by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Jul 8, 2018 | Direct Action
Editor’s note: The following is from the chapter “A Taxonomy of Action” of the book Deep Green Resistance: A Strategy to Save the Planet. This book is now available for free online.
by Aric McBay
There are four basic ways to directly confront those in power. Three deal with land, property, or infrastructure, and one deals specifically with human beings. They include:
Obstruction and occupation;
Reclamation and expropriation;
Property and material destruction (threats or acts); and
Violence against humans (threats or acts)
In other words, in a physical confrontation, the resistance has three main options for any (nonhuman) target: block it, take it, or break it.
Let’s start with nondestructive obstruction or occupation—block it. This includes the blockade of a highway, a tree sit, a lockdown, or the occupation of a building. These acts prevent those in power from using or physically destroying the places in question. Provided you have enough dedicated people, these actions can be very effective.
But there are challenges. Any prolonged obstruction or occupation requires the same larger support structure as any direct action. If the target is important to those in power, they will retaliate. The more important the site, the stronger the response. In order to maintain the occupation, activists must be willing to fight off that response or suffer the consequences.
An example worth studying for many reasons is the Oka crisis of 1990. Mohawk land, including a burial ground, was taken by the town of Oka, Quebec, for—get ready—a golf course. The only deeper insult would have been a garbage dump. After months of legal protests and negotiations, the Mohawk barricaded the roads to keep the land from being destroyed. This defense of their land (“We are the pines,” one defender said) triggered a full-scale military response by the Canadian government. It also inspired acts of solidarity by other First Nations people, including a blockade of the Mercier Bridge. The bridge connects the Island of Montreal with the southern suburbs of the city—and it also runs through the Mohawk territory of Kahnawake. This was a fantastic use of a strategic resource. Enormous lines of traffic backed up, affecting the entire area for days.
At Kanehsatake, the Mohawk town near Oka, the standoff lasted a total of seventy-eight days. The police gave way to RCMP, who were then replaced by the army, complete with tanks, aircraft, and serious weapons. Every road into Oka was turned into a checkpoint. Within two weeks, there were food shortages.
Until your resistance group has participated in a siege or occupation, you may not appreciate that on top of strategy, training, and stalwart courage—a courage that the Mohawk have displayed for hundreds of years—you need basic supplies and a plan for getting more. If an army marches on its stomach, an occupation lasts as long as its stores. Getting food and supplies into Kanehsatake and then to the people behind the barricades was a constant struggle for the support workers, and gave the police and army plenty of opportunity to harass and humiliate resisters. With the whole world watching, the government couldn’t starve the Mohawk outright, but few indigenous groups engaged in land struggles are lucky enough to garner that level of media interest. Food wasn’t hard to collect: the Quebec Native Women’s Association started a food depot and donations poured in. But the supplies had to be arduously hauled through the woods to circumvent the checkpoints. Trucks of food were kept waiting for hours only to be turned away.31 Women were subjected to strip searches by male soldiers. At least one Mohawk man had a burning cigarette put out on his stomach, then dropped down the front of his pants.32 Human rights observers were harassed by both the police and by angry white mobs.33
The overwhelming threat of force eventually got the blockade on the bridge removed. At Kanehsatake, the army pushed the defenders to one building. Inside, thirteen men, sixteen women, and six children tried to withstand the weight of the Canadian military. No amount of spiritual strength or committed courage could have prevailed.
The siege ended when the defenders decided to disengage. In their history of the crisis, People of the Pines, Geoffrey York and Loreen Pindera write, “Their negotiating prospects were bleak, they were isolated and powerless, and their living conditions were increasingly stressful … tempers were flaring and arguments were breaking out. The psychological warfare and the constant noise of military helicopters had worn down their resistance.”34 Without the presence of the media, they could have been raped, hacked to pieces, gunned down, or incinerated to ash, things that routinely happen to indigenous people who fight back. The film Kanehsatake: 270 Years of Resistance documents how viciously they were treated when the military found the retreating group on the road.
One reason small guerilla groups are so effective against larger and better-equipped armies is because they can use their secrecy and mobility to choose when, where, and under what circumstances they fight their enemy. They only engage in it when they reasonably expect to win, and avoid combat the rest of the time. But by engaging in the tactic of obstruction or occupation a resistance group gives up mobility, allowing the enemy to attack when it is favorable to them and giving up the very thing that makes small guerilla groups so effective.
The people at Kanehsatake had no choice but to give up that mobility. They had to defend their land which was under imminent threat. The end was written into the beginning; even 1,000 well-armed warriors could not have held off the Canadian armed forces. The Mohawk should not have been in a position where they had no choice, and the blame here belongs to the white people who claim to be their allies. Why does the defense of the land always fall to the indigenous people? Why do we, with our privileges and resources, leave the dirty and dangerous work of real resistance to the poor and embattled? Some white people did step up, from international observers to local church folks. But the support needs to be overwhelming and it needs to come before a doomed battle is the only option. A Mohawk burial ground should never have been threatened with a golf course. Enough white people standing behind the legal efforts would have stopped this before it escalated into razor wire and strip searches. Oka was ultimately a failure of systematic solidarity.
Let’s start with nondestructive obstruction or occupation—block it. This includes the blockade of a highway, a tree sit, a lockdown, or the occupation of a building. These acts prevent those in power from using or physically destroying the places in question. Provided you have enough dedicated people, these actions can be very effective.
But there are challenges. Any prolonged obstruction or occupation requires the same larger support structure as any direct action. If the target is important to those in power, they will retaliate. The more important the site, the stronger the response. In order to maintain the occupation, activists must be willing to fight off that response or suffer the consequences.
An example worth studying for many reasons is the Oka crisis of 1990. Mohawk land, including a burial ground, was taken by the town of Oka, Quebec, for—get ready—a golf course. The only deeper insult would have been a garbage dump. After months of legal protests and negotiations, the Mohawk barricaded the roads to keep the land from being destroyed. This defense of their land (“We are the pines,” one defender said) triggered a full-scale military response by the Canadian government. It also inspired acts of solidarity by other First Nations people, including a blockade of the Mercier Bridge. The bridge connects the Island of Montreal with the southern suburbs of the city—and it also runs through the Mohawk territory of Kahnawake. This was a fantastic use of a strategic resource. Enormous lines of traffic backed up, affecting the entire area for days.
At Kanehsatake, the Mohawk town near Oka, the standoff lasted a total of seventy-eight days. The police gave way to RCMP, who were then replaced by the army, complete with tanks, aircraft, and serious weapons. Every road into Oka was turned into a checkpoint. Within two weeks, there were food shortages.
Until your resistance group has participated in a siege or occupation, you may not appreciate that on top of strategy, training, and stalwart courage—a courage that the Mohawk have displayed for hundreds of years—you need basic supplies and a plan for getting more. If an army marches on its stomach, an occupation lasts as long as its stores. Getting food and supplies into Kanehsatake and then to the people behind the barricades was a constant struggle for the support workers, and gave the police and army plenty of opportunity to harass and humiliate resisters. With the whole world watching, the government couldn’t starve the Mohawk outright, but few indigenous groups engaged in land struggles are lucky enough to garner that level of media interest. Food wasn’t hard to collect: the Quebec Native Women’s Association started a food depot and donations poured in. But the supplies had to be arduously hauled through the woods to circumvent the checkpoints. Trucks of food were kept waiting for hours only to be turned away.31 Women were subjected to strip searches by male soldiers. At least one Mohawk man had a burning cigarette put out on his stomach, then dropped down the front of his pants.32 Human rights observers were harassed by both the police and by angry white mobs.33
The overwhelming threat of force eventually got the blockade on the bridge removed. At Kanehsatake, the army pushed the defenders to one building. Inside, thirteen men, sixteen women, and six children tried to withstand the weight of the Canadian military. No amount of spiritual strength or committed courage could have prevailed.
The siege ended when the defenders decided to disengage. In their history of the crisis, People of the Pines, Geoffrey York and Loreen Pindera write, “Their negotiating prospects were bleak, they were isolated and powerless, and their living conditions were increasingly stressful … tempers were flaring and arguments were breaking out. The psychological warfare and the constant noise of military helicopters had worn down their resistance.”34 Without the presence of the media, they could have been raped, hacked to pieces, gunned down, or incinerated to ash, things that routinely happen to indigenous people who fight back. The film Kanehsatake: 270 Years of Resistance documents how viciously they were treated when the military found the retreating group on the road.
One reason small guerilla groups are so effective against larger and better-equipped armies is because they can use their secrecy and mobility to choose when, where, and under what circumstances they fight their enemy. They only engage in it when they reasonably expect to win, and avoid combat the rest of the time. But by engaging in the tactic of obstruction or occupation a resistance group gives up mobility, allowing the enemy to attack when it is favorable to them and giving up the very thing that makes small guerilla groups so effective.
The people at Kanehsatake had no choice but to give up that mobility. They had to defend their land which was under imminent threat. The end was written into the beginning; even 1,000 well-armed warriors could not have held off the Canadian armed forces. The Mohawk should not have been in a position where they had no choice, and the blame here belongs to the white people who claim to be their allies. Why does the defense of the land always fall to the indigenous people? Why do we, with our privileges and resources, leave the dirty and dangerous work of real resistance to the poor and embattled? Some white people did step up, from international observers to local church folks. But the support needs to be overwhelming and it needs to come before a doomed battle is the only option. A Mohawk burial ground should never have been threatened with a golf course. Enough white people standing behind the legal efforts would have stopped this before it escalated into razor wire and strip searches. Oka was ultimately a failure of systematic solidarity.
Expropriation has been a common tactic in various stages of revolution. “Loot the looters!” proclaimed the Bolsheviks during Russia’s October Revolution. Early on, the Bolsheviks staged bank robberies to acquire funds for their cause.36 Successful revolutionaries, as well as mainstream leftists, have also engaged in more “legitimate” activities, but these are no less likely to trigger reprisals. When the democratically elected government of Iran nationalized an oil company in 1953, the CIA responded by staging a coup.37 And, of course, guerilla movements commonly “liberate” equipment from occupiers in order to carry out their own activities.
Sabotage is an essential part of war and resistance to occupation. This is widely recognized by armed forces, and the US military has published a number of manuals and pamphlets on sabotage for use by occupied people. The Simple Sabotage Field Manual published by the Office of Strategic Services during World War II offers suggestions on how to deploy and motivate saboteurs, and specific means that can be used. “Simple sabotage is more than malicious mischief,” it warns, “and it should always consist of acts whose results will be detrimental to the materials and manpower of the enemy.”38 It warns that a saboteur should never attack targets beyond his or her capacity, and should try to damage materials in use, or destined for use, by the enemy. “It will be safe for him to assume that almost any product of heavy industry is destined for enemy use, and that the most efficient fuels and lubricants also are destined for enemy use.”39 It encourages the saboteur to target transportation and communications systems and devices in particular, as well as other critical materials for the functioning of those systems and of the broader occupational apparatus. Its particular instructions range from burning enemy infrastructure to blocking toilets and jamming locks, from working slowly or inefficiently in factories to damaging work tools through deliberate negligence, from spreading false rumors or misleading information to the occupiers to engaging in long and inefficient workplace meetings.
Ever since the industrial revolution, targeting infrastructure has been a highly effective means of engaging in conflict. It may be surprising to some that the end of the American Civil War was brought about in large part by attacks on infrastructure. From its onset in 1861, the Civil War was extremely bloody, killing more American combatants than all other wars before or since, combined.40 After several years of this, President Lincoln and his chief generals agreed to move from a “limited war” to a “total war” in an attempt to decisively end the war and bring about victory.41
Historian Bruce Catton described the 1864 shift, when Union general “[William Tecumseh] Sherman led his army deep into the Confederate heartland of Georgia and South Carolina, destroying their economic infrastructures.”42Catton writes that “it was also the nineteenth-century equivalent of the modern bombing raid, a blow at the civilian underpinning of the military machine. Bridges, railroads, machine shops, warehouses—anything of this nature that lay in Sherman’s path was burned or dismantled.”43 Telegraph lines were targeted as well, but so was the agricultural base. The Union Army selectively burned barns, mills, and cotton gins, and occasionally burned crops or captured livestock. This was partly an attack on agriculture-based slavery, and partly a way of provisioning the Union Army while undermining the Confederates. These attacks did take place with a specific code of conduct, and General Sherman ordered his men to distinguish “between the rich, who are usually hostile, and the poor or industrious, usually neutral or friendly.”44
Catton argues that military engagements were “incidental” to the overall goal of striking the infrastructure, a goal which was successfully carried out.45 As historian David J. Eicher wrote, “Sherman had accomplished an amazing task. He had defied military principles by operating deep within enemy territory and without lines of supply or communication. He destroyed much of the South’s potential and psychology to wage war.”46 The strategy was crucial to the northern victory.
In resistance movements, offensive violence is rare—virtually all violence used by historical resistance groups, from revolting slaves to escaping concentration camp prisoners to women shooting abusive partners, is a response to greater violence from power, and so is both justifiable and defensive. When prisoners in the Sobibór extermination camp quietly killed SS guards in the hours leading up to their planned escape, some might argue that they committed acts of offensive violence. But they were only responding to much more extensive violence already committed by the Nazis, and were acting to avert worse violence in the immediate future.
There have been groups which engaged in systematic offensive violence and attacks directed at people rather than infrastructure. The Red Army Faction (RAF) was a militant leftist group operating in West Germany, mostly in the 1970s and 1980s. They carried out a campaign of bombings and assassination attempts mostly aimed at police, soldiers, and high-ranking government or business officials. Another example would be the Palestinian group Hamas, which has carried out a large number of violent attacks on both civilians and military personnel in Israel. (It is also a political party and holds a legally elected majority in the Palestinian National Authority. It’s often ignored that much of Hamas’s popularity comes from its many social programs, which long predate its election to government. About 90 percent of Hamas’s activities are these social programs, which include medical clinics, soup kitchens, schools and literacy programs, and orphanages.48)
It’s sometimes argued that the use of violence is never justifiable strategically, because the state will always have the larger ability to escalate beyond the resistance in a cycle of violence. In a narrow sense that’s true, but in a wider sense it’s misleading. Successful resistance groups almost never attempt to engage in overt armed conflict with those in power (except in late-stage revolutions, when the state has weakened and revolutionary forces are large and well-equipped). Guerilla groups focus on attacking where they are strongest, and those in power are weakest. The mobile, covert, hit-and-run nature of their strategy means that they can cause extensive disruption while (hopefully) avoiding government reprisals.
Furthermore, the state’s violent response isn’t just due to the use of violence by the resistance, it’s a response to the effectiveness of the resistance. We’ve seen that again and again, even where acts of omission have been the primary tactics. Those in power will use force and violence to put down any major threat to their power, regardless of the particular tactics used. So trying to avoid a violent state response is hardly a universal argument against the use of defensive violence by a resistance group.
The purpose of violent resistance isn’t simply to do violence or exact revenge, as some dogmatic critics of violence seem to believe. The purpose is to reduce the capacity of those in power to do further violence. The US guerilla warfare manual explicitly states that a “guerrilla’s objective is to diminish the enemy’s military potential.”49 (Remember what historian Bruce Catton wrote about the Union Army’s engagements with Confederate soldiers being incidental to their attacks on infrastructure.) To attack those in power without a strategy, simply to inflict indiscriminant damage, would be foolish.
The RAF used offensive violence, but probably not in a way that decreased the capacity of those in power to do violence. Starting in 1971, they shot two police and killed one. They bombed a US barracks, killing one and wounding thirteen. They bombed a police station, wounding five officers. They bombed the car of a judge. They bombed a newspaper headquarters. They bombed an officers’ club, killing three and injuring five. They attacked the West German embassy, killing two and losing two RAF members. They undertook a failed attack against an army base (which held nuclear weapons) and lost several RAF members. They assassinated the federal prosecutor general and the director of a bank in an attempted kidnapping. They hijacked an airliner, and three hijackers were killed. They kidnapped the chairman of a German industry organization (who was also a former SS officer), killing three police and a driver in the attack. When the government refused to give in to their demands to release imprisoned RAF members, they killed the chairman. They shot a policeman in a bar. They attempted to assassinate the head of NATO, blew up a car bomb in an air base parking lot, attempted to assassinate an army commander, attempted to bomb a NATO officer school, and blew up another car bomb in another air base parking lot. They separately assassinated a corporate manager and the head of an East German state trust agency. And as their final militant act, in 1993 they blew up the construction site of a new prison, causing more than one hundred million Deutsche Marks of damage. Throughout this period, they killed a number of secondary targets such as chauffeurs and bodyguards.
Setting aside for the time being the ethical questions of using offensive violence, and the strategic implications of giving up the moral high ground, how many of these acts seem like effective ways to reduce the state’s capacity for violence? In an industrial civilization, most of those in government and business are essentially interchangeable functionaries, people who perform a certain task, who can easily be replaced by another. Sure, there are unique individuals who are especially important driving forces—people like Hitler—but even if you believe Carlyle’s Great Man theory, you have to admit that most individual police, business managers, and so on will be quickly and easily replaced in their respective organizations.50 How many police and corporate functionaries are there in one country? Conversely, how many primary oil pipelines and electrical transmission lines are there? Which are most heavily guarded and surveilled, bank directors or remote electrical lines? Which will be replaced sooner, bureaucratic functionaries or bus-sized electrical components? And which attack has the greatest “return on investment?” In other words, which offers the most leverage for impact in exchange for the risk undertaken?
As we’ve said many times, the incredible level of day-to-day violence inflicted by this culture on human beings and on the natural world means that to refrain from fighting back will not prevent violence. It simply means that those in power will direct their violence at different people and over a much longer period of time. The question, as ever, is which particular strategy—violent or not—will actually work.

by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Jul 1, 2018 | Strategy & Analysis
Editor’s note: The following is from the chapter “A Taxonomy of Action” of the book Deep Green Resistance: A Strategy to Save the Planet. This book is now available for free online.
by Aric McBay
As we’ve made clear, acts of omission are not going to bring down civilization. Let’s talk about action with more potential. We can split all acts of commission into six branches:
- lobbying;
- protests and symbolic acts;
- education and awareness raising;
- support work and building alternatives;
- capacity building and logistics;
- and direct confrontation and conflict.
The illustration “Taxonomy of Action” groups them by directness. The most indirect tactics are on the left, and become progressively more direct when moving from left to right. More direct tactics involve more personal risk. (The main collective risk is failing to save the planet.) Direct acts require fewer people.
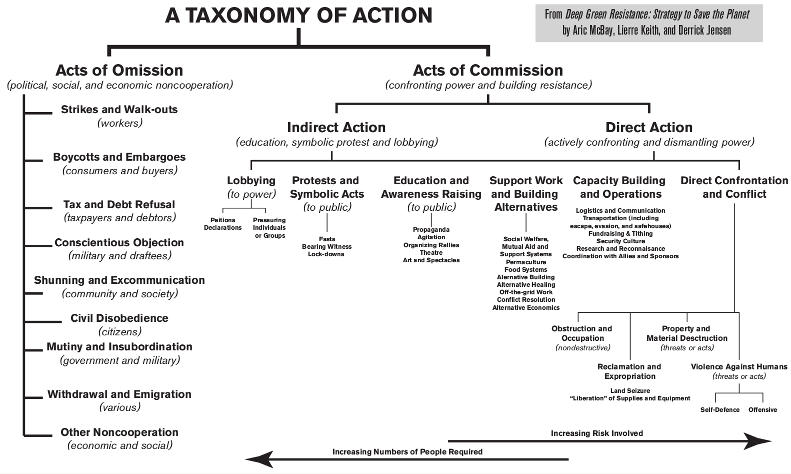
Figure 6-1. Click for larger image.
Lobbying seems attractive because if you have enough resources (i.e., money), you can get government to do things for you, magnifying your actions. Success is possible when many people push for minor change, and unlikely when few people push for major change. But lobbying is too indirect—it requires us to try to convince someone to convince other people to make a decision or pass a law, which will then hopefully be enacted by other people, and enforced by yet a further group.
Lobbying via persuasion is a dead end, not just in terms of taking down civilization, but in virtually every radical endeavor. It assumes that those in power are essentially moral and can be convinced to change their behavior. But let’s be blunt: if they wanted to do the right thing, we wouldn’t be where we are now. Or to put it another way, their moral sense (if present) is so profoundly distorted they are almost all unreachable by persuasion.
And what if they could be persuaded? Capitalists employ vast armies of professional lobbyists to manipulate government. Our ability to lobby those in power (which includes heads of governments and corporations) is vastly outmatched by their ability to lobby each other. Convincing those in power to change would require huge numbers of people. If we had those people, those in power wouldn’t be convinced—they would be replaced. Convincing them to mend their ways would be irrelevant, because we could undertake much more effective action.
Lobbying is simply not a priority in taking down civilization. This is not to diminish or insult lobbying victories like the Clean Water Act and the Wildlife Act, which have bought us valuable time. It is merely to point out that lobbying will not work to topple a system as vast as civilization.
When effective, demonstrations are part of a broader movement and go beyond the symbolic. There have been effective protests, such as the civil rights actions in Birmingham, but they were not symbolic; they were physical obstructions of business and politics. This disruption is usually illegal. Still, symbolic protests can get attention. Protests are most effective at “getting a message out” when they focus on one issue. Modern media coverage is so superficial and sensational that nuances get lost. But a critique of civilization can’t be expressed in sound bytes, so protests can’t publicize it. And civilization is so large and so ubiquitous that there is no one place to protest it. Some resistance movements have employed protests, to show strength and attract recruits, but the majority of people will never be on our side; our strategy needs to be based on effectiveness, not just numbers.
For public education to work, several conditions must be met. The resistance education and propaganda must be able to outcompete the mass media. The general public must be able and willing to unravel the prevailing falsehoods, even if doing that contravenes their own social, psychological, and economic self-interest. They must have accessible ways to change their actions, and they must choose morally preferable actions over convenient ones. Unfortunately, none of these conditions are in place right now.
Another drawback of education is its built-in delay; it may take years before a given person translates new information into action. But as we know, the planet is being murdered, and the window for effective action is small. For deep green resisters, skills training and agitation may be more effective than public education.
Education won’t directly take down civilization, but it may help to radicalize and recruit people by providing a critical interpretation of their experiences. And as civilization continues to collapse, education may encourage people to question the underlying reasons for a declining economy, food crises, and so on.
These support structures directly enable resistance. The Quakers’ Society of Friends developed a sturdy ethic of support for the families of Quakers who were arrested under draconian conditions of religious persecution (see Chapter 4: “Loyalty, Material Support, & Leadership”). People can take riskier (and more effective) action if they know that they and their families will be supported.
Building alternatives won’t directly bring down civilization, but as industrial civilization unravels, alternatives have two special roles. First, they can bolster resistance in times of crisis; resisters are more able to fight if they aren’t preoccupied with getting food, water, and shelter. Second, alternative communities can act as an escape hatch for regular people, so that their day-to-day work and efforts go to autonomous societies rather than authoritarian ones.
To serve either role, people building alternatives must be part of a culture of resistance—or better yet, part of a resistance movement. If the “alternative” people are aligned with civilization, their actions will prolong the destructiveness of the dominant culture. Let’s not forget that Hitler’s V2 rockets were powered by biofuel fermented from potatoes. The US military has built windmills at Guantanamo Bay, and is conducting research on hybrid and fuel-cell vehicles. Renewable energy is a necessity for a sustainable and equitable society, but not a guarantee of one. Militants and builders of alternatives are actually natural allies. As I wrote in What We Leave Behind, “If this monstrosity is not stopped, the carefully tended permaculture gardens and groves of lifeboat ecovillages will be nothing more than after-dinner snacks for civilization.” Organized militants can help such communities from being consumed.
In addition, even the most carefully designed ecovillage will not be sustainable if neighboring communities are not sustainable. As neighbors deplete their landbases, they have to look further afield for more resources, and a nearby ecovillage will surely be at the top of their list of targets for expansion. An ecovillage either has to ensure that its neighbors are sustainable or be able to repel their future efforts at expansion.
In many cultures, what might be considered an “alternative” by some people today is simply a traditional way of life—perhaps the traditional way of life. Peoples struggling with displacement from their lands and dealing with attempts at assimilation and genocide may be mostly concerned with their own survival and the survival of their way of life. And for many indigenous groups, expressing their traditional lifestyle and culture may be in itself a direct confrontation with power. This is a very different situation from people whose lives and lifestyles are not under immediate threat.
Of course, even people primarily concerned with the perpetuation of their traditional cultures and lifestyles are living with the fact that civilization has to come down for any of us to survive. People born into civilization, and those who have benefitted from its privilege, have a much greater responsibility to bring it down. Despite this, indigenous peoples are mostly fighting much harder against civilization than those born inside of it.
Every successful historical resistance movement has rested upon a subsistence base of some kind. Establishing that base is a necessary step, but that alone is not sufficient to stop the world from being destroyed.
Capacity Building and Logistics
Capacity building and logistics are the backbone of any successful resistance movement. Although direct confrontation and conflict may get the glory, no sustained campaign of direct action is possible without a healthy logistical and operational core. That includes the following:
Resistance movements of all kinds must be able to screen recruits or volunteers to assess their suitability and to exclude infiltrators. Members of the group must share certain essential viewpoints and values (either assured through screening or teaching) in order to maintain the group’s cohesion and focus.
Resisters need to be able to communicate securely and rapidly with one another to share information and coordinate plans. They may also need to communicate with a wider audience, for propaganda or agitation. Many resistance groups have been defeated because of inadequate communications or poor communications security.
Resistance requires funding, whether for offices and equipment, legal costs and bail, or underground activities. In aboveground resistance, procurement is mostly a subset of fund raising, since people can buy the items or materials they need. In underground resistance, procurement may mean getting specialized equipment without gathering attention or simply getting items the resistance otherwise would be unable to get.
Of course, fund raising isn’t just a way to get materials, but also a way to support mutual aid and social welfare activities, support arrestees and casualties or their families, and allow core actionists to focus on resistance efforts rather than on “making a living.”
People and equipment need access to transportation in order to reach other resisters and facilitate distribution of materials. Conventional means of transportation may be impaired by collapse, poverty, or social or political repression, but there are other ways. The Underground Railroad was a solid resistance transportation network. The Montgomery bus boycott was enabled by backup transportation systems (especially walking and carpooling) coordinated by civil rights organizers who scheduled carpools and even replaced worn-out shoes.
Security is necessary for any group big enough to make a splash and become a target for state intelligence gathering and repression. Infiltration is definitely a concern, but so is ubiquitous surveillance. This does not apply solely to people or groups considering illegal action. Nonviolent, law-abiding groups have been and are surveilled and disrupted by COINTELPRO-like entities. Many times it is the aboveground resisters who are more at risk as working aboveground means being identifiable.
Research and reconnaissance are equally important logistical tools. To be effective, any strategy requires critical information about potential targets. This is true whether a group is planning to boycott a corporation, blockade a factory, or take out a dam.
Imagine how foolish you’d feel if you organized a huge boycott against some military contractor, only to find that they’d recently converted to making school buses. Resistance researchers can help develop a strategy and identify potential targets and weaknesses, as well as tactics likely to be useful against them. Research is also needed to gain an understanding of the strategy and tactics of those in power.
There are certain essential services and care that keep a resistance movement running smoothly. These include services like the repair of equipment, clothing, and so on. Health care skills and equipment can be extremely valuable, and resistance groups should have at least basic health care capabilities, including first aid and rudimentary emergency medicine, wound care, and preventative medicine.
Coordination with allies and sponsors is often a logistical concern. Many historical guerilla and insurgent groups have been “sponsored” by other established revolutionary regimes or by states hoping to foment revolution and undermine unfriendly foreign governments. For example, in 1965 Che Guevera left postrevolutionary Cuba to help organize and train Congolese guerillas, and Cuba itself had the backing of Soviet Russia. Both Russia and the United States spent much of the Cold War “sponsoring” various resistance groups by training and arming them, partly as a method of trying to put “friendly” governments in power, and partly as a means of waging proxy wars against each other.
Resistance groups can also have sponsors and allies who are genuinely interested in supporting them, rather than attempting to manipulate them. Resistance in WWII Europe is a good example. State-sponsored armed partisan groups and other partisan and underground groups supported resistance fighters such as those in the Warsaw Ghetto.
Direct Conflict and Confrontation
Ultimately, success requires direct confrontation and conflict with power; you can’t win on the defensive. But direct confrontation doesn’t always mean overt confrontation. Disrupting and dismantling systems of power doesn’t require advertising who you are, when and where you are planning to act, or what means you will use.
Back in the heyday of the summit-hopping “antiglobalization” movement, I enjoyed seeing the Black Bloc in action. But I was discomfited when I saw them smash the windows of a Gap storefront, a Starbucks, or even a military recruiting office during a protest. I was not opposed to seeing those windows smashed, just surprised that those in the Black Bloc had deliberately waited until the one day their targets were surrounded by thousands of heavily armed riot police, with countless additional cameras recording their every move and dozens of police buses idling on the corner waiting to take them to jail. It seemed to be the worst possible time and place to act if their objective was to smash windows and escape to smash another day.
Of course, their real aim wasn’t to smash windows—if you wanted to destroy corporate property there are much more effective ways of doing it—but to fight. If they wanted to smash windows, they could have gone out in the middle of the night a few days before the protest and smashed every corporate franchise on the block without anyone stopping them. They wanted to fight power, and they wanted people to see them doing it. But we need to fight to win, and that means fighting smart. Sometimes that means being more covert or oblique, especially if effective resistance is going to trigger a punitive response.
That said, actions can be both effective and draw attention. Anarchist theorist and Russian revolutionary Mikhail Bakunin argued that “we must spread our principles, not with words but with deeds, for this is the most popular, the most potent, and the most irresistible form of propaganda.”30 The intent of the deed is not to commit a symbolic act to get attention, but to carry out a genuinely meaningful action that will serve as an example to others.

by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Jun 2, 2018 | Strategy & Analysis
Editor’s note: The following is from the chapter “A Taxonomy of Action” of the book Deep Green Resistance: A Strategy to Save the Planet. This book is now available for free online.
by Aric McBay
All acts of omission require very large numbers of people to be permanently effective on a large scale. There are plenty of examples of strikes shutting down factories temporarily, but what if you don’t ever want that factory to run again? What if you work at a cruise missile factory or a factory that manufactures nuclear warheads? Is everyone working there willing to go on strike indefinitely? The large pool of unemployed or underpaid working poor means that there are always people willing to step in to work for a wage, even a relatively low one. Failing that, the company in question could just move the factory overseas, as so many have. All of this is especially true in a time when capitalism falters, and attempting to bring down civilization would definitely make capitalism falter.
The same problems apply to economic boycotts. You and I could stop buying anything produced by a given company. Or we could stop buying anything that had been sold through the global capitalist economy. We probably willsee widespread acts of economic omission, but only when large numbers of people get too poor to buy mass-produced consumer luxuries. But because of globalization and automation, these acts of omission will be less effective than they were in the past.
Which isn’t to say we shouldn’t undertake such acts when appropriate. Acts of omission are commonly part of resistance movements; they may be implicit rather than explicit. Pre-Civil War abolitionists would not have owned slaves. But this was an implicit result of their morality and political philosophy rather than a means of change. Few abolitionists would have suggested that by refraining from personally owning slaves they were posing a serious or fundamental threat to the institution of slavery.
An effective resistance movement based on acts of omission might need 10 percent, or 50 percent, or 90 percent of the population to win. One in a thousand people withdrawing from the global economy would have negligible impact. Acts of commission are a different story. What if one out of a thousand people joined a campaign of direct action to bring down civilization? Seven million brave and smart people could ensure the survival of our planet.

If we are going to talk about survival—or about courage, for that matter—we should talk about Sobibór. Sobibór was a Nazi concentration camp built in a remote part of Poland near the German border. Brought into operation in April 1943, Sobibór received regular train loads of prisoners, almost all Jewish. Like other Nazi concentration camps, Sobibór was also a work camp, both for prisoners skilled in certain trades and for unskilled labor, such as body removal. Sobibór was not the largest concentration camp, but it ran with murderous efficiency. Records show that by October 1944 a quarter of a million people had been murdered there, and some argue the casualties were significantly higher.26
Sobibór presented two distinct faces. Upon arrival to the camp, those selected to be killed received a polite welcoming speech from the Nazis (sometimes dressed in lab coats to project expertise and authority), and heard classical music played over loudspeakers. The door to the extermination “showers” was decorated with flowers and a Star of David. Touches like these encouraged them to go quietly and calmly to what some surely realized was their death. In contrast, those who were selected for work were shown a more overtly violent face, suffering arbitrary beatings and sometimes killed for even the smallest failure in cooperation. As at other concentration camps, if individual prisoners even attempted to escape, other prisoners would be killed as a reprisal. (At Auschwitz it was common practice for the SS to kill ten random prisoners for each escapee.)
Sobibór is a lesson for us because it became the site of the most successful—and also the most audacious—concentration camp uprising during the entire Holocaust. A small number of prisoners recognized that it was only a matter of time until they, too, were murdered, and decided that it was worth the risk to escape. However, they knew that those left behind would suffer the consequences of their act. So they hatched a bold plan to allow everyone in the camp to escape.
This was not an easy task. The camp was surrounded by multiple razor wire fences and a minefield, beyond which was forest. In addition to the SS, the camp had SS-trained guards of various Eastern European nationalities, guards who had themselves been brought in from POW camps. The perimeter of the camp had bright lighting systems and numerous machine gun towers.
A breakthrough came with the arrival of a group of Jewish-Russian POWs, with whom the long-time prisoners joined together and devised an escape plan. But to avoid being discovered, they had to keep the plan secret from all but a small group, meaning that the majority of the prisoners would be expected to escape at a moment’s notice without preparation. A Russian POW leader, Alexander “Sasha” Aronowicz Pechersky, understood the benefits. “As a military man, I was aware that a surprise attack is worth a division of solders. If we can maintain secrecy until the last minute of the outbreak, the revolt is 80 percent accomplished. The biggest danger was deconspiration.”27 In preparation for the escape, the conspirators used their trade skills to make or steal knives and axes small enough to conceal in their clothes.
At four o’clock on the day of the escape, they sprang into action. Carefully but quickly, they began to lure SS guards into private locations one by one, under various false pretexts. Then, small groups of prepared prisoners would quickly and quietly kill the SS men by striking them on the head with an axe, or by covering their mouths and stabbing them to death. Within an hour they had killed eleven SS men, half of the SS guards present at the time, and concealed the bodies. At five o’clock they came together for evening roll call, but they arrived slightly early, before the remaining SS men had gathered. Their plan was to avoid the minefield by simply marching as a group to the front gate, as though they were on their way to a work detail. Upon reaching the gate, they hoped to shoot the two Ukrainian guards present and then rush out the front way.
Though they had been lucky so far, one of the bodies was discovered at the last moment, before they could make for the front gate. The Russian Sasha made a very brief “every man for himself” speech and encouraged everyone to escape immediately. The camp then burst into chaos, with some proceeding to the front gate, and others breaking their way through the fence and taking their chances with the mine field. All had to deal with machine gun fire from the guard towers.
Of the roughly 550 prisoners, 150 were unwilling or unable to escape. Some were separated in a different subcamp and were out of communication, and others simply refused to run. Anyone unable or unwilling to fight or run was shot by the SS. About eighty of those who did run were killed by the mines or by hostile fire. Still, more than 300 people (mostly with no preparation) managed to escape the camp into the surrounding woodlands.
Tragically, close to half of these people were captured and executed over the following weeks because of a German dragnet. But since they would have been killed by the SS regardless, the escape was still a remarkable success. Better yet, within days of the uprising, humiliated SS boss Heinrich Himmler ordered the camp shut down, dismantled, and replanted with trees. (See, they don’t always rebuild.)28 And a number of the escapees joined friendly partisan groups in the area and continued to fight the Nazis (including Sasha, who later returned to the Red Army and was sent to a gulag by Stalin for “allowing” himself to be captured in the first place).
The survivors would spend decades mulling over the escape. In many ways, they could hardly have hoped for better luck. If their actions had been discovered any earlier, it’s very possible that everyone in the camp would have been executed. Furthermore, it’s simply amazing that half of the group—very few of whom had any weapons, survival, or escape and evasion training—managed to avoid capture by the Nazis.
They certainly would have benefitted from further training or preparation, although in this case that was at odds with their priority of security. Another issue identified by survivors was that almost all of the firearms went to the Russian POWs, meaning that most escapees were defenseless. They also lacked prearranged cells or affinity groups, and many people who did know each other became separated during the escape. A further problem was the fact that the prisoners did not have contact with Allies or resistance groups who could have helped to arrange further escape or provide supplies or weapons. In the end, a large number of escaped prisoners ended up being killed by anti-Semitic Polish nationals, including some Polish partisans.
Despite these issues, we can learn a lot from this story. The prisoners made remarkable use of their limited resources to escape. The very fact that they attempted escape is inspiring, especially when literally millions of others went to their deaths without fighting back. Indeed, considering that so many of them lacked specific combat and evasion skills and equipment, it was solely the courage to fight back that saved many lives.
No withdrawal or refusal would help them—their lives were won only by audacious acts of commission.

by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Aug 28, 2017 | Toxification
Peak oil extraction has passed and extraction will decline from this point onward. No industrial renewables are adequate substitutes. Richard C. Duncan sums it up in his “Olduvai Theory” of industrial civilization. Duncan predicted a gradual per capita energy decline between 1979 and 1999 (the “slope”) followed by a “slide” of energy production that “begins in 2000 with the escalating warfare in the Middle East” and that “marks the all-time peak of world oil production.” After that is the “cliff,” which “begins in 2012 when an epidemic of permanent blackouts spreads worldwide, i.e., first there are waves of brownouts and temporary blackouts, then finally the electric power networks themselves expire.”34 According to Duncan, 2030 marks the end of industrial civilization and a return to “global equilibrium”—namely, the Stone Age.
Natural gas is also near peak production. Other fossil fuels, such as tar sands and coal, are harder to access and offer a poor energy return. The ecological effects of extracting and processing those fuels (let alone the effects of burning them) would be disastrous even compared to petroleum’s abysmal record.
Will peak oil avert global warming? Probably not. It’s true that cheap oil has no adequate industrial substitute. However, the large use of coal predates petroleum. Even postcollapse, it’s possible that large amounts of coal, tar sands, and other dirty fossil fuels could be used.
Although peak oil is a crisis, its effects are mostly beneficial: reduced burning of fossil fuels, reduced production of garbage, and decreased consumption of disposable goods, reduced capacity for superpowers to project their power globally, a shift toward organic food growing methods, a necessity for stronger communities, and so on. The worst effects of peak oil will be secondary—caused not by peak oil, but by the response of those in power.
Suffering a shortage of fossil fuels? Start turning food into fuel or cutting down forests to digest them into synthetic petroleum. Economic collapse causing people to default on their mortgages? Fuel too expensive to run some machines? The capitalists will find a way to kill two birds with one stone and institute a system of debtors prisons that will double as forced labor camps. A large number of prisons in the US and around the world already make extensive use of barely paid prison laborers, after all. Mass slavery, gulags, and the like are common in preindustrial civilizations. You get the idea.
Featured image: Mogolokwena Platinum Mine, South Africa

by DGR News Service | Jul 30, 2016 | ANALYSIS, Colonialism & Conquest, Repression at Home, The Problem: Civilization
Aric McBay
Originally published at inthewake.org
When some people hear that we want to “end civilization” they initially respond negatively, because of their positive associations with the word “civilization.” This piece is an attempt to clarify, define and describe what I mean by “civilization.”
One dictionary definition1 reads:
civilization
- a society in an advanced state of social development (eg, with complex legal and political and religious organizations); “the people slowly progressed from barbarism to civilization” [syn: civilisation]
- the social process whereby societies achieve civilization [syn: civilisation]
- a particular society at a particular time and place; “early Mayan civilization” [syn: culture, civilisation]
- the quality of excellence in thought and manners and taste; “a man of intellectual refinement”; “he is remembered for his generosity and civilization” [syn: refinement, civilisation]
The synonyms include “advancement,” “breeding,” “civility,” “cultivation,” “culture,” “development,” “edification,” “education,” “elevation,” “enlightenment,” “illumination,” “polish,” “progress,” and “refinement”. Of course. As Derrick Jensen asks, “can you imagine writers of dictionaries willingly classifying themselves as members of ‘a low, undeveloped, or backward state of human society’?”
In contrast, the antonyms of “civilization” include “barbarism,” “savagery,” “wilderness,” and “wildness.” These are the words that civilized people use to refer to those they view as being outside of civilization—in particular, indigenous peoples. “Barbarous,” as in “barbarian,” comes from a Greek word, meaning “non-Greek, foreign.” The word “savage” comes from the Latin “silvaticus” meaning “of the woods.” The origins seem harmless enough, but it’s very instructive to see how civilized people have used these words2:
barbarity
- The quality of being shockingly cruel and inhumane [syn: atrocity, atrociousness, barbarousness, heinousness]
- A brutal barbarous savage act [syn: brutality, barbarism, savagery]
savagery
- The quality or condition of being savage.
- An act of violent cruelty.
- Savage behavior or nature; barbarity.
These associations of cruelty with the uncivilized are, however, in glaring opposition to the historical record of interactions between civilized and indigenous peoples.
Let us take one of the most famous examples of “contact” between civilized and indigenous peoples. When Christopher Columbus first arrived in the “Americas” he noted that he was impressed by the indigenous peoples, writing in his journal that they had a “naked innocence … They are very gentle without knowing what evil is, without killing, without stealing.”
And so he decided “they will make excellent servants.”
In 1493, with the permission of the Spanish Crown, he appointed himself “viceroy and governor” of the Caribbean and the Americas. He installed himself on the island now divided between Haiti and the Dominican republic and began to systematically enslave and exterminate the indigenous population. (The Taino population of the island was not civilized, in contrast to the civilized Inca who the conquistadors also invaded in Central America.) Within three years he had managed to reduce the indigenous population from eight million to three million. By 1514 only 22,000 of the indigenous population remained, and after 1542 they were considered extinct.3
The tribute system, instituted by [Columbus] sometime in 1495, was a simple and brutal way of fulfilling the Spanish lust for gold while acknowledging the Spanish distaste for labor. Every Taino over the age of fourteen had to supply the rulers with a hawk’s bell of gold every three months (or, in gold-deficient areas, twenty-five pounds of spun cotton; those who did were given a token to wear around their necks as proof that they had made their payment; those did not were … “punished” – by having their hands cut off … and [being] left to bleed to death.4
More than 10,000 people were killed this way during Columbus’ time as governor. On countless occasions, these civilized invaders engaged in torture, rape, and massacres. The Spaniards
… made bets as to who would slit a man in two, or cut off his head at one blow; or they opened up his bowels. They tore the babes from their mother’s breast by their feet and dashed their heads against the rocks … They spitted the bodies of other babes, together with their mothers and all who were before them, on their swords.5
On another occasion:
A Spaniard … suddenly drew his sword. Then the whole hundred drew theirs and began to rip open the bellies, to cut and kill – men, women, children and old folk, all of whom were seated off guard and frightened … And within two credos, not a man of them there remains alive. The Spaniards enter the large house nearby, for this was happening at its door, and in the same way, with cuts and stabs, began to kill as many as were found there, so that a stream of blood was running, as if a number of cows had perished.6
This pattern of one-way, unprovoked, inexcusable cruelty and viciousness occurred in countless interactions between civilized and indigenous people through history.

This phenomena is well-documented in excellent books including Ward Churchill’s A Little Matter of Genocide: Holocaust and Denial in the Americas, 1492 to the Present, Kirkpatrick Sale’s The Conquest of Paradise: Christopher Columbus and the Columbian Legacy, and Dee Brown’s Bury My Heart at Wounded Knee: An Indian History of the American West. Farley Mowat’s books, especially Walking on the Land, The Deer People, and The Desperate People document this as well with an emphasis on the northern and arctic regions of North America.
There is also good information in Howard Zinn’s A People’s History of the United States and Voices of a People’s History of the United States. Eduardo Galeando’s incredible Memory of Fire trilogy covers this topic as well, with an emphasis on Latin America (this epic trilogy reviews numerous related injustices and revolts). Jack D Forbes’ book Columbus and Other Cannibals: The Wetiko Disease of Exploitation, Imperialism and Terrorism is highly recommended. You can also find information in Jared Diamond’s Guns, Germs and Steel: The Fates of Human Societies, although I often disagree with the author’s premises and approach.
The same kind of attacks civilized people committed against indigenous peoples were also consistently perpetrated against non-human animal and plant species, who were wiped out (often deliberately) even when civilized people didn’t need them for food; simply as blood-sport. For further readings on this, check out great books like Farley Mowat’s extensive and crushing Sea of Slaughter, or Clive Ponting’s A Green History of the World: The Environment and the Collapse of Great Civilizations (which also examines precivilized history and European colonialism).
With this history of atrocity in mind, we should (if we haven’t already) cease using the propaganda definitions of civilized as “good” and uncivilized as “bad” and seek a more accurate and useful definition. Anthropologists and other thinkers have come up with a number of somewhat less biased definitions of civilization.
Nineteenth century English anthropologist E B Tylor defined civilization as life in cities that is organized by government and facilitated by scribes (which means the use of writing). In these societies, he noted, there is a resource “surplus”, which can be traded or taken (though war or exploitation) which allows for specialization in the cities.
Derrick Jensen, having recognized the serious flaws in the popular, dictionary definition of civilization, writes:
I would define a civilization much more precisely, and I believe more usefully, as a culture – that is, a complex of stories, institutions, and artifacts – that both leads to and emerges from the growth of cities (civilization, see civil: from civis, meaning citizen, from latin civitatis, meaning state or city), with cities being defined – so as to distinguish them from camps, villages, and so on – as people living more or less permanently in one place in densities high enough to require the routine importation of food and other necessities of life.
Jensen also observes that because cities need to import these necessities of life and to grow, they must also create systems for the perpetual centralization of resources, yielding “an increasing region of unsustainability surrounded by an increasingly exploited countryside.”

Contemporary anthropologist John H Bodley writes: “The principle function of civilization is to organize overlapping social networks of ideological, political, economic, and military power that differentially benefit privileged households.”7 In other words, in civilization institutions like churches, corporations and militaries exist and are used to funnel resources and power to the rulers and the elite.
The twentieth century historian and sociologist Lewis Mumford wrote one of my favourite and most cutting and succinct definitions of civilization. He uses the term civilization
… to denote the group of institutions that first took form under kingship. Its chief features, constant in varying proportions throughout history, are the centralization of political power, the separation of classes, the lifetime division of labor, the mechanization of production, the magnification of military power, the economic exploitation of the weak, and the universal introduction of slavery and forced labor for both industrial and military purposes.8
Taking various anthropological and historical definitions into account, we can come up with some common properties of civilizations (as opposed to indigenous groups).
- People live in permanent settlements, and a significant number of them in cities.
- The society depends on large-scale agriculture (which is needed to support dense, non-food-growing urban populations).
- The society has rulers and some form of “aristocracy” with centralized political, economic, and military power, who exist by exploiting the mass of people.
- The elite (and possibly others) use writing and numbers to keep track of commodities, the spoils of war, and so on.
- There is slavery and forced labour either by the direct use of physical violence, or by economic coercion and violence (through which people are systematically deprived of choices outside the wage economy).
- There are large armies and institutionalized warfare.
- Production is mechanized, either through physical machines or the use of humans as though they were machines (this point will be expanded on in other writings here soon).
- Large, complex institutions exist to mediate and control the behaviour of people, through as their learning and worldview (schools and churches), as well as their relationships with each other, with the unknown, and with the nature world (churches and organized religion).
Anthropologist Stanley Diamond recognized the common thread in all of these attributes when he wrote; “Civilization originates in conquest abroad and repression at home”.9
This common thread is control. Civilization is a culture of control. In civilizations, a small group of people controls a large group of people through the institutions of civilization. If they are beyond the frontier of that civilization, then that control will come in the form of armies and missionaries (be they religious or technical specialists). If the people to be controlled are inside of the cities, inside of civilization, then the control may come through domestic militaries (ie, police). However, it is likely cheaper and less overtly violent to condition of certain types of behaviour through religion, schools or media, and related means, than through the use of outright force (which requires a substantial investment in weapons, surveillance and labour).
That works very effectively in combination with economic and agricultural control. If you control the supply of food and other essentials of life, people have to do what you say or they die. People inside of cities inherently depend on food systems controlled by the rulers to survive, since the (commonly accepted) definition of a city is that the population is dense enough to require the importation of food.
For a higher degree of control, rulers have combined control of food and agriculture with conditioning that reinforces their supremacy. In the dominant, capitalist society, the rich control the supply of food and essentials, and the content of the media and the schools. The schools and workplaces act as a selection process: those who demonstrate their ability to cooperate with those in power by behaving properly and doing what they’re told at work and school have access to higher paying jobs involving less labour. Those who cannot or will not do what they’re told are excluded from easy access to food and essentials (by having access only to menial jobs), and must work very hard to survive, or become poor and/or homeless. People higher on this hierarchy are mostly spared the economic and physical violence imposed on those lower on the hierarchy. A highly rationalized system of exploitation like this helps to increase the efficiency of the system by reducing the chance of resistance or outright rebellion of the populace.
The media’s propaganda systems have most people convinced that this system is somehow “natural” or “necessary”—but of course, it is both completely artificial and a direct result of the actions of those in power (and the inactions of those who believe that they benefit from it, or are prevented from acting through violence or the threat of violence).
In contradiction to the idea that the dominant culture’s way of living is “natural,” human beings lived as small, ecological, participatory, equitable groups for more than 99% of human history. There are a number of excellent books and articles comparing indigenous societies to civilization:
These sources show there were healthy, equitable and ecological communities in the past, and that they were the norm for countless generations. It is civilization that is monstrous and aberrant.
Living inside of the controlling environment of civilization is an inherently traumatic experience, although the degree of trauma varies with personal circumstance and the amounts of privilege different people have in society. Derrick Jensen makes this point very well in A Language Older than Words (Context Books, 2000), and Chellis Glendinning covers it as well in My name is Chellis.
Endnotes
1. Definition of “civilization” is from WordNet R 2.0, 2003, Princeton University
2. Definitions of “barbarity” and “savagery” are from The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language, Fourth Edition, 2000, Houghton Mifflin Company.
3. I owe many of the sources in this section to the research of Ward Churchill. The figure of eight million is from chapter six of Essays in Population History, Vol I by Sherburn F Cook and Woodrow Borah (Berkeley: University of California Press, 1971). The figure of three million is from is from a survey at the time by Bartolome de Las Casas covered in J B Thatcher, Christopher Columbus, two volumes (New York: Putnam’s, 1903-1904) Vol 2, page 384 ff. They were considered extinct by the Spanish census at the time, which is summarized in Lewis Hanke’s The Spanish Struggle for Justice in the Conquest of America (Philapelphia: University of Pennsylvania Press, 1947) page 200 ff.
4. Sale, Kirkpatrick. The Conquest of Paradise: Christopher Columbus and the Columbian Legacy (New York: Alfred A Knopf, 1990) page 155.
5. de Las Casas, Bartolome. The Spanish Colonie: Brevisima revacion (New York: University Microfilms Reprint, 1966).
6. de Las Casas, Bartolome. Historia de las Indias, Vol 3, (Mexico City: Fondo Cultura Economica, 1951) chapter 29.
7. Bodley, John H, Cultural Anthropology: Tribes, States and the Global System. Mayfield, Mountain View, California, 2000.
8. Mumford, Lewis. Technics and Human Development, Harcourt Brace Jovanovich, New York, 1966, page 186.
9. Diamond, Stanley, In Search of the Primitive: A Critique of Civilization, Transaction Publishers, New Brunswick, 1993, page 1.
Photo by Henry Chen on Unsplash








