
by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Jun 27, 2016 | Colonialism & Conquest
Featured Image: The Orang Rimba have lived in the forests of Sumatra for generations, but now they are under threat. © Survival International
By Survival International
Members of the nomadic Orang Rimba tribe in Indonesia have been attacked and their possessions burned as part of an eviction from a palm oil plantation on their ancestral land.
The Orang Rimba are a nomadic hunter-gatherer tribe who have been dependent on and managed their forest home in Sumatra for generations. Although a national park was created to protect local wildlife and – unprecedented in Indonesia – the tribe, the Indonesian government has signed over most of their ancestral lands to palm oil, timber and other plantation companies.
As a result many Orang Rimba are forced to live in plantations, collecting palm oil seeds and hunting wild boar. For collecting the seeds, the tribe have been accused of theft by the company operating in the area, even though the oil palm is on Orang Rimba ancestral land and the tribe do not regard such foraging as theft.
One Orang Rimba man said: “That is our ancestral land. Our life and death are in that land. How can it be that we are forbidden? It’s forbidden for children to take the seeds which have fallen from the palm oil trees. How can it be forbidden? They planted palm oil trees all over our land.”
The palm oil company PT Bahana Karya Semestra (BKS), which is owned by Sinar Mas, has recently ordered the Orang Rimba to leave. Members of the tribe have reported that they were already preparing to go when they were attacked, beaten and stabbed by security staff from BKS.
Security staff then set fire to their shelters, vehicles and hundreds of loin cloths. According to custom, these are regarded as the tribespeople’s most precious possessions. They represent wealth and prestige and are used to pay fines in Orang Rimba customary law.
The Orang Rimba’s land and resources are being stolen, and they are being subjected to violence in the name of ‘’progress.’’ Survival International, the global movement for tribal peoples rights, is calling for the Orang Rimba’s right to their ancestral lands to be recognized.

by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Jun 22, 2016 | Colonialism & Conquest
Featured image: The Guarani feel a deep sense of connection to their land and have protested against its theft and destruction
© CIMI/Survival
By Survival International
The Olympic torch is set to arrive on June 25 in a state where the Guarani tribe is widely feared to be facing annihilation due to systematic land theft, malnutrition, suicide and violence.
The torch’s arrival in Mato Grosso do Sul in the southwest of Brazil comes as part of a nationwide tour before the start of the Rio de Janeiro Olympics in August. It is set to be carried by Rocleiton Ribeiro Flores, an indigenous man from the Terena people, in the city of Dourados which is close to Guarani territory.
Last week, one Guarani man was killed and several others – including a twelve year old boy – were seriously injured in an attack by ranchers’ gunmen on Tey’i Jusu community.
The previous day, Survival received audio through its Tribal Voice project documenting a separate armed attack on Pyelito Kuê community. Elsewhere, another community, Apy Ka’y, is facing eviction after a land reoccupation in 2013.
With the eyes of the world on Brazil, many campaigners are hoping that the Olympics will raise global awareness of the genocidal violence, slavery and racism that have been inflicted on indigenous Brazilians past and present in the name of “progress” and “civilization.”
Over the past few decades, most of the Guarani’s land has been stolen by destructive agribusiness, and they have been forced to live on roadsides and in overcrowded reservations. Guarani children starve and many of their leaders have been assassinated. Hundreds of Guarani men, women and children have killed themselves and the Guarani Kaiowá group suffer the highest suicide rate in the world.

Damiana, a Guarani woman, performs a ceremony on her land. What used to be forest is now a vast farm.
© Paul Patrick Borhaug/Survival International
Tonico Benites Guarani, a spokesman for the tribe, recently visited Europe to urge international action on his people’s plight and told Survival: “A slow genocide is taking place. There is a war being waged against us. We are scared. They kill our leaders, hide their bodies, intimidate and threaten us… If nothing changes many more young people will kill themselves, and others will die of malnutrition. The impunity of the ranchers will continue and the Brazilian government will be able to continue killing us.”
The Guarani have made numerous attempts to reoccupy their lands, but have been harassed, intimidated and attacked by ranchers’ gunmen.
Under international and Brazilian law, the tribe has a right to their land. If the government returns it to them, they will have a chance to defend their lives, protect their lands and determine their own futures.
In April, Survival International launched its “Stop Brazil’s Genocide” campaign to draw attention to the threats facing the Guarani, the plight of Brazil’s uncontacted tribes – who are among the most vulnerable peoples on the planet – and PEC 215, a proposed change to Brazilian law which would undermine tribal land rights and lead to the break up and exploitation of existing indigenous territories.
As the Olympics approach, Survival supporters around the world are pushing Brazil to return the Guarani’s land and stop PEC 215, and to map out the territory of the uncontacted Kawahiva people to prevent their annihilation.
Survival’s Director Stephen Corry said: “This is undoubtedly the most serious and sustained attack on indigenous rights that Brazil has seen since the end of the military dictatorship, and it’s picking up pace. The media has focused on Brazil’s political turmoil in the run up to the Olympics, but very little has been said about the systematic annihilation of Brazilian indigenous peoples through the violation of their land rights. It was the genocide of Brazilian tribal peoples that prompted the foundation of Survival in 1969, and enormous progress has been made since. Now, almost half a century later, genocide is back on the table.”
by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Jun 18, 2016 | Colonialism & Conquest
By Laura Hobson Herlihy / Cultural Survival
The Miskitu people (pop. 185,000) live in Muskitia, a rainforest region that stretches along the Central American Caribbean coast from Black River, Honduras to just south of Bluefields, Nicaragua. Two-thirds of Muskitia and the Miskitu people reside in Nicaragua. The Miskitu people in Nicaragua today are in a crisis situation. Armed mestizo colonists are attacking their communities, pillaging and confiscating their rainforest lands. This article is a cry for help.
The Miskitu people have legal ownership of their lands guaranteed by Nicaraguan Law 445, the ILO Convention 169, and the UN Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous People. Yet, mestizo colonists (called, colonos) from the interior and Pacific coast have invaded, and now illegally occupy, nearly half of their lands. In September 2015, violence over land conflicts erupted in the Miskitu territories of Wangki Twi-Tasba Raya and Li Aubra. These territories are located near the Coco or Wangki River, the international border between Nicaragua and Honduras.
Since September, mestizo colonists with automatic weapons have killed, injured, and kidnapped more than 80 Miskitu men with impunity. In fear for their lives, between 1-2,000 Miskitu refugees have fled to Waspam and Puerto Cabezas-Bilwi and Honduran border communities. The refugees–mainly women, children, and elders–are suffering from starvation and lack medical supplies. Children have not attended school for six months. Meanwhile, periodic attacks continue on Miskitu communities in Wangki Twi-Tasba Raya.
Much of the violence now occurring revolves around article 59 of the Communal Property Law (law 445). Article 59 requires the Nicaraguan state to complete saneamiento, the cleansing or the removal of colonists and industries from Indigenous and Afro-descendant territories. The current Nicaraguan government publically agreed to saneamiento but has not responded. Similarly, the government still has not provided protection to the Miskitu communities under attack or assistance to the refugees. As a result of the government’s delayed reaction to the crisis, the Miskitu people now suspect the Sandinista (FSLN) state to be complicit with the colonists’ invasion of their Indigenous territories.
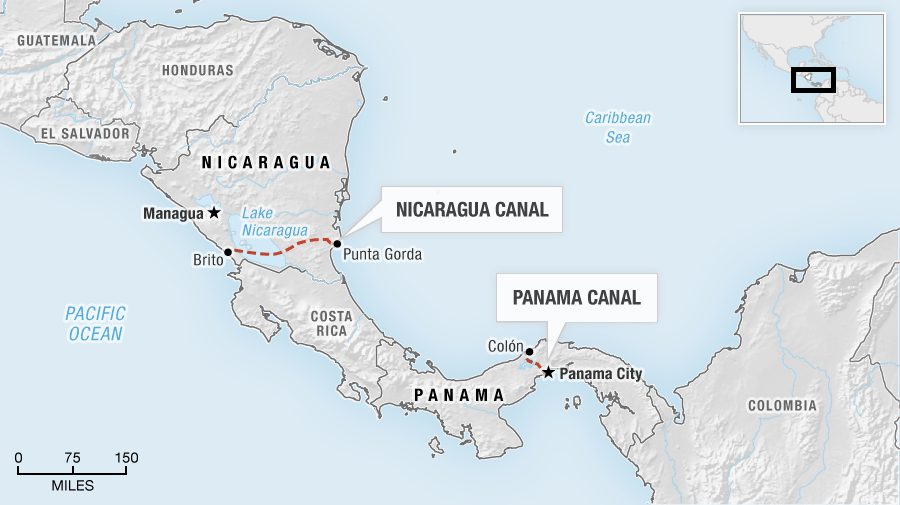
In a separate but related issue, the FSLN government passed the Canal Law (Act 840) that approved the Chinese-backed (HKND) inter-oceanic canal to cut through the ancestral homeland of the Indigenous and Afro-descendant peoples along the Nicaraguan Caribbean coast. Tensions are rising over Indigenous territoriality and land rights, especially between the Miskitu people and President Daniel Ortega’s Sandinista government. The tense situation over land rights today bares eerie similarities to the war-torn years of the 1980s in Nicaragua, when Ortega first served as President (1985-1990) and the Miskitu fought as counter-revolutionary warriors in the Contra war within the Sandinista revolution (1979-1990).
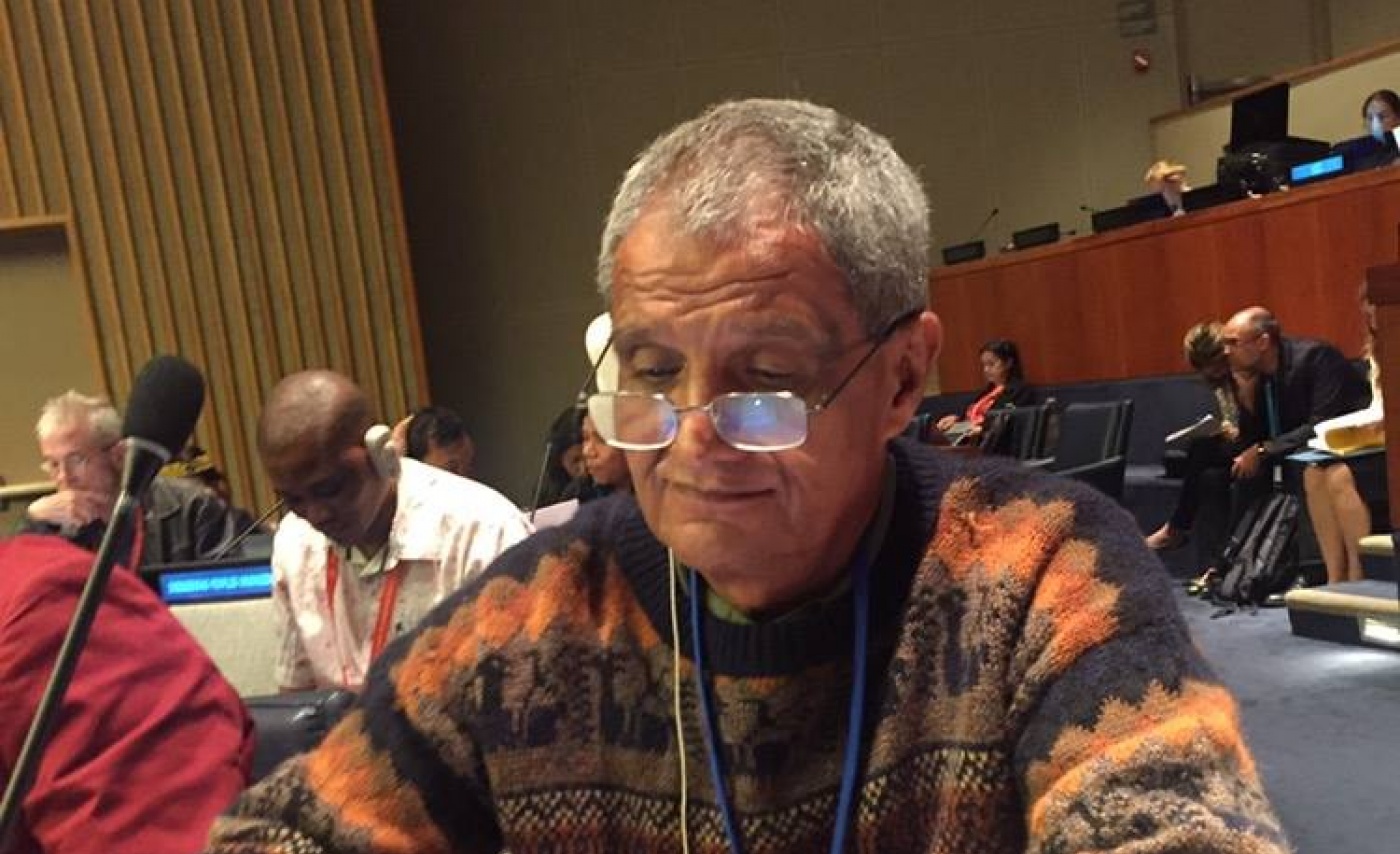
As a US anthropologist who has worked for over twenty years with the Honduran and Nicaraguan Miskitu people, I had the opportunity to attend the 2016 United Nations Permanent Forum on Indigenous Issues (May 9-20). On Thursday, May 12, I recorded Miskitu leader Brooklyn Rivera’s intervention in the session, “Dialogue with Indigenous Peoples.” Rivera has served as the Líder Máximo (literally, Highest Leader) of the Nicaraguan Miskitu people for over 30 years; after rising to power as a military leader in the revolution and war, Rivera in 1987 founded and became the long-term director of the Indigenous organization Yatama (Yapti Tasba Masraka Nanih Aslatakanka/Sons of Mother Earth). Special thanks to Costa Rican anthropologist Fernando Montero (ABD, Columbia) for transcribing Rivera’s United Nations intervention in Spanish and translating it to the English below.

English Version
My name is Brooklyn Rivera. I am both a son and the highest leader of the Miskitu people of the Nicaraguan Muskitia. As we know, the rights of Indigenous peoples are essentially human rights. According to Article 1 of the UN Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples, Indigenous people have the right, both as peoples and as individuals, to the full enjoyment of their human rights and fundamental liberties. In my country of Nicaragua, the rights of Indigenous people have suffered severe setbacks in the last several years. Indeed, the current Sandinista government–contrary to its rhetoric in international forums and in flagrant violation of the rights of Indigenous peoples–freely acts against Indigenous peoples, advancing a consistent policy of aggression and internal colonialism.
Consider the following within the specific sphere of Indigenous peoples’ rights: the government imposes violence against our communities by means of settlers who invade ancestral territories, carrying out armed attacks, murders, kidnappings, rape, and displacement, producing refugees, most of whom are women, children, and people of old age. All this occurs in the face of governmental and institutional passivity, even complicity. Moreover, the Nicaraguan government is currently implementing a policy of militarization in our communities and fishing territories, committing murders such as that of our brother and leader Mario Lehman last September. In like manner, the government is overtly trampling on our communities’ right to ancestral autonomy by interfering with the election of their leaders according to their own practices and customs, devoting itself to destroying the structure and traditional procedures of our communities with the aim of replacing them with the so-called Sandinista Leadership Committees, part of their party structure. In this way they create and impose a spurious and noxious structure parallel to Indigenous authorities. You will understand that, by applying this policy, the government and the ruling party are fomenting division within families and communities, destroying their social fabric, cultural values and [imposing] heightened suffering and poverty. In addition, in open violation of the right to work, the Sandinista government denies jobs and government positions to Indigenous professionals and technicians, demanding that they become members of their party before considering them for these positions.
With regard to the sphere of the environment of our peoples in Nicaragua, I must first point out the dispossession of lands and territories suffered by Miskitu communities perpetrated by cattle ranchers, mining companies, and wealthy sectors linked to the government and the ruling party, who use settlers as spearheads. In this invasion, armed settlers arrive in our lands, advance the agricultural frontier, occupy extensions of territory, and destroy the habitats and ecosystems of Indigenous peoples, preying on their fauna, flora, and marine ecology. Needless to say, this extractivist policy involves the looting of ancestral communal resources such as forests, flora, mineral resources, water resources, and land itself with the illegal land sales in which settlers participate. I must also mention the promotion of megaprojects such as the interoceanic canal and the Tumarin hydroelectric dam in Awaltara, both of which violate Indigenous peoples’ right to prior, free, and informed consent. These megaprojects render entire communities vulnerable to disappearing along with their culture and language. This is the case of the Rama people, a small, vulnerable people in danger of extinction who reside in the Southern Moskitia. In the face of this crude reality and despite its demonstrated lack of political will and its disrespect for international laws and institutions—not to mention my own arbitrary, illegal expulsion from the National Parliament—once again we demand from the Nicaraguan government:
1. The immediate application of the recommendations issued last December by the UN Special Rapporteur on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples, in reference to the cleansing [“saneamiento”] of Indigenous territories and the protection of our communities in the face of settler invasion;
2. The immediate enactment of the precautionary measures suggested by the OAS’ Human Rights Commission on behalf of the Indigenous communities in the regions of Tasba Raya and Wangki Li Auhbra (location in the municipality of Waspam), approved in October 2015 and expanded in January 2016;
3. The immediate launch of a process of genuine dialogue and negotiation with Indigenous peoples via their organizations and leaders to reach real solutions based on respect for Indigenous peoples and the recognition of their dignity, as outlined in existing frameworks;
4. Finally, the immediate restitution of the undersigned as legislator, in accordance with his status as a popularly elected official put in power thanks to the votes of Indigenous peoples, whose constitutional and legal rights were violated with my arbitrary and illegal expulsion from Parliament.
I end my intervention by asking all participants, especially the Indigenous peoples in this forum, to engage in active solidarity with the Indigenous peoples of Nicaragua and their organizations as they resist and demand dignity, rights, and justice from the Sandinista government in Nicaragua.
Thank you, Mr. President.
En Espanol
Soy Brooklyn Rivera, hijo del pueblo mískitu de la Mosquitia nicaragüense y su dirigente principal. Como sabemos, los derechos de los pueblos indígenas son esencialmente derechos humanos. Como se establece en el artículo 1 de la Declaración de la ONU sobre los Pueblos Indígenas, los indígenas tienen derecho como pueblos o como individuos al disfrute pleno de todos sus derechos humanos y las libertades fundamentales. El país de donde vengo yo, Nicaragua, en los últimos años ha experimentado un grave retroceso en el ejercicio de los derechos de nuestros pueblos indígenas, recogido en el marco legal interno y externo del país. En efecto, el actual gobierno sandinista, contrario a su retórica en los foros internacionales y en abierta violación de los derechos de los pueblos indígenas reconocidos en la Constitución Política y en las demás leyes y los instrumentos internacionales suscritos, se dedica a actuar libremente en su contra impulsando toda una política de agresión y colonialismo interno.
Veamos: en el ámbito específico de los derechos humanos de nuestros pueblos indígenas, a través de los colonos invasores de los territorios ancestrales, impone una situación de violencia en contra de nuestras comunidades mediante ataques armados, cometiendo asesinatos, secuestros, violaciones y desplazamentos, produciendo refugiados, mayormente niños, mujeres y ancianos. Todo esto ocurre ante la pasividad y aun la complicidad del gobierno y sus instituciones. Más aún, el gobierno nicaragüense implementa una política de militarización de las comunidades y las áreas de pesca, en las que cometen asesinatos como en el caso del crimen del hermano dirigente Mario Lehman ocurrido en el mes de septiembre pasado. De la misma forma, el gobierno aplica un abierto atropello al derecho de autonomía ancestral de nuestras comunidades en la elección de sus autoridades basada en los usos y costumbres, cuando a través de sus turbas partidarias y con el acompañamiento de sus policías y hasta de militares, aún así sin el mínimo respeto a las leyes y formas organizativas propias, se empecina en destruir la estructura y los procedimientos tradicionales de nuestras comunidades con el fin de sustituirlos con los llamados Comités de Liderazgo Sandinista, una estructura de su partido en el poder, creando e imponiendo así una estructura espuria y nociva, paralela a las autoridades indígenas. Como comprenderán, aplicando esta política el gobierno y su partido crean división entre las familias y comunidades, destruyendo sus tejidos sociales, valores culturales y mayor sufrimiento y pobreza. Además, el gobierno sandinista en abierta discriminación al derecho al trabajo, niega a los profesionales y técnicos de los pueblos indígenas el derecho al trabajo cuando exige que debe convertir a ser miembro de su partido para ocupar cargos o empleo en el país.
En relación al ámbito del medio ambiente de nuestros pueblos en Nicaragua, debo iniciar señalando el despojo de las tierras y territorios que sufren las comunidades en la Mosquitia de parte de los terratenientes ganaderos, empresas mineras y grupos adinerados vinculados al gobierno y a su partido, utilizando a los colonos como punta de lanza. En la invasión, los colonos armados llegan a nuestras tierras, aplican un avance agropecuario, ocupan extensiones de territorio y destruyen los hábitats y los ecosistemas de los pueblos indígenas, cometiendo depredaciones ambientales en su fauna, flora y entorno marino. Lógicamente, con esta política extractivista pasa por el saqueo de los bienes comunales ancestrales tales como los bosques, la flora, los recursos mineros, los recursos hídricos y la misma tierra con el tráfico ilegal de parte de los colonos. También aquí debo mencionar el impulso de los megaproyectos tales como el canal interocéanico y el hidroeléctrico Tumarín en Awaltara, en ambos casos violentando el derecho al consentimiento previo, libre e informado de los pueblos, impulsan sus megaproyectos en los que exponen la desaparición de comunidades enteras junto con su cultura y su idioma. Tal es el caso del pueblo Rama, pueblo pequeño, vulnerable y en proceso de extinción, ubicado en la Mosquitia Sur. Ante esta cruda realidad y a pesar de su falta de voluntad política demostrada y de su irrespeto a las leyes y las instituciones internacionales, así como de mi expulsión arbitrario e ilegal del Parlamento Nacional, como un esfuerzo de solución al conflicto impuesto, una vez más exigimos al gobierno nicaragüense:
- La inmediata aplicación de las recomendaciones de la Relatora Especial de las Naciones Unidas sobre los Derechos de los Pueblos Indígenas, emitidas en el mes de diciembre pasado, referentes al cumplimiento de la etapa de saneamiento de los territorios y de la protección de nuestras comunidades ante la invasión de los colonos;
- El inmediato cumplimiento de las medidas cautelares presentadas de parte de la Comisión de Derechos Humanos de la OEA a favor de las comunidades indígenas de la zona de Tasba Raya y de Wangki Li Auhbra en el municipio de Waspam, y abrobadas en el mes de octubre 2015 y ampliadas en enero de 2016;
- La inmediata apertura de un proceso genuino de diálogo y negociaciones con los pueblos indígenas a través de sus organizaciones y líderes que conduzcan a unas soluciones reales basadas en el respeto y el reconocimiento de la dignidad y los derechos de nuestros pueblos reconocidos en las normativas;
- Finalmente, la restitución inmediata del suscrito como legislador electo popularmente con los votos de sus pueblos indígenas, violentando mis derechos constitucionales y legales con el despojo arbitrario e ilegal cometido durante mi expulsión del Parlamento.
Termino mi intervención requiriendo a todas y todos los participantes, mayormente a los pueblos indígenas de este foro, una solidaridad activa con los pueblos indígenas y sus organizaciones en Nicaragua en el marco de su resistencia y demanda de dignidad, derecho y justicia ante el gobierno sandinista en Nicaragua.
Gracias, Presidente.

by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Jun 8, 2016 | Colonialism & Conquest
By Alexandre Dereims / Organic the Jarawas
Images copyright by Claire Beilvert
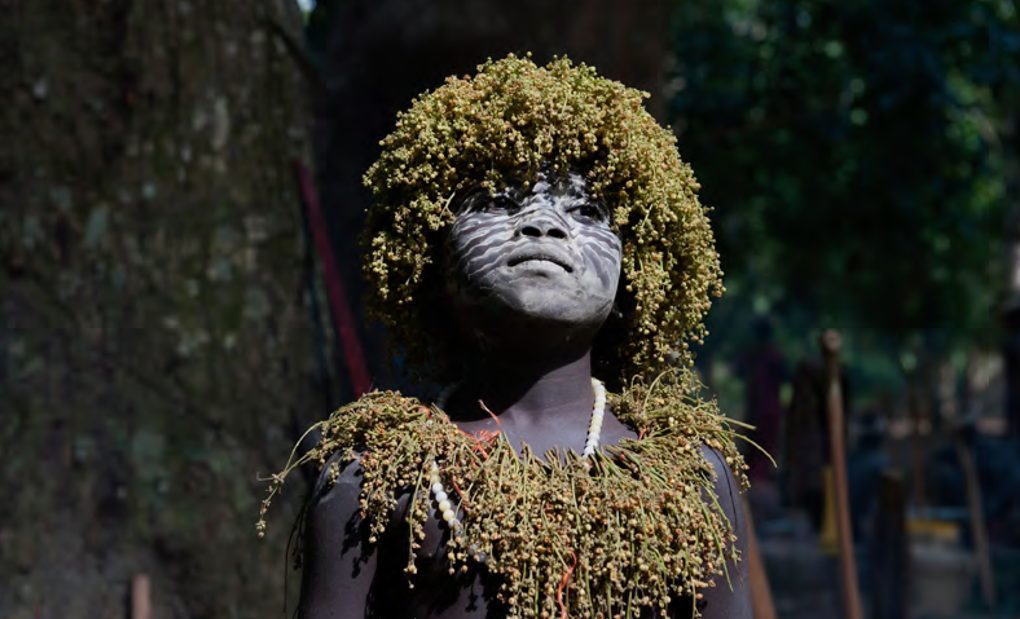
The Jarawa are hunters-gatherers. They have been living on the Indian Andaman Islands for thousands and thousands of years. According to recent studies, they are believed to have taken part in the very first human migrations from Africa to the rest of the world, some 70,000 years ago. And they first encountered Indian citizens only a decade ago. Since then, their situation has severely deteriorated. Women have been abducted and raped by Indians. The Jarawa have lodged several complaints to the Andaman authorities, to no avail.
The Jarawa are also victims of human safaris, organised by local tour operators. These safaris are taking place along the Andaman Truck Road, which was built illegally and cuts through the Jarawa’s territory. Dozens of vehicles, escorted by Indian armed forces, take it every day to photograph the Jarawa. Yet, it is forbidden to enter their territory, subject to prison sentences.
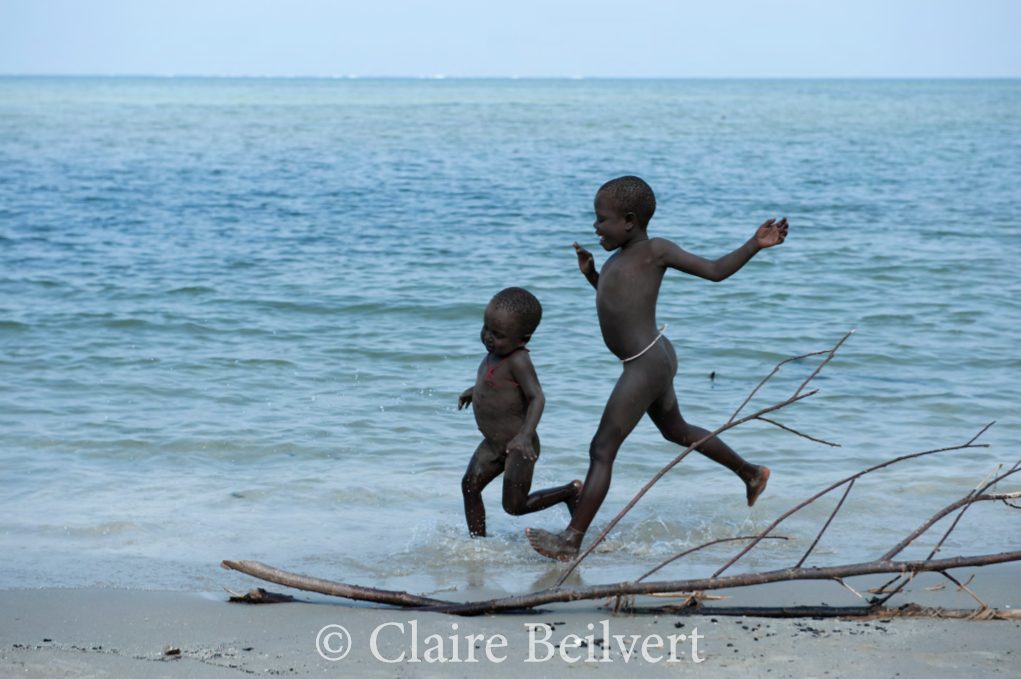

In 2013, Andaman MP Bishnu Pada Ray had even stated in the press that the Jarawa had expressed the desire to join the Indian community. But until now, no one has ever asked them if this was the case.
Alexandre Dereims, a French journalist, and Claire Beilvert, a French press photographer, succeeded in meeting them to ask them that question. They bypassed the ban on entering the reserve. They took every precaution to keep from transmitting diseases to them. The Jarawa allowed them to stay a few days with them to conduct interviews. For the very first time, members of this endangered people are speaking to the outside world.
They told them their story of their foreseeable disappearance, of forceful assimilation. Soon, the starving Jarawa will have no choice but to leave their territory and beg for food along the road. Journalists are sounding the alarm. New Delhi has recently decided to turn Port Blair, the capital city of the Andaman Islands, into the largest port on the Indian Ocean. The nationalist government led by Narendra Modi wants to enhance the tourism potential of these islands, which have become as popular as the Seychelles or the Maldives for the new Indian middle class. It is urgent to ponder about the survival of the most ancient people of Asia. The Indian government is already responsible for the disappearance of the Bo and the Onges, two others afro-asian people of the Andaman islands.
Journalists have launched an online petition to demand that the Indian government enforce the 2013 Supreme Court order to close the Andaman Truck Road. They also demand that the Jarawa’s territory be fully protected and that the AAJVS provide regular communication regarding the situation of the Jarawa people.
Link: http://bit.ly/savethejarawa
Website: http://www.organicthejarawa.com
by Deep Green Resistance News Service | May 31, 2016 | Agriculture, Colonialism & Conquest
Featured image: Combine harvesters crop soybeans during a demonstration for the press, in Campo Novo do Parecis, Brazil, on March 27, 2012. By Phys.org.
By Manuela Picq / Intercontinental Cry
Soy has become quite fashionable as a “wonder food.” Praised for its nutritional values, soy has the highest protein content of any bean making it a favorite among vegans, animal defenders and even young hipsters who swear by their morning soy latte. For many, however, soy is an ethical and political choice. By switching to soy, we get to spare our bodies and the planet from the harmful effects of the meat and dairy industry, its extensive use of antibiotics and its heavy contribution to the ever-growing climate crisis.
The problem is, soy production is a veritable criminal enterprise. The impressive bean that so many of us love is grown by multinational corporations that poison soil and water with toxic agrochemicals. What’s more, the bean is a Monsanto genetically modified crop the full impacts of which are still unknown. Soy is also used extensively by livestock producers alongside genetically modified corn as a base for animal feed. On top of this toxic burden, the soy agribusiness industry expropriates Indigenous Peoples. Also it destroys forests. And, like the meat and dairy industry, it’s fueling the climate crisis.
Let’s take a closer look at these four interrelated reasons why we need to move away from soy, in its many forms.
1) THE EXPANSION OF SOY MONOCULTURE IS RESPONSIBLE FOR MASSIVE DEFORESTATION AND CLIMATE CHANGE
Growing soy requires vast extensions of land. In fact, it requires so much land that soy monoculture a leading factor in the destruction of the world’s biodiversity. Soy farms now cover more than one million square kilometers of the world – the total combined area of France, Germany, Belgium and the Netherlands. The soy agriculture industry is having an especially devastating impact in Amazonia but also in the Cerrado and the Chaco. Almost 4 million hectares of forests are destroyed every year, 2.6 million in Brazil alone, the world’s leading soy producer.
Compounding this rampant devastation, when forests are transformed into farmland, soil quality deteriorates, leading to increased pollution, increased flooding and increased sedimentation that can clog waterways. This can cause a significant decline in fish populations and other life. Agrochemical residues degrade soil even further, along with the local water table and natural processes such as pollination. Such loss of biodiversity is a key factor of climate change.
2) THE GLOBAL SOY INDUSTRY HAS INDIGENOUS BLOOD ON ITS HANDS
The expansion of soy is made possible through land grabbing and by provoking land conflicts. Indigenous Peoples are often the main victims of this expropriation and dispossession and are often forced into urban poverty as a result. Indigenous resistance, however, is brutally repressed.
In Brazil, the Kaiowá-Guarani peoples have denounced over three hundred assassinations. Indigenous peoples defending their land are being killed by private militias hired by large soy corporations like Raizen, Breyfuss, Bunge, Syngenta and the French-Swiss Louis Dreyfus Commodities. “The soy you consume is stained with Guarani Kaiowá blood,” said Valdelice Veron, the daughter of cacique killed by a soy producer in 2003.
One emblematic case was the brutal homicide of a young leader in the state of Mato Grosso in 2014. Marinalva Kaiowá was stabbed 35 times only two weeks after defending the demarcation of Guyraroká lands in a court ruling at the federal Supreme Court in Brasilia. Her killing is, unfortunately, no exception. It is emblematic of a larger massacre. The Kaiowá-Guarani have a homicide rate nearly 500 times higher than the Brazilian average, exceeding that of countries at war.
One in two assassinations of Indigenous peoples in Brazil is related to the expansion of soy. The state of Mato Grosso do Sul, the world’s largest producer of soy, concentrates nearly 55 % of indigenous homicides in Brazil. Historian Marcelo Zelic told a special parliamentary commission that the state accounted for 377 of the 687 recorded cases of Indigenous peoples killed between 2003 and 2014. In other words, the state at the heart of soy’s agribusiness has a rate of Indigenous homicides three times higher than all other Brazilian states together.
Soy expansion is also forcing Indigenous peoples into smaller territories. There are 24 Indigenous territories in Mato Grosso do Sul, but lands for non-Indigenous peoples is 4 inhabitants per sq kilometers, 96 per sq/km for Terena Indians, and 34 per sq/km for the Guarani-Kaiowá.
The expansion of soy on Indigenous territories is feeding a devastating death toll and governments are often accomplice. In Brazil, Congress pleased the soy sector with a new bill (PEC 215) facilitating the redefinition of previously demarcated Indigenous territories into farmland. The law, accused of being unconstitutional, was designed to pursue an even more aggressive expropriation of Indigenous lands in Amazonia.
3) SOY IS A BILLION DOLLAR INDUSTRY THAT CONCENTRATES LAND AND ACCENTUATES INEQUALITY
Make no mistake. Soy is a massive commercial enterprise that is controlled by a few major landowners and corporations that don’t have our best interests at heart. In Brazil, many farms average 1,000 ha and some reach 50,000 ha (for the soccer aficionados out there, that is about 70,000 soccer fields). In Argentina, the world’s third producer after the USA, soy has replaced small farming, provoking rural migration to the cities and the disappearance of small towns in the Chaco region.
There are no labor benefits either. Since land is concentrated into the hands of few, mechanization drastically reduces farm jobs. When there is labor, it is prone to abuse. For instance, Greenpeace has documented workers being duped into coming to ranches where their papers are taken away and they are forced to work in soy farms.
4) SOY IS PLAIN BAD FOR YOUR HEALTH
Most soybeans are genetically modified to tolerate agrochemical farming, which means they are not only nutritionally inferior but also contain toxic chemicals. While there is little scientific data available on the physiological impacts of GMOs on the human body, GMO soy production is dependent on the heavy use of chemicals that poison our bodies and the environment. A study in Brazil’s Mato Grosso, for example, tested 62 samples of breast milk and found traces of one or more toxic agrochemicals in each and every sample. Not surprisingly, a documentary investigating the impacts of growing soy in South America to feed factory farms in Europe is called Killing Fields.
Monsanto crops have poisoned Argentina. The country’s entire soy crop is genetically modified which has skyrocketed the need for agrochemicals. Today, Argentine farmers apply an estimated 4.3 pounds of agrochemical concentrate per acre, more than twice what farmers in the U.S. rely on. The arrival of Monsanto crops brought birth defects and high rates of cancer among the rural population. But it doesn’t end there. Argentina exports most of its soy to Europe. If you live in Europe, chances are your morning soy latte and that tasty slice of in-house tofu cheesecake you had at lunch is made with Monsanto crops farmed in Argentina.
It’s almost impossible to avoid GM soy these days. Since it was first introduced in 1996, GM soy now dominates the industry comprising some 90% of all soy production. Countries like Argentina and the United States rely almost entirely on GM soy. More than a few local organic soybean businesses have collapsed because their soybeans were allegedly accidentally contaminated with patented strains of GM soy. Some claim that just 0.1% of world production is certified organic soy.
Soy is everywhere and we often eat it without our knowledge or consent. The overwhelming majority of the global soy production (80%) goes to feed animals, especially chickens and pigs, which means we are eating it too. The same goes for dairy products, since soy is also used in cattle feed. Soy is also the second most consumed oil in the world (after palm oil). If you check the labels in your kitchen cupboards you’re bound to find it.
It’s laudable to boycott the global cattle industry for its many harms to the earth, but we cannot reject one contaminating industry to endorse another. That is, unless our goal is to perpetrate a fraud at the expense of Indigenous Peoples, ecosystems and our own bodies.
If that’s not the sort of thing you can stomach we have no choice but to go conflict free. It’s not easy; but, then, nothing good in life ever is.

by Deep Green Resistance News Service | May 23, 2016 | Colonialism & Conquest
By Survival International
Featured image: Many Baiga have already been evicted from their forest homes, and now face lives of poverty in resettlement camps © Survival International
Several tribal villages in central India face annihilation as they are being forced to leave their ancestral land in Achanakmar tiger reserve, close to the area which inspired Rudyard Kipling’s Jungle Book.
The Baiga tribespeople have been repeatedly harassed and told that they will have to move from their villages to a muddy clearing outside the reserve, even though there is no evidence their presence in the reserve is harming tigers. Such evidence is required if the tribe’s eviction is to be lawful, but in fact the number of tigers in the reserve reportedly rose from 12 to 28 between 2011 and 2015.
One Baiga man from Rajak village said: “We don’t want to go, we can’t go. What should we do?”
A local witness told Survival: “There is nothing around the new site for them, nothing will grow in the land, there is no water and they won’t be able to take anything from the forest. That’s why they are so adamant that they won’t leave, because if they go they will just die out.”
Some have been told that if they don’t leave their ancestral land, guards will release bears and snakes into their villages. Others have been arrested and harassed – in 2009 one man was jailed for three months for eating a squirrel he had found dead on the forest floor.
Those who have already been evicted from Achanakmar now live in inadequate government camps and face lives of poverty on the fringes of mainstream Indian society.
One Baiga person from Chirahatta village, which is facing eviction, said: “They’ve been placing restrictions on us for two or three years. They don’t let us live. They take us to jail and threaten us. They are harsh and strict. They put us in jail for nothing. If we say anything they threaten to put us in jail. They are making it difficult for us to live.”
Elsewhere, Baiga people do back-breaking manual labour in bauxite mines in terrible working conditions.
Across India, tribespeople are being illegally evicted from tiger reserves, despite there being no evidence that their presence harms tigers. They face arrest and, in some places, beatings, torture and even summary execution for trying to re-enter their ancestral land, while large-scale tiger-spotting tourism is encouraged.

Baiga work in terrible conditions in the Bodai-Daldali bauxite mine, Chhattisgarh. Having once lived sustainable lives in the forests, they now endure exploitation and poverty after eviction from their land. © Sayantan Bera/Survival
Last year, Survival learned that tiger numbers had increased at well above the Indian national average in BRT, the one reserve in India where tribes have been formally allowed to stay on their land, demonstrating that tribal villages within wildlife reserves do not pose a substantial threat to tigers or their habitat.
Survival has written to WWF, the world’s largest conservation organization, which equips and trains the forest guards in the region.
Evidence proves that tribal peoples are better at looking after their environment than anyone else. Despite this, they are being illegally evicted from their ancestral homelands in the name of conservation. The big conservation organizations are guilty of supporting this. They never speak out against evictions.
Survival’s director Stephen Corry said: “It’s illegal and immoral to target tribes, who have coexisted with the tiger for centuries, when industrialization and mass-scale colonial-era hunting are the real reason the tiger became endangered. It’s also ineffective, because targeting tribespeople diverts action away from tackling the true poachers – criminal gangs. Big conservation organisations should be partnering with tribal peoples, not propping up the Forest Departments that are guilty of brutalizing them. Targeting tribal people harms conservation.”









