
by DGR News Service | May 20, 2022 | Mining & Drilling, NEWS
Editor’s note: As global warming and ecological collapse accelerates, governments and corporations are unwilling to invest in real solutions. Instead, public fear is increasingly being weaponized to mobilize public subsidies for the so-called “green technology” industry, and a new sacrifice zone is emerging.
For example, instead of moving to relocalize and reduce energy use, electric cars are being promoted as a “plug-and-play” substitute for gasoline cars. This approach will do nothing to halt the ecological crisis, will only negligibly reduce rising greenhouse gas emissions, and is accelerating new harms such as an explosion in mining for lithium, cobalt, copper, and other materials.
It’s Not Just Thacker Pass. The Entire Region is on the Chopping Block.
by Elisabeth Robson / Protect Thacker Pass
In their June 2021 Fact Sheet about the Thacker Pass Lithium Mine Project, Lithium Americas includes a two page document about biodiversity at Thacker Pass and claim they have engineered the project “to minimize its environmental footprint.” On the second page is a map showing the Thacker Pass Project area in the bottom part of the McDermitt Caldera, which straddles the border of Nevada and Oregon.
 Lithium Americas claims that protecting the Montana Mountains is their priority, writing “Lithium Americas made the decision in 2018 to move the project south of the Montana Mountains to avoid disturbing sensitive ecological areas located within the mountains,” and that “[T]he project will not involve any direct physical disturbance of sage grouse leks or golden eagle nests”.
Lithium Americas claims that protecting the Montana Mountains is their priority, writing “Lithium Americas made the decision in 2018 to move the project south of the Montana Mountains to avoid disturbing sensitive ecological areas located within the mountains,” and that “[T]he project will not involve any direct physical disturbance of sage grouse leks or golden eagle nests”.
Putting aside for the moment that any industrial disturbance to the Thacker Pass area will have significant impacts on wildlife and sensitive areas, including pronghorn who migrate through Thacker Pass, many species of birds, including sage-grouse who are exquisitely sensitive to noise, and countless other species who call Thacker Pass home or rely on it for some part of their life cycle, one might believe, reading their propaganda, that Lithium Americas is going to limit the scope of their mining operations in Thacker Pass to the project area already defined for the Thacker Pass mine. If you think that, you’d be wrong.
In the article “Proposed lithium mine raises worries in Humboldt County” in the Las Vegas Sun on May 3, 2022, Lithium Nevada Corporation, a subsidiary of Lithium Americas, claims again that the project is designed to “avoid environmentally sensitive and rugged terrain”. However, they also say that the project allows for future potential expansions. Lithium Nevada made these plans for potential expansion clear in the project documents the company filed with the SEC and with the Environmental Impact Statement, so this is no secret.
The same article quotes John Hadder, director of Great Basin Resource Watch, who says that in the future a series of mines could line the Montana mountain range, creating, as he says, an “enormous mining district”.
The “Independent Technical Report for the Thacker Pass Project, Humboldt County, Nevada, USA” document filed with the SEC by Lithium Americas on February 15, 2018, includes a map that illustrates the plans the company has for the region, showing the area of Lithium Nevada Corporation’s mining claims and the known areas of lithium mineralization. This map shows the claims and potential mining areas stretching at least 30 miles north of Thacker Pass, through the heart of the Montana Mountains, the last great sage-grouse habitat on the planet.
 Why, then, does the company say in their 2-page fact sheet that they moved the Thacker Pass project south to avoid disturbing sensitive ecological areas within the mountains when they have every intention of expanding the mining project into the Montana Mountains where the sage-grouse leks are located? Do they believe that once the first project is begun, it will be easier to get further mining projects in the region approved?
Why, then, does the company say in their 2-page fact sheet that they moved the Thacker Pass project south to avoid disturbing sensitive ecological areas within the mountains when they have every intention of expanding the mining project into the Montana Mountains where the sage-grouse leks are located? Do they believe that once the first project is begun, it will be easier to get further mining projects in the region approved?
This projected expansion by Lithium Nevada and its parent company, Lithium Americas, along with the two other large lithium claims on the Oregon side of the border, one in the McDermitt Caldera by Australian company Jindalee Resources Limited and the other just outside the Caldera by Acme Lithium Inc., will turn this entire region into a fully industrialized area with roads, mining pits, refineries, waste dumps, a dramatic increase in truck and other vehicle traffic, and new housing and/or man camps and other developments to support the many hundreds if not thousands of workers that will be required to mine the area.
To understand the scope and scale of what is being proposed here, take a look at the mining plans illustrated in three images from the three mining companies—Lithium Nevada, Jindalee, and Acme—combined into one:

Image created by Protect Thacker Pass
As Kale Telage writes in “Lithium Americas: Yesterday, Today and Tomorrow” on the investing site Seeking Alpha on April 26, 2022, “Thacker Pass may just be the beginning.” The land, the wild beings, and the local people of this area are in for a shock. If built, these industrial projects will utterly and irrevocably destroy this wild and quiet region currently thrumming with life and beauty and turn it forever into a wasteland.
What are the roots that clutch, what branches grow
Out of this stony rubbish? Son of man,
You cannot say, or guess, for you know only
A heap of broken images, where the sun beats,
And the dead tree gives no shelter, the cricket no relief,
And the dry stone no sound of water. Only
There is shadow under this red rock,
(Come in under the shadow of this red rock),
And I will show you something different from either
Your shadow at morning striding behind you
Or your shadow at evening rising to meet you;
I will show you fear in a handful of dust.
— T.S. Eliot, The Waste Land
Featured image: Max Wilbert

by DGR News Service | Apr 4, 2022 | NEWS
Editor’s note: Fossil fuels are highly polluting, their extraction is linked to human rights abuses, and their continued use is killing the planet. However, renewable energy technologies also have massive unrecognized costs. Our conclusion is that resistance to both of these industries is a moral imperative.
In this article we highlight two scientific studies examining these harms. It is critical that we act proactively to defend threatened land before development plans are cemented and it becomes too late.
Researchers have warned that mining threats to biodiversity caused by renewable energy production could surpass those averted by climate change mitigation.
A University of Queensland study found protected areas, key biodiversity areas and the world’s remaining wilderness would be under growing pressure from mining the minerals required for a clean energy transition.
UQ’s Dr. Laura Sonter said renewable energy production was material-intensive—much more so than fossil fuels—and mining these materials would increase as fossil fuels were phased out.
“Our study shows that mining the materials needed for renewable energy such as lithium, cobalt, copper, nickel and aluminum will create further pressure on the biodiversity located in mineral-rich landscapes,” Dr. Sonter said.
The research team mapped the world’s mining areas, according to an extensive database of 62,381 pre-operational, operational and closed mining properties, targeting 40 different commodities.
They found that areas with potential mining activity covered 50 million square kilometers of the planet—35 percent of the Earth’s terrestrial land surface excluding Antarctica—and many of these areas coincided with places critical for biodiversity conservation.
“Almost 10 percent of all mining areas occur within currently protected sites, with plenty of other mining occurring within or nearby sites deemed a priority for future conservation of many species,” Dr. Sonter said.
“In terms of mining areas targeting materials needed specifically for renewable energy production, the story is not much better. We found that 82 percent of mining areas target materials needed for renewable energy production, of which, 12 percent coincide with protected areas, 7 percent with key biodiversity areas and 14 percent with wilderness. And, of the mining areas that overlapped protected areas and wilderness, those that targeted materials for renewable energy contained a greater density of mines than the mining areas that targeted other materials.”
Professor James Watson, from UQ’s Center for Biodiversity and Conservation Science and the Wildlife Conservation Society, said the impacts of a green energy future on biodiversity were not considered in international climate policies.
“New mining threats aren’t seriously addressed in current global discussions about the post-2020 United Nation’s Strategic Plan for Biodiversity,” Professor Watson said.
The research team said careful strategic planning was urgently needed.
“Mining threats to biodiversity will increase as more mines target materials for renewable energy production,” Dr. Sonter said.
“Combine this risk with the extensive spatial footprint of renewable energy infrastructure, and the risks become even more concerning.”
More information
Laura J. Sonter et al. Renewable energy production will exacerbate mining threats to biodiversity, Nature Communications (2020). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-17928-5
A University of Queensland study found protected areas, key biodiversity areas and the world’s remaining wilderness would be under growing pressure from mining the minerals required for a clean energy transition.
UQ’s Dr. Laura Sonter said renewable energy production was material-intensive—much more so than fossil fuels—and mining these materials would increase as fossil fuels were phased out.
“Our study shows that mining the materials needed for renewable energy such as lithium, cobalt, copper, nickel and aluminum will create further pressure on the biodiversity located in mineral-rich landscapes,” Dr. Sonter said.
The research team mapped the world’s mining areas, according to an extensive database of 62,381 pre-operational, operational and closed mining properties, targeting 40 different commodities.
They found that areas with potential mining activity covered 50 million square kilometers of the planet—35 percent of the Earth’s terrestrial land surface excluding Antarctica—and many of these areas coincided with places critical for biodiversity conservation.
“Almost 10 percent of all mining areas occur within currently protected sites, with plenty of other mining occurring within or nearby sites deemed a priority for future conservation of many species,” Dr. Sonter said.
“In terms of mining areas targeting materials needed specifically for renewable energy production, the story is not much better. We found that 82 percent of mining areas target materials needed for renewable energy production, of which, 12 percent coincide with protected areas, 7 percent with key biodiversity areas and 14 percent with wilderness. And, of the mining areas that overlapped protected areas and wilderness, those that targeted materials for renewable energy contained a greater density of mines than the mining areas that targeted other materials.”
Professor James Watson, from UQ’s Center for Biodiversity and Conservation Science and the Wildlife Conservation Society, said the impacts of a green energy future on biodiversity were not considered in international climate policies.
“New mining threats aren’t seriously addressed in current global discussions about the post-2020 United Nation’s Strategic Plan for Biodiversity,” Professor Watson said.
The research team said careful strategic planning was urgently needed.
“Mining threats to biodiversity will increase as more mines target materials for renewable energy production,” Dr. Sonter said.
“Combine this risk with the extensive spatial footprint of renewable energy infrastructure, and the risks become even more concerning.”
The research is published in Nature Communications.
More information: Laura J. Sonter et al. Renewable energy production will exacerbate mining threats to biodiversity, Nature Communications(2020). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-17928-5
A World at Risk: Aggregating Development Trends to Forecast Global Habitat Conversion
Abstract
A growing and more affluent human population is expected to increase the demand for resources and to accelerate habitat modification, but by how much and where remains unknown. Here we project and aggregate global spatial patterns of expected urban and agricultural expansion, conventional and unconventional oil and gas, coal, solar, wind, biofuels and mining development. Cumulatively, these threats place at risk 20% of the remaining global natural lands (19.68 million km2) and could result in half of the world’s biomes becoming >50% converted while doubling and tripling the extent of land converted in South America and Africa, respectively. Regionally, substantial shifts in land conversion could occur in Southern and Western South America, Central and Eastern Africa, and the Central Rocky Mountains of North America. With only 5% of the Earth’s at-risk natural lands under strict legal protection, estimating and proactively mitigating multi-sector development risk is critical for curtailing the further substantial loss of nature.
More information
Oakleaf JR, Kennedy CM, Baruch-Mordo S, West PC, Gerber JS, Jarvis L, et al. (2015) A World at Risk: Aggregating Development Trends to Forecast Global Habitat Conversion. PLoS ONE 10(10): e0138334. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0138334
![Electric Vehicles: Back to the Future? [Part 2/2]](https://dgrnewsservice.org/wp-content/uploads/sites/18/2021/11/Illustration_017.jpg)
by DGR News Service | Nov 21, 2021 | Climate Change, Mining & Drilling, The Problem: Civilization
By Frédéric Moreau
Read Part 1 of this article here.
While the share of solar and wind power is tending to increase, overall energy consumption is rising from all sources — development, demography (a taboo subject that has been neglected for too long), and new uses, such as digital technology in all its forms (12% of the electricity consumed in France, and 3% worldwide, a figure that is constantly rising, with digital technology now emitting more CO2 than air transport⁴⁴). Digital technology also competes with vehicles, especially electric ones, in terms of the consumption of metals and rare earths. This is perfectly logical since the renewable energy industry, and to a lesser extent the hydroelectric industry (dams), requires oil, coal and gas upstream to manufacture the equipment. Solar panels look indeed very clean once installed on a roof or in a field and which will later produce so-called “green” electricity.

We almost systematically forget, for example, the 600 to 1,500 tons of concrete for the wind turbine base, often not reused (change of model or technology during its lifespan, lack of financing to dismantle it, etc.), which holds these towers in place. Concrete that is also difficult to recycle without new and consequent energy expenditures, or even 5,000 tons for offshore wind turbines⁴⁵. Even hydrogen⁴⁶, which inveterate techno-futurists are now touting as clean and an almost free unlimited energy of tomorrow, is derived from natural gas and therefore from a fossil fuel that emits CO2. Because on Earth, unlike in the Sun, hydrogen is not a primary energy, i.e. an energy that exists in its natural state like wood or coal and can be exploited almost immediately. Not to mention that converting one energy into another always causes a loss (due to entropy and the laws of thermodynamics; physics once again preventing us from dreaming of the mythical 100% clean, 100% recyclable and perpetual motion).

Consequently oil consumption, far from falling as hoped, has instead risen by nearly 15% in five years from 35 billion barrels in 2014 to 40 billion in 2019⁴⁷. Moreover, industry and services cannot resign themselves to the randomness of the intermittency inherent in renewable energies. We cannot tell a driver to wait for the sun to shine or for the wind to blow again, just as the miller in bygone days waited for the wind to grind the wheat, to charge the batteries of his ZOE. Since we can hardly store it in large quantities, controllable electricity production solutions are still essential to take over.

Jean-Marc Jancovici⁴⁸, an engineer at the École des Mines, has calculated that in order to charge every evening for two hours the 32 million electric cars, that will replace the 32 million thermal cars in the country⁴⁹, the current capacity of this electricity available on demand would have to be increased sevenfold from 100GW to 700GW. Thus instead of reducing the number of the most polluting installations or those considered rightly or wrongly (rather rightly according to the inhabitants of Chernobyl, Three Miles Island and Fukushima) potentially dangerous by replacing them with renewable energy production installations, we would paradoxically have to increase them. These “green” facilities are also much more material-intensive (up to ten times more) per kWh produced than conventional thermal power plants⁵⁰, especially for offshore wind turbines which require, in addition to concrete, kilometers of additional large cables. Moreover the nuclear power plants (among these controllable facilities) cooling, though climate change, are beginning to be made problematic for those located near rivers whose flow is increasingly fluctuating. And those whose water, even if it remains abundant, may be too hot in periods of heat wave to fulfill its intended purpose, sometimes leading to their temporary shutdown⁵¹. This problem will also be found with many other power plants, such as those located in the United States and with a number of hydroelectric dams⁵². The disappearance of glaciers threaten their water supply, as is already the case in certain regions of the world.
After this overview, only one rational conclusion can be drawn, namely that we did not ask ourselves the right questions in the first place. As the historian Bernard Fressoz⁵³ says, “the choice of the individual car was probably the worst that our societies have ever made”. However, it was not really a conscious and deliberate “choice” but a constraint imposed on the population by the conversion of the inventors/artisans of a still incipient automobile sector, whose limited production was sold to an equally limited wealthy clientele. The first cars being above all big toys for rich people who liked the thrills of real industrialists. Hand in hand with oil companies and tire manufacturers, they rationalized production by scrupulously applying Taylorist recipes and developed assembly lines such as Ford’s Model T in 1913. They then made cars available to the middle classes and over the decades created the conditions of compulsory use we know today.

Streetcars awaiting destruction. Photo: Los Angeles Times photographic archive.
It is this same trio (General Motors, Standard Oil and Firestone mainly, as well as Mack Truck and Phillips Petroleum) that was accused and condemned in 1951 by the Supreme Court of the United States of having conscientiously destroyed the streetcar networks and therefore electric public transport. They did so by taking advantage after the 1929 crash, of the “godsend” of the Great Depression, which weakened the dozens of private companies that ran them. Discredited and sabotaged in every conceivable way — including unfair competition, corruption of elected officials and high ranking civil servants, and recourse to mafia practices — streetcars were replaced first by buses, then by cars⁵⁴. This was done against a backdrop of ideological warfare, that began decades before the “official” Cold War, which an equally official History tells us about: socialist collectivism — socialist and anarchist ideas, imported at the end of the nineteenth century by immigrants from Europe and Russia, deemed subversive because they hindered the pursuit of private interests legitimized by Protestantism — countered, with the blessing of the State, by liberal individualism. This unbridled liberalism of a country crazing for the “no limits” way was also to promote the individual house of an “American dream” made possible by the private car, which explains so well the American geography of today, viable only thanks to fossil fuels⁵⁵.
Today not many people are aware of this, and very few people in the United States remember, that city dwellers did not want cars there. They were accused of monopolizing public space, blamed for their noise and bad odors. Frightened by their speed and above all they were dangerous for children who used to play in the streets. Monuments to those who lost their lives under their wheels were erected during demonstrations gathering thousands of people as a painful reminder⁵⁶. In Switzerland the canton of Graubünden banned motorized traffic throughout its territory at the beginning of the nineteenth century. It was only after quarter of a century later, after ten popular votes confirming the ban, that it was finally lifted⁵⁷.

Left: Car opposition poster for the January 18th, 1925, vote in the canton of Graubünden, Switzerland. Right: Saint-Moritz, circa 1920. Photo: Sammlung Marco Jehli, Celerina.
The dystopia feared by the English writer George Orwell in his book 1984 was in fact already largely underway at the time of its writing as far as the automobile is concerned. In fact by deliberately concealing or distorting historical truths, although they have been established for a long time and are very well documented, it is confirmed that “Who controls the past controls the future: who controls the present controls the past.” A future presented as inescapable and self-evident, which is often praised in a retroactive way, because when put in the context of the time, the reticence was nevertheless enormous⁵⁸. A future born in the myth of a technical progress, also far from being unanimously approved, in the Age of Enlightenment. The corollary of this progress would be the permanent acquisition of new, almost unlimited, material possessions made accessible by energy consumption-based mass production and access to leisure activities that also require infrastructures to satisfy them. International tourism, for example, is by no means immaterial, which we should be aware of when we get on a metallic plane burning fossil fuel and stay in a concrete hotel.
With the electric car, it is not so much a question of “saving the planet” as of saving one’s personal material comfort, which is so important today, and above all of saving the existing economic model that is so successful and rewarding for a small minority. This minority has never ceased, out of self-interest, to confuse the end with the means by equating freedom of movement with the motorization of this very movement.
The French Minister of the Economy and Finance, Bruno Le Maire declared before the car manufacturers that “car is freedom⁵⁹”. Yet this model is built at best on the syllogism, at worst on the shameless and deliberate lie of one of the founders of our modern economy, the Frenchman Jean-Baptiste. He said: “Natural resources are inexhaustible, for without them we would not obtain them for free. Since they can neither be multiplied nor exhausted, they are not the object of economic science⁶⁰“. This discipline, which claims to be a science while blithely freeing itself from the constraints of the physical environment of a finite world, that should for its part submit to its theories nevertheless by exhausting its supposedly inexhaustible resources and destroying its environment. The destruction of biodiversity and its ten-thousand-years-old climatic stability, allowed the automobile industries to prosper for over a century. They have built up veritable financial empires, allowing them to invest massively in the mainstream media which constantly promote the car, whether electric or not, placing them in the permanent top three of advertisers.
To threaten unemployment under the pretext that countless jobs depend on this automobile industry, even if it is true for the moment, is also to ignore, perhaps voluntarily, the past reluctance of the populations to the intrusion of automobiles. The people who did not perceive them at all as the symbol of freedom, prestige and social marker, even as the phallic symbol of omnipotence that they have become today for many⁶¹. It is above all to forget that until the 1920s the majority of people, at least in France, were not yet wage earners. Since wage employment was born in the United Kingdom with the industrial revolution or more precisely the capitalist revolution, beginning with the textile industry: enclosure and workhouses transformed peasants and independent artisans into manpower. Into a workforce drawn under constraint to serve the private capital by depriving them of the means of their autonomy (the appropriation of communal property). Just as imported slaves were on the other side of the Atlantic until they were replaced by the steam engine, which was much more economical and which was certainly the true abolitionist⁶². It is clear that there can be no question of challenging this dependence, which is now presented as inescapable by those who benefit most from it and those for whom it is a guarantee of social stability, and thus a formidable means of control over the populace.
Today, we are repeatedly told that “the American [and by extension Western] way of life is non-negotiable⁶³. “Sustainable development,” like “green growth,” “clean energy” and the “zero-carbon” cars (as we have seen above) are nothing but oxymorons whose sole purpose is to ensure the survival of the industries, on which this way of life relies to continue enriching their owners and shareholders. This includes the new information and communication industries that also want to sell their own products related to the car (like artificial intelligence for the autonomous car, and its potential devastating rebound effect). To also maintain the banking and financial systems that oversee them (debt and shareholders, eternally dissatisfied, demanding continuous growth, which is synonymous with constant consumption).

Cheerful passengers above flood victims queing for help, their car is shown as a source of happiness. Louisville, USA, 1937. Photo: Margaret Bourke-White, Museum of Fine Arts, Boston.
All this with the guarantee of politicians, often in blatant conflicts of interest. And all too often with the more or less unconscious, ignorant or irresponsible acceptance of populations lulled into a veritable culture of selfishness, more than reluctant from now on to consent to the slightest reduction in material comfort. Which they have been so effectively persuaded can only grow indefinitely but made only possible by the burning of long-plethoric and cheap energy. This explains their denial of the active role they play in this unbridled consumerism, the true engine of climate change. Many claim, in order to relieve themselves of guilt, to be only poor insignificant creatures that can in no way be responsible for the evils of which they are accused. And are quick to invoke natural cycles, even though they are often not even aware of them (such as the Milankovitch cycles⁶⁴ that lead us not towards a warming, but towards a cooling!), to find an easy explanation that clears them and does not question a comfortable and reassuring way of life; and a so disempowering one.
Indeed people, new Prometheus intoxicated by undeniable technical prowess, are hypersensitive to promises of innovations that look like miracle solutions. “Magical thinking”, and its avatars such as Santa Claus or Harry Potter, tends nowadays to last well beyond childhood in a highly technological society. Especially since it is exalted by the promoters of positive thinking and personal development. Whose books stuff the shelves in every bookstore, reinforcing the feeling of omnipotence, the certainty of a so-called “manifest destiny”, and the inclination to self-deification. But this era is coming to an end. Homo Deus is starting to have a serious hangover. And we are all already paying the price in social terms. The “gilets jaunes” or yellow vests in France, for example, were unable to accept a new tax on gas for funding renewables and a speed reduction on the roads from 90km/h down to 80km/h. Paying in terms of climate change, which has only just begun, from which no one will escape, rich and powerful included.
Now everyone can judge whether the electric car is as clean as we are constantly told it is, even to the point of making it, like in Orwell’s novel, an indisputable established truth, despite the flagrant contradiction in terms (“war is peace, freedom is slavery, ignorance is strength”). Does the inalienable freedom of individual motorized mobility, on which our modern societies are based, have a radiant future outside the imagination and fantasies of the endless technophiles who promise it to us ; just as they promised in the 1960s cities in orbit, flying cars, space stations on the Moon and Mars, underwater farms… And just as they also promised, 70 years ago, and in defiance of the most elementary principle of precaution, overwhelmed by an exalted optimism, to “very soon” find a definitive “solution” to nuclear waste; a solution that we are still waiting for, sweeping the (radioactive) dust under the carpet since then…
Isn’t it curious that we have focused mainly on the problem of the nature of the energy that ultimately allows an engine to function for moving a vehicle and its passengers, ignoring everything else? It’s as if we were trying to make the car as “dematerialized” as digital technology and the new economy it allows. Having succeeded in making the charging stations, the equipment, the satellites and the rockets to put them in orbit, the relay antennas, the thousands of kilometers of cables, and all that this implies of extractivism and industries upstream, disappear as if by magic (and we’re back to Harry Potter again). Yet all very material as is the energy necessary for their manufacture and their functioning, the generated pollution, the artificialization of the lands, etc.⁶⁵

Everlasting promises of flying cars, which would turn humans into new Icarius, arenearly one and a half century old. Future is definitely not anymore what it used to be…
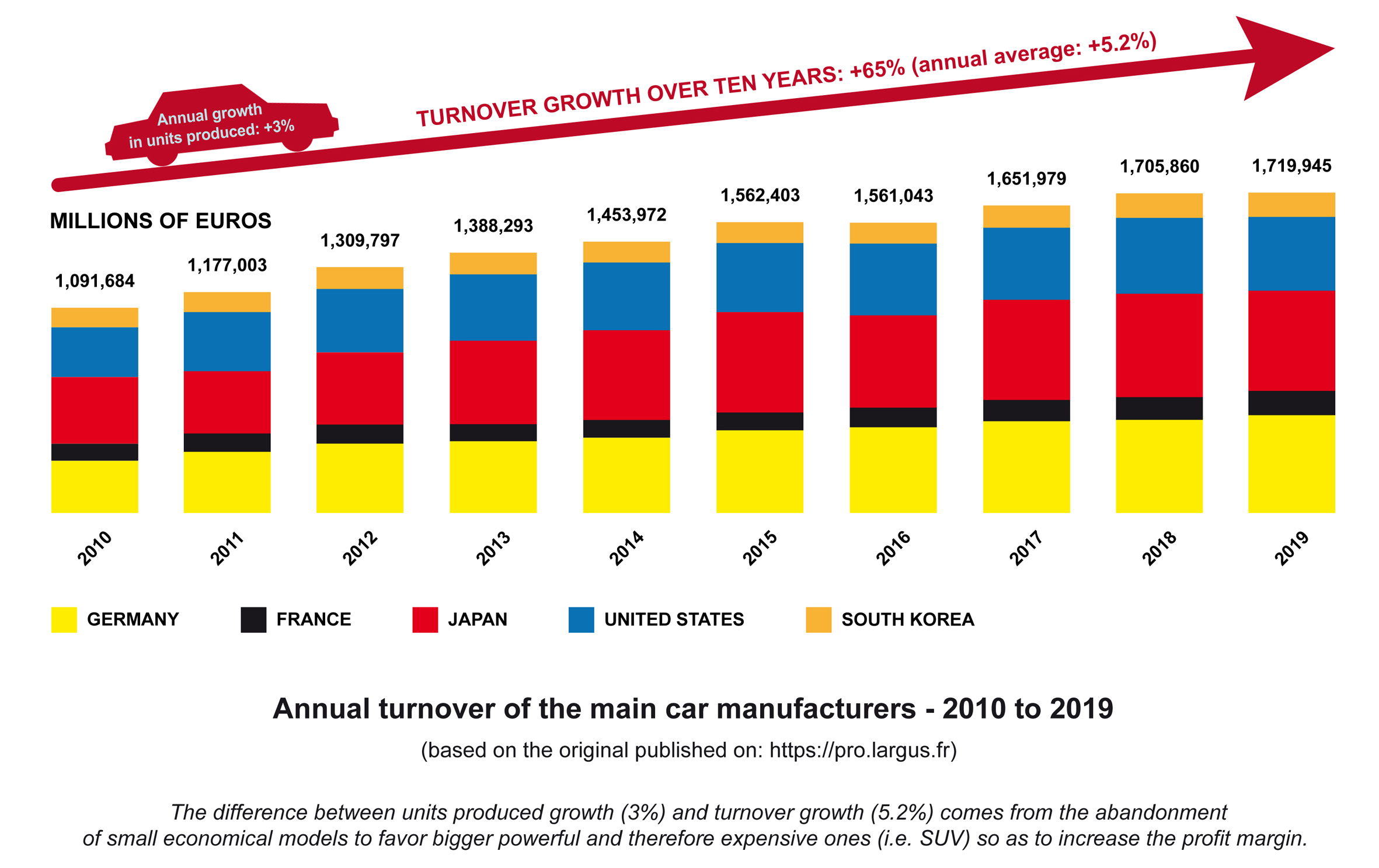
Everyone remains free to continue to take the word of economists who cling like a leech to their sacrosanct infinite growth. To believe politicians whose perception of the future is determined above all by the length of their mandate. Who, in addition to being subject to their hyperactive lobbying, have shares in a world automobile market approaching 1,800 billion Euros per year⁶⁶ (+65% in 10 years, neither politicians nor economists would balk at such growth, which must trigger off climax at the Ministry of the Economy!). That is to say, the 2019 GDP of Italy. Moreover, in 2018 the various taxes on motor vehicles brought in 440 billion Euros for European countries⁶⁷. So it is implicitly out of the question to question, let alone threaten the sustainability of, this industrial sector that guarantees the very stability of the most developed nations.
It is also very difficult to believe journalists who most often, except a few who are specialized, have a very poor command of the subjects they cover. Especially in France, even when they don’t just copy and paste each other. Moreover, they are mostly employed by media financed in large part, via advertising revenues among other things, by car manufacturers who would hardly tolerate criticism or contradiction. No mention of CO2-emitting cement broadcasted on the TF1 channel, owned by the concrete builder Bouygues, which is currently manufacturing the bases for the wind turbines in Fécamp, Normandy. No more than believing startups whose primary vocation is to “make money”, even at the cost of false promises that they know very few people will debunk. Like some solar panels sold to provide more energy than the sun works only for those who ignore another physical fact, the solar constant. Which is simply like making people believe in the biblical multiplication of loaves and fishes.
So, sorry to disappoint you and to hurt your intimate convictions, perhaps even your faith, but the electric car, like Trump’s coal, will never be “clean”. Because as soon as you transform matter from one state to another by means of energy, you dissipate part of this energy in the form of heat. And you inevitably obtain by-products that are not necessarily desired and waste. This is why physicists, scientists and Greta Thunberg kept telling us for years that we should listen to them. The electric car will be at best just “a little less dirty” (in the order of 0 to 25% according to the various studies carried out concerning manufacturing and energy supply of vehicles, and even less if we integrate all the externalities). This is a meager advantage that is probably more socially acceptable but it is quickly swallowed up if not solely in their renewal frequency. The future will tell, at least in the announced increase of the total number of cars, with a 3% per year mean growth in terms of units produced, and of all the infrastructures on which they depend (same growth rate for the construction of new roads). 3% means a doubling of the total number of vehicles and kilometers of roads every 23 years, and this is absolutely not questioned.
Brittany, France, August 2021.


42 With 8 billion tons consumed every year, coal stands in the very first place in terms of carbon dioxide emissions. International Energy Outlook, 2019.
43 https://www.statistiques.developpement-durable.gouv.fr/edition-numerique/chiffres-cles-du-climat/7-repartition-sectorielle-des-emissions-de
44 & https://web.archive.org/web/20211121215259/https://en.reset.org/knowledge/our-digital-carbon-footprint-whats-the-environmental-impact-online-world-12302019
45 https://actu.fr/normandie/le-havre_76351/en-images-au-havre-le-titanesque-chantier-des-fondations-des-eoliennes-en-mer-de-fecamp_40178627.html
46 https://www.connaissancedesenergies.org/fiche-pedagogique/production-de-lhydrogene
47 https://www.iea.org/fuels-and-technologies/oil & https://www.bp.com/content/dam/bp/business-sites/en/global/corporate/pdfs/energy-economics/statistical-review/bp-stats-review-2019-full-report.pdf & https://www.ufip.fr/petrole/chiffres-cles
48 https://jancovici.com/
49 Atually there are 38.2 million cars in France, more than one for two inhabitants:
50 Philippe Bihouix and Benoît de Guillebon, op. cit., p. 32.
51 https://www.lemonde.fr/energies/article/2019/07/22/canicule-edf-doit-mettre-a-l-arret-deux-reacteurs-nucleaires_5492251_1653054.html & https://www.ucsusa.org/resources/energy-water-collision
52 https://www.reuters.com/business/sustainable-business/inconvenient-truth-droughts-shrink-hydropower-pose-risk-global-push-clean-energy-2021-08-13/
53 Co-author with Christophe Bonneuil of L’évènement anthropocène. La Terre, l’histoire et nous, Points, 2016 (The Shock of the Anthropocene: The Earth, History and Us, Verso, 2017).
54 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/242431866_General_Motors_and_the_Demise_of_Streetcars & Matthieu Auzanneau, Or noir. La grande histoire du pétrole, La Découverte, 2015, p.436, and the report written for the American Senate by Bradford C. Snell, Public Prosecutor specialized in anti-trust laws.
55 James Howard Kunstler, The Geography of Nowhere: The Rise and Decline of America’s Man-Made Landscape, Free Press, 1994.
56 Peter D. Norton, Fighting Traffic. The Dawn of the Motor Age in the American City, The MIT Press, 2008.
57 https://www.avenir-suisse.ch/fr/vitesse-puanteur-bruit-et-ennuis/ & Stefan Hollinger, Graubünden und das Auto. Kontroversen um den Automobilverkehr 1900-1925, Kommissionsverlag Desertina, 2008
58 Emmanuel Fureix and François Jarrige, La modernité désenchantée, La Découverte, 2015 & François Jarrige, Technocritiques. Du refus des machines à la contestation des technosciences, La Découverte, 2014.
59 Journée de la filière automobile, Bercy, December 02, 2019.
60 Cours complet d’économie politique pratique, 1828.
61 Richard Bergeron, le Livre noir de l’automobile, Exploration du rapport malsain de l’homme contemporain à l’automobile, Éditions Hypothèse, 1999 & Jean Robin, Le livre noir de l’automobile : Millions de morts et d’handicapés à vie, pollution, déshumanisation, destruction des paysages, etc., Tatamis Editions, 2014.
62 Domenico Losurdo, Contre-histoire du libéralisme, La Découverte, 2013 (Liberalism : A Counter-History, Verso, 2014) & Howard Zinn, A People’s History of the United States, 1492-Present, Longman, 1980 (Une Histoire populaire des Etats-Unis de 1492 a nos jours, Agone, 2003) & Eric Williams, Capitalism & Slavery, The University of North Carolina Press, 1943.
63 George H.W. Bush, Earth Summit, Rio de Janeiro, 1992.
64 https://planet-terre.ens-lyon.fr/ressource/milankovitch-2005.xml
65 Guillaume Pitron, L’enfer numérique. Voyage au bout d’un like, Les Liens qui Libèrent, 2021.
66 https://fr.statista.com/statistiques/504565/constructeurs-automobiles-chiffre-d-affaires-classement-mondial/
67 Source: ACEA Tax Guide 2020, fiscal income from motor vehicles in major European markets.

 Lithium Americas claims that protecting the Montana Mountains is their priority, writing “Lithium Americas made the decision in 2018 to move the project south of the Montana Mountains to avoid disturbing sensitive ecological areas located within the mountains,” and that “[T]he project will not involve any direct physical disturbance of sage grouse leks or golden eagle nests”.
Lithium Americas claims that protecting the Montana Mountains is their priority, writing “Lithium Americas made the decision in 2018 to move the project south of the Montana Mountains to avoid disturbing sensitive ecological areas located within the mountains,” and that “[T]he project will not involve any direct physical disturbance of sage grouse leks or golden eagle nests”. Why, then, does the company say in their 2-page fact sheet that they moved the Thacker Pass project south to avoid disturbing sensitive ecological areas within the mountains when they have every intention of expanding the mining project into the Montana Mountains where the sage-grouse leks are located? Do they believe that once the first project is begun, it will be easier to get further mining projects in the region approved?
Why, then, does the company say in their 2-page fact sheet that they moved the Thacker Pass project south to avoid disturbing sensitive ecological areas within the mountains when they have every intention of expanding the mining project into the Montana Mountains where the sage-grouse leks are located? Do they believe that once the first project is begun, it will be easier to get further mining projects in the region approved?




![Electric Vehicles: Back to the Future? [Part 2/2]](https://dgrnewsservice.org/wp-content/uploads/sites/18/2021/11/Illustration_017.jpg)








