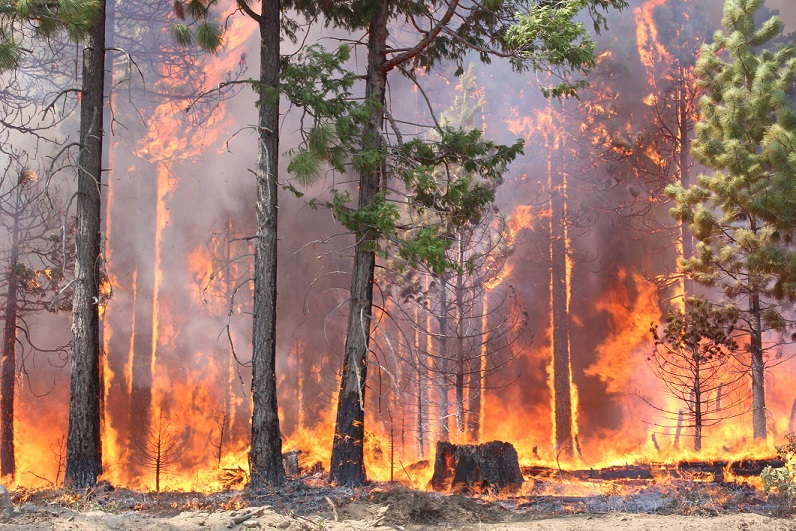

by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Sep 30, 2017 | Biodiversity & Habitat Destruction
Editor’s note: The following is the testimony of Dr. Dominick A. DellaSala, Chief Scientist of Geos Institute, Ashland, Oregon, before the U.S. House of Representatives Natural Resources Committee, Subcommittee on Oversight and Investigations, “Exploring Solutions to Reduce Risks of Catastrophic Wildfire and Improve Resilience of National Forests,” on September 27, 2017.
Chairman Westerman, Ranking member Hanabusa, and subcommittee members, thank you for the opportunity to discuss wildfires on national forests. I am the Chief Scientist of the nonprofit organization, Geos Institute in Ashland, Oregon. Geos Institute works with agencies, landowners, and decision makers in applying the best science to climate change planning and forest management. As a scientist, I have published in peer-reviewed journals on fire ecology and climate change, I am on the editorial board of several leading journals and encyclopedias, and I have been on the faculty of Oregon State University and Southern Oregon University. A recent book I co-authored with 28 other scientists outlined the ecological importance of mixed-severity fires in maintaining fire-resilient ecosystems, including ways to coexist with wildfire (DellaSala and Hanson 2015).
Wildfires are necessary natural disturbance processes that forests need to rejuvenate. Most wildfires in pine and mixed-conifer forests of the West burn in mixed fire intensities at the landscape scale that produce large and small patches of low to high tree mortality. This tapestry of burned patches is associated with extraordinary plant and wildlife diversity, including habitat for many big game and bird species that thrive in the newly established forests. From an ecosystem perspective, natural disturbances like wildfires are not an ecological catastrophe. However, given there are now 46 million homes in naturally fire-prone areas (Rasker 2015), and no end in sight for new development, we must find ways to coexist with natural disturbance processes as they are increasing in places due to climate change.
In my testimony today, I will discuss how proposals that call for increased logging and decreased environmental review in response to wildfires and insect outbreaks are not science driven, in many cases may make problems worse, and will not stem rising wildfire suppression costs. I will also discuss what we know about forest fires and beetle outbreaks in relation to climate change, limitations of thinning and other forms of logging in relation to wildfire and insect management, and I will conclude with recommendations for moving forward based on best available science.
I. WHAT WE KNOW ABOUT RECENT FOREST FIRE INCREASES
Recent increases in acres burned of forests are mainly due to a changing climate – Scientists have known for sometime that fire activity tracks regional weather patterns, which in turn, are governed by global climatic forces such as the Pacific Decadal Oscillation (PDO – a recurring long-lived El Niño-like pattern of Pacific climate variability– see chart 1). For instance, the very active fire seasons of the 1910-1930s, occurred during prolonged drought cycles determined by the PDO that resulted in much larger areas burning historically than today (Powell et al. 1994; Interagency Federal Wildland Fire Policy Review Working Group 2001; Egan 2010) (chart 1). In fact, compared to the historic warm PDO phase of the early 1900s, most of the West is actually experiencing a fire deficit (Littell et al. 2009, Parks et al. 2012). However, with warming temperatures, early spring snowmelt, and longer fire seasons over the past few decades more acres are burning each year (Westerling et al. 2006; Littell et al. 2009) (chart 1).
For instance, wildfire season in the West has lengthened from an average of five to seven months, and the number of large wildfires (>1,000 acres) has increased since the 1980s (Dennison et al. 2014) from 140 to 250 per year (UCS 2017). This is occurring as average annual temperature in the West has risen by nearly 2 degrees F since 1970s and winter snow pack has declined (UCS 2017). If measures are not taken to stem greenhouse gas emissions, wildfire acres are projected to increase further in dry areas as annual temperatures are expected to rise another 2.5 to 6.5 degrees F by mid century (UCS 2017). Some researchers estimate more than half of the increase in acres burned over the past several decades is related to climate change (Abatzoglou and Williams 2016). This increase is expected to continue with additional warming leading to even greater suppression costs if the agencies continue to suppress fires across the landscape (Schoennagel et al. 2017).
Increasing Human Development is Lengthening Wildfire Seasons and Adding to Fire Ignitions – The direct role of human-access via roads and development in the Wildlands Urban Interface (WUI) is increasing wildfire activity. Scientists recently evaluated over 1.5 million government records of wildfires nationwide from 1992 to 2012 (Balch et al. 2015). During that time, human-caused fire ignitions have vastly expanded the spatial and seasonal occurrence of fire, accounting for 84 percent of all wildfire starts and 44 percent of the total area burned nationally. We now have the phenomenon of a human-caused fire season, which was three times longer than the lightning-caused fire season and added an average of 40,000 wildfires per year across the US over this 20-year period of time. Ignitions caused by people – whether accidental or arson – have substantial economic costs. This will only worsen with continued development of the WUI adding to the 46 million homes (Rasker 2015) already in these fire-prone areas.
Thus, given expansion of homes in the WUI, the best way to limit damage to homes is to reduce fire risks by working from the home-outward instead of the wildlands-inward (Syphard et al. 2013). For instance, if a fire-brand travels miles ahead and lands on a flammable roof that home is very likely to burn compared to a home that has a fire resistant roof and cleared vegetation within a narrow defensible space of 100-200 feet immediately surrounding the home (Cohen 2000). Logging outside of this narrow zone does not change home ignition factors.
II. WHAT WE KNOW ABOUT FIRE AND FOREST MANAGEMENT
Wilderness and other protected areas are not especially prone to forest fires – proposals to remove environmental protections to increase logging for wildfire concerns based on the assumption that unmanaged – or protected areas – burn more intensely are misplaced. For instance, scientists (Bradley et al. 2016 of which I was a co-author) recently examined the intensity of 1,500 forest fires affecting over 23 million acres during the past four decades in 11 western states. We tested the common perception that forest fires burn hottest (most intensely) in wilderness and national parks while burning cooler (less intensely) or not at all in areas where logging had occurred. What we found was the opposite – fires burned most intense in previously logged areas, while they burned in natural fire mosaic patterns in wilderness, parks, and roadless areas, thereby, maintaining resilient forests (see chart 2). Consequently, there is no reason for reducing environmental protections.
State lands are not at lower wildfire risks compared to federal lands – there is much discussion about whether state lands are being managed in a way that reduces fire occurrence and intensity. However, in a recent report of wildfire risk (that included acres likely to burn), scientists (Zimmerman and Livesay 2017) used the West Wide Wildfire Risk Assessment model, an important assessment tool of the Council of Western State Foresters and Western Forestry Leadership Coalition. They evaluated risk for western states based on historical fire data, topography, vegetation, tree cover, climate, and other factors. According to the Center for Western Priorities analysis, state (22%) and federal (23%) lands have approximately equivalent levels of fire risks in the West, and for some states, risks were higher than federal lands. Notably, allegations of higher fire risk based solely on the number of federal acres burned in a fire season are misleading as there are over 7 times as many federal lands (362 million acres) in 11 Western states as compared to state-owned lands (49 million acres) (Zimmerman and Livesay 2017).
Thinning is Ineffective in Extreme Fire Weather – thinning/logging is most often proposed to reduce fire risk and lower fire intensity. Thinning-from-below of small diameter trees followed by prescribed fire in certain forest types can reduce fire severity (Brown et al. 2004, Kalies and Kent 2016) but only when there is not extreme fire weather (Moritz et al. 2014, Schoennagel et al. 2017). Fires occurring during extreme fire-weather (high winds, high temperatures, low humidity, low fuel moisture) will burn over large landscapes, regardless of thinning, and in some cases can burn hundreds or thousands of acres in just a few days (Stephens et al. 2015, Schoennagel et al. 2017). Fires driven by fire weather are unstoppable and are unsafe for fire fighters to attempt putting them out, and, as discussed, are more likely under a changing climate.
Further, there is a very low probability of a thinned site actually encountering a fire during the narrow window when tree density is lowest. For example, the probability of a fire hitting an area that has been thinned is about 3-8% on average, and thinning would need to be repeated every 10-15 years (depending on site productivity) to keep fuels at a minimum (Rhodes and Baker 2008).
Thinning too much of the overstory trees in a stand, especially removal of large fire-resistant trees, can increase the rate of fire spread by opening tree canopies and letting in more wind, can damage soils, introduce invasive species that increase flammable understory fuels, and impact wildlife habitat (Brown et al. 2004). Thinning also requires an extensive and expensive roads network that can degrade water quality by altering hydrological functions, including chronic sediment loads.
Post-disturbance salvage logging reduces forest resilience and can raise fire hazards –commonly practiced after natural disturbances like fires or insect outbreaks, post-disturbance logging hinders forest resilience by compacting soils, killing natural regeneration of conifer seedlings and shrubs associated with forest renewal, increasing fine fuels from slash left on the ground that aids the spread of fire, removing the most fire-resistant large live and dead trees, and degrading fish and wildlife habitat. Further roads that increase sediment flow to streams triggering widespread water quality problems (Lindenmayer et al. 2008).
III. WHAT WE KNOW ABOUT BEETLE-KILLED FORESTS AND FOREST MANAGEMENT
Beetle Killed Forests are Not More Susceptible to Forest Fires – forests in the West are being affected by the largest outbreaks of bark beetles in decades, which has caused concern about forest resilience and wildfire risk and led to proposals for widespread tree removals. Such proposals stem in part from the rationale that bark beetle outbreaks increase wildfire risks due to dead trees and that logging in beetle-affected forests would therefore lower such risks. However, beetle-killed forests are not more susceptible to forest fires (Bond et al. 2009, Hart et al. 2015, Meigs et al. 2016). This is mainly because when conifers die due to drought or native bark beetles, the combustible oils in the needles quickly begin to dissipate, needles and small twigs begin to fall to the ground. Without the fine fuels that facilitate fire spread, potential crown fires are actually lowered in forests with beetle mortality (Donato et al. 2013). The beetle-killed standing dead trees (snags) are the least flammable part of the forest and act more like a large log in a campfire, rather than kindling which is what causes fire spread.
In fact, studies of beetle-killed forests in the West found that when fires occurred during or immediately after the pulse of snag recruitment from beetle kill, fire severity consistently declined in the stands with high snag densities in the following decades (Meigs et al. 2016). In pine and mixed-conifer forests of the San Bernardino National Forest (CA), fires occurred immediately after a large pulse of snag recruitment from drought and beetles. However, scientists (Bond et al. 2009) found “no evidence that pre-fire tree mortality influenced fire severity.” In studies of beetles and wildfires across the western U.S., scientists (Hart et al. 2015) stated “contrary to the expectation of increased wildfire activity in recently infested red-stage stands, we found no difference between observed area and expected area burned in red-stage or subsequent gray-stage stands during three peak years of wildfire activity, which account for 46 percent of area burned during the 2002–2013 period.” And finally, in a comprehensive review of fire-beetle relations in mixed-conifer and ponderosa pine forests of the Pacific Northwest, scientists (Meigs et al. 2016) found: “in contrast to common assumptions of positive feedbacks, we find that insects generally reduce the severity of subsequent wildfires. Specific effects vary with insect type and timing, but insects decrease the abundance of live vegetation susceptible to wildfire at multiple time lags. By dampening subsequent burn severity, native insects could buffer rather than exacerbate fire regime changes expected due to land use and climate change.”
Most importantly, climate change is allowing more insects to survive the winter, triggering the rash of recent outbreaks (Meigs et al. 2016).
Thinning cannot limit or contain beetle outbreaks – once beetle populations reach widespread epidemic levels, thinning treatments aimed at stopping them do not reduce outbreak susceptibility as beetles over run natural forest defenses with or without thinning (Black et al. 2013).
IV. CLOSING REMARKS AND RECOMMENDATIONS
In sum,
Recent increases in wildfires and insect outbreaks are a result of a changing climate coupled with human-activities including expansion of homes and roads into the WUI that will only continue to drive up fire suppression costs.
Policies should be examined that discourage continued growth in the WUI; any new development must include defensible space and construction from non-flammable materials.
The most effective way to protect homes is to create defensible space in the immediate 100 feet of a structure and use of non-flammable materials. Wildland fire policy should fund defensible space, not more logging and thinning miles away from communities.
No amount of logging can stop insect outbreaks or large fires under extreme fire weather. Logging may, in fact, increase the amount of unnatural disturbances by homogenizing landscapes with more even aged trees, residual slash left on the ground, and compounding cumulative impacts to ecosystems.
Thinning of small trees in certain forest types, maintaining canopy closure and in combination with prescribed fire can reduce fire intensity but treatment efficacy is limited in extreme fire weather, and by the small chance that a thinned site will encounter a fire during a very narrow window when fuels are lowest.
CITATIONS
Balch, J. K., B.A. Bradley, J.T. Abatzoglou et al. 2016. Human-started wildfires expand the fire niche across the United States. PNAS 114: 2946-2951.
Black, S.H., D. Kulakowski, B.R. Noon, and D.A. DellaSala. 2013. Do bark beetle outbreaks increase wildfire risks in the Central U.S. Rocky Mountains: Implications from Recent Research. Natural Areas Journal 33:59-65.
Bond, M.L., D.E. Lee, C.M. Bradley, and C.T. Hanson. 2009. Influence of pre-fire tree mortality on fire severity in conifer forests of the San Bernardino Mountains, California. The Open Forest Science Journal 2:41-47.
Bradley, C.M., C.T. Hanson, and D.A. DellaSala. 2016. Does increased forest protection correspond to higher fire severity in frequent-fire forests of the western United States? Ecosphere 7:1-13.
Brown, R.T., J.K. Agee, and J.F. Franklin. 2004. Forest restoration and fire: principles in the context of place. Conservation Biology 18:903-912.
Cohen, J.D. 2000. Preventing disaster: home ignitability in the wildland-urban interface. Journal of Forestry 98: 15-21.
DellaSala, D.A., and C.T. Hanson. 2015. The ecological importance of mixed-severity fires: nature’s phoenix. Elsevier: Boston, MA.
Dennison, P., S. Brewer, J. Arnold, and M. Moritz. 2014. Large wildfire trends in the western United States, 1984-2011. Geophysics Research Letters 41:2928-2933.
Donato, D.C., B.J. Harvey, W.H. Romme, M. Simard, and M.G. Turner. 2013. Bark beetle effects on fuel profiles across a range of stand structures in Douglas-fir forests of Greater Yellowstone. Ecological Applications 23:3-20.
Egan, T. 2010. The Big burn. Huffman Mifflin Harcourt: Boston.
Hart, S.J., T.T. Veblen, N. Mietkiewicz, and D. Kulakowski. 2015. Negative feedbacks on bark beetle outbreaks: widespread and severe spruce beetle infestation restricts subsequent infestation. PlosOne: DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0127975
Kalies, E.I., and L.L. Yocom Kent. 2016. Tamm Review: Are fuel treatments effective at achieving ecological and social objectives? A systematic review. Forest Ecology and Management 375-84-95.
Lindenmayer, D.B., P.J. Burton, and J.F. Franklin. 2008. Salvage logging and its ecological consequences. Island Press: Washington, D.C.
Littell, J.S., D. McKenzie, D.L. Peterson, and A.L. Westerling. 2009. Climate and wildfire area burned in western U.S. ecoprovinces, 1916-2003. Ecological Applications 19:1003-1021.
Meigs, G.W., H.S.J. Zald, J. L. Campbell, W.S. Keeton, and R.E. Kennedy. 2016. Do insect outbreaks reduce the severity of subsequent forest fires? Environmental Research Letters 11 doi:10.1088/1748-9326/11/4/045008.
Moritz, M.A., E. Batllori, R.A. Bradstock, A.M. Gill, J. Handmer, P.F. Hessburg, J. Leonard, S. McCaffrey, D.C. Odion, T. Schoennagel, and A.D. Syphard. 2014. Learning to coexist with wildfire. Nature 515: 58-66.
Parks, S.A., C. Miller, M.A. Parisien, L.M. Holsinger et al. 2012. Wildland fire deficit and surplus in the western United States, 1984-2012.
Powell, D.S., J.L. Faulkner, D.R. Darr, et al. Forest resources of the United States, 1992. USDA Forest Service General Technical Report RM-234 (revised).
Rasker, R. 2015. Resolving the increasing risk from wildfires in the American West. www.thesolutionsjournal.org; March-April 2015 p. 55- 62.
Rhodes, J.J., and W.L. Baker. 2008. Fire probability, fuel treatment effectiveness and ecological tradeoffs in western U.S. public forests. The Open Forest Science Journal 1: 1-7.
Schoennagel, T., J.K. Balch, H. Brenkert-Smith, P.E., Dennison, et al. 2017. Adapt to more wildfire in western North American forests as climate changes. PNAS
114:4582-4590.
Stephens, S.L., M. P. North, and B.M. Collins. 2015. Largte wildfires in forests: what can be done? ActionBioscience April 15
Syphard, A. D., A. Bar Massada, V. Butsic, and J. E. Keeley. 2013. Land use planning and wildfire: development policies influence future probability of housing loss. PLoS ONE 8(8):e71708
Union of Concerned Scientists (UCS). 2017. Western wildfires and climate change. http://www.ucsusa.org/…/infographic-wildfires-climate-chang…
Westerling, A.L., H.G. Hidalgo, D.R. Cayan, and T.W. Swetnam. 2006. Warming and earlier spring increase western U.S. forest wildfire activity. Science 313:940-943.
Zimmerman, G., and L. Livesay. 2017. Fire lines: comparing wildfire risk on state and U.S. public lands. Center for Western Priorities.
http://westernpriorities.org/…/fire-lines-comparing-wildfi…/
by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Sep 25, 2017 | Colonialism & Conquest
Featured image: World Wildlife Fund (WWF) has been working in the Congo Basin for decades – supporting squads who have committed violent abuse against tribal people. © WWF
by Survival International
A new Survival International report details widespread and systematic human rights abuses in the Congo Basin, by wildlife guards funded by the World Wildlife Fund (WWF) and other big conservation organizations.
The report documents serious instances of abuse between 1989 and the present day in Cameroon, the Republic of Congo, and the Central African Republic (CAR) by guards funded and equipped by WWF and the Wildlife Conservation Society (WCS), the parent organization of New York’s Bronx zoo.
It lists more than 200 instances of abuse since 1989, including pouring hot wax onto exposed skin, beating, and maiming with red-hot machetes. These incidents are likely just a tiny fraction of the full picture of systematic and ongoing violence, beatings, torture and even death.
As well as these especially cruel incidents, the report also documents the forms of harassment that have become part of everyday life for many people, including threats, and the destruction of food, tools and personal belongings.
Read the full report here.

WWF funded guards in Gabon. © WWF
As well as Survival, over the past three decades, numerous independent experts and NGOs have raised concerns about these abuses. These have included NGOs like Greenpeace, Oxfam, UNICEF, Global Witness, Forest Peoples Programme, and research specialists from University College London, the University of Oxford, Durham University, and Kent University.
WWF and WCS have even partnered with several logging companies, despite evidence that their activities are unsustainable, and have not had the consent of tribal peoples as required by international law and their own stated policies.
One Bayaka man said: “A wildlife guard asked me to kneel down. I said: “Never, I could never do that.” He said: “If you don’t get down on your knees I’m going to beat you.”
A Baka woman said: “They took me to the middle of the road and tied my hands with rubber cord. They forced my hands behind my back and cut me with their machete.”

Survival has documented hundreds of instances of abuse, and collected testimonies from many “Pygmy” people. © Survival International
A Bayaka woman said: “They started kicking me all over my body… I had my baby with me. The child had just been born three days before.”
Tribal peoples have been dependent on and managed their environments for millennia. Their lands are not wilderness. Evidence proves that tribal peoples are better at looking after their environment than anyone else.
But big conservation organizations like WWF are partnering with industry and tourism and destroying the environment’s best allies. Now tribal people are accused of “poaching” because they hunt to feed their families. And they face arrest and beatings, torture and death, while big game trophy hunters are encouraged.
Survival’s Director Stephen Corry said: “This shocking report lays out, in detail, the abuse and persecution that “conservation” has brought the indigenous and tribal peoples of the Congo Basin. These are just the cases that have been documented, it’s impossible to imagine there aren’t a lot more which remain hidden.
“The big conservation organizations should admit that their activities in the region have been catastrophic, both for the environment and for the tribal peoples who guarded these forests for so long.
“WWF and WCS supporters might ask these organizations how they could have let this situation carry on for so long – and what they’re going to do now to make sure it stops.”
“Pygmy” is an umbrella term commonly used to refer to the hunter-gatherer peoples of the Congo Basin and elsewhere in Central Africa. The word is considered pejorative and avoided by some tribespeople, but used by others as a convenient and easily recognized way of describing themselves.

by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Sep 24, 2017 | Alienation & Mental Health
by Lara Gardner / Random Thoughts on Everything & Nothing
The Eagle Creek fire is destroying forests all around Mt. Hood in Oregon and across the river in Washington. There are many fires raging, but this one is particularly wretched because it is known that it was begun by a teenager playing with fireworks. The woman who reported his action and the actions of the other teens with him described them as non-reactive to the likelihood they had started a fire in a very dry forest (see the story here). She said the girls were giggling and that they all were encouraging his behavior. They filmed it, like it was something fun to put on SnapChat or something. The woman’s description of these kids sounded like children who are very disconnected from their actions and the consequences for those actions.
In My Name is Chellis and I’m in Recovery from Western Civilization, Chellis Glendinning describes the split, the dissociation from the self, that occurs in humans when they become “civilized.” Civilization is built on abuse and destruction. We began by destroying the land in order to grow things according to our own will. This led to abuse upon abuse upon abuse, to the point where abuse is the norm. Derrick Jensen, in The Myth of Human Supremacy, describes how in western civilization, we are indoctrinated from the moment of birth into a belief system whereby humans rule everything and that all the world is at their disposal. To my mind, the original sin was that of humans leaving the earth to “tame” and control it, bending it to their will, first through agriculture and on to the world we have today, where every aspect of the world is under human control. The Garden of Eden was the world before humans decided that they were “special” and that everything should be as humans decree. Thus, the split was born. Humans disconnect first from their selves, then from others, and finally from the world around them. Humans are the most invasive species, and the world is suffering because of it.
Today, that indoctrination begins practically before a child is born. It is not uncommon in this country for doctors and parents to schedule births induced by chemicals. That such births often result in the death of the fetus or the mother, or in an invasive surgical Caesarean section is no matter; it is a given that in most western births, induction of some sort will be the norm. Those of us who choose to have children at home with no drugs or medical intervention are considered bizarre and dangerous, as if the control of the hospital and the intervention of drugs is the more safe, and therefore, more sane route to childbirth. We are the wild west parents, putting ourselves and our delicate children in danger rather than having a birth controlled by chemicals and machines (or a doctor’s golf schedule).
Once the child is born, it is immediately placed into a system designed to disconnect it from anything remotely resembling connection to the self or its parents. The split is encouraged early. A “good” baby is one that sleeps all night as young as possible, without interrupting its parent’s lifestyle. One of the most common early questions of new parents is whether their child is sleeping through the night (because a baby who isn’t sleeping through the night makes it impossible for parents to sleep through the night, and discomfort of any kind is to be avoided at all costs in civilization).
Thousands of books have been written on the subject of getting children to sleep through the night alone. Doctors create systems such as that of Dr. Richard Ferber, whereby parents let their tiny infants scream and cry until they learn that their cries bring nothing and they finally give up and shut up. It is the ultimate in teaching children from a very early age not to trust that the world around them will be safe and welcoming. The parents hover outside, periodically going in and patting the child, then retreating to let it cry even further, viewing the action from a monitor in another room. It is pure insanity.
Children cannot tolerate sleeping away from their parents, and small babies need to be fed more frequently than once every eight hours, but never mind this. Parents still do it in western culture. Children are placed in cages in separate rooms away from their parents to sleep alone within days of birth. The parents hover over electronic monitors and cameras, rather than have their children in the same room or indeed, even in the same bed as them. In western civilization, a child who sleeps with its parents is considered to be “spoiled,” like a piece of meat gone bad. I have often wondered how bizarre it would be if wolves and bears laid their cubs in separate caves far from their mothers. What if mice placed each bare infant in multiple holes far from their warm breasts? Mammals have breasts for feeding infants. Only human mammals place their children in cages far from their breasts forcing them to ignore their own needs and call it normal (it’s an entire other subject and outside the scope of this rant how our language encourages all this crazy nonsense).
In addition to putting children in cages and ignoring their basic needs, parents feed them fake milk from plastic nipples rather than from their own breasts. In spite of multiple studies showing that this is bad for babies, bad for mothers, and even bad for the economy (which I could care less about, but which is a major force in this culture), breastfeeding children as long as nature intended remains a rare thing indeed among western mothers.
By the time children are two or three years old, they are already completely desensitized from what they were meant to be biologically. With the advent of iPads and other screen devices that further entertain and rewire the brain (see here, and here, and here), screens as babysitters are the norm. It’s no wonder that by the time some children are teenagers, they can toss firecrackers into a dry ravine and giggle as a fire begins to rage.
I could go on and on. This culture is crazy. Civilization is not how life is meant to be on this planet. We are the Earth. The Earth is us. Yet we continue to pretend we are separate and above it even as the obvious fact that we are not and that our attempts to control everything do not work. Mama Nature knows what is best. Sadly, we seem unable to see what is right in front of our faces and senseless destruction is the result.

by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Sep 23, 2017 | Male Violence
by Meghan Murphy / Feminist Current
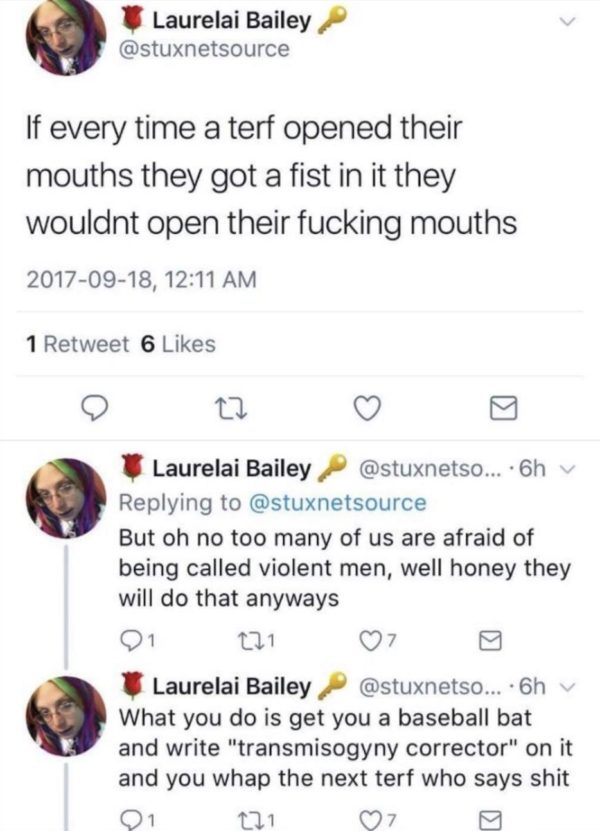
Last week, a 60-year-old woman was beaten up at Speaker’s Corner by several men. She was there with a group of women, who had chosen the historic corner of Hyde Park as a meeting place, before heading off to a talk called, “What is Gender.” The men who punched and kicked Maria MacLachlan had come to protest the women on account of their interest in feminism and in discussing the way new conversations and legislation around “gender identity” could impact the women’s movement and women’s rights. The protestors did not frame their anger and inflammatory rhetoric in this way, though. Instead, they labelled the women “TERFs” (trans exclusionary radical feminists) — a word that has come to signify a modern witch: to be silenced, threatened, harassed, punched, and — yes — killed.
The idea that feminists who question the notion of “gender identity” should be beaten and murdered has very rapidly become accepted by self-described leftists. We’re not just talking about Twitter eggs, here. Men with large platforms who are publicly associated with Antifa and groups like the Democratic Socialists of America (DSA) have amplified the “punch TERFs” and “TERFs get the guillotine” message proudly, with the support of their comrades. In reference to The Handmaid’s Tale, many have taken to saying “TERFs get the wall.”
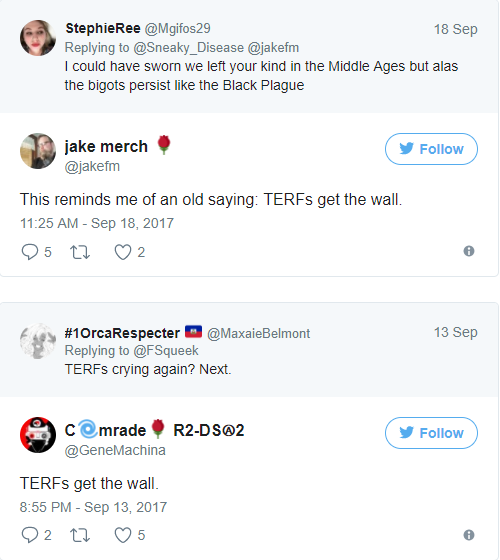
The comparison is a surprisingly (and frighteningly) truthful admission in terms of the intent of these men. “The wall” in The Handmaid’s Tale is where executed bodies are hung, often with placards around their necks that read “Gender Treachery.” The dead bodies serve as a warning to others: do not rebel, do not fight back, do not reject the patriarchal order of things. And this is precisely what these men who use the term “TERF” are saying to women: obey our rule or you will be punished.
Rather than condemning the violence at Speaker’s Corner, numerous trans activists and self-identified leftist men have celebrated and encouraged it.
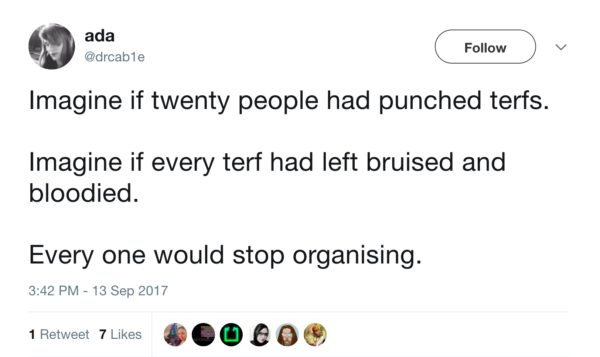
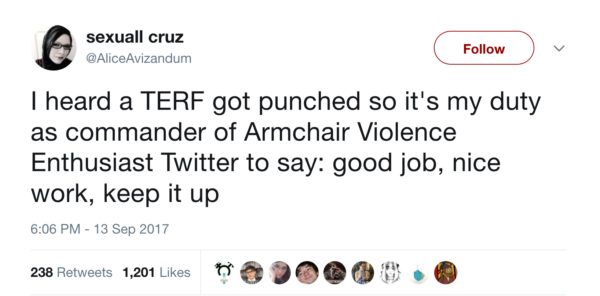
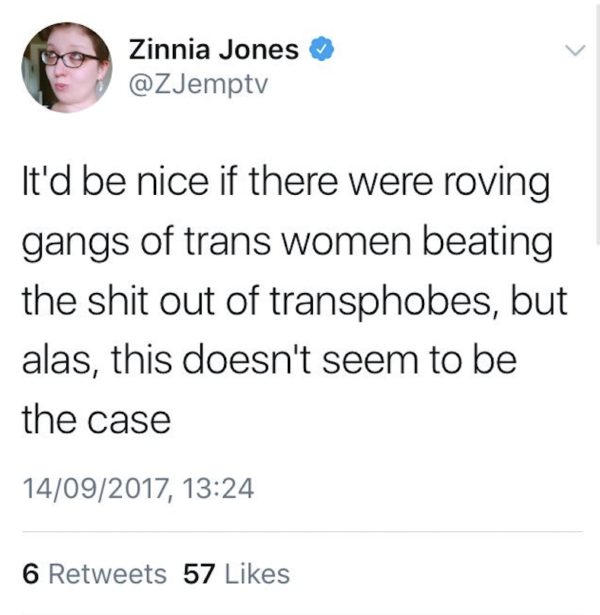




While some will claim the word “TERF” is neutral, it’s use demonstrates the opposite. It is not a word that women have claimed for themselves — like “slut,” “cunt,” or “bitch,” “TERF” is a word imposed on women to shut them up, bully them, condemn them, smear them, humiliate them, and dismiss them. But more than that: it is a threat. If I think about the times in my life I have been called these words — cunt, bitch, slut — by a man, I have almost always felt the threat of violence behind them. The spitting rage behind those words — the desire to follow through with a punch — is too often present. I have always known these words are used against me as an explicit reminder: you are subordinate. No matter how confident, tough, self-assured, strong, or brave a woman is, these words still put her in her place.
The term, “TERF,” is itself is an intentional manipulation, intended to reframe feminist ideas and activism as “exclusionary,” rather than foundational to the women’s liberation movement. In other words, it is an attack on women-centered political organizing and the basic theory that underpins feminist analysis of patriarchy.
For example, those of us called “TERF” are labelled as such for numerous crimes, including:
- Understanding that women are members of an oppressed class of people (a sex class or caste, as feminists like Kate Millett and Sheila Jeffreys have called it)
- Challenging the notion of innate or internal gender
- Having conversations about “gender identity”
- Questioning whether or not children should begin the process of transitioning
- Associating with or defending women who have been labelled “TERF”
- Understanding that the root of women’s oppression and male supremacy is in biological sex
- Understanding that gender is imposed, and is oppressive/exists to create a hierarchy between men and women.
- Questioning dogma and mantras like “transwomen are women”
- Supporting woman-only space
- Disputing an ideology that claims “male” and “female” are not a material reality
These things are not only not criminal, but are at the root of feminism. In other words, in order to understand how patriarchy works, you must first understand who is a member of the dominant class and who is a member of the subordinate class. You must understand that male violence against women is systemic. You must understand that women are not inherently “feminine,” and that men are not inherently “masculine.” You must be willing to have critical conversations and ask challenging questions about the status quo, about dominant ideology, and about political discourse. You must understand that patriarchy began as a means to control women’s reproductive capacity, and that, therefore, women’s biology is very much central to their status as “less than.” You must understand that feminism is a woman-centered movement, and that women have the right to meet and to organize amongst themselves, without members of the oppressor class (men), to advocate toward their own liberation.
What people are saying when they say “TERF” is “feminist.” It is “uppity woman.” What they mean when they say “exclusionary” is not, as is often claimed, “exclusive of trans-identified people,” but “exclusive of males.” Gender non-conformity is welcomed in feminism — feminism is about not conforming to gender norms. If we were interested in conforming, we would, as is often suggested to us, sit down and shut up.
While “TERF” has always been a slur, what has become clear of late is that it is no longer just that: it is hate speech.
Deborah Cameron, a feminist linguist and professor in language and communication at Oxford, explains that there are key questions we must ask to determine whether a term constitutes a slur, such as:
- Has the term been imposed or has it been adopted voluntarily by the group the term has been applied to?
- Is the word commonly understood to convey hatred or contempt?
- Does the word have a neutral counterpart which denotes the same group without conveying hatred/contempt?
- Do the people the word is applied to regard it as a slur?
Considering the answers to these questions — that, yes, the term has been imposed on feminists, it is always understood as pejorative, it does have a neutral counterpart (i.e. one could just use the term “feminist”), and feminists have consistently stated that the term is a slur — “TERF” is undoubtedly that. Considering that women are the primary target of this slur and that it is commonly attached to threats of (and, as of late, real-life) violence, there is something more we must now contend with.
Following the violent incident at Speaker’s Corner (which was no accident — one of the perpetrators had publicly expressed his intention to “fuck some terfs up”), I have received hundreds of death threats from men online. I’m not alone, either. Any woman who challenged men’s celebration or defense of the violence at Speaker’s Corner became a target. All of these threats have been attached to the term, “TERF.” Feminists have been labelled in this way specifically to dehumanizethem, to spread outrageous lies about their politics (claiming feminists want to kill trans-identified people or that they advocate genocide), to reframe them as oppressors of males who identify as gender non-conforming, and to paint them, generally, as evil witches, therefore deserving of violence.
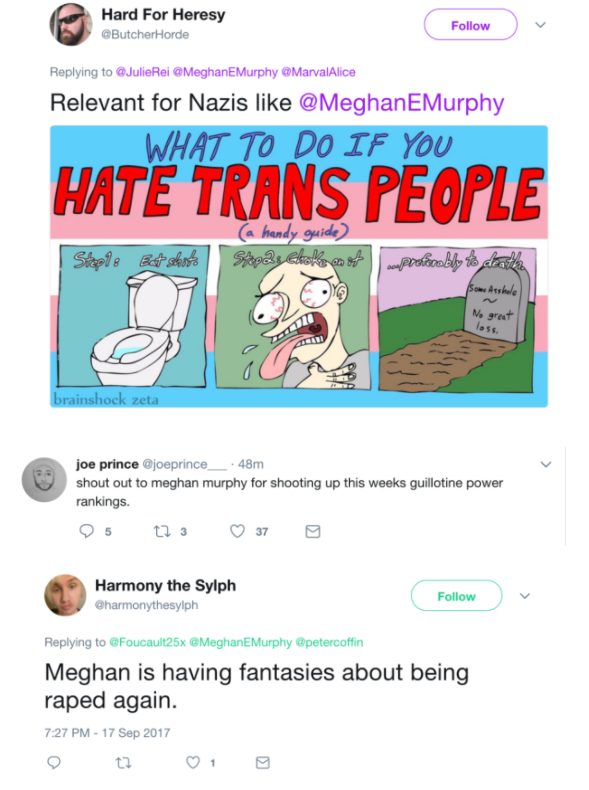





Proliferating lies about and dehumanizing an oppressed group of people in order to justify abuse is a longtime strategy of racists and xenophobes. Hitler used these tools to commit genocide against the Jews. Indeed, propaganda was a key tool of the Nazis in their efforts to spread antisemitism, quell dissent, and turn people against one another. German newspapers printed cartoons and ads depicting antisemitic images and messages.
“If you tell a lie big enough and keep repeating it, people will eventually come to believe it,” was Hilter’s guiding mantra. He trusted that people wouldn’t think for themselves and would simply act out of fear or intellectual laziness, jumping on bandwagons without thoroughly questioning the purpose and foundation of those bandwagons. The Holocaust was successful because the public went along with it — because individuals believed the myths and lies proliferated by the Nazis, and because they didn’t stand up, think critically, or push back.
While hate speech laws differ from place to place (and can be blurry), as a general rule, making statements intended to expose people to hatred or violence, or that advocate genocide, constitute hate speech.
Because feminists who challenge gender identity ideology are often (strategically) accused of advocating genocide, let’s be clear: “genocide” does not mean arguing that biological sex is a real thing, challenging the idea that femininity and masculinity are innate, or suggesting certain spaces should be for women and girls alone. What genocide does mean is: killing members of an identifiable group or deliberately inflicting conditions of life aimed to bring about the physical destruction of an identifiable group.
In other words, suggesting that feminists should all be destroyed, fired from their jobs, forced into homelessness, harassed, silenced, removed from society, abused, and sent to the Gulag.

Under the law, advocating or promoting genocide is an indictable offence. Likewise, those who promote hatred against an identifiable group or communicate statements in public that incite hatred or violence against an identifiable group that are likely to lead to a breach of the peace (i.e. for example: what happened at Speaker’s Corner) are guilty of an indictable offence.
But these laws are hard to enforce. Which is not necessarily a bad thing. We should not be charging people willy-nilly for things they say on Twitter. What we most certainly should be doing is holding men to account for inciting violence against women and holding media and other institutions to account for normalizing hate speech.
So, beyond the law, let’s talk about accountability. When the media normalizes hate speech, they become culpable. A publication would not use the n-word to describe a black person or the word “kike” to describe a Jewish person. This is because we know that these terms reinforce racism and justify discrimination and/or abuse against particular groups of people who have been historically and systemically oppressed. When the media, institutions, and authorities become aware that a particular term is being used to incite violence against women, it is their responsibility to condemn or simply refrain from encouraging the use of that language.
And yet we have seen various media outlets using the term uncritically, of late.
The fact that the vast majority of those connecting the word “TERF” to threats of violence, death, and genocide are men is notable. The word has been offered up to those who identify as leftists, who have been, on some level, prevented from making misogynistic statements publicly or otherwise advocating violence against women. Their “progressive” credentials meant that they had to maintain a facade of political correctness. But because women labelled “TERF” have been compared to Nazis and bigots, and because trans activism claims to be allied with the interests of the marginalized (despite its overt anti-feminism and individualist ideology), these leftist men have a socially acceptable excuse. Indeed, they seem to revel in it. It’s as if they were given the green light to scream “bitch” (or perhaps “witch” would be more accurate, considering the targeting of specific unruly women to “punch”… or burn…) over and over again, cheered on by their comrades.
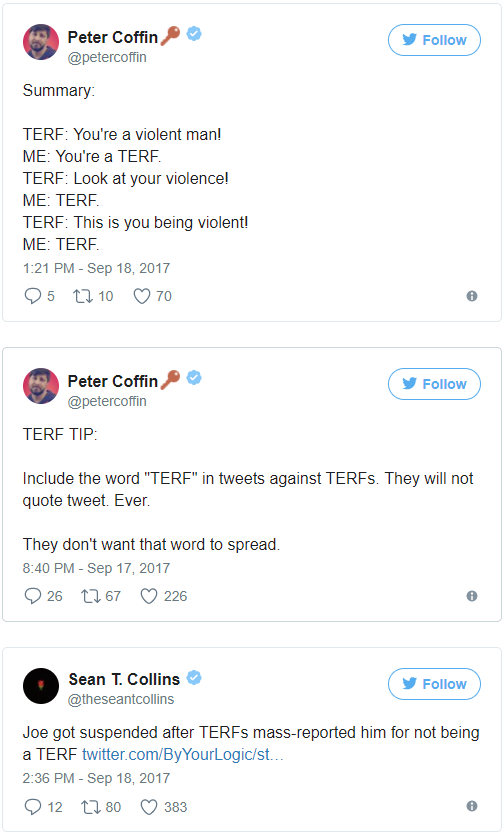
If “TERF” were a term that conveyed something purposeful, accurate, or useful, beyond simply smearing, silencing, insulting, discriminating against, or inciting violence, it could perhaps be considered neutral or harmless. But because the term itself is politically dishonest and misrepresentative, and because its intent is to vilify, disparage, and intimidate, as well as to incite and justify violence against women, it is dangerous and indeed qualifies as a form of hate speech. While women have tried to point out that this would be the end result of “TERF” before, they were, as usual, dismissed. We now have undeniable proof that painting women with this brush leads to real, physical violence. If you didn’t believe us before, you now have no excuse.

by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Sep 14, 2017 | Colonialism & Conquest, Mining & Drilling
Featured image: A still from aerial footage from 2011 of an uncontacted Amazon tribe in Brazil near the Peruvian border. © BBC/FUNAI/Survival
by Survival International
Brazilian Indians have appealed for global assistance to prevent further killings after the reported massacre of uncontacted tribespeople, and have denounced the government cuts that left their territories unprotected.
Paulo Marubo, a Marubo indigenous leader from western Brazil, said: “More attacks and killings are likely to happen. The cuts to FUNAI’s funding are harming the lives of indigenous people, especially uncontacted tribes, who are the most vulnerable.” (FUNAI is Brazil’s indigenous affairs agency).
Mr. Marubo is the leader of Univaja, an indigenous organization defending tribal rights in the Uncontacted Frontier, the area with the highest concentration of uncontacted tribes in the world.

Paulo Marubo, leader of a Javari Valley indigenous organization from the Uncontacted Frontier. © Amazonas Atual
COIAB, the organization representing Indians across the Brazilian Amazon, denounced the massive cutbacks to FUNAI’s budget that has left many tribal territories unprotected:
“We vehemently condemn these brutal and violent attacks against these uncontacted Indians. This massacre shows just how much the rights of indigenous peoples in this country have been set back [in recent years].
“The cuts and dismantling of FUNAI are being carried out to further the interests of powerful politicians who want to continue ransacking our resources, and open up our territories for mining.”
Unconfirmed reports first emerged from the Amazon last week that up to 10 uncontacted tribal people had been killed by gold miners, and their bodies mutilated and dumped in a river.
The miners are reported to have bragged about the atrocity, whose victims included women and children, in a bar in a nearby town. The local prosecutor’s office has opened an investigation.

These Sapanawa Indians made contact in 2014. They reported their community had been attacked, and so many members of the village killed that they could not bury the dead. © FUNAI/Survival
The alleged massacre was just the latest in a long line of previous killings of isolated Indians in the Amazon, including the infamous Haximu massacre in 1993, in which 16 Yanomami Indians were killed by a group of gold miners.
More recently, a group of Sapanawa Indians emerged in the Uncontacted Frontier, reporting that their houses had been attacked and burnt to the ground by outsiders, who had killed so many members of the community that they had not been able to bury all the bodies.
All uncontacted tribal peoples face catastrophe unless their land is protected. Survival International is campaigning to secure their land for them, and to give them the chance to determine their own futures.
Survival’s Director Stephen Corry said: “The decision by the Brazilian government to slash funding for the teams that protect uncontacted Indians’ territories was not an innocent mistake. It was done to appease the powerful interests who want to open up indigenous lands to exploit – for mining, logging and ranching. These are the people the Indians are up against, and the deaths of uncontacted tribes won’t put them off. Only a global outcry can even the odds in the Indians’ favor, and prevent more such atrocities. We know public pressure works – many Survival campaigns have succeeded in the face of similar odds.”

by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Sep 9, 2017 | Colonialism & Conquest
Featured image: Evidence of an attack? Burnt communal houses of uncontacted Indians, seen in December 2016, could be signs of another massacre in the Uncontacted Frontier. © FUNAI
by Survival International
Public prosecutors in Brazil have opened an investigation after reports that illegal gold miners in a remote Amazon river have massacred “more than ten” members of an uncontacted tribe. If confirmed, this means up to a fifth of the entire tribe have been wiped out.
Two miners have been arrested.
The killings allegedly took place last month along the River Jandiatuba in western Brazil, but the news only emerged after the miners started boasting about the killings, and showing off “trophies” in the nearest town.
Agents from Brazil’s indigenous affairs agency, FUNAI, confirmed details of the attack to Survival International. Women and children are believed to be among the dead. FUNAI and the public prosecutor’s office are currently investigating.
The area is known as the Uncontacted Frontier, as it contains more uncontacted tribes than anywhere else on Earth.
Several government teams who had been protecting uncontacted indigenous territories have recently had their funding slashed by the Brazilian government, and have had to close down.

Uncontacted Indians in the Brazilian Amazon, filmed from the air in 2010. © G.Miranda/FUNAI/Survival
President Temer’s government is fiercely anti-Indian, and has close ties to the country’s powerful and anti-indigenous agribusiness lobby.
The territories of two other vulnerable uncontacted tribes – the Kawahiva and Piripkura – have also reportedly been invaded. Both are surrounded by hundreds of ranchers and land invaders.
Uncontacted tribes are the most vulnerable peoples on the planet. However, when their rights are respected, they continue to thrive.
All uncontacted tribal peoples face catastrophe unless their land is protected. Survival International is doing everything it can to secure their land for them, and to give them the chance to determine their own futures.
Survival’s Director Stephen Corry said: “If these reports are confirmed, President Temer and his government bear a heavy responsibility for this genocidal attack. The slashing of FUNAI’s funds has left dozens of uncontacted tribes defenseless against thousands of invaders – miners, ranchers and loggers – who are desperate to steal and ransack their lands. All these tribes should have had their lands properly recognized and protected years ago – the government’s open support for those who want to open up indigenous territories is utterly shameful, and is setting indigenous rights in Brazil back decades.”



























