2017 and this equates to a 5% increase in annual average total leaf area across the entire planet
- over the period 2000-2017 the total surface area covered by leaves in the planet’s vegetated zones has grown. The increase is spread out across the world but if put together would be roughly equal in size to the Amazon rainforest.
- in addition to this, about 30% of land that was already green in 2000 is even greener now and about 5% is less green now
- the “dominant drivers” of this overall increase in greenness are “climate change and CO2 fertilization effects”. In other words – the Greenhouse Effect. These indirect effects of human activity account for 70% of the increased greenness across the planet.
- the remaining 30% is due to direct effects of human activity and this is concentrated in China and India
- in China:
- 42% of the increase in greenness is due to large scale tree plantings.
- 32% of the increase in greenness is due to agricultural intensification
(that is, greater use of irrigation, fertiliser (particularly Nitrogen), pesticides and fossil fuels.)
- in India:
- only 4% of the increase is due to large scale tree plantings.
- and fully 82% of the increase is due to agricultural intensification.

A worker in China plants a pine sapling as part of the country’s ambitious plan to reforest its landscape. Credit: Xinhua/ZUMA Wire
Now, if you’ve made it this far through the article and all that accurate science reporting hasn’t put you to sleep, you’ll see that this tree story isn’t half as green as it seemed. Indeed its only 42% of 25% of 5% as green as it seemed. It’s precisely 0.525% as green as it seemed.
So the great news about the tree plantings in China (and it really IS great news) is sadly only the thin silver lining on an otherwise dark cloud of climate change and ‘business-as-usual’ industrial agriculture.
Am I disappointed the world isn’t 5% greener due to tree plantings? Yes, I am. But I am much more disappointed that the research has not been reported honestly by a respected scientific institution, and that literally dozens of news services that trust that institution are now promulgating the spin, fake news, and greenwash of its story. Why would the Ames Research Center spin the story this way? Who knows. Maybe it’s just a staffer in their communications department with a particularly optimistic disposition, who lacks the skills to actually read the original article properly. Maybe it goes much deeper than this and comes down to political influence. But regardless of where it sits on the spectrum, from inept to devious, it stinks!
If, like me, harsh realities like this tend to make you sad, angry and perhaps despairing, let me encourage you to take that energy and invest it in a positive way. Do what you can – everything you can – to stop being part of the problem and, as much as is within your power, every day strive to be part of the solution.
The original scientific publication is here:
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41893-019-0220-7
NASA’s post is here:
https://www.nasa.gov/feature/ames/human-activity-in-china-and-india-dominates-the-greening-of-earth-nasa-study-shows

by DGR News Service | Feb 14, 2019 | The Problem: Civilization
This is an excerpt from the book Deep Green Resistance – Strategy to save the planet
by Lierre Keith
You cannot live a political life, you cannot live a moral life if you’re not willing to open your eyes and see the world more clearly. See some of the injustice that’s going on. Try to make yourself aware of what’s happening in the world. And when you are aware, you have a responsibility to act.
—Bill Ayers, cofounder of the Weather Underground
A black tern weighs barely two ounces. On energy reserves less than a small bag of M&M’s and wings that stretch to cover twelve inches, she flies thousands of miles, searching for the wetlands that will harbor her young. Every year the journey gets longer as the wetlands are desiccated for human demands. Every year the tern, desperate and hungry, loses, while civilization, endless and sanguineous, wins.
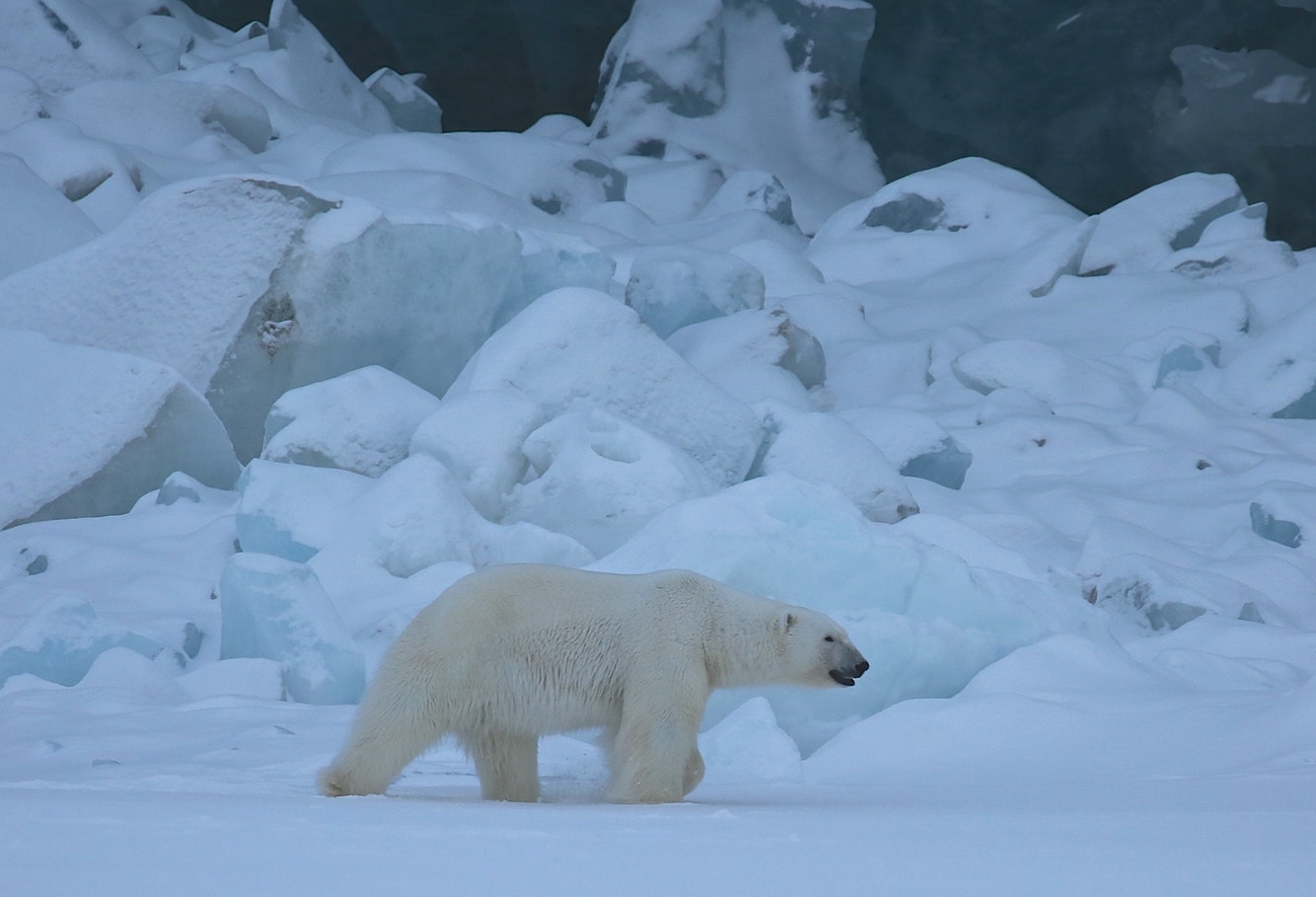
A polar bear should weigh 650 pounds. Her energy reserves are meant to see her through nine long months of dark, denned gestation, and then lactation, when she will give up her dwindling stores to the needy mouths of her species’ future. But in some areas, the female’s weight before hibernation has already dropped from 650 to 507 pounds.1 Meanwhile, the ice has evaporated like the wetlands. When she wakes, the waters will stretch impassably open, and there is no Abrahamic god of bears to part them for her.
The Aldabra snail should weigh something, but all that’s left to weigh are skeletons, bits of orange and indigo shells. The snail has been declared not just extinct10, but the first casualty of global warming. In dry periods, the snail hibernated. The young of any species are always more vulnerable, as they have no reserves from which to draw. In this case, the adults’ “reproductive success” was a “complete failure.”2 In plain terms, the babies died and kept dying, and a species millions of years old is now a pile of shell fragments.
What is your personal carrying capacity for grief, rage, despair? We are living in a period of mass extinction. The numbers stand at 200 species a day.3 That’s 73,000 a year. This culture is oblivious to their passing, feels entitled to their every last niche, and there is no roll call on the nightly news.
There is a name for the tsunami wave of extermination: the Holocene extinction event. There’s no asteroid this time, only human behavior, behavior that we could choose to stop. Adolph Eichman’s excuse was that no one told him that the concentration camps were wrong. We’ve all seen the pictures of the drowning polar bears. Are we so ethically numb that we need to be told this is wrong?
There are voices raised in concern, even anguish, at the plight of the earth, the rending of its species. “Only zero emissions can prevent a warmer planet,” one pair of climatologists declare.4 James Lovelock, originator of the Gaia hypothesis, states bluntly that global warming has passed the tipping point, carbon offsetting is a joke, and “individual lifestyle adjustments” are “a deluded fantasy.”5 It’s all true, and self-evident. “Simple living” should start with simple observation: if burning fossil fuels will kill the planet, then stop burning them.
But that conclusion, in all its stark clarity, is not the popular one to draw. The moment policy makers and environmental groups start offering solutions is the exact moment when they stop telling the truth, inconvenient or otherwise. Google “global warming solutions.” The first paid sponsor, Campaign Earth, urges “No doom and gloom!! When was the last time depression got you really motivated? We’re here to inspire realistic action steps and stories of success.” By “realistic” they don’t mean solutions that actually match the scale of the problem. They mean the usual consumer choices—cloth shopping bags, travel mugs, and misguided dietary advice—which will do exactly nothing to disrupt the troika of industrialization, capitalism, and patriarchy that is skinning the planet alive. As Derrick has pointed out elsewhere, even if every American took every single action suggested by Al Gore it would only reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 21 percent.6 Aric tells a stark truth: even if through simple living and rigorous recycling you stopped your own average American’s annual one ton of garbage production, “your per capita share of the industrial waste produced in the US is still almost twenty-six tons. That’s thirty-seven times as much waste as you were able to save by eliminating a full 100 percent of your personal waste.”7 Industrialism itself is what has to stop. There is no kinder, greener version that will do the trick of leaving us a living planet. In blunt terms, industrialization is a process of taking entire communities of living beings and turning them into commodities and dead zones. Could it be done more “efficiently”? Sure, we could use a little less fossil fuels, but it still ends in the same wastelands of land, water, and sky. We could stretch this endgame out another twenty years, but the planet still dies. Trace every industrial artifact back to its source—which isn’t hard, as they all leave trails of blood—and you find the same devastation: mining, clear-cuts, dams, agriculture. And now tar sands, mountaintop removal, wind farms (which might better be called dead bird and bat farms). No amount of renewables is going to make up for the fossil fuels or change the nature of the extraction, both of which are prerequisites for this way of life. Neither fossil fuels nor extracted substances will ever be sustainable; by definition, they will run out. Bringing a cloth shopping bag to the store, even if you walk there in your Global Warming Flip-Flops, will not stop the tar sands. But since these actions also won’t disrupt anyone’s life, they’re declared both realistic and successful.
The next site’s Take Action page includes the usual: buying light bulbs, inflating tires, filling dishwashers, shortening showers, and rearranging the deck chairs. It also offers the ever-crucial Global Warming Bracelets and, more importantly, Flip-Flops. Polar bears everywhere are weeping with relief.
The first noncommercial site is the Union of Concerned Scientists. As one might expect, there are no exclamation points, but instead a statement that “[t]he burning of fossil fuel (oil, coal, and natural gas) alone counts for about 75 percent of annual CO2emissions.” This is followed by a list of Five Sensible Steps. Step One? No, not stop burning fossil fuels—“Make Better Cars and SUVs.” Never mind that the automobile itself is the pollution, with its demands—for space, for speed, for fuel—in complete opposition to the needs of both a viable human community and a living planet. Like all the others, the scientists refuse to call industrial civilization into question. We can have a living planet and the consumption that’s killing the planet, can’t we?
The principle here is very simple. As Derrick has written, “[A]ny social system based on the use of nonrenewable resources is by definition unsustainable.”8 Just to be clear, nonrenewable means it will eventually run out. Once you’ve grasped that intellectual complexity, you can move on to the next level. “Any culture based on the nonrenewable use of renewable resources is just as unsustainable.” Trees are renewable. But if we use them faster than they can grow, the forest will turn to desert. Which is precisely what civilization has been doing for its 10,000 year campaign, running through soil, rivers, and forests as well as metal, coal, and oil. Now the oceans are almost dead and their plankton populations are collapsing, populations that both feed the life of the oceans and create oxygen for the planet. What will we fill our lungs with when they are gone? The plastics with which industrial civilization is replacing them? In parts of the Pacific, plastic outweighs plankton 48 to 1.9 Imagine if it were your blood, your heart, crammed with toxic materials—not just chemicals, but physical gunk—until there was ten times more of it than you. What metaphor is adequate for the dying plankton? Cancer? Suffocation? Crucifixion?
But the oceans don’t need our metaphors. They need action. They need industrial civilization to stop destroying and devouring. In other words, they need us to make it stop.
Which is why we are writing this book.

by DGR News Service | Feb 13, 2019 | Colonialism & Conquest
by Rudolph C. Rÿser / Intercontinental Cry
Ever since the German Nazis committed horrendous mass murders of Jews, homosexuals, Roma, and Catholics, many commentators, analysts and scholars have made the mistake of associating “genocide” with “executions and gassing” of people en masse.
The originator of the term “genocide” attorney and author Raphael Lemkin’s analysis essentially explains this error when his analysis points to how the Holocaust is not a synonym for genocide, but the consequence of Nazi imperialism and Colonialism in Europe. While the massive murders by the Nazi government was a horrific case of human destruction the genocide had already begun before the killings. Read from Lemkin’s book, Axis Rule in Occupied Europe (Washington, DC: Carnegie Council, 1944) on page 79 how he describes genocide:
Genocide has two phases: one, destruction of the national pattern of the oppressed group: the other, the imposition of the national pattern of the oppressor. This imposition, in turn, may be made upon the oppressed population, which is allowed to remain, or upon the territory alone, after removal of the population and the colonization of the area by the oppressor’s own nationals.
In other words, when a distinct people is systematically occupied by an outside population with the intention of replacing that population with the invading people under the instrumentality of a government or other organized agent monopolizing violence, that process is genocide. All events after the occupation—the Colonization—are the result of the initial genocide.
Scholars claim that there have been no fewer than 181 “genocides” since what they describe as the “beginning of genocides” in 1945–that is, instances where human beings have been massively killed with the intention of destroying that human population.
The Center for World Indigenous Studies is conducting a study of “Genocides against Fourth World Peoples” to learn about the extent of genocide (in the Lemkin sense and in the latter-day scholars’ sense) committed against Fourth World peoples and what alternatives exist to establish justice and prevent occurrences of genocide.
By simply examining the continental figures for Africa, the Americas, Asia, Europe and the Middle East gathered by contemporary scholars tabulating the killings of groups by particular perpetrators we find that 156 Fourth Nations have been invaded with the resultant killing of an estimated 12.482 million people between 1945 and 2017.
Up to 58 UN member state governments and the militias they supported were responsible for all 156 invasions and ultimate killings of Fourth World peoples.
ESTIMATED POST-GENOCIDE KILLINGS FROM 1945-2017
| CONTINENT |
PEOPLE KILLED |
FW NATIONS OCCUPIED |
| Africa |
7,153,400 |
77 |
| Americas |
544,000 |
15 |
| Asia |
3,953,500 |
34 |
| Europe |
400,000 |
12 |
| Middle East |
431,100 |
18 |
| TOTALS |
12,482,000 |
156 |
© CWIS 2018
Our initial finding is that “governments” (Republics, Dictatorships, Empires, Kingdoms) commit the vast majority of genocides in both the Lemkin and the latter-day scholars’ sense.
According to our estimate, UN member states committed an average of 51% of all 181 incidents of genocide counted by contemporary scholars. That figure alone is astonishing, since invasions and killings of Fourth World nations account for about 86% of all “genocides” counted by contemporary scholars since 1945.
Clearly by these numbers alone, cultural genocide and massive killings constitute a major feature of genocide over the last 70 years and beyond. But, curiously, despite the International Convention on Genocide (1948) and the Rome Statute of 2002 that created the International Criminal Court, the cultural genocide of a people in whole or in part has not been prosecuted. And, of equal interest is the fact that not one of the governments responsible for invasions and then killing of Fourth World people has been sanctioned by the international community or any juridical forum.
Ongoing genocides are taking place now in China against the Uyghurs, Iraq against the Yezidi, Madaeans, Zoroastrians, and Assyrians; and against the Rohingya in Burma; and many other nations.
CASE STUDY: THE INDIGENOUS UYGHURS
Many Fourth World nations are suffering under invasion, occupation and killings similar to the Rohingya in southwestern Burmawhat and the Uyghurs. States cannot be permitted to continue the carnage.
Uyghuristan is the homeland of more than 12 million Uyghurs neighboring Mongolia, China, Russia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, and Afghanistan. It has been an established nation of people for more than 2,500 years and the peoples’ written history extends to 1,480 BP. According to the TENGRITAGH AKADEMIYESI Uyghur Academy of Arts and Science Uyghurs were identified by Europeans as “Turkic” and referred to as “Taranchi.” The Russians referred to the Uyghurs as “Sart” or “Turk.” That their language is related to neighboring Turkic languages may have been the reason for these misapplied names. The Kuomintang government of China grouped all Uyghurs as part of the 11 million mostly Moslem Hui people who are located in northwestern China. Despite the practice of Islam, they are completely separate peoples.
Since the Peoples’ Republic of China under Mao Zedong and his successors annexed Uyghuristan the Uyghurs have pursued their independence and have frequently attempted to call the world’s attention to China’s cultural genocide against the Uyghurs.
Until China claimed Uyghuristan in 1949, the Uyghur population constituted more than 94% of the total population in the country. China has systematically relocated Han Chinese into Uyghuristan reducing the Uyghur proportion of the total population to a little more than 45%. Effectively the Chinese have committed cultural genocide by invading, occupying and attempted to replace the Uyghur population with its own population. The Uyghur resistance is strong and persistent to the point where the Chinese government as recently as 25 January 2018 began placing Uyghurs in “re-education camps” to force their fealty to the Chinese government. They have imprisoned tens of thousands and, under the veil of “terrorism” as their justification, killed many thousands more.
Yes, 156 Fourth World nations have suffered cultural genocide since 1945 and not one government responsible for invasions and killings of millions of people have been called to account.
Rudolph Ryser is the Chair of the Center for World Indigenous Studies.








