Editor’s Note: In the Fight for Who We Love series, we introduce you to one species every month. These nonhuman species are what inspires most of us to join the environmental movement and to continue to fight for the natural world. We hope you find this series inspiring, informative, and a break from news on industrial civilization. Let us know what you think in comments! Also, if there is a species that you want us to cover in the upcoming months, please make suggestions in the comments. Today it is Adélie penguins.
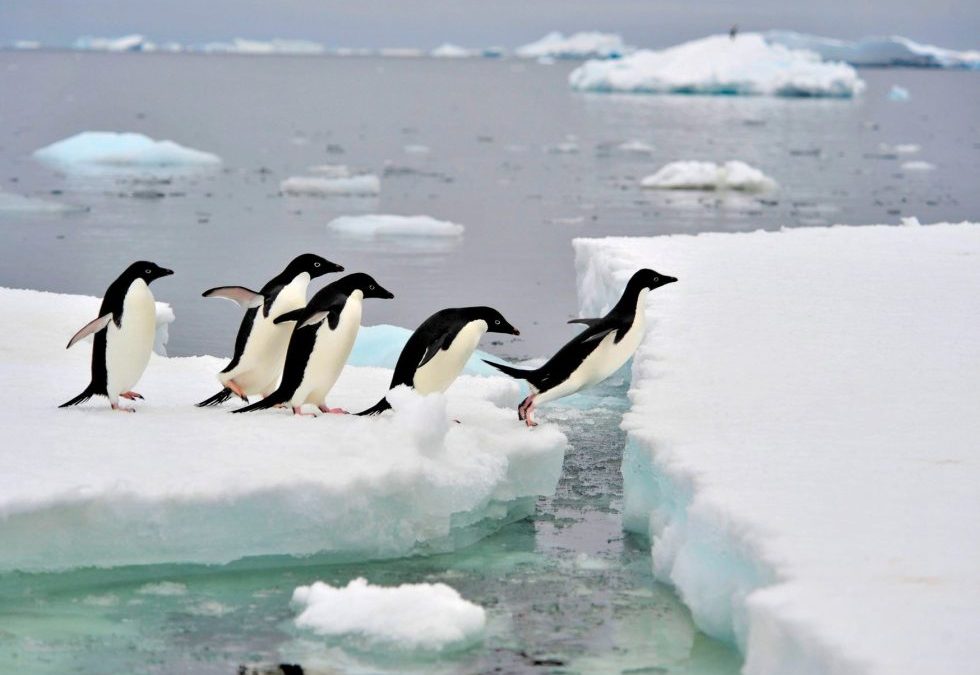
Adélie (pronounced uh-DELL-ee) penguins live in the deep south: Antarctica.
You know that movie Happy Feet featuring dancing penguins? Yeah, so those aren’t actually Adélie penguins they’re emperor penguins (the other primary penguin species who exclusively call Antarctica home).
But just because Adélies didn’t star in their own film doesn’t make them any less cute or important. Because they are rather attractive creatures with some extraordinary capabilities.
DID YOU KNOW?
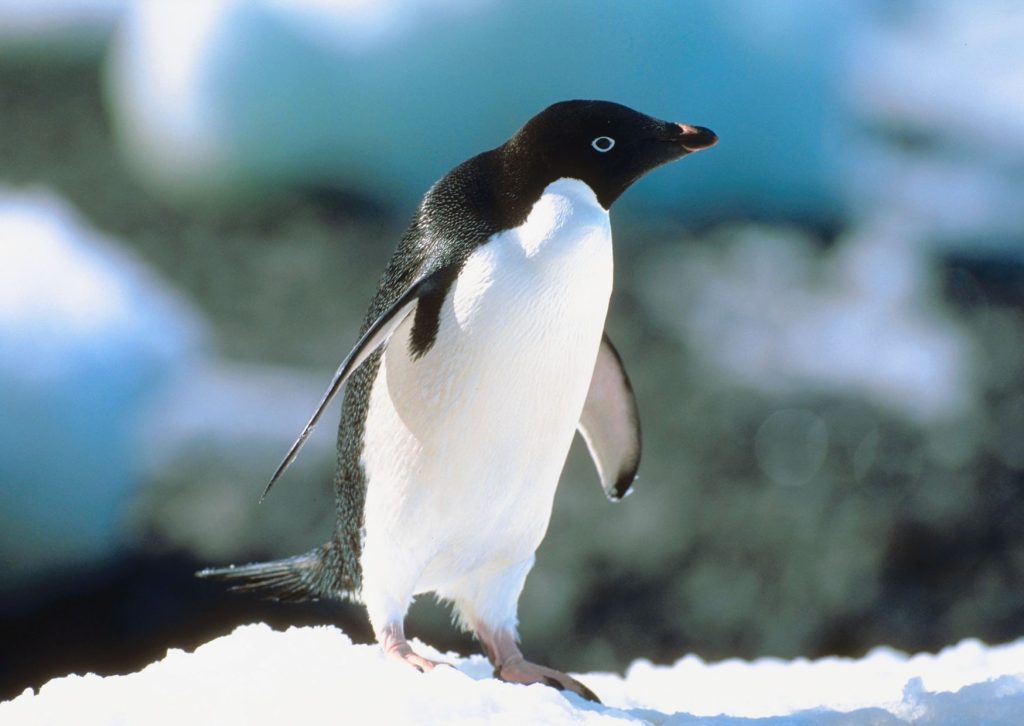

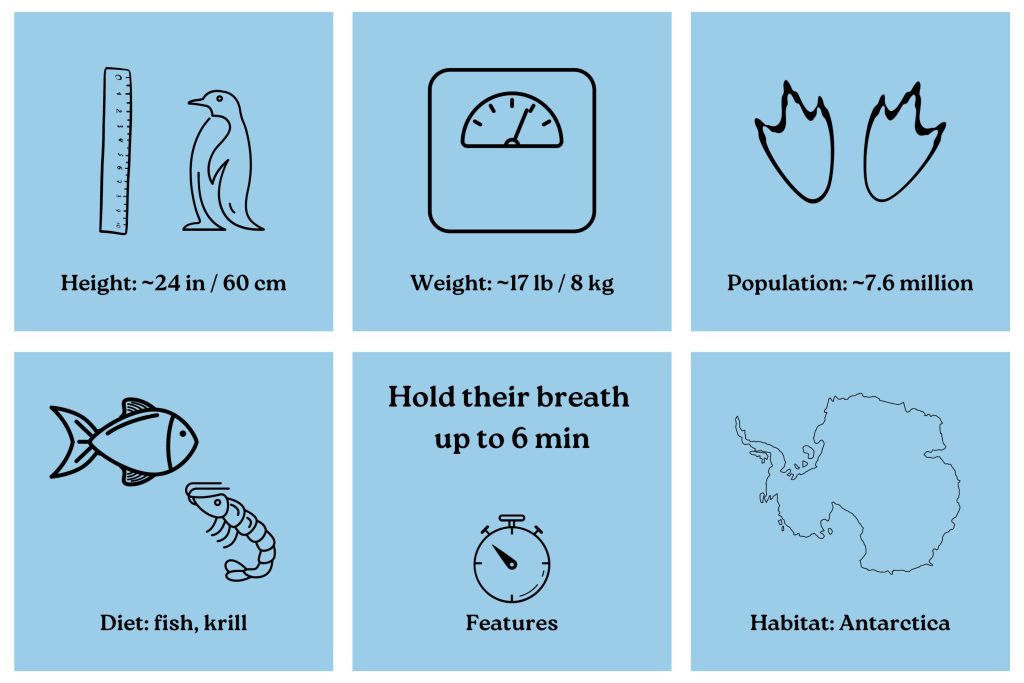
The Adélie penguins live on average from 10 to 20 years in the wild, can grow to about 24in/60cm tall, and spend most of their lives in the water, holding their breath for up to about six minutes and diving over 500ft/150m.
They’re also capable of swimming more than 100mi/160km in search of food. These expeditions are far reaching and can last more than 70 hours. 70 hours! That’s, like, nearly 5 days! I don’t know about you, but I can’t imagine having the endurance for trips like that.
The Adélies are not only adept swimmers, but very good walkers and can traverse over 30mi/50km at a time. Given their waddle-like tendencies, perhaps that’s not a skill most of us would’ve imagined. I mean, how many of us humans walk that much? Sure, some of us do, but probably not many and not often.
THE BIGGEST THREAT
“…[I]t’s possible that up to 60 percent of current Adélie penguin colonies could experience population declines by the end of this century.” —Megan Cimino, Scripps Institution of Oceanography
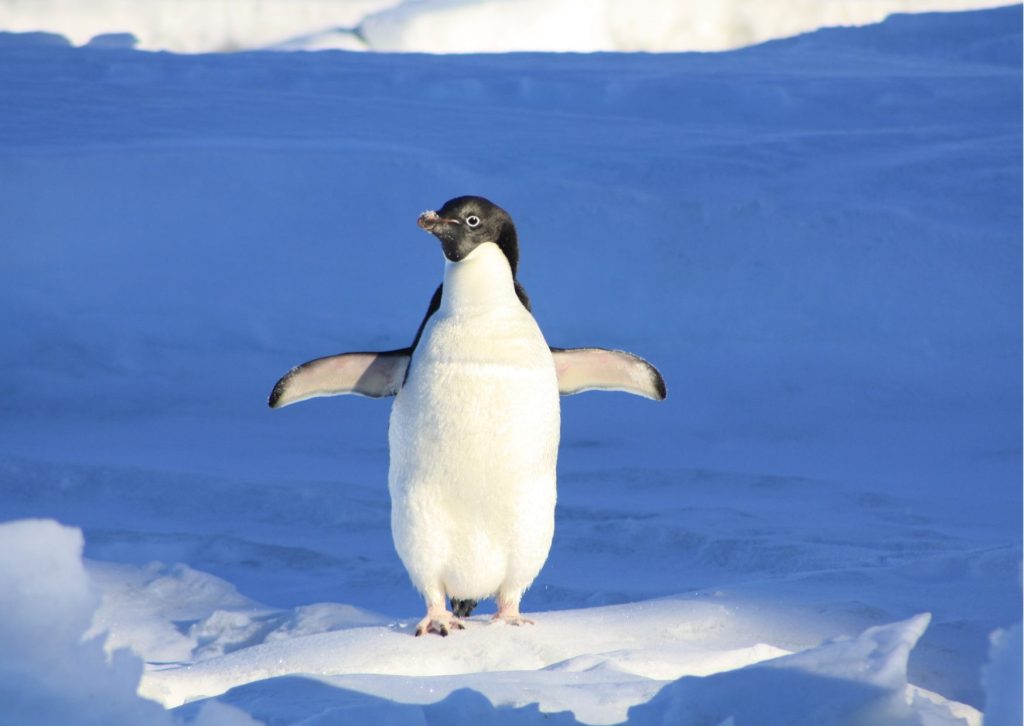

Climate Change is not only the biggest threat to Adélies, but to entire species across the globe. Bill Fraser, a biologist who has been visiting the Adélies over the past thirty years, was interviewed in the 2022 documentary series Frozen Planet II by James Reed and talks about one of the reasons why Adélie penguins are dying: the rain.
We humans often grumble a bit if we have to put on our raincoats when the weather is “bad.” But the Adélies can’t so easily deal with such drastic weather changes.
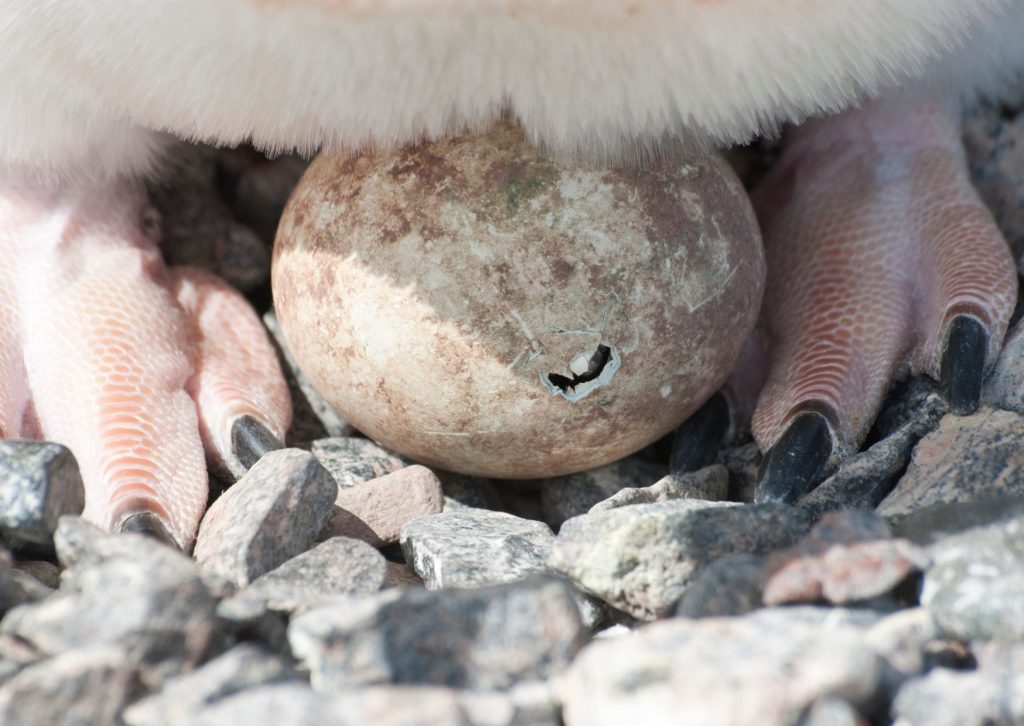
Since they are uniquely adapted to the cold temperatures and dry air in Antarctica, Adélies struggle to survive when the weather is rainy and humid. The penguins build their nests on bare ground using small stones, often returning to the same place to nest. But changes in the climate — for example, too much rain —seriously threatens the Adélies’ ability to nest. The rain soaks and flattens the chicks’ down feathers, which means that they no longer have built-in insulation against the cold.
NOAA’s (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration) Carbon Dioxide Information Analysis Center (CDIAC) could prove in ice core samples that carbon dioxide (CO₂), methane, and nitrous oxides have increased in the last hundred years.
Over the last 800,000 years the levels of CO₂ ranged steadily from 170 to 300 parts per million (PPM), and in 2010 they reached a record high of 386 PPM. “In all ice core samples, there is a shocking increase in air pollutants in the last 100 years that directly correlates to car use and an industrializing global economy,” write scientists of the International Pollution Issues, an electronic research journal.
Pollution in Antarctica is also exacerbated by the “grasshopper effect, which causes persistent organic pollutants (POPs) to move from a warmer to a colder climate where they are consumed by several species. Species higher in the food chain, such as seals, penguins, and whales, are affected the most because they eat organisms that have already stored POPs in their fat and tissue. This is called bioaccumulation.
Native landscapes millions of years old are being bulldozed in the name of technological progress to make room for industrial civilization and human infrastructure — things like second homes, parking lots, and factories. These devastating changes to the earth have extreme effects on the weather patterns, and create conditions that never before existed in a region.
Human-induced changes also affect the ozone layer, a stratospheric layer which shields Earth from damaging ultraviolet radiation. According to the National Science Foundation to the United States, the ozone layer above Antarctica is being depleted during long, icy winters when stratospheric clouds harbor small particulates of chlorofluorocarbons and other aerosols. And this hole that has appeared in the ozone layer above Antarctica was reported by NASA in 2014 to cover an area of roughly 9.2 million mi2/24 million km2.
“Scientists predict that more than half of Adélie colonies will be in decline by the end of the century.”

Why we fight
The Adélie penguins matter to the world and are one of countless reason why we fight.

Further Reading + Sources
- General information can be found here, here, and here
- 10 facts about Adélie penguins
- Climate change may shrink Adélie penguin range by end of century
- Adelie Penguins May Play a Role as an Indicator Species
- About the series Frozen Planet II
- An entry about the penguins from Bill Fraser’s Antarctic Journal
- Adelie Penguins In Danger NPR interview
- Pollution issues in Antarctica here and here
Text, picture editing and graphic: by Kim and Benja Weller
Featured image: by Vladsilver via Canva.com


Wonderful series… and shows how inter-related everything being, included the elements, is.
Hey Mankh, yes, true! We’re glad you like the series.
This series is a good idea, thanks for doing it. If we can create love and caring for non-humans, maybe we can get people to change their attitudes, which is at the heart of the problem here.
I think that all life is “cute,” but obviously some species appeal to people in this way more than others. Additionally, cuteness is very subjective.
The roots of all these problems are people’s feelings and attitudes toward the Earth, its ecosystems & habitats, and all the other non-human life here. Maybe if people were overwhelmed by feeling that all this non-human life is cute, and read articles and watch videos like this, humans would act much better toward them.
This is our intention, to make people aware of a greater caring towards non-human animals. And yes, all animals are worthy in this big web of life, not only the so called cute ones, thanks for your good comment
Beautiful, heartwarming, happy video (near top of page) had me smiling all the way through. And lovely photos. This is one of my first visits here and I intend to make it a regular now that I’m happy to support DGR. It’s lovely to see these positive images as a change from reading all the time about all the negatives in the world. And it’s an inspiration for why it’s worth fighting for.