by DGR Colorado Plateau | Jan 18, 2015 | Biodiversity & Habitat Destruction, Lobbying, Obstruction & Occupation, Strategy & Analysis
Featured image by Sierra Forests Legacy
By Michael Carter / Deep Green Resistance Colorado Plateau
Read Part 1 of this series here
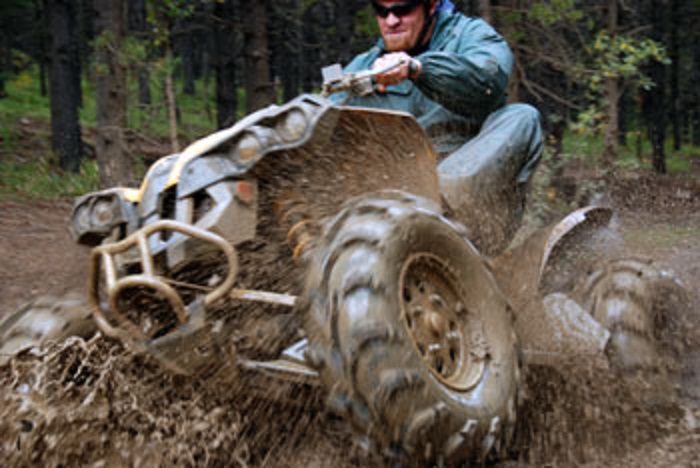
Law enforcement has been so ineffective in preventing illegal ORV use that citizens are usually left to face the problem on their own. Stopping ORVs isn’t easy, but short of an end to gasoline—which we can’t wait for—impacts will continue to worsen if there’s no intervention. In remote areas like the Mojave Desert and Colorado Plateau, where would-be activists are scattered and overwhelmed and the police are essentially powerless and blasé, all strategies for stopping ORVs involve active and sustained effort. Here are a few:
Pressure law enforcement to do their jobs. Carry a camera with you always, and photograph illegal activity, if at all possible getting clear images of license plates. Document the time, place, and circumstances. Bring it to the attention of both the local and federal police, if on federal land. Be polite but persistent.
Physically close illegal trails. This can be surprisingly effective. Adopt an area and close off illegal trails with rocks, logs, whatever is handy and doesn’t further disturb the land. ORVers will keep trying to use the trail, but continued discouragement might eventually work.
Physically close legal trails. Similar to the last category, people may choose to carry out underground actions that close legal routes. [1] There must be a strict firewall between aboveground and underground activists: people or groups choosing to use underground tactics should not engage in aboveground actions, and vice versa. [2]
Close and reclaim established, authorized routes through administrative and legal channels. It’s the open roads that draw ORVs deeper into land they can then illegally violate, so every closed road is particularly helpful. This, too, takes a long and sustained effort. One helpful organization is Wildlands CPR (Now Wild Earth Guardians), [3] but don’t expect any non-profit group to have the resources to do the job for you. If you love the land you live in, be prepared to fight for it—a simple solution of hard, dedicated effort. Organize with those who agree with you, and fight.
Coyote Canyon Revisited
Private landowners neighboring Coyote Canyon in southeast Utah fought the originally illegal ORV use of the canyon, and tried to stop the BLM from sanctioning it. They pleaded with the public via every venue they could think of to write letters to the BLM opposing the move, yet ORV interests grossly outnumbered the effort. Fewer than ten opponents to the trail even bothered writing letters, and when the decision to open the canyon to ORVs was made the BLM didn’t even bother notifying the respondents, a violation of the National Environmental Policy Act.
Otherwise, however, the agency had prepared its documents thoroughly and neighbors were advised that a legal challenge probably wouldn’t have been effective. Although the BLM offered a number of concessions—the trail is only open Friday and Saturday to registered users, from 9:00 a.m. until 5:00 p.m., among other restrictions—the agency legitimized crime, rewarding criminals with the sacrifice of another dwindling scrap of feral public land.
The Coyote Canyon example highlights several reasons why so few are willing to protect the land, and why they’re losing so badly. One is fear of reprisals from enemies (such as intentional trespass and vandalism of property, already an issue for neighbors of Coyote Canyon). Another is a reasonable assumption that their efforts will be ineffective—though of course making no effort will certainly be ineffective. Yet people tend to accept whatever situation they’re given. It’s uncommon to question an established arrangement, whatever it may be, and if one continues to question it life gets more uncomfortable. A resister will always face ridicule, accusations of poor mental, emotional and social adjustment, eventual ostracizing and occasionally murder. Yet social changes demand challenges to established practice.
When the BLM announced their decision to open Coyote Canyon to oil spills, noise, litter, piles of shit and soiled rags of toilet paper, almost everyone who was asked to help offered only a passing moment of sympathy. Not “what can I do,” not “what are our options,” but “that’s too bad.” It’s no wonder fights like this are frequently lost, when reactions are so feeble.
Industry and recreation groups, by contrast, are well organized and ready to rush to their own common cause. The right wing tends to be more accepting of orders; the boss says jump, they ask how high. They have something tangible they’re working for, a thing they like doing, a righteous maintenance of their privilege—such as driving anywhere they want. They stand to gain something where resistance stands only to prevent something—at least in situations like Coyote Canyon, where no comparable force opposes them.

Fighting Back
Resistance is tough. It means making one’s self unpopular, a hard thing to do among those who’ve been taught their whole lives that popularity is everything. Organizing can provide the possibility of overcoming our fear of reprisal, of ridicule, and of failure; it’s the only chance at effectively confronting injustices. Those who wish to prevent agency actions like the Coyote Canyon trail, or to promote re-localization of food production—any defensive or restorative action—can become an effective force if they work together, consistently and reliably supporting one another. Many progressives have been bled off by dogmas of non-confrontation, by intoxicating feel-good-ness, and by the idea that individualism is of primary importance. They’ve become lazy, fatalistic, and cynical; committed, organized struggle seems to be the sorry lot of desperately poor people in faraway places.
The examples that we have of committed resistance movements often are of desperately poor people, immediately threatened by the activities of rich and powerful enemies. The Movement for the Emancipation of the Niger Delta is one good example, and so are the more than 130 First Nations governments in western Canada that have gathered against the tar-sands Enbridge Northern Gateway Project and the Kinder Morgan pipeline and tanker projects. [4] We who are in a position to protect the land mostly lack the ability to respond, to turn our empathy for places like Coyote Canyon into action.
The situation at the frontiers of wild land is desperate, too. Wealth and privilege let us pretend it isn’t, because we get food from supermarket shelves and water from a tap. We see little or no connection between the health of the land and our own well-being. Public land use is an issue that can be influenced relatively easily—unlike, say, racism—because land managers so routinely ignore or violate laws and effective tactics usually have to do with citizen enforcement. But environmentalists continue to lose, partly because exploiters have miscast conflict as user-group obstruction—framing the terms of the debate to ridicule love of the wild world, separating its fate from human fate. By allowing this, would-be activists surrender the land and leave the future to sadists and imbeciles.
The destruction of the planet, however easy it is to ignore, will catch up with us all. The civilized economies that steal from the poor to give to the rich will eventually end. They need to consume limited resources to exist and those resources—fossil fuels, topsoil—will not last forever. When this happens, we will again depend upon the land to sustain us. If that land is stripped of its capacity to sustain life by industry, agriculture, and recreation, then there will be nowhere else to go, and nothing to do but wage war and starve.
Abuse of the land is now normalized by faith in nonexistent frontiers (of renewable energy and electric cars, for example) and by misguided tolerance. Naming abuse—the destruction of the land in the name of fun or individualistic pursuits and the destruction of our selves by abusive people and systems—is often portrayed as abusive in itself. This is outrageous and infuriating, but should be expected.
Though it is far less damaging than industry and agriculture, the evidence for ORV destruction is well documented and easy to come by. It’s not even really contested by ORVers themselves. Those of us determined to stop this behavior face the same problem law enforcement does: the damage is so widespread and difficult to regulate that there’s little anyone can do. But there’s also a serious lack of activists with effective tactics and a coherent strategy to follow through on. This doesn’t mean, though, that we should back down.

Identifying with the Real World
Once on Cedar Mesa, in Southeast Utah, I watched an ORV intentionally veer to crush a dozing snake. The reptile churned and writhed in the machine’s track, dead or near dead as its nerves popped and struggled and ran down. I went to it, to witness its pointless death. A thick and handsome bull snake, it spent its last moments bleeding out in the dust. Why? Why do this? What drives this sick, stupid behavior? Why does our culture hate every living thing?
I lifted the snake into the sage and blackbrush so it could at least die in its home. “If they can’t evolve to get out of the way,” someone once told me about road killed animals, “then that’s their problem.” Of course, not evolving to changing conditions is what causes extinction. There’s little doubt that our culture will not voluntarily evolve to halt the worsening conditions that industry and recreation are creating on the planet. So how does anyone fight activity like this? How do we stop deforestation, global warming, ocean acidification? And given those immense problems, is ORV land abuse something to focus limited energy and resources on?
In addition to the suggestions made in these articles, activists can develop tactics and strategies and their way forward will eventually become clear. With hard work and determination a chance of winning would almost certainly emerge. But in a world of Keystone XL pipelines and epidemic levels of fracking, is the effort worth it? If you caretake a few acres of land, blocking travel and pulling weeds, how much does it matter if you stop, or get distracted, or die? If those acres are again immediately vulnerable, is your effort a waste?
Few things anger me more that seeing wanton destruction for fun. I wonder, though, if this is an unhelpful distraction. It’s easy to get angry at something so obviously disrespecting of the land. In terms of permanent impacts, though, industry is much worse, and the scale of destruction is enormous. Of course what runs it is oil. Always this—the temporary, illusory power locked in a liquid hydrocarbon, driving ORVs, factory fishing trawlers, factory farms, and industrial agriculture. It’s warming the atmosphere and leading us to a horribly impoverished future, where most of us will be unable to afford the lifestyle we’ve been subjected and addicted to, let alone find enough to eat.
Remove the oil and the engines stop, and a besieged biosphere can begin to heal. This is part of the strategy that Deep Green Resistance has proposed. [5] But in the meanwhile…ORVs, just one part of the picture, continue to cut apart what little wild life remains, the last seed bank of evolution as we’ll ever know it. The momentum of established civilized practice is now enormous—seemingly unstoppable—and its terminal is in global destruction, the eradication of all complex life. Challenge to this system is so psychologically and practically difficult that most of us ignore it.
Fighting for the real, wild world can begin with the understanding that humans are not everything, and that the fate of the world is ultimately our fate. It is much different to fight for your own beloved family than for a rocky canyon you’ll never visit. We progressives like to talk about how hatred of “other” races cannot be tolerated (not that much is ever done about that). But we hardly ever extend this principle to the non-human world—constant victim of our culture’s violence—because we’ve been conditioned to believe that humans are all that matter. The loons, the snakes, the too-slow creatures smeared across the roads and ground under rubber tires into the dirt, they and the people yet to come who won’t be able to live as we have because the oil is gone—none of them will care about our abstract, self-indulgent moral wrestling. That is the wall that human supremacy has built around us; it must be torn down.
Imagine again that an occupying culture, whose every act is force and theft, was destroying the means of your survival. Imagine them extracting fuel to use the world as a playground. Of course, it is not enough to stop them from driving their toys in every possible place. To survive in the long term we must also stop the extraction, the root of the problem, and eliminate the fuel for destruction. We must reclaim our adult responsibilities and stand up to defend the land where we live, knowing that until oil extraction and consumption is ended, there will always be a new group of occupiers finding new ways to destroy the land.
Endnotes
[1] Foreman, Dave. Ecodefense: A Field Guide to Monkeywrenching. Tucson: Ned Ludd Books, 1987, 89-109.
[2] Security Culture: A Handbook for Activists (PDF)
[3] “Resources,” Wild Earth Guardians, accessed July 13, 2014, http://www.wildearthguardiansresources.org/
[4] Carrie Saxifrage, “How the Enbridge Pipeline Issue Unified Northern BC,” The Vancouver Observer, February 13, 2012, http://www.vancouverobserver.com/politics/2012/02/13/nation-building-how-enbridge-pipeline-issue-unified-northern-bc
“Interior First Nations Pipeline Ban,” Dogwood Initiative, You Tube, December 2, 2010, http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4G5KtqPSW8Q
Carrie Saxifrage, “No Oil Pipeline Here: Enbridge Northern Gateway Joint Review Panel in Smithers finds 100% opposition,” The Vancouver Observer, January 17, 2012, http://www.vancouverobserver.com/sustainability/2012/01/17/enbridge-northern-gateway-joint-review-panel-smithers-finds-100-opposition
[5] “Decisive Ecological Warfare,” Deep Green Resistance, accessed August 28, 2014
by DGR News Service | May 21, 2014 | Strategy & Analysis
By Kim Hill / Deep Green Resistance Australia
Life itself has been stolen from us.
Genes, the very basis of life, no longer belong to the living beings who embody them, but to institutions that convert life into profit.
Our basic needs, of food and water, no longer come from the land where we live, but from distant corporations that use the exact same food and water as a dumping ground for their wastes.
Monsanto executives take up positions of power in the US Food and Drug Administration, and Environmental Protection Authority. These bodies, instead of protecting our food and water as they were intended to do, now protect the interests of those who are causing the harm.
Governments exist within the rules of Free Trade Agreements and The World Bank, institutions that exist to protect the profits of corporations. Governments have little power to create change.
So we cannot ask governments to act.
In India, 250,000 farmers have committed suicide by drinking Monsanto pesticides after their Bt cotton crops, sold to them by Monsanto, failed, and they were no longer able to provide for their families. Monsanto obstructs labelling laws, and suppresses the results of research that are not in its favour. It is not going to listen to the demands of the people. The purpose of a corporation is to make profit, regardless of the costs to other people and living beings. It is not possible for it to act in any other interest.
So we cannot ask corporations to act.
Even if Monsanto were stopped, there are plenty of other biotechnology companies ready to take their place. The entire economic system is structured to see living beings only as an opportunity for profits, or as standing in the way of profits. For life to continue, the entire system needs to be dismantled.
It is up to us to act.
As human beings, we are part of a natural community of rivers, forests, soil and myriad living beings. This community provides our food and water.
We need to act, not as consumers, not as citizens, but as humans.
We are accountable not to profits or institutions, but to the land that provides for us.
Actions that ask governments and corporations to change – rallies, petitions and letters – can never be effective on their own. Those who are profiting from the theft of life itself need to be physically stopped.
Every day, people are taking real action, by destroying GM crops, sabotaging equipment and infrastructure, and engaging in cyber-attacks against corporations. These actions are essential to stop Monsanto and all those profiting from the destruction of living communities.
On behalf of those whose lives have been stolen and manipulated for profit, those who cannot speak and cannot act, we need to give our full support to the people who are risking their own lives and freedom to defend life itself.

by DGR News Service | Mar 30, 2014 | Male Supremacy, Strategy & Analysis, White Supremacy
By Kourtney Mitchell / Deep Green Resistance
On June 28, 1964, Malcolm X gave a speech at the Founding Rally of the Organization for Afro-American Unity (OAAU) at the Audubon Ballroom in New York. In the speech, he stated what became his most famous quote:
We declare our right on this earth to be a man, to be a human being, to be respected as a human being, to be given the rights of a human being in this society, on this earth, in this day, which we intend to bring into existence by any means necessary.
Interestingly, X was popularizing a line from a play titled Dirty Hands by the French intellectual Jean-Paul Sartre, which debuted in 1948:
I was not the one to invent lies: they were created in a society divided by class and each of us inherited lies when we were born. It is not by refusing to lie that we will abolish lies: it is by eradicating class by any means necessary.
There are some really important ideas presented in both of these quotes. Sartre succinctly summarized the primary struggle for the socially conscious – that society as we know it is divided into classes, and that social change is not achieved merely by refusing to behave like dominant classes, but by ultimately dismantling the power structures upholding this stratification.
X’s spin on this was equally profound. The white power structure of his time enacted brutal and morally reprehensible repression on the masses of black people in the United States, and X was stating the very real yet existential condition: that this repression was a dehumanizing tactic, upheld by violence and enslavement, and that the response to this repression must equal the scope of the problem. Simply put, white supremacism will use any and all means necessary to maintain power, and thus those fighting against it must do the same.
The modern environmental and social justice movement could learn a thing or two from these quotes. Any one who is not meditating in a cave should realize by now that this culture we live in – industrial civilization – is quickly killing the planet. All life support systems on Earth are declining, and have been doing so for several decades. As a matter of fact, since the publication of Rachel Carson’s Silent Spring, generally considered the birth of the modern environmental movement, there has not been a single peer-reviewed article contradicting that statement.
This should ring some alarms for everyone, but surely for those in the movement, right? One would think so, but unfortunately this does not seem to be the case. Instead, what we are seeing is a continued ignorance of the true scale of environmental destruction, and a refusal to be honest about what it will take to stop it. What we are seeing is a constant faith on popular protest and nonviolence as the end goal of resistance, a hegemonic adherence to pacifism.
At the same time that nearly all native prairies are disappearing, and insect populations are collapsing, and the oceans are being vacuumed, and nearly two hundred species of animals are going extinct every single day, women are also being raped at a rate of one every two minutes. A black male is killed by police or other vigilantes at a rate of one every 28 hours. There are more slaves today than at any time during the Trans-Atlantic Slave Trade. And indigenous cultures and languages are being wiped off the planet.
It is apparently certain that for all of our good intentions – our feelings of loving-kindness, taking the moral high ground and being the change we wish to see in the world – we are failing, and miserably. We are losing.
This must change.
It is time to face the truth, a truth climate scientists, indigenous warriors and anyone who is half awake have been telling us for a really long time – our planet is being killed, and we must fight back to end the destruction before all life on the planet perishes for good.
A starting point for establishing an effective response to environmental destruction and social oppression is to develop a clear understanding of the mechanisms for this arrangement. The dominant classes of people who are enacting this brutality utilize concrete systems of power to do so, namely industrial capitalism, patriarchy, white supremacy and human supremacism.
These institutions of power are run by people – human beings, who instead of holding a reverence for life and love of freedom, value privilege and power above all else. This system is based upon, and would quickly collapse without, widespread and pervasive violence. Privilege is upheld by violence, because no one willingly cedes their freedom and autonomy unless forced to do so.
There is a necessary realization one must have when considering all of this, and it is a realization many in the so-called movement are yet to have: as the oppression of human and non-human communities and the destruction of the planet is being enacted by a particular class of people – that is, a group of people sharing a real or perceived identity and having similar goals and the means to achieve those goals – it is also being endured by a particular class of people.
Men, as a class of people whose collective behavior has a very real effect, are oppressing women as a class. This is not to claim that every single man on the planet has some palpable sense of hating women, but it does mean that to be a man in this society is to behave in a socialized manner that oppresses women.
Whites as a class of people are oppressing people of color. This is not to say that every single white-identified person on the planet has some palpable sense of hating people of color, but that to be white in this society is to behave in a manner that oppresses people of color in at least some ways.
If the violence is enacted by classes, the resistance must also exist on the class-level. It has never been enough for the individual to make personal, lifestyle changes so that they can feel better about themselves while the rest of the people in their class suffer. Systems of oppression are not defeated by individuals – they are defeated by organizing with others, a collective struggle.
This is what it means to be radical. As radicals, we aim to get to the root of the problem. Radical anti-racists understand that the white identity is based upon privilege, and that privilege is inherently oppressive to people of color. Radical anti-sexists understand that the concept of gender is built upon male dominance and female submission, which is inherently oppressive to women. And radical environmentalists understand that industrial civilization – based upon extraction, destructive agricultural practices and the genocide of indigenous cultures – is killing the planet.
From there, we draw the line. A radical’s primary goal is not to combat the symptoms of oppression – we do not merely wish to navigate the gender spectrum, toying with it at will as some kind of protest. We wish to abolish gender, recognizing it as the primary basis for women’s oppression. And we do not wish to merely give people of color a bigger slice of the pie in the white supremacist power structure. We wish to abolish white supremacy altogether, and furthermore to overcome the concept of race itself. Radical environmentalists cannot afford to continue to espouse technological fixes for a problem caused by technology and extraction. No, industrial civilization is wholly irredeemable, and no amount of technology can fix it.
What should be apparent is that our movement needs more than nonviolence and good feelings. We need to mount a serious threat to the power structures, one that is forceful and continuous. We need militant action. Those killing the planet will not stop unless forced to do so.
Nonviolence is a powerful tactic when correctly applied, but it alone cannot match the scale of destruction. When coupled with strategic attacks on the infrastructure of oppression, it can result in concrete, lasting change.
And this is the strategy of Deep Green Resistance. As an aboveground movement, we use nonviolent direct action, putting our bodies between life and those who wish to destroy it. Though we have no connection to (and no desire to have a connection with) any underground that may exist, we actively support the formation of an underground, encouraging militant resistance that will bring down oppressive institutions for good.
DGR is also dedicated to the work of helping to rebuild or to build new, sustainable human communities. We are working towards a culture of resistance – where oppression and ecocide are not tolerated, and where people incorporate resistance into their everyday lives. We work to establish solidarity and genuine alliance with oppressed communities, always keeping an eye towards justice, liberating our hearts and minds from the hegemonic tendencies of privileged classes. DGR understands that marginalized communities have been on the front lines of resistance from the very beginning, defending their way of life and reclaiming their autonomy. For too long, pacifists and dogmatic nonviolent activists have left the hard work of actual resistance to those marginalized groups, shying away from the real fight. No more – it is now time for men to combat sexism, for whites to combat racism, and for the civilized of this culture to fight against industrial empire and bring it down.
This analysis and this strategy should be inspiring. But what is more inspiring is that we have the means to achieve our goals. We know how to bring down industrial capitalism, which is controlled by critical nodes of technology and extraction. When these nodes are attacked and brought down in a way preventing their rebuilding, the system begins to collapse. The mechanisms of control – the military, the police and the media – cannot operate without consistent input of fossil fuels and willing agents.
When this system falls, the living world will rejoice. Two hundred species of animals who would have gone extinct will instead live and flourish. Indigenous communities will reclaim their traditional homelands. The salmon will begin to spawn anew with each dam taken down, and the rivers will rush with life.
This is the world for which we fight. And we intend to win.
Let’s Get Free! is a column by Kourtney Mitchell, a writer and activist from Georgia, primarily focusing on anti-oppression and building genuine alliance with oppressed communities. Contact him at kourtney.mitchell@gmail.com.

by DGR News Service | Mar 27, 2014 | People of Color & Anti-racism, Property & Material Destruction, Strategy & Analysis, White Supremacy
By Deep Green Resistance UK
We have had several months to reflect on the life and legacy of Nelson Mandela. Since his death, world leaders have attempted to coopt this legacy. It is especially interesting to see how many who once branded Mandela a terrorist are rushing to pay their respects. [1]
His freedom fighter past has been quietly forgotten. Mainstream writers, intellectuals, and politicians prefer to focus on his life after prison. A simple Google search for Mandela is dominated by articles about tolerance and acceptance.
But often lost in discussions of Mandela are the details about why he was sent to prison by the Apartheid Government. He rose to leadership in the African National Congress (ANC) against Apartheid and his role in the creation of its militant wing, the Umkhonto We Sizwe (MK) which means “Spear of the Nation” in Zulu and Xhosa.
Mandela’s autobiography Long Walk to Freedom is very well written bringing the reader on Nelson’s journey with him. He dedicated his life to the struggle to create a South Africa where all are equal.
For a detailed summary of Mandela’s path to militant resistance see the DGR Nelson Mandela Resister Profile.
Mandela came from a privileged background and was groomed to council the leaders of his tribe. He received an excellent ‘western’ education. He moved to Johannesburg and trained as a lawyer. In Johannesburg, he came into contact with ANC members. His radicalisation began as he attended ANC meetings and protests.
On page 109 of Mandela’s autobiography he explains that he cannot pinpoint the moment when he knew he would spend his life in the liberation struggle. He states that any African born in South Africa is politicised from birth with the oppression and inequality Africans in South Africa suffer. “I had no epiphany, no singular revelation, no moment of truth, but a steady accumulation of a thousand slights, a thousand indignities and a thousand unremembered moments that produced in me an anger, a rebelliousness, a desire to fight the system that imprisoned my people.”
In 1948, the Nationalist (Apartheid) Party won the general election and formed a government that remained in power until 1994. Following the election, the ANC increased activities resulting in deaths at protests by the police. In response, the government introduced legislation that steadily increased the oppression on Africans in South Africa.
The ANC National Executive including Mandela discussed the necessity for more violent tactics in the early 1950s but it was decided the time was not yet right. Mandela consistently pushed the ANC to consider using violent tactics. During the forced eviction of Sophiatown in 1953, Nelson gave a speech.
As I condemned the government for its ruthlessness and lawlessness, I overstepped the line: I said that the time for passive resistance had ended, that non-violence was a useless strategy and could never overturn a white minority regime bent on retaining its power at any cost. At the end of the day, I said, violence was the only weapon that would destroy apartheid and we must be prepared, in the near future, to use that weapon.
The fired up crowd sang a freedom song with the lyrics ‘There are the enemies, let us take our weapons and attack them’. Nelson pointed at the police and said “There are our enemies!”
Mandela saw that the Nationalist government was making protest impossible. He felt Gandhi had been dealing with a foreign power that was more realistic than the Afrikaners. Mandela knew non-violence resistance works if the opposition is playing by the same rules but if peaceful protest is met with violence then tactics must evolve. For Mandela “non-violence was not a moral principle but a strategy; there is no moral goodness in using an ineffective weapon.”
This is a lesson that should be learned for the current resistance to the destruction of our world. The current strategy of non-violence in the environmental movement is simply ineffective.
The Sophiatown anti-removal campaign was long running, with rallies twice a week. The final eviction was in February 1955. This campaign confirmed Mandela’s belief that in the end there would be no alternative to violent resistance. Non-violent tactics were met by ‘an iron hand’. “A freedom fighter learns the hard way that it is the oppressor who defines the nature of the struggle. And the oppressed is often left no recourse but to use methods that mirror those of the oppressor. At a certain point, one can only fight fire with fire.”
Following the Sharpville massacre in March 1960, where 69 people were murdered by the police and then the ANC was declared an illegal organisation in April 1960, the National Executive agreed that the time for violence had come:
At the meeting I argued that the state had given us no alternative to violence. I said it was wrong and immoral to subject our people to armed attacks by the state without offering them some kind of alternative. I mentioned again that people on their own had taken up arms. Violence would begin whether we initiated it or not. Would it not be better to guide this violence ourselves, according to principles where we saved lives by attacking symbols of oppression, and not people? If we did not take the lead now, I said, we would soon be latecomers and followers to a movement we did not control.
This new military movement would be a separate and independent organisation, linked to the ANC but fundamentally autonomous. The ANC would still be the main part of the struggle until the time for the military wing was right. “This was a fateful step. For fifty years, the ANC had treated non-violence as a core principle, beyond question or debate. Henceforth the ANC would be a different kind of organisation.”
The parallels with the modern environmental movement’s commitment to non-violence over the last fifty years are uncanny.
The military organisation was named Umkhonto we Sizwe (The Spear of the Nation) or MK for short. Mandela, now underground hiding from the authorities, formed the high command and started recruiting people with relevant knowledge and experience. The mandate was to wage acts of violence against the state. At this point, precisely what form those acts would take was yet to be decided. The intention was to begin with acts least violent to individuals but more damaging to the state.
Mandela began reading and talking to experts especially on guerrilla warfare. In June 1961, Mandela released a letter to the press explaining he continued to fight the state and encouraged everyone to do the same. In October 1961, Mandela moved to Liliesleaf Farm in Rivonia, where the Umkhonto we Sizwe constitution was drafted.
In planning the direction and form that MK would take, we considered four types of violent activities: sabotage, guerrilla warfare, terrorism and open revolution. For a small and fledgling army, open revolution was inconceivable. Terrorism inevitably reflected poorly on those who used it, undermining any public support it might otherwise garner. Guerrilla warfare was a possibility, but since the ANC had been reluctant to embrace violence at all, it made sense to start with the form of violence that inflicted the least harm against individuals: sabotage.
Because Sabotage did not involve loss of life, it offered the best hope for reconciliation among the races afterwards. We did not want to start a blood-feud between white and black. Animosity between Afrikaner and Englishman was still sharp fifty years after the Anglo-Boer war; what would race relations be like between white and black if we provoked a civil war? Sabotage had the added virtue of requiring the least manpower.
Our strategy was to make selective forays against military installation, power plants, telephone lines and transportation links; targets that would not only hamper the military effectiveness of the state, but frighten National Party supporters, scare away foreign capital, and weaken the economy. This we hoped would bring the government to the bargaining table. Strict instructions were given to members of MK that we would countenance no loss of life. But if sabotage did not produce the results we wanted, we were prepared to move on to the next stage: guerrilla warfare and terrorism.
DGR is following a similar strategy in the hope that we can transition to a truly sustainable society. We think that its unlikely that those in power will allow this. So phase four of the DGR strategy Decisive Ecological Warfare calls for decisive dismantling of all infrastructure.
On December 16th 1961, MK carried out its first operation. “Homemade bombs were exploded at electric power stations and government offices in Johannesburgh, Port Elizabeth and Durban. On the same day, thousands of leaflets were circulated around the country announcing the birth of Umkhonto we Sizwe. The attacks took the government by surprise and “shocked white South Africans into the realization that they were sitting on top of a volcano”. Black South Africans now knew that the ANC was no longer a passive resistance organisation. A second attack was carried out on New Year’s Eve.
Nelson was arrested in 1962 for inciting persons to strike illegally (during the 1961 stay-at-home campaign) and that of leaving the country without a valid passport. During this trial he gave his famous ‘Black man in a white court‘ speech. Nelson was sentenced to five years in prison.
In May 1963, Nelson and a number of other political prisoners were moved to Robben Island and forced to do long days of manual labour. Then in July 1963, Nelson and a number of other prisoners were back in court, now charged with sabotage. There had been a police raid at the MK Rivonia farm during a MK meeting where they had been discussing Operation Mayibuye, a plan for guerrilla warfare in South Africa. A number of documents about Operation Mayibuye were seized.
What become known as the Rivonia Trial begin on October 9th, 1963 in Pretoria. Huge crowds of supporters gathered outside the court each day and the eleven accused could hear the singing and chanting. The Crown concluded its case at the end of February 1964, with the defence to respond in April.
Right from the start we had made it clear that we intended to use the trial not as a test of the law but as a platform for our beliefs. We would not deny, for example, that we had been responsible for acts of sabotage. We would not deny that a group of us had turned away from non-violence. We were not concerned with getting off or lessening our punishment, but with making the trial strengthen the cause for which we were struggling – at whatever cost to ourselves. We would not defend ourselves in a legal sense so much as in a moral sense. We saw the trial as a continuation of the struggle by other means.
Then on April 20th, 1964, Nelson gave his famous ‘I am prepared to die’ speech. Three important sections are:
“I must deal immediately and at some length with the question of violence. Some of the things so far told to the Court are true and some are untrue. I do not, however, deny that I planned sabotage. I did not plan it in a spirit of recklessness, nor because I have any love of violence. I planned it as a result of a calm and sober assessment of the political situation that had arisen after many years of tyranny, exploitation, and oppression of my people by the Whites.”
“We of the ANC had always stood for a non-racial democracy, and we shrank from any action which might drive the races further apart than they already were. But the hard facts were that fifty years of non-violence had brought the African people nothing but more and more repressive legislation, and fewer and fewer rights.”
“During my lifetime I have dedicated myself to this struggle of the African people. I have fought against white domination, and I have fought against black domination. I have cherished the ideal of a democratic and free society in which all persons live together in harmony and with equal opportunities. It is an ideal which I hope to live for and to achieve. But if needs be, it is an ideal for which I am prepared to die.”
Eight of the eleven, including Nelson were sentenced to life imprisonment on Robben Island. These eight had been expecting the death sentence. Nelson was released after 27 years in prison on February 11th, 1990.
He was aware that his family suffered because of his focus but knew that the needs of the many in South Africa were more important than the needs of the few. It is important to remember that Nelson Mandela and his family are only human, with faults and issues. His first wife accused him of domestic violence, which he always denied. His second wife is accused of ordering a number of brutal acts while Mandela was in prison. And some of Mandela’s children found him difficult. [2]
It is true that Mandela embraced non-violence upon his release from prison in 1990. But, he did this once he felt the disintegration of Apartheid was inevitable. Despite what the vast majority of media coverage would have us believe, a combined strategy of violence and non-violence were necessary to bring down Apartheid.
DGR is committed to stopping the destruction of the world. We recognize that combined tactics are necessary. As Mandela did, we need a calm and sober assessment of the political situation. It is a situation that is murdering the world. We need to leave every tactic on the table whether it is violent or non-violent. There simply isn’t enough time to restrict ourselves to exclusively non-violent tactics.
References
[1] http://www.forbes.com/sites/rickungar/2013/12/06/when-conservatives-branded-nelson-mandela-a-terrorist/
[2] http://www.dailymail.co.uk/news/article-2349335/Nelson-Mandela-death-ballroom-dancing-ladies-man-tempestuous-love-life.html
Time is Short: Reports, Reflections & Analysis on Underground Resistance is a bulletin dedicated to promoting and normalizing underground resistance, as well as dissecting and studying its forms and implementation, including essays and articles about underground resistance, surveys of current and historical resistance movements, militant theory and praxis, strategic analysis, and more. We welcome you to contact us with comments, questions, or other ideas at undergroundpromotion@deepgreenresistance.org
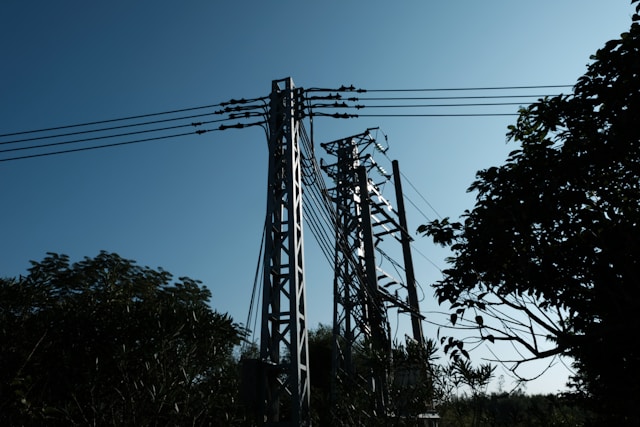

by DGR News Service | Mar 18, 2014 | NEWS, Strategy & Analysis
By Rebecca Smith / Wall Street Journal
The U.S. could suffer a coast-to-coast blackout if saboteurs knocked out just nine of the country’s 55,000 electric-transmission substations on a scorching summer day, according to a previously unreported federal analysis.
The study by the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission concluded that coordinated attacks in each of the nation’s three separate electric systems could cause the entire power network to collapse, people familiar with the research said.
A small number of the country’s substations play an outsize role in keeping power flowing across large regions. The FERC analysis indicates that knocking out nine of those key substations could plunge the country into darkness for weeks, if not months.
No federal rules require utilities to protect vital substations except those at nuclear power plants. Regulators recently said they would consider imposing security standards.
FERC last year used software to model the electric system’s performance under the stress of losing important substations. The substations use large power transformers to boost the voltage of electricity so it can move long distances and then to reduce the voltage to a usable level as the electricity nears homes and businesses.
The agency’s so-called power-flow analysis found that different sets of nine big substations produced similar results. The Wall Street Journal isn’t publishing the list of 30 critical substations studied by FERC. The commission declined to discuss the analysis or to release its contents.
Some federal officials said the conclusions might overstate the grid’s vulnerability.
Electric systems are designed to be resilient and it would be difficult for attackers to disable many locations, said David Ortiz, an Energy Department deputy assistant secretary who was briefed on the FERC study. The agency’s findings nevertheless had value “as a way of starting a conversation on physical security,” he said.
The study’s results have been known for months by people at federal agencies, Congress and the White House, who were briefed by then-FERC Chairman Jon Wellinghoff and others at the commission. As reported by the Journal last month, Mr. Wellinghoff was concerned about a shooting attack on a California substation last April, which he said could be a dress rehearsal for additional assaults.
“There are probably less than 100 critical high voltage substations on our grid in this country that need to be protected from a physical attack,” he said by email this week. “It is neither a monumental task, nor is it an inordinate sum of money that would be required to do so.” Mr. Wellinghoff left FERC in November and is a partner at law firm Stoel Rives LLP in San Francisco.
FERC has given the industry until early June to propose new standards for the security of critical facilities, such as substations.
Executives at several big utilities declined to discuss the risks to substations but said they are increasing spending on security. Virginia-based Dominion Resources Inc., for example, said it planned to spend $300 million to $500 million within seven years to harden its facilities.
A memo prepared at FERC in late June for Mr. Wellinghoff before he briefed senior officials made several urgent points. “Destroy nine interconnection substations and a transformer manufacturer and the entire United States grid would be down for at least 18 months, probably longer,” said the memo, which was reviewed by the Journal. That lengthy outage is possible for several reasons, including that only a handful of U.S. factories build transformers.
The California attack “demonstrates that it does not require sophistication to do significant damage to the U.S. grid,” according to the memo, which was written by Leonard Tao, FERC’s director of external affairs. Mr. Tao said his function was to help Mr. Wellinghoff simplify his report on the analysis.
The memo reflected a belief by some people at the agency that an attack-related blackout could be extraordinarily long, in part because big transformers and other equipment are hard to replace. Also, each of the three regional electric systems-the West, the East and Texas-have limited interconnections, making it hard for them to help each other in an emergency.
Some experts said other simulations that are widely used in the electricity industry produced similar results as the FERC analysis.
“This study used a relatively simplified model, but other models come to the same conclusion,” said A.P. “Sakis” Meliopoulos, professor of electrical and computer engineering at the Georgia Institute of Technology in Atlanta. He estimated it would take “a slightly larger number” of substation attacks to cause a U.S.-wide blackout.
In its modeling, FERC studied what would happen if various combinations of substations were crippled in the three electrical systems that serve the contiguous U.S. The agency concluded the systems could go dark if as few as nine locations were knocked out: four in the East, three the West and two in Texas, people with knowledge of the analysis said.
The actual number of locations that would have to be knocked out to spawn a massive blackout would vary depending on available generation resources, energy demand, which is highest on hot days, and other factors, experts said. Because it is difficult to build new transmission routes, existing big substations are becoming more crucial to handling electricity.
In last April’s attack at PG&E Corp.’s Metcalf substation, gunmen shot 17 large transformers over 19 minutes before fleeing in advance of police. The state grid operator was able to avoid any blackouts.
The Metcalf substation sits near a freeway outside San Jose, Calif. Some experts worry that substations farther from cities could face longer attacks because of their distance from police. Many sites aren’t staffed and are protected by little more than chain-link fences and cameras.
While the prospect of a nationwide blackout because of sabotage might seem remote, small equipment failures have led to widespread power outages. In September 2011, for example, a failed transmission line in Arizona set off a chain reaction that created an outage affecting millions of people in the state and Southern California.
Sabotage could wreak worse havoc, experts said.
“The power grid, built over many decades in a benign environment, now faces a range of threats it was never designed to survive,” said Paul Stockton, a former assistant secretary of defense and president of risk-assessment firm Cloud Peak Analytics. “That’s got to be the focus going forward.”
From Wall Street Journal: http://online.wsj.com/news/articles/SB10001424052702304020104579433670284061220
Photo by Howard Zheng on Unsplash
by DGR News Service | Feb 6, 2014 | Building Alternatives, Noncooperation, Strategy & Analysis
By Norris Thomlinson / Deep Green Resistance Hawai’i
The situation in many third world countries could actually improve because of the global economic collapse. First world countries would no longer enforce crushing debt repayment and structural adjustment programs, nor would CIA goons be able to prop up “friendly” dictatorships. The decline of export-based economies would have serious consequences, yes, but it would also allow land now used for cash crops to return to subsistence farms.
–from the Deep Green Resistance Decisive Ecological Warfare strategy
David Holmgren, co-originator of permaculture, has a long history of thoughtful and thought-provoking publications, including design books from the original Permaculture One to his 2002 Permaculture: Principles & Pathways Beyond Sustainability. He’s written numerous essays over 35 years, ranging from the specifics of agricultural vs forestry biomass for fuel, to the future of energy decline.
I’ve long admired and respected Holmgren’s thinking, so I was looking forward to reading his new “Crash on Demand” (PDF), an update of his 2007 “Future Scenarios” projections for global developments. I felt especially intrigued that he has arrived at conclusions similar to my own, regarding not just the inevitability, but the desirability of a crash of the financial system as soon as possible. But the article disappointed me; I think Holmgren is soft-selling his realizations to make them palatable to a hoped-for mass movement. Interestingly, even this soft-sell is being rejected by the permaculture blogging community.
Holmgren argues:
“For many decades I have felt that a collapse of the global economic system might save humanity and many of our fellow species great suffering by happening sooner rather than later because the stakes keep rising and scale of the impacts are always worse by being postponed.” (p 9)
“It seems obvious to me that it is easier to convince a minority that they will be better off disengaging from the system than any efforts to build mass movements demanding impossible outcomes or convincing elites to turn off the system that is currently keeping them in power.” (p 14)
“Mass movements to get governments to institute change have been losing efficacy for decades, while a mass movement calling for less seems like a hopeless case. Similarly boycotts of particular governments, companies and products simply change the consumption problems into new forms.” (p 22)
Holmgren proposes a possible solution:
“Given the current fragilities of global finance, I believe a radical change in the behaviour of a relatively small proportion of the global middle class could precipitate such a crash. For example a 50% reduction of consumption and 50% conversion of assets into building household and local community resilience by say 10% of the population in affluent countries would show up as 5% reduction in demand in a system built on perpetual growth and a 5% reduction in savings capital available for banks to lend.” (p 13)
Where I Agree
Holmgren couches his proposal almost rhetorically, apologetically, as if proactively halting the ecocidal system is crazy talk. He need not be so shy about advocating for collapsing the system! It follows very logically if you agree that:
- Industrial civilization is degrading our landbases every day it continues, far faster than we’re healing them
- Industrial civilization will collapse sooner or later regardless of what we do
- Industrial civilization will not divert its resources into healing our landbases before it collapses
The facts back up Holmgren’s assessment of our dire situation, including imminent climate catastrophe if we continue with anything like business as usual. Industrial civilization is driving 200 species extinct each day and threatening humans with extinction or at best a very miserable future on a burning planet. It is deforesting, desertifying, polluting, and acidifying forests, croplands, landbases, and oceans orders of magnitude faster than nature and all the hard-working permaculturists can heal the damage. The industrial economy consists of turning living ecosystems into dead commodities, and it won’t stop voluntarily. It’s headed for an endgame of total planetary destruction before itself collapsing.
So I fully agree with crashing the system as soon as possible, and I fully agree with getting as many people as possible to withdraw their dependence on and allegiance to the systems and structures of industrial civilization. We desperately need people preparing for crash and building resiliency, in human and in broader ecological communities.
Where I Disagree
We also need a viable strategy to stop the dominant culture in its tracks. We are, and will remain, a tiny minority fighting a system of massive power. Individual lifestyle changes do not affect the larger political systems. People “dropping out” is not enough, is not a solution, is not an effective, leveraged way to crash the system.
I worry about Holmgren’s speculative numbers. I assume the elite, who control a hugely disproportionate percentage of income and wealth, will be even harder to convince of voluntary simplicity than the average citizen. The poor generally don’t have the option to cut spending by 50%, and have few or no assets to divest from global corporate investments. My rough calculations (based on data here) suggest that in the US, 15% of earners between the 40th and 80th percentile (more or less the middle class) must adopt this economic boycott to slow consumption by 5%, and nearly 50% of the middle class must divest their savings to reduce nationwide investment in the global financial system by 5%.
Even hoping for just 15% of the US middle class, 18 million people would have to embrace substantial short-term sacrifice. (While decreasing consumption 50% and building gardens and other resiliency infrastructure, people must still work the same hours at their jobs. Otherwise they’ll simply be replaced by those who want to live the consumptive dream.) This lofty goal seems inconsistent with Holmgren’s recognition of the infeasibility of a mass movement.
History throws up more red flags. Again and again, when growth economies have encountered sustainable cultures, people from the growth economies have forced the others off their land, requiring them to integrate into the cash economy. The dominant culture will not gently relinquish access to resources or to consumer markets. It will retaliate with weapons honed over centuries, from taxes and outlawing sustainability to displacement and blatant conquest. On a less dramatic scale, banks can, if divestments sufficiently diminish the cash they’ve been hoarding for years, adjust fractional reserve rates to compensate. (Though precipitating a fast “run” on the banks could work very nicely to crash the financial system and wipe out faith in fiat money.)
Permaculture activists and thousands of other individuals and groups have for years urged people to consume less. Many good people have adopted voluntary simplicity, dropped out of the global economy, and built regenerative local systems. While this has immense value for the adopting individuals, and often ripples out to benefit the wider community, it hasn’t put a dent in the destruction by the larger financial system. New people are born or assimilated into the culture of consumption faster than people are dropping out.
Holmgren advocates more of the same permaculture activism, with little explanation of why it would now convince people in numbers thousands of times greater than in the past. He hopes the ever-more-obvious signs of imminent collapse will prompt a more rapid shift, but given our fleeting window of opportunity to act, we can’t bank on that hope.
Another Approach
Deep Green Resistance is a design book of what makes a good resistance movement, a permaculture analysis of influencing power and political systems. It arrives at the same conclusion as does Holmgren: we need to prepare for crash by building local resiliency, but the sooner industrial civilization comes down, the better. Its crash will leave the majority of humans better off short-term, as their landbases will no longer be plundered by the rich for resources. Crashing the system now will benefit all humans long-term, giving future generations better odds of enjoying liveable landbases on a liveable planet. And crashing the system now will obviously benefit the vast majority of non-humans, currently being poisoned, displaced, and exterminated.
If we truly hold as our goals halting ecocide and slashing greenhouse gas emissions as dramatically as Holmgren suggests, we must devise a realistic plan, based on a realistic assessment of our numbers and strengths, the vulnerabilities of industrial civilization, and how much longer the planet can absorb its blows. Recognizing our tiny numbers and relative weakness compared to the global system, and limited time before our planet is beaten into full ecosystem collapse, we must apply the permaculture principle of making the least change to achieve maximum effect.
The Deep Green Resistance book, as part of its strategy of implementing Decisive Ecological Warfare, examines more than a dozen historic and contemporary militant resistance movements. It concludes that “a small group of intelligent, dedicated, and daring people can be extremely effective, even if they only number one in 1,000, or one in 10,000, or even one in 100,000. But they are effective in large part through an ability to mobilize larger forces, whether those forces are social movements […] or industrial bottlenecks.”
Holmgren notes that it’s easier to convince a minority to disengage from the system than to spark a majority mass movement for true sustainability, but his plan relies on 10% of the population making dramatic change. DGR’s analysis suggests it’s easier yet to convince a tiny minority to take strategic direct action. The rest of the sympathetic population, whether 10% or just 1% of the general public, can provide material support and loyalty with much less immediate sacrifice than in Holmgren’s proposal.
The Movement to Emancipate the Niger Delta (MEND), with small numbers of people and meager resources, has used militant tactics against oil companies to routinely reduce oil output in Nigeria by 10-30%.
In April 2013, saboteurs in San Jose CA shot out transformers in an electrical substation, causing damage that took weeks to repair. The New York Times explains some of the difficulties involved in replacing transformers, especially if many were to fail in a short period of time.
We have more promising strategies available than hoping we can persuade 10% of the population to adopt voluntary simplicity, and hoping that will crash the financial system.
Conclusion
While I wholeheartedly agree with Holmgren’s analysis of our global predicament, and the desirability of crashing the system, his proposal for doing so seems ineffective. Certainly, we should work to disengage ourselves and neighbors from the global system, but we must combine building alternative structures with actively resisting and strategically sabotaging the dominant system.
Many people will disagree with the necessity of crashing the system, because they don’t think conditions are that bad, because they hold vague hopes that God or technology or permaculture will save us, because they fear that fighting back will increase the anger of our abusers, or because they value their own comfort more than the life of the planet. That’s fine; we can agree to disagree, though I encourage those people to further explore these ideas with their minds and with their hearts.
Many people do see the destructiveness of this culture, the inevitability of its crash, and the desirability of it crashing sooner than later; but won’t want to participate directly in bringing it down for any of many perfectly legitimate reasons. That’s fine, too. There’s lots of work to do, and a role for everyone. You can work on restoration of your landbase or crash preparation for your community while providing material and ideological support to those on the front lines. We can join together as “terra-ists”, with our hands not just in the soil as Holmgren defines the term, but also working with wrenches upon the wheels, the levers, and all the apparatus of industrial civilization.
Suggested Resources
- Endgame by Derrick Jensen, two volume analysis of the problems of civilization and the solution. Many excerpts available at the website.
- Deep Green Resistance book, laying out a realistic strategy to save the planet
- Liberal vs Radical video presentation by Lierre Keith, explaining the different approaches of these two different frameworks for perceiving the world
From Permaculture, Perennial Polycultures, and Resistance: Demand Crash! — A response to Holmgren’s “Crash on Demand”