
by DGR News Service | May 18, 2019 | Toxification
True change can only be driven by revolutionary action and long-term radical organizing — not chemical collusion and compromise.
Last year, I volunteered to plant native species at the Spencer Creek-Coyote Creek wetlands southwest of Eugene, Oregon. This site, owned by the McKenzie River Trust (MRT), is an important riparian area at the confluence of two streams and is habitat for a wide range of plants, mammals, amphibians, birds, and other forms of life.
After arriving at the site, we learned during the orientation that herbicides had been applied in the area we were to be working to remove undesired plants. This did not sit well with me. I contacted McKenzie River Trust several months later and met with their conservation director to discuss chemical use. He explained that organizations like MRT are tasked with conserving large areas of land and don’t have the volunteer resources or staff to conduct non-chemical restoration. I suggested that MRT engage the community in dialogue around these issues in order to attempt an alternative.
The McKenzie River Trust disclosed that it has used pesticides including Glyphosate (aquatic formulation), triclooyr 3A, clethodim, aminipyralid, clopyralid, and flumioxazin over the past two years. MRT also uses chemicals at the Green Island site at the confluence of the Willamette and McKenzie rivers. The organization even has job descriptions that include specific reference to “Chemical control of invasive species… apply herbicides” in the activities list. It maintains a certified herbicide expert on staff. A representative of McKenzie River Trust told me that the organization has changed its volunteer policy to prevent the sort of herbicide exposure volunteers had earlier this year at the Spencer-Coyote Wetlands — but this doesn’t address the ecological impacts, or impacts on local residents.
I sympathize with relatively small organizations like McKenzie River Trust. They are operating in a bind whereby they are forced to either concede important habitat to aggressive invasive species, use poison, or attempt to mobilize the community to maintain land by hand. As they write in a fact sheet, “When working on large acreages, [herbicides] are the most efficient and cost-effective tool at our disposal.”
However, there is no excuse for manufacturing these substances, let alone deliberately releasing them into the environment.
We all assume that restoration and conversation groups have the best interests of the natural world at heart. But many of these groups regularly use chemical pesticides for land management, including chemicals that have been shown to cause cancer, birth defects, hormonal issues, and other health problems in humans and other species. This includes not just small local groups like The McKenzie River Trust and The Center for Applied Ecology, which are based in my region of western Oregon, but also large NGOs like The Nature Conservancy (TNC).
I have spoken with representatives of each of these organizations, and have confirmed that they actively use chemical herbicides.
The Nature Conservancy, for instance, uses organophosphate herbicides (the class that includes Glyphosate, the active ingredient of the popular weed-killer RoundUp) and a range of other chemicals on non-native species in the Willow Creek Preserve in southwest Eugene as well as thousands of other locations globally. The organization notes on its website that “herbicide use to control invasive species is an important land management strategy.”
The intentional release of toxic chemicals into the environment is an ironic policy for environmental groups, given that the modern environmental movement was founded on opposition to the use of pesticides (a category which includes herbicides). The 1962 publication of Rachel Carson’s book Silent Spring is taken by many as the beginning of the modern environmental movement.
Pesticides are a persistent, serious threat to all forms of wildlife and to the integrity of ecology on this planet.
Amphibians, due to their permeable skin, are especially sensitive to the effects of pesticides. These creatures often spend their entire lives on the ground or underground, where pesticides may seep. Even at concentrations of 1/10th the recommended level, many pesticides cause harm or are fatal to amphibians.
Bees exposed to herbicides may be unable to fly, have trouble navigating, experience difficulty foraging and nest building. Exposure may lead to the death of bees and larva. One study showed that Glyphosate effects bees’ ability to think and retain memory “significantly.”
While herbicides are less toxic to birds and large mammals than other pesticides that are used to kill bugs and small animals like mice, several studies have shown interference with reproduction. Not all poisoning results in immediate death. Impacts might include reduced body mass, reproductive failure, smaller broods, weakening, or other effects.
Pesticides, in general, are implicated in dramatic collapses in bat populations, threaten invertebrates, and kill or harm fish. Additionally, they bioaccumulate in flesh — that is, their levels concentrate in the bodies of predators (including humans) and scavengers that eat poisoned rats or other animals that we deem as pests.
Pesticides are applied much more widely than most people realize. They are used along roads, in parks, in front of businesses, and along power lines. In forestry and agriculture, thousands of tons of chemicals are applied in Oregon every year. The Oregon Department of Transportation uses herbicides to spray roadsides across the state. A recent “off-label” use of a herbicide has caused the death of hundreds of Ponderosa pines along a 12-mile stretch near Sisters, OR. Across much of the United States, insecticides are sprayed widely in cities and water bodies to kill mosquitoes. And private organizations and individuals use pesticides widely as well. A southern California study that took place between 1993 and 2016 found a 500 percent increase in the number of people with glyphosate in their bloodstream during that period, and a 1208 percent increase in the average levels of glyphosate they had in their blood.
The effects of these chemicals on humans can be disastrous. Pesticides are linked to neurological, liver, lymphatic, endocrine, cardiovascular, respiratory, mental health, immune, and reproductive damage, as well as cancer risk. As far back as 1999, pesticide use was believed to kill 1 million humans per year. Yet these toxic chemicals continue to be used today.
***
According to permaculture expert Tao Orion, author of Beyond the War on Invasive Species, more volunteer work, or active harvesting, perhaps through collaboration with Indigenous groups, can eliminate the need for chemicals entirely. “If you’re considering that one or two people are going to manage 500 acres,” she said, “you’re setting yourself up for herbicide use. It’s a cop-out… Tending these areas may cause rare plants to increase. There is a lot of evidence now that this is indeed the case. But that goes against the [commonly accepted] American wilderness ideology.”
Orion says the use of toxic herbicide mixes is common as well. “I did an interview with the founder of the Center for Applied Ecology, and he said ‘we often just mix up RoundUp and 2, 4-D, that’s a surefire mix we’ve found,’” Orion said. As some may remember, 2, 4-D is one-half of the Agent Orange defoliant that was widely used in the ecocidal Vietnam War and has been linked to extremely serious human and non-human health issues.
In her book Beyond the War on Endangered Species, Orion details Agribusiness giant Monsanto and other pesticide industry corporations making a deliberate shift to market and sell chemicals to ecological restoration organizations. This is often done with the help of incomplete or poorly executed science claiming that pesticides are harmless. Jonathan Lundgren disagrees. This Presidential Early Career award winner for Science and Engineering was forced out of his USDA research scientist position after exposing damage caused by pesticides. Lundgren says that the science of pesticide safety “is for sale to the highest bidder.”
TNC and other restoration organizations are heavily influenced by research produced by land-grant colleges. Land-grant schools were set up in the late 1800’s to provide education on agriculture, engineering, and warfare. These schools maintain a fundamentally extractive, colonial mindset. “The pesticide manufacturers fund research and professorships at universities like Oregon State and other land-grant colleges,” Orion said. She also explained that these groups regularly receive grants from the federal government and sometimes from corporations directly. Land grant schools were a major factor in the industrialization of agriculture over the past 130 years.
One result of this corporatization of science is a revolving door between big organizations like The Nature Conversancy and industry. For instance, TNC’s managing director for Agriculture and Food Systems, Michael Doane, worked at Monsanto for 16 years prior to joining the organization.
The Nature Conservancy’s collaboration with big business goes well beyond Monsanto. Its “Business Council” is made up of a select group of 14 corporations including BNSF, Bank of America, Boeing, BP, Cargill, Caterpillar, Chevron, Dow Chemical, Duke Energy, Monsanto, and PepsiCo. Previous partners include mining giant Rio Tinto, ExxonMobil, and Phillips. The Nature Conservancy has received 10’s of millions in funding from these corporate partners, who are collectively responsible for a substantial portion of global ecocide and who have profited to the tune of hundreds of billions of dollars.
I spoke with a local beekeeper who called TNC to inquire about pesticide use at Willow Creek. The TNC representative confirmed the use of multiple different herbicides. Though the beekeeper explained his fear for his bees, and described health concerns related to an elderly family member with Parkinson’s disease (a malady they believe is connected to past RoundUp exposure), the TNC representative refused to entertain any neighborly idea of notifying adjacent landowners about chemical use.
“He told me ‘this is private land, and we can do whatever the hell we want,’” the beekeeper told me.
This response is not a surprise: The Nature Conservancy’s entire approach is based on privatization. At the Willow Creek site, and most Nature Conservancy properties, land is not accessible by the public. Fences block access and signs warn against trespassing.
This privatization model mirrors the Royal “hunting preserve” and “King’s forest” commonly found in historic monarchies. It’s an approach that is regularly critiqued by other conservation groups, who see responsible interaction with the land as essential for creating a land ethic. Groups like Survival International regularly report on the negative impacts this approach has on Indigenous people throughout the world, especially in Africa, where TNC and other large groups such as the World Wildlife Fund regularly purchase and privatize lands once held in common. According to Survival International, this approach is often counterproductive. The group notes that Indigenous people’s presence on ancestral lands is actually the number one predictor of biological diversity and ecosystem health.
***
Given the decades-long effort by chemical companies to market their products as safe and the clear evidence this is not the case, it’s important to grow a mass movement that questions the use of chemicals.
Locals, including Orion, members of the Stop Aerial Spraying Coalition, and the beekeeper I spoke with want TNC and other conservation groups to change their approach to eliminate chemical use, and appreciate TNC’s experimentation with prescribed fire, which may reduce or eliminate the need for chemicals. Prescribed burning is a traditional practice among many Indigenous communities. Other chemical-free practices that can reduce undesirable species and increase biodiversity include targeted grazing, reintroduction of extirpated species, hand removal, and beneficial harvesting.
These approaches aren’t as fast as poison, but they can be sustainable.
The Nature Conservancy does some good work. So do many nonprofits, especially the smaller, grassroots organizations. However, cases like this illustrate why lasting environmental victories aren’t likely to emerge from large environmental NGOs or from corporate collaboration. TNC’s refusal to engage in political struggle over pressing issues such as drilling in the Arctic National Wildlife Refuge, let alone global climate change and major threats to the planet, show the limitations of these groups. Their defensive work to protect a given species or area is important, but this “whack-a-mole” method cannot proactively address the global issues we face.
The perils of collaboration with corporations can be seen throughout the environmental movement, not just in this case. Corporations and wealthy individuals have long recognized the existential threat posed by a radical environmental movement. When you question the destruction of one mountain or meadow or forest, it isn’t long until you question capitalism and industrialism too. Thus, they direct their funding to mainstream environmental groups, which present technological and policy change as the solution. I’ve called this a “pressure relief valve” for popular discontent. Others have labeled it one half of the “twin tactics of control: reform and repression.”
We must be wary of foundation funded and large NGOs. Nonprofits that are reliant on outside funding always must speak to the lowest common denominator: the funders. They must avoid offending these individuals and groups, and must supply deliverables to meet grant requirements. This focus on short term bullet-points relegates broader visioning to the fringes, and results in institutions and organizations with a systemic inability to think big or lead revolutionary change.
Despite the massive nonprofit industrial complex, every indicator of ecological health is heading in the wrong direction. I have always advocated both reform and revolution. But in today’s world, there is no shortage of tepid, chemical-soaked reform. To turn this around, we will need fundamental changes in the economic system and the structure of society, changes that can only be driven by revolutionary action and long-term radical organizing — not chemical collusion and compromise.

by DGR News Service | May 14, 2019 | Climate Change, The Problem: Civilization, The Solution: Resistance
Editor’s Note: This 2012 research article from University of Utah physicist and researcher Timothy Garrett concludes that “If civilization does not collapse quickly this century, then CO2 levels will likely end up exceeding 1000 ppmv.” We see this as further evidence that the Deep Green Resistance strategy of purposefully accelerating a managed collapse will provide the best chance for continuation of life on this planet.
No way out? The double-bind in seeking global prosperity alongside mitigated climate change.
Abstract. In a prior study (Garrett, 2011), I introduced a simple economic growth model designed to be consistent with general thermodynamic laws. Unlike traditional economic models, civilization is viewed only as a well-mixed global whole with no distinction made between individual nations, economic sectors, labor, or capital investments. At the model core is a hypothesis that the global economy’s current rate of primary energy consumption is tied through a constant to a very general representation of its historically accumulated wealth. Observations support this hypothesis, and indicate that the constant’s value is λ = 9.7 ± 0.3 milliwatts per 1990 US dollar. It is this link that allows for treatment of seemingly complex economic systems as simple physical systems. Here, this growth model is coupled to a linear formulation for the evolution of globally well-mixed atmospheric CO2 concentrations. While very simple, the coupled model provides faithful multi-decadal hindcasts of trajectories in gross world product (GWP) and CO2. Extending the model to the future, the model suggests that the well-known IPCC SRES scenarios substantially underestimate how much CO2 levels will rise for a given level of future economic prosperity. For one, global CO2 emission rates cannot be decoupled from wealth through efficiency gains. For another, like a long-term natural disaster, future greenhouse warming can be expected to act as an inflationary drag on the real growth of global wealth. For atmospheric CO2 concentrations to remain below a “dangerous” level of 450 ppmv (Hansen et al., 2007), model forecasts suggest that there will have to be some combination of an unrealistically rapid rate of energy decarbonization and nearly immediate reductions in global civilization wealth. Effectively, it appears that civilization may be in a double-bind. If civilization does not collapse quickly this century, then CO2 levels will likely end up exceeding 1000 ppmv [emphasis added]; but, if CO2 levels rise by this much, then the risk is that civilization will gradually tend towards collapse.
Originally published as Garrett, T. J.: No way out? The double-bind in seeking global prosperity alongside mitigated climate change, Earth Syst. Dynam., 3, 1-17, https://doi.org/10.5194/esd-3-1-2012, 2012.
https://www.earth-syst-dynam.net/3/1/2012/esd-3-1-2012.html

by DGR News Service | May 13, 2019 | Biodiversity & Habitat Destruction, The Solution: Resistance
via The Pinyon-Juniper Alliance
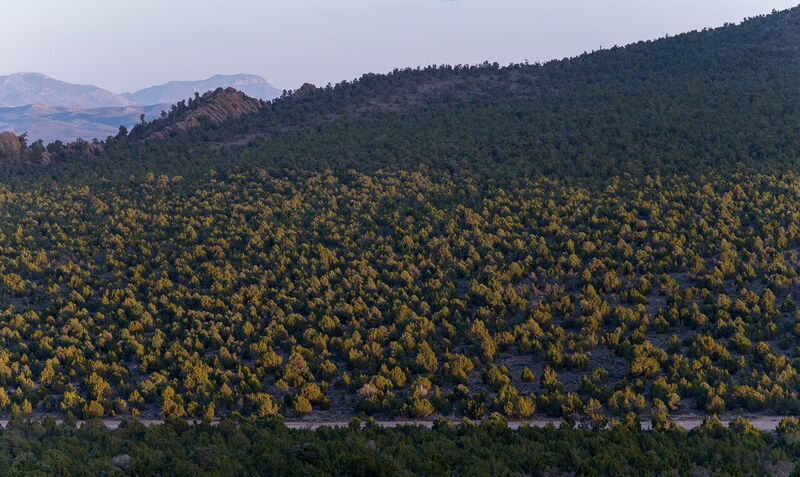
The Pinyon-Juniper Alliance was formed several years ago to protect Pinyon-Pine and Juniper forests from destruction under the BLM’s and Forest Service’s misguided “restoration” plan. Since that time, we have attended public meetings, organized petitions, talked with politicians and locals, coordinated with other groups, written articles and given presentations, and commented on public policy.
Things now are worse than ever. The latest project we’ve seen aims to remove PJ forest from more than 130,000 acres of Grand Staircase-Escalante National Monument. That’s more than 200 square miles in one project.
Everywhere we go, we see juniper trees cut. Most recently, just this past weekend in Eastern Oregon, an entire mountainside was littered with chainsawed juniper trees. Earlier today, one of our organizers spoke with an elder from the Ely-Shoshone Tribe. She told us about two conversations she had with agency employees who referred to old pinyon-pines as “useless” trees that needed to be removed. She responded by saying “I wouldn’t be here without those trees,” and told them about the importance of pine nuts to Great Basin indigenous people.
And still the mass destruction continues.
However, looming behind these atrocities is an even bigger threat. Due to global warming, drought is becoming almost continuous throughout most of the intermountain West. The possibility of a permanent dust bowl in the region appears increasingly likely as governments worldwide have done nothing to avert climate catastrophe.
Pinyon-Pine and Juniper are falling to the chainsaw. However, they have been able to survive the saws of men for two hundred years. It is unlikely they will be able to survive two hundred years of unabated global warming.
The biggest threat to Pinyon-Juniper forests isn’t chainsaws or the BLM. The biggest threat is the continuation of industrial civilization, which is leading to climate meltdown. Stopping industrial civilization would limit this threat, and would also stop the flow of fossil fuels that powers the ATVs and Masticators and Chainsaws currently decimating Pinyon-Juniper forests.
Derrick Jensen has said that often people who start out trying to protect a certain forest or meadow end up questioning the foundations of western civilization. We have undergone this process ourselves.
Given our limited time, energy, and resources, our responsibility is to focus on what we see as the larger threats. Therefore, the founders of the Pinyon-Juniper Alliance have turned to focus on revolutionary work aimed at overturning the broader “culture of empire” and the global industrial economy that powers it. We are not leaving the PJ struggle behind. If you are engaged in this fight, please reach out to us. We need to network, share information, and work together to have a chance of success. We are shifting the form of our struggle. If this struggle is won, it will result in a world that Pinyon-Juniper forest can inhabit and spread across freely once again. And if it’s lost, our work at the local level is unlikely to matter. There are few revolutionaries in the world today, and we have a responsibility to do what is necessary.
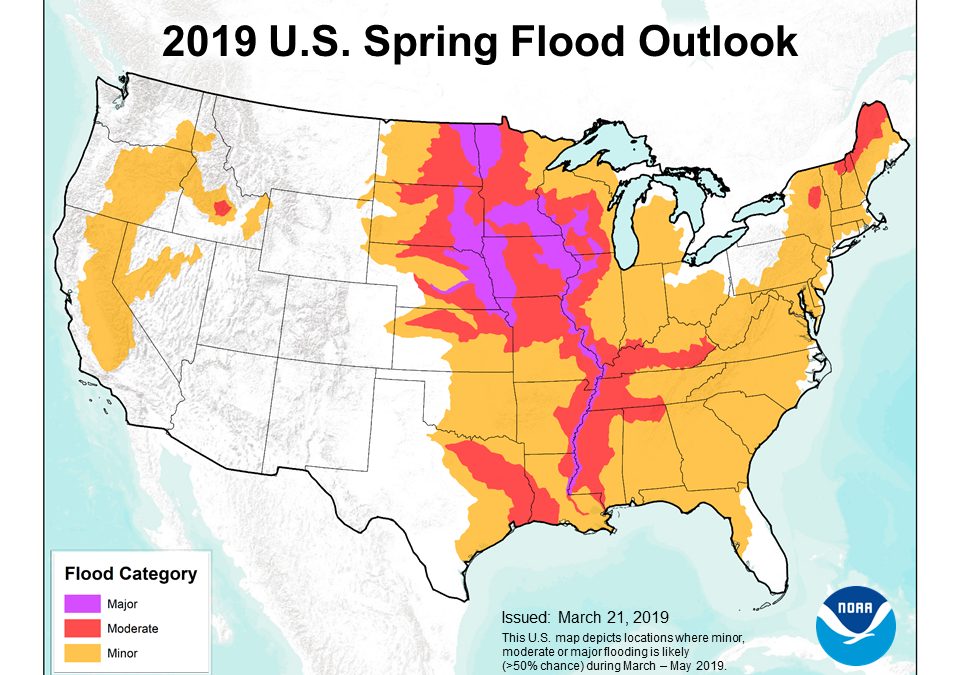
by DGR News Service | May 9, 2019 | Climate Change
By Elisabeth Robson / Art for Culture Change
The catastrophic flooding across the midwest isn’t getting much coverage on the coasts, but it is a multibillion $ disaster for multiple states and indigenous nations.
Over a million wells may be contaminated.
Farmers will lose their farms.
The top soil is washing away.
The cattle losses have yet to be tallied but are likely to be huge.
8 EPA superfund sites have been inundated and no one knows what toxic nastiness is washing into the ground and water from those sites.
And of course all the little ways toxins make their way into the water from inundated septic systems, landfill sites, dumps, oil on the ground, and flooded energy infrastructure.
The flood waters are washing not just soil, but decades of accumulated synthetic fertilizers and many other toxins, into the Mississippi river, all of which will eventually flow into the Gulf of Mexico. The yearly “dead zone” in the Gulf is already notorious–agriculture runoff creates algae growth, which in turn creates hypoxic zones, and all marine life in those zones dies from lack of oxygen.
This year’s “dead zone” could be the largest ever.
This winter, we can expect high food prices throughout the country. The flooded region produces wheat, corn, and soy, used to feed millions of feed lot cattle, and produce our industrial food products (bread, cereals, etc.)
The fields have not only lost topsoil; many are now covered with sand and other debris. It will be years, decades, or more before these fields return to full production–of course, their “full production” now is based on industrial agriculture, so it’s highly unnatural, but it does feed much of this country, so it’s something to keep in mind.
And of course along with those losses, many farmers will now be out of work.
Once upon a time, long ago, before the rivers in this country were dammed and levied and corralled into submission, flooding like this used to bring nutrients to the prairies and regenerate the land. Once upon a time, floods like this were a temporary hardship for a long term gain in productivity for all the wild things of the vast prairies of the continent.
In our modern times, flooding like this is a disaster, one that will have decades of repercussions of poisoned soil and water, poverty, and misery.
Image by NOAA of 2019 Spring Flood Outlook for the USA.

by DGR News Service | May 8, 2019 | Human Supremacy
By Beth Robson / Art for Culture Change
I love the cover of the New York Times Magazine, by Pablo Delcan, for this week’s big story, “The Problem with Putting a Price on the End of the World.”
The article discusses the challenge with pricing carbon emissions properly so that we use less fossil fuels: because fossil fuels are so fundamental to every aspect of how we live in this modern culture, to price emissions higher means bringing a world of hurt to people who just want to be able to afford a home, or to commute to work, or put the next meal on the table.
The basic problem with pricing carbon as a solution to climate change is not, as the article states (and most people like to claim), that it is a “market failure”.
The problem is that pricing carbon doesn’t address the underlying issue: that our modern culture is inherently unsustainable, no matter how much we pay for the energy to run it.
The article argues that pricing carbon leads to a sluggish economy, which is bad.
No, what’s bad is the economy, period. Our modern economy is based on continual growth. We can’t “fix” the economy; we have to abolish it. Eliminate it. And to do that we need a vision of what is to replace it (and no, not “clean energy”!!) — because without a vision, people just get angry when they can no longer afford the necessities of life.
Unfortunately but unsurprisingly, this article pins hopes for the future on “clean” energy (something that doesn’t actually exist), and a growth economy based on renewables, within the framing of shifting away from fossil fuels not because carbon is expensive, but because renewables are a better, cheaper option, cause less pollution and less carbon, and will create jobs (i.e., basically the same argument as The Green New Deal). This approach simply changes the energy source that runs our unsustainable economy; it doesn’t change the underlying problem: the economy and the way we live our lives because of that economy.
The real problem of putting a price on the world (whether that’s carbon, or “ecosystem services”) is that it turns everything in the world into a commodity, into something that can be calculated into our growth economy. And it is our economy: our consumer-based, capitalist, infinitely growing economy that is killing the planet. It doesn’t matter how you power that economy—with so-called “clean” energy or fossil fuels.
As long as we have growth—more people, buying more stuff, building more roads, houses, cars—we are in trouble.
As long as we think of nature as property—as something that can be bought and sold on the market, rather than as something we are, that we must prioritize above all else, because without nature, we do not exist—we will never succeed in solving the existential crisis in which we find ourselves today.
Pablo Delcan’s cover for the magazine is a good reminder that we cannot sell planet Earth and expect to survive. We have already sold most of the planet as “property”, and once we think of nature as property, then we use it and destroy it for profit.
Our only way forward is to see nature as intrinsically valuable for its own sake, and to remember that we are not consumers, that money is just a figment of our imagination, and that the real world, the physical world, filled with intact and flourishing ecosystems, is the only thing that matters.
Photo by CHUTTERSNAP on Unsplash
by DGR News Service | May 7, 2019 | Biodiversity & Habitat Destruction
By Will Falk and Sean Butler / Voices for Biodiversity
On December 18, 2018, the Center for Biological Diversity and the Wild Fish Conservancy threatened the Trump administration with a lawsuit under the Endangered Species Act (ESA) for allowing salmon fisheries to take too many salmon, which the critically endangered Southern Resident orcas depend on for food.
The impulse to protect the orcas is a good one. Southern Resident orcas are struggling to survive — only 75 remain. According to the statement by the Center for Biological Diversity and Wild Fish Conservancy, “The primary threats to Southern Resident killer whales are starvation from lack of adequate prey (predominantly Chinook salmon), vessel noise …that interferes with … foraging … and toxic contaminants that bioaccumulate in the orcas’ fat.”
You probably assume, when reading that list of primary threats to the orcas, that the threatened lawsuit would demand an end to these harmful activities. But it doesn’t. Instead, the organizations are merely asking the National Marine Fisheries Service — the agency responsible for issuing permits to Pacific coast fisheries — to deal with alleged violations of the ESA.
The Center for Biological Diversity and the Wild Fish Conservancy aren’t asking that activities harmful to Chinook salmon, and consequently to the Southern Resident orcas, be stopped. They aren’t asking for noisy vessels that disturb the whales’ foraging behaviors to be prohibited. They aren’t even asking for an end to the toxic contaminants that accumulate in the whales’ fat.
Why aren’t they asking for any of these things? Because under American law they aren’t allowed to ask for them.
All they are asking is that these harmful activities receive the proper permits.
Right now, laws like the Endangered Species Act are the main legal means for protecting threatened species and habitat in the United States. But these laws only allow us to challenge permit applications and ask that projects complete the permit process.
While it may hard to believe, these permits are designed to give permission to cause harm. Regulatory agencies only regulate the amount of harm that takes place. They do not, and cannot, stop ecocide. Instead they allow for softer, sometimes slower versions of ecocide.
To understand this, it helps to know a bit about how the Endangered Species Act actually works. The Act prohibits any person, including any federal agency, from “taking” an endangered species without proper authorization. “Take” is defined as: “to harass, harm, pursue, hunt, shoot, wound, kill, trap, capture, or collect, or to attempt to engage in any such conduct.”
You might expect that the Act completely prohibits any activity that “takes” an endangered species. But it doesn’t. Under the Act, federal agencies may harm members of an endangered species as long as the activity is “not likely to jeopardize the continued existence of any endangered species.”
While that may sound more promising, it isn’t. When a proposed action is likely to jeopardize an endangered species, the agency can then issue an Incidental Take Statement (ITS), which merely sets a limit on the number of individuals of an endangered species that can be taken.
In other words, a species that has already endured so much destruction can legally be further harmed if that harm is in compliance with certain terms and the correct forms are filled out.
So an ITS allows a federal agency to harm endangered species. But there are also Incidental Take Permits (ITPs). These allow private entities to harm endangered species. All a private entity needs to do to get an ITP is create a plan that purportedly minimizes and mitigates harm to an endangered species.
The irony is not lost on Professor J.B. Ruhl, who describes the situation in his aptly-titled law review article, “How to Kill Endangered Species, Legally”:
“Rather, when we strip away its noble purpose… at bottom the ESA is little different from the modern pollution control statutes which broadly prohibit a defined activity with one hand, then with the other hand give back authority to do the same activity under regulated conditions.”
In the original 1973 version of the Endangered Species Act, ITS and ITP exemptions did not exist. They are the result of amendments passed by Congress in 1982 to undermine several pro-environmental Supreme Court decisions that interpreted the Act as broadly protecting endangered species. Those amendments are a powerful and dangerous loophole.
In a 2011 report, a trial attorney with the Environmental Crimes Section of the U.S. Department of Justice, Patrick Duggan, found that ITPs are being issued at alarming rates — and with ever-broader scopes. “In the first decade after the 1982 Amendments, there were 14 ITPs issued, by August 1996, there were 179, and by April 2010, there were 946 approved by the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service (FWS) alone.” Even FWS has acknowledged this trend of permissiveness, recently noting how the number of approved plans has “exploded.”
Most people mistakenly believe that regulations are being enforced by regulatory agencies. They’re not. Some environmental lawyers call this the “regulatory fallacy.” Not surprisingly, this drains focus from potentially more effective tactics by funneling it into a belief that government agencies will actually protect people and natural communities by denying permits.
The system isn’t working — and it’s very unlikely that it will protect the critically endangered Southern Resident orcas. But why doesn’t it work?
To begin to understand why the Endangered Species Act is failing, it’s helpful to acknowledge perhaps the most fundamental assumption of the Act and all similar pollution control statutes, as Professor Ruhl calls them. That assumption is that we have an inalienable right to use the natural world for our own purposes.
The answer to the regulatory fallacy, then, is to turn this on its head. If we truly want to protect endangered species like the Southern Resident orcas, our laws cannot treat them and their essential food source as objects or property. Instead, we must acknowledge their inherent rights to exist, and create laws that uphold and enforce those rights. True sustainability requires transforming the status of nature from a legal object to a rights-bearing subject.
This transformation begins with granting nature the legal right to challenge the conduct of someone else in court. As Supreme Court Justice William O. Douglas wrote in his famous 1972 dissent in Sierra Club v. Morton, this “would be simplified and also put neatly in focus if we fashioned a federal rule that allowed environmental issues to be litigated before federal agencies or federal courts in the name of the inanimate object about to be despoiled, defaced, or invaded by roads and bulldozers…”
In the US, the rights-based approach has been pioneered by the Community Environmental Legal Defense Fund (CELDF), a nonprofit, public interest law firm. Since 2006, CELDF has helped dozens of communities in ten states enact rights of nature laws. Their model uses a “Community Bill of Rights,” which declares that citizens of the city or county have a right to clean air, clean water, etc., and that the natural communities within its borders have a right to exist, flourish, regenerate and naturally evolve. Natural communities are specifically granted legal standing and citizens are empowered to bring lawsuits to enforce these rights. This is similar to the way guardians represent children in court.
Southern Resident orcas range from as far south as California and along the coasts of Oregon and Washington. If the communities along the West Coast had rights of nature laws, they could now bring a lawsuit on behalf of the Southern Resident orcas, with claims that fishery practices, dams, shipping activities and pollution violate the whales’ rights to exist, flourish, regenerate and naturally evolve. They could ask the courts to completely ban harmful fishery practices in order to protect the rights of nature, and to order those responsible for harm to pay for the regeneration of the natural community. They could seek this relief from the courts because the fundamental rights of the ocean and its residents are being violated.
What’s more, because the plaintiff in such a lawsuit would be a whole population of salmon or whales, or even an entire ecosystem like the Salish Sea, the damages awarded would be measured according to the losses suffered by the natural communities themselves. And any award of damages would go toward the restoration of those communities, rather than to human plaintiffs who might not use it to benefit the ecosystem that has been damaged.
“We’d be having very different conversations and much more effective results if we approached recovery with the orcas’ best interests in mind,” says Elizabeth M. Dunne, Esq., who is part of a coalition that helped draft the Declaration for the Rights of the Southern Resident Orcas, led by the grassroots community group, Legal Rights for the Salish Sea. Dunne explains that, “by signing the Declaration, we want people, organizations and governments to recognize that the Southern Residents’ have inherent rights, to recognize that we have a responsibility to protect those rights, and to commit to taking concrete actions to protect and advance those rights.”
Environmentalists who engage within today’s regulatory framework and rights of nature proponents begin in the same place. They both want to protect the natural world. But the way they frame the issue could not be more different. Environmentalists who rely on regulatory laws frame the issue as one of improperly prepared reports or how many parts per million of toxins may permissibly be released into water supplies. For example, the Center for Biological Diversity and Wild Fish Conservancy want to protect the Southern Resident orcas, but all they can ask for under the ESA is that the responsible federal agency “reinitiate and complete consultation on the Pacific Coast salmon fisheries” with new scientific information.
Rights of nature proponents, on the other hand, affirm nonhumans’ value as subjective beings, framing the issue in terms of whether a proposed action violates their fundamental rights. Though we cannot put an orca on the witness stand to testify about the impacts that the National Marine Fisheries Service’s plan has on her species, empowering humans to speak for her through enforcement of her legal rights brings nature’s voice directly into the courtroom.
Originally listed as endangered in 2005, Southern Resident orca numbers have continued to decline. The Center for Biological Diversity reports that the population is at its lowest point in 34 years. And, “In 2014, a population viability study estimated that under status quo conditions, the Southern Resident killer whales…would reach an expected population size of 75 in one generation (or by 2036).” Instead, it was just four years later that the Southern Resident orca population stood at 75.
In the end, the only measure of success in this case should be the whales’ recovery. The people of Washington aren’t concerned that regulations haven’t been followed— we’re concerned that our neighbors, the Southern Resident orcas, are starving. We’re horrified that these beautiful animals’ right to life is not being respected and that their ecosystem is being destroyed. And we’re outraged because deep down we believe that the natural world does have inherent value — and therefore inherent rights.
It’s time to stop begging for regulatory table scraps. It’s time to have the courage of our convictions and create new laws that recognize the inherent rights of the Southern Resident orcas and the Salish Sea as a whole to exist, flourish and evolve.





