
by DGR News Service | Aug 21, 2021 | Biodiversity & Habitat Destruction, Climate Change, Indigenous Autonomy, Listening to the Land, Mining & Drilling, Movement Building & Support, Obstruction & Occupation, Toxification
This article originally appeared in Protect Thacker Pass.
By Max Wilbert
The great poet and playwright James Baldwin wrote in 1953 that “People who shut their eyes to reality simply invite their own destruction.”
Perhaps never has this been truer than in this era of converging ecological crises: global warming, biodiversity collapse, desertification and soil erosion, ocean acidification, dead zones, plastic pollution, sprawling habitat destruction, and the total saturation of our environment with radioactive or toxic chemicals.
Ignorance is not bliss; it is dangerous.
That is why I am so concerned that, while searching for solutions to global warming, many people imagine that fossil fuels can be simply replaced with solar and wind energy, that gas tanks can be swapped for lithium batteries, and that this will solve the problem.
For years, I have been arguing that this is wrong, and that we need much more fundamental changes to our economy, our society, and our way of life.
For the last 6 months, I have been camped at a place in northern Nevada called Thacker Pass, which is threatened by a vast planned open-pit mine that threatens to destroy 28 square miles of biodiverse sagebrush habitat, release millions of tons of greenhouse gas emissions, bulldoze Paiute and Shoshone sacred sites, and leave behind piles of toxic waste for generations to come.
Electric cars and fossil fuel cars don’t differ as much as lithium mining companies would like us to believe. In fact, a direct link connects the water protectors fighting the new Line 3 oil pipeline in the Ojibwe territory in Minnesota and the land defenders working to protect Peehee Mu’huh, the original name for Thacker Pass in the Paiute language.
The new Line 3 pipeline would carry almost a million barrels a day of crude oil from the Alberta Tar Sands, the largest and most destructive industrial project on the planet, to refineries in the United States. On the way, it would threaten more than 200 waterbodies and carve a path through what CNN called “some of the most pristine woods and wetlands in North America.” The project would be directly responsible for millions of tons of greenhouse gas emissions.
For the last 7 years, indigenous water protectors and allies have rallied, petitioned, established resistance camps, held events, protested, and engaged in direct action to stop the Line 3 pipeline from being built. More than 350 people have been arrested over the past few months, but pipeline construction continues to progress for now.
Ironically, the proposed Thacker Pass lithium mine would require importing nearly 700,000 tons of sulfur per year — roughly equivalent to the mass of two Empire State Buildings — for processing the lithium. This sulfur would likely come (at least in part) from the Alberta tar sands, perhaps even from oil that would flow through Line 3.
Almost all sulfur, which is used in a wide range of chemical processes and fertilizers, comes from oil and gas refineries, where it’s a byproduct of producing low-sulfur fuels to meet air-quality regulations around acid rain.
According to the U.S. Geological Survey, tar sands contain 11 times as much sulfur as conventional heavy crude oil, and literal “mountains” of sulfur are piling up in Alberta and at other refineries which process tar sands fuel. Sulfur sales revenue is important to the economics of tar sands oil extraction. One report released in the early years of tar sands extraction found that “developing a plan for storing, selling or disposing of the sulfur [extracted during processing] will help to ensure the profitability of oil sands operations.”
This means that Thacker Pass lithium destined for use in “green” electric cars and solar energy storage batteries would almost certainly be directly linked to the Line 3 pipeline and the harms caused by the Tar Sands, including the destruction of boreal forest, the poisoning of the Athabasca River and other waters, and an epidemic of cancers, rare diseases, and missing and murdered indigenous women facing Alberta First Nations. And, of course, the tar sands significantly exacerbate global warming. Canadian greenhouse gas emissions have skyrocketed over recent decades as tar sands oil production has increased.
Mining is exceptionally destructive. There is no getting around it. According to the EPA, hard-rock mining is the single largest source of water pollution in the United States. The same statistic probably applies globally, but no one really knows how many rivers have been poisoned, how many mountains blown up, how many meadows and forests bulldozed for the sake of mining.
The water protectors at Line 3 fight to protect Ojibwe territory, wild rice beds, and critical wildlife habitat from a tar sands oil pipeline, oil spills, and the greenhouse gas emissions that would harm the entire world. Here at Thacker Pass, we fight the same fight. The indigenous people here, too, face the destruction of their first foods; the poisoning of their water; the desecration of their sacred sites; and the probability of a toxic legacy for future generations. I fight alongside them for this place.
Our fights are not separate. Our planet will not cool, our waters will not begin to flow clean again, our forests will not regrow, and our children will not have security unless we organize, stop the destruction, and build a new way of life. The Line 3 pipeline, and all the other pipelines, must be stopped. And so must the lithium mines.
The wind howls at Thacker Pass. Rain beats against the walls of my tent. A steady drip falls onto the foot of my sleeping bag. It’s June, but we are a mile above sea level. Summer is slow in coming here, and so the storm rages outside, and I cannot sleep. Nightmare visions of open-pit mines, climate breakdown, and ecological collapse haunt me.
James Baldwin gave good advice. In this time, we must not shut our eyes to the reality that industrial production, including the production of oil and the production of electric cars, results in industrial devastation. And with our eyes wide open, we must take action to protect our only home, and the future generations who rely on us.
Also available at The Sierra Nevada Ally, Dispatches from Thacker Pass series.


by DGR News Service | Jun 20, 2021 | Biodiversity & Habitat Destruction, Colonialism & Conquest, Indigenous Autonomy, Mining & Drilling, NEWS, Repression at Home, Toxification
- Vale, the Brazilian mining company responsible for two deadly dam collapses since 2015, has another dam that’s at “imminent risk of rupture,” a government audit warns.
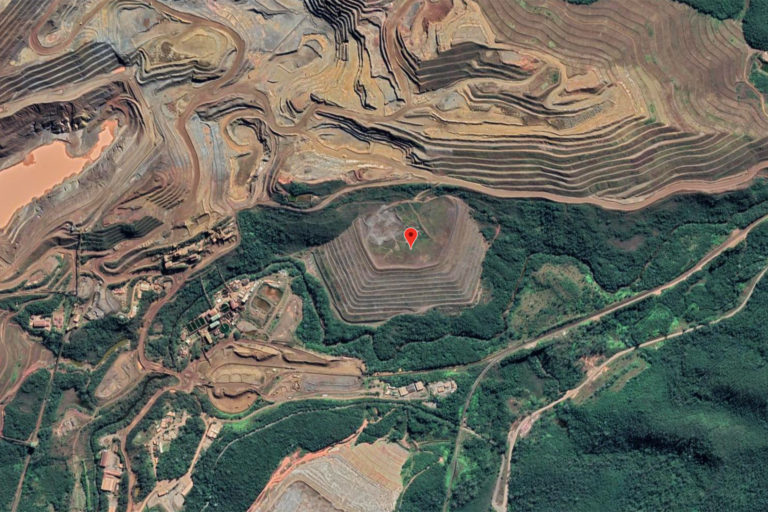
- The Xingu dam at Vale’s Alegria mine in Mariana municipality, Minas Gerais state, has been retired since 1998, but excess water in the mining waste that it’s holding back threatens to liquefy the embankment and spark a potentially disastrous collapse.
- Liquefaction also caused the collapse of a Vale tailings dam in 2019 in Brumadinho municipality, also in Minas Gerais, that killed nearly 300 people; the 2015 collapse of another Vale dam, in Mariana in 2015, caused extensive pollution and is considered Brazil’s worst environmental disaster to date.
- Vale has denied the risk of a collapse at the Xingu dam and says it continues to monitor the structure ahead of its decommissioning; regulators, however, say the company still hasn’t carried out requested measures to improve the structure’s safety, and have ordered an evacuation of the immediate vicinity.
This article originally appeared in Mongabay.
Featured image: Vale’s Xingu mining complex in Mariana. Image by Google.
by Juliana Ennes
A dam holding back mining waste from Brazilian miner Vale is at risk of collapsing, a government audit says. The same company was responsible for two tailings dam collapses since 2015 that unleashed millions of gallons of toxic sludge and killed hundreds of people in Brazil’s southeastern state of Minas Gerais.
The retired Xingu dam at Vale’s Alegria iron ore mine in Mariana — the same municipality where a Vale tailings dam collapsed in November 2015 in what’s considered Brazil’s worst environmental disaster to date — is at “serious and imminent risk of rupture by liquefaction,” according to an audit report from the Minas Gerais state labor department (SRT), cited by government news agency Agência Brasil. The SRT did not immediately reply to Mongabay’s emailed requests for comment; it also did not answer any phone calls.
In the May 20 audit report, only released last week, the SRT said the Xingu dam “does not present stability conditions.” “It is, therefore, an extremely serious situation that puts at risk workers who perform activities, access or remain on the crest, on the downstream slopes, in the flood area and in the area on the tailings upstream of the dam,” the document says.
In a statement, Vale denied the imminent risk, saying the dam “is monitored and inspected daily.” It said the structure’s conditions and safety level remain unchanged, rated level 2 on a three-point scale.
The 2015 collapse of the Fundão tailings dam belonging to Samarco, a joint venture between Vale and Anglo-Australian miner BHP Billiton, killed 19 people in the village of Bento Rodrigues, burying them in toxic mud, and flushing mining waste into rivers that affected 39 municipalities across two states. The mining waste eventually flowed more than 650 kilometers (400 miles) from its source to the Atlantic Ocean.
The district prosecutor’s office in Mariana told Mongabay that the Minas Gerais state prosecutor-general has requested the National Mining Agency (ANM) to assess the real risk of the dam rupture. “Any irregularity in the change in the classification of the structure will be evaluated after the inspection carried out by the ANM and, if necessary, with subsequent investigations,” the district prosecutor’s office said.
The ANM rated the Xingu dam’s safety at level 2 in a September 2020 assessment, after requesting Vale to improve the structure. Vale has fulfilled part of the request, but has sought a deadline extension for other repair works, without major changes in the structure, according to the ANM’s website.
In its most recent inspection, on May 5, ANM identified structural problems where no corrective measures had been implemented, according to its website. By then, the ANM considered the potential environmental impact “relevant” and the socioeconomic impact “medium,” given the concentration of residential, farming and industrial facilities located downstream of the dam.
Vale ceased dumping mining waste in the Xingu dam in 1998, but keeps workers on site to monitor the dam’s stability until it’s fully decommissioned. The decommissioning plans is in place but hasn’t been carried out yet, according to Ronilton Condessa, director of the Mariana mining workers’ union, Metabase. No timeline has been given for the decommissioning; a similar structure, the Doutor dam at Vale’s Timbopeba mine in neighboring Ouro Preto municipality, will take up to nine years.
Last week, Vale announced the suspension of train operations to the Mariana complex where its Alegria mine is located, after an evacuation order from labor auditors. The area in the immediate vicinity of the mine, known as the self-rescue zone, remains evacuated. Work at both the Timbopeba and Alegria mines has been halted.
Condessa said that because the Xingu dam is located inside the mining complex, workers continue to pass by it daily on their way to other mines that are still active.
Vale has scheduled a meeting with workers from the dam for June 16 to explain the current situation, according to Condessa. “The evacuation orders look like a preventive measure, but we still need to see a technical study in order to properly evaluate the risk,” he told Mongabay in a phone interview.
The Minas Gerais state civil defense agency said the evacuation of the self-rescue zone was ordered on a “preventive basis to protect the lives of people living downstream of the dam.”
“In collaboration with the SRT, Vale is taking measures to continue to guarantee the safety of workers, in order to resume activities,” Vale said in a June 4 statement.
A two-and-a-half-hour drive west of the Alegria mine in Mariana is the municipality of Brumadinho. This was the site in 2019 of Brazil’s deadliest mining disaster, when a tailings dam at Vale’s Córrego do Feijão iron ore mine collapsed, killing nearly 300 people. The cause of the dam’s failure was attributed to a process known as liquefaction, in which excess water weakens the dam’s embankment. This is the same risk recently identified at the Xingu dam at Vale’s Alegria mine.
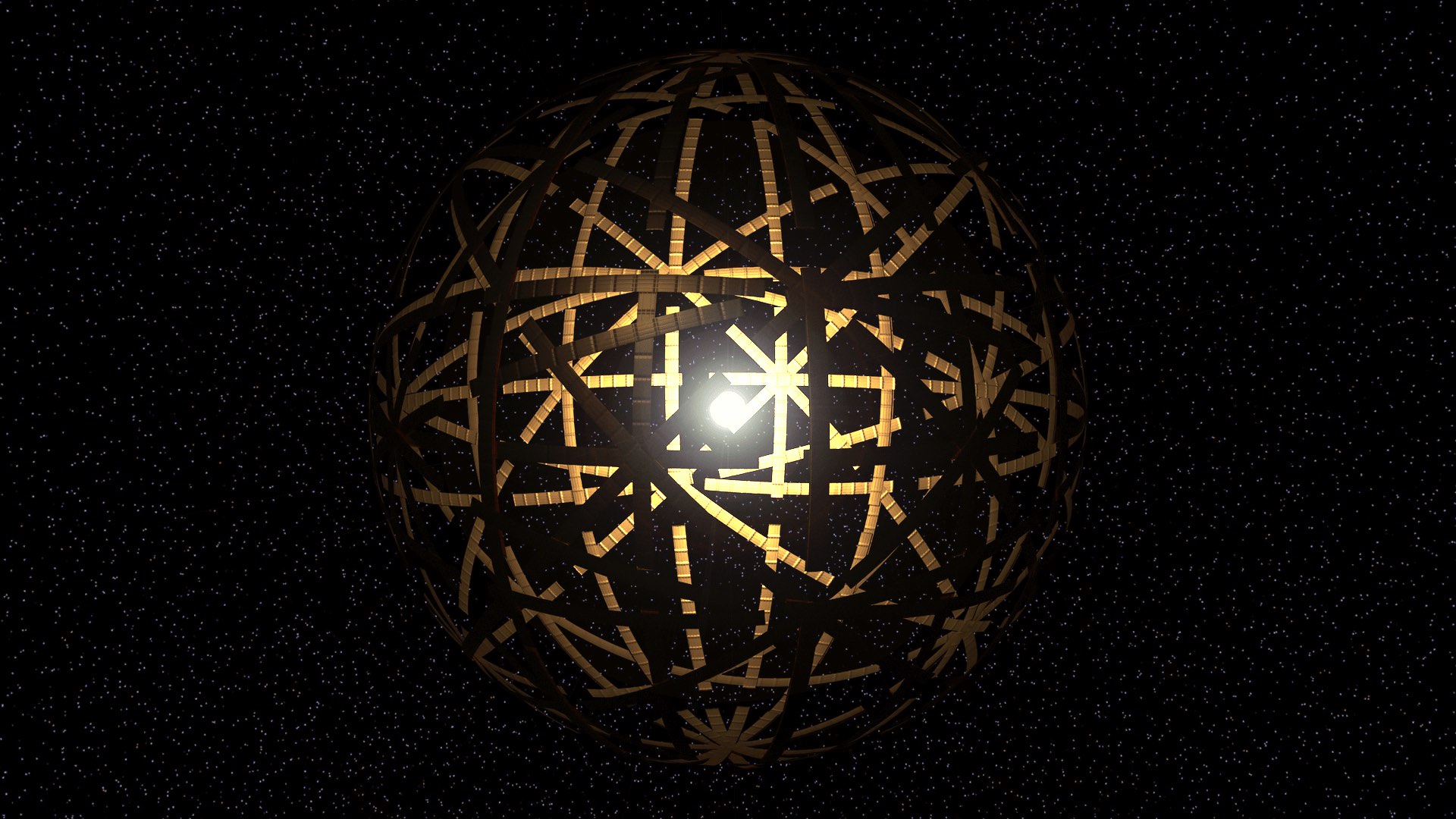
by DGR News Service | Aug 29, 2020 | Human Supremacy
This is the second in a series of articles reflecting on a recent study which predicts collapse of industrial society within a few decades. In the first essay, Max Wilbert discusses how in the long-run, collapse will benefit both humans and nature alike. This second essay in the series explores a “solution” proposed by the original authors of the study—a “Dyson sphere”—and why it will not save us from a collapse.
By Salonika / DGR Asia-Pacific
A Dyson sphere is a theoretical energy harvesting, a metal sphere that completely encompasses a star, and harnesses 100% of the solar energy. The solar panels that form its membranes would capture and transmit energy to Earth’s surface through microwave or laser. A concept that originated from a science fiction, it has been considered to be the ultimate “solution” to an industrial civilization’s ever increasing demand for energy.
There are a lot of problems with this theoretical solution. The authors of the study themselves are skeptical about the possibility of building a Dyson sphere by the time of their predicted collapse. We are going to deal with this issue in later parts of this series. In this piece, I will explore the improbable scenario that a Dyson sphere is built to fulfill the fantastical visions of the technocrats and whether that could prevent the ensuing collapse.
Is energy crisis the only crisis we are facing?
The obsession of the current environmental movement with renewable energy could easily confuse anyone regarding the scale of the ecological crisis that we are facing. We now witness a mass delusion that the energy crisis is, in fact, the only crisis that civilization is facing. In reality, the energy crisis represents just a facet of the ecological crisis.
Let’s consider global deforestation, which was used in the model for the study. The authors assert that once the Dyson sphere is used to “solve” our energy problems, the global deforestation would halt, ensuring the longevity of human civilization on Earth. This assertion is based on an unstated assumption that forests are being cleared primarily for fuel. As a matter of fact, fuel is only one driver of deforestation. Forests are also cleared for agriculture, cattle ranching, human settlements, buildings, mining, and roads. Unlimited energy does not “solve” or remove these pressures.
The same is true for all other forms of ecocide. Ninety percent of large fish in the oceans are gone, not to exploit their bodies for fuel, but due to overconsumption of fish as food. Bees colonies are collapsing, not for fuel, but, scientists estimate, due to pesticides, malnutrition, electromagnetic radiation, and genetically modified crops. Two hundred species are disappearing every day. That’s one every six minutes. That’s a result of habitat destruction, climate change, overexploitation, and toxification, not the need for energy.
A Dyson sphere (if it is ever created) could solve only the so-called energy crisis. All the other crises – habitat destruction, toxic environmental pollution, land clearing for agriculture, mining, overexploitation of species, and so on – would still continue. Indeed, the very existence of a Dyson sphere could increase the exploitation of the environment.
How is a Dyson sphere created?
First, a Dyson sphere would bemore massive than Earth itself. It would demands an astronomical (pun intended!) amount of raw materials, particularly metals. Procurement of these raw materials would require resource extraction on an unprecedented scale. Resource extraction (like mining) is one of the primary causes of environmental degradation, including global deforestation. Proponents advocate mitigating this harm by mining asteroids rather than planet Earth, but developing and building the fleet of spacecraft necessary for such an endeavor would necessarily begin on Earth, and would be incredibly harmful. In a single launch, a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket emits 1352 tonnes of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. (That’s nearly 300 times what an average car emits every year.)
Once created, a Dyson sphere would also need to be maintained. On average, a solar panel lasts about 25-30 years, after which the amount of energy produced will decline by a significant amount. It means that in every thirty years, the entire Dyson sphere would have to be rebuilt again. Let’s assume that the solar panels of the Dyson sphere would be more durable than the ones we use now. Even so, they will be subjected to different risks, like damage from asteroids or comets. A Dyson sphere would create a perpetual demand for (and, inevitably, overconsumption of) nonrenewable materials.
Additionally, the Dyson sphere could not function on its own. A new set of infrastructures would need to be built in order to utilize the energy harnessed. These include laser beam or microwave transmitters for wireless energy transmission from space to earth, additional photovoltaic cells in Earth to receive the transmitted solar energy, transmission wires (and poles) to supply the energy to industrial areas, and batteries to store the energy for when clouds block microwave transmission.
These building blocks come with additional costs. Wireless transmission of such vast quantities of energy can potentially cause eye and skin damage and other harm to human health, change the weather, and are potential culprits behind bees colony collapse. And what about birds? Traditional transmission lines are a prime cause of deforestation. Photo-voltaic cells usually end up in landfills or are sent to a developing country with lax environmental laws. Creating, maintaining, and disposing of solar panels pollutes the environment at every step.
An Authoritarian Technic
Lewis Mumford distinguishes between authoritarian technics and democratic technics based on whether a piece of technology requires a large-scale hierarchical structure, and whether it reinforces this structure. The Dyson sphere can be considered an authoritarian technic based on both of these criteria. The Dyson sphere requires a massive hierarchical infrastructure to exist in the first place: only specific group of individuals – those who have access and control over these infrastructures – can control its creation. Once created, it will be used to perpetuate the very hierarchical structure that created the conditions for its existence.
A Dyson sphere could exist only in an explicitly human supremacist, and implicitly colonial and patriarchal, culture. It will require resource extraction (primarily mining), on a scale much larger than what we have seen before. Extraction is inherently an ecocidal practice based on forced labor. It has been responsible for the destruction of numerous biospheres, and displacement of both humans and nonhuman communities.
The beneficiaries of this so-called technological “innovation” would be those who are already on the upper rungs of the hierarchical structure. Those on the bottom, on the other hand, would face the consequences. The same is true for other forms of technological innovations that we use every day. Consider a cell phone, for example. For the “haves” of the industrialized society, cell phones are little short of a basic necessity of life, the cost of which are covered by the “have-nots” through perpetual conflicts over resources, forced labor in modern day sweatshops, or even their lives.
The Root of the Problem: Overconsumption
Most importantly, the Dyson sphere does not address the core cause of the civilization’s impending collapse: overconsumption. Despite the claims that technology contributes to efficiency of resource consumption, technology seems to have very little (or even adverse) effect on the global energy consumption. With the exception of 2009 (the year of the global economic recession), consumption has only increased each year since 1990. When the demand for a product is constantly rising, no matter how efficient the production process gets, it will lead to greater consumption of resources.
On the contrary, the authors present a Dyson sphere as a solution to their predicted population collapse. They assume that, the perpetual energy source would lead to a lowered consumption of natural resources, allowing a sustained human population of 10 billion. Even if the culture’s energy demands are met by the perpetual source, in face of a growing (industrialized) human population, we can only presume, the need for more food, more land, more “progress,” and – inevitably – more deforestation.
Furthermore, an implicit (yet obvious) motive for creation of a Dyson sphere is to facilitate our increasing levels of consumption. It will promote an energy intensive way of life. The more energy intensive a way of life is, the more it is based on (over)consumption. In fact, the very existence of a Dyson sphere would demand an exploitation of resources.
A Dyson sphere would not halt deforestation; neither would it stop the acidification of oceans. We’re facing an emergency: an imminent collapse. Many nonhumans have already faced its brutal reality (think about the last member of the species that died while you were reading this article). Now is not the time to indulge in fantasies of a non-existent technology that will salvage the civilization: it is the time to stop whatever is causing the collapse (hint: it’s overconsumption).
Salonika is a member of Deep Green Resistance Asia-Pacific. She believes that the needs of the natural world should trump the wants of the extractive culture.
Featured image: rendering of Dyson swarm by Kevin M. Gill, cc-by-2.0.

by DGR News Service | May 8, 2020 | The Problem: Civilization
Understanding Patterns of Civilization Collapse
By Kara Huntermoon
Ecology is the basis of all economies. No human economic system can exist without the gifts of water, land, plants, animals, insects, air, and other members of our ecological communities. When capitalism treats “natural resources” as free and unlimited, it ignores the fact that these are living, spirit-filled entities who have needs, preferences, and boundaries. All over the world, we have already crossed their limits.
‘Economy’ means how humans meet their daily needs.
Human groups have options about how to meet their daily needs. Capitalism is only one option. It is a relatively new and short-lived option which is coming to an end. Capitalism is inherently oppressive and relies on separating people into constituencies which are given more or less power and privilege. Capitalism is also inherently destructive to the ecological basis of all life. It is not possible to have capitalism without oppression and ecological destruction.
Humans need direct relationships with ecology in order to receive feedback about whether their economic activities are enhancing, destroying, or neutral to the systems of life that support daily human needs. Ecological feedback is often so slow that multiple generations of humans must be engaged in the conversation before the feedback is understood and human communities are able to respond to the information. The information received through ecological relationships is often coded into religious practices and educational systems, including stories told to children.
‘Civilization’ means a human community organized around cities and their adjacent exploited ecological communities.
When human populations concentrate in cities, large areas of surrounding ecology are required to support urban human life, but the ‘consumers’ are not able to directly listen to the ecological feedback. Consequently, the human culture becomes disconnected from the information needed to support all life. Humans throughout time and place have tried organizing in urban centers and importing their needs from their surrounding ecology, including through empire (controlling adjacent ecological communities and importing goods from them).
No civilization has ever been sustainable. Civilizations collapse when the human-ecological relationship breaks down far enough for the ecology to be unable to continue supporting the urban infrastructure and population. Cities are not a sustainable way to organize human communities and ecologies. When city-states are organized into empires, the civilization collapses unevenly. In some areas, life seems to continue in a way that would support the city continuing. In other areas, cities collapse and are abandoned earlier in the widespread empire’s collapse.
‘Collapse’ means that social and physical infrastructure is abandoned or destroyed as it becomes obvious that it is obsolete. The amount of true wealth available from ecological relationships is no longer enough to maintain the unsustainable infrastructure. The amount of physical infrastructure decreases, the overall population of humans decreases, and a greater proportion of the human population returns to a direct relationship with ecological communities (subsistence agriculture, foraging, hunting).
The Early Stages of Civilization Collapse.
During the early stages of an empire’s collapse, people flee collapsing cities and move to other cities that are not yet collapsing. Sometimes those cities collapse because of empire-related economic shifts (as in the “Rust Belt” cities of the US), sometimes because of ecological destruction (as in New Orleans after Hurricane Katrina, or Paradise after the Camp Creek Fire). Regardless of the reason, the cities are not rebuilt because the ecological basis for creating true wealth (the capacity to meet human needs) is unable to support the rebuilding.
Later stages of collapse.
During later stages of an empire’s collapse, people flee cities to return to the countryside where they can grow food and attempt to meet their needs. There is a steep learning curve while the relationship communication between humans and their ecology is not robust enough to support the current human population size. People die because they do not know how to relate to the plants, animals, soils, and waters who support life. The conversation also begins with the ecological communities running at a deficit, impoverished by the collapsing civilization’s exploitation.
It takes time for recovery, relationship building, and forgiveness.
Historically speaking, the average time it takes a civilization to collapse is about 300 years. Civilizations collapse in a stair-step pattern, with large-scale economic shocks followed by partial recoveries. In our recent history, collapse shocks happened in the 1970s (“Energy Crisis”), in 2007 during the sub-prime mortgage crisis (“The Great Recession”), and now during the Covid-19 Pandemic (“The Global Downturn of 2020”).
Most of us remember the “Great Recession” and the Occupy Movement, and we have heard federal officials claim that the economy recovered from that and was booming (“the best ever” before Covid-19). Concurrent with these claims, visible markers of decline have led to an increase of the number of homeless people on the streets in most major cities, including Eugene. Buildings are demolished without funding to replace them, including Eugene’s City Hall. There is increasing personal and government debt and decreasing possibility of gaining stable well-paid employment, even with a college degree.
It is reasonable to assume that we are in the early stages of our civilization’s collapse, and that we will continue to see stair-step degradations in physical and social infrastructure.
Considering history, it is likely we will have a partial economic recovery after the pandemic ends. Considering climate change, we need to be prepared for further rapid down-steps as ecological shocks increase and spread. We may not live to see the end of our civilization, but we will see continued disorder, political circuses, domestic and international violence, and rapid economic shifts as a ‘new normal.’
Within seven generations, our descendents will see the end of our civilization.
Marked by a complete abandonment of city infrastructure and a return to direct relationship with ecological economies. There is much we can do now to prepare them. For the purpose of our own preparation for the future, we should assume that there will never be a recovery. This is it. Things will never “return to normal.” We are not going to get through this and continue our previous lives. We cannot expect our children to have access to the same privileges we have enjoyed.
How can we impact the way our communities respond to the Covid-19 Pandemic and the resulting economic crisis? In what ways can we support and organize alternatives to the current economic system and its inherent systems of oppression? How can we organize our own lives to be fully in service of sustainability and liberation? How can we reach for people we love, people in our neighborhoods, people in our workplaces, and model for them the changes we wish to see?
The pandemic will bring up early feelings that are not about present time.
Unhealed emotional scars from childhood can confuse us as we try to think about responding to novel situations. To help free our minds of early distresses, we can spend time journalling, talking to trusted loved ones, or meditating on the following: In what ways do you try to avoid suffering? What suffering of your earlier life do you never want to experience again? Go back there and give that young person a hand. You survived that. You won. It’s actually over, and you won. I know it doesn’t feel like you won; it feels like you barely escaped and you are irreparably harmed, no longer intact. But that is just a feeling.
The truth is that you won.
If you can make friends with those feelings―of loss, isolation, hopelessness, discouragement, terror, powerlessness―you will be able to notice that you are intact. You survived. You won. You get to have a big life now. You don’t have to settle for what you can salvage. You get to have people close-in who can fully support you.
We get to work together to make big lives for ourselves.
It is possible to see the current pandemic, economic collapse, and climate emergency as a fascinating challenge that will never stop giving us meaningful work to do.
It is possible to feel satisfied that we are fulfilling our reasons for coming to this life, that we are giving fully of our gifts to our communities.
Let us reach for each other, reach for full acceptance of ourselves at all stages of our lives, and reach for implementing our visions of a sustainable society in full communication with its ecological community.
Kara Huntermoon is one of seven co-owners of Heart-Culture Farm Community, near Eugene, Oregon. She spends most of her time in unpaid labor in service of community: child-raising, garden-growing, and emotion/relationship management among the community residents. She also teaches Liberation Listening, a form of co-counseling that focuses on ending oppression.
Featured image: Deep Green Resistance food distribution in response to the CoViD-19 pandemic.
Spring 2020 Fundraiser
Right now, Deep Green Resistance organizers are at work building a political resistance resistance movement to defend the living planet and rebuild just, sustainable human communities.
In Manila, Kathmandu, Auckland, Denver, Paris—all over the world—we are building resistance and working towards revolution. We Need Your Help.
Not all of us can work from the front lines, but we can all contribute. Our radical, uncompromising stance comes at a price. Foundations and corporations won’t fund us because we are too radical. We operate on a shoestring budget (all our funding comes from small, grassroots donations averaging less than $50) and have only one paid staff.
Current funding levels aren’t sustainable for the long-term, even with our level of operations now. We need to expand our fundraising base significantly to build stronger resistance and grow our movement.
Click here to support our work.

by DGR News Service | Apr 17, 2020 | The Problem: Civilization
Whether by war, famine, resource depletion, socioeconomic failure, or destruction of the natural environment, all empires eventually crumble. What will happen when the collapse of the American empire culminates?
By Max Wilbert
History is a graveyard of civilizations: the Western Chou, the Mayan, the Harappan, the Mesopotamian, the Olmec, the Chacoans, the Hohokam, the Mississippian, the Tiahuanaco, the Mycenean, the Roman, and countless others.
These societies were overrun by disease, or war, or famine. In most cases, they undermined their own ecological foundations—a situation that may sound familiar.
“Collapse,” writes archaeologist and historian Joseph Tainter, “is a recurrent feature of human societies.” But there is an important distinction to be made between societies that create an ideology of growth and an economy of ecological imperialism, and those that do not.
To choose two examples, both the San people of the Kalahari and the various Aboriginal Nations, in what is now Australia, existed in a more or less stable-state for tens of thousands of years. But these were not civilizations, according to the definition I am using. In other words, they were not ecological imperialists, but rather ecological participants.
For the average person living today in Washington D.C., Beijing, or London, the collapse of civilization is hard to fathom. Similarly, the people of ancient cities could not imagine their world crumbling around them—until it did.
With the globalization of capitalism and the neoliberal free-trade economy, industrial civilization now dominates the entire planet.
Goods and services are traded around the world. The average dinner plate contains ingredients grown in five different nations. Rather than living in an empire with discrete boundaries, we live within a global civilization. It feels stable, permanent.
At least, it did until recently. The past month has upended many of our preconceptions. And the reality, of course, is that modern civilization is neither stable nor permanent. This society is destroying the ecological foundation that not only allows it to exist, but supports the fabric of life itself.
People living in rich nations are insulated from the reality of this ecological collapse, since our food no longer comes from the land where we live, but is imported from far away. Technology allows us to ignore the collapse of fish populations, of plankton populations, of topsoil. When the cod fisheries collapse, the industrial fishing corporations can simply begin to fish another far-flung corner of the globe, until that ocean too is devoid of fish. When the soil is lifeless, desiccated, and eroded, industrial farmers can simply apply more chemical fertilizers.
Modern life is based on the use of non-renewable resources, and on the over-exploitation of renewable resources. By definition, this cannot last.
The decline and fall of the American empire has already begun.
Pulitzer Prize-winning journalist Chris Hedges, in his book America: The Farewell Tour, estimates that the Chinese will overtake the United States for world hegemony sometime around 2030. Historian of empire Alfred W. McCoy, in his latest book In the Shadows of the American Century, agrees with Hedges.
McCoy estimates that, no later than 2030, the US dollar will cease to the currency of global trade. This “reserve currency” status makes the US the center of the global economy, and directly provides the US economy with more than $100 billion in “free money” per year. As McCoy writes, “One of the prime benefits of global power is being on the winning side of grand imperial bargain: you get to send the nations of the world bundles of brightly colored paper, whether British pound notes or US Treasury bills, and they happily hand over goods of actual value like automobiles, minerals, or oil.” A fall from reserve currency status will lead, McCoy says, to sustained “rising prices, stagnant wages, and fading international competitiveness” in the United States.
“Will there be a soft landing for America thirty or forty years from now?
Don’t bet on it. The demise of the United States as the preeminent global power could come far more quickly than anyone imagines. Despite the aura of omnipotence empires often project, most are surprisingly fragile, lacking the inherent strength of even a modest nation-state.”
As he reminds us, the Portuguese empire collapsed in a year, the Soviet Union in two years, and Great Britain in seventeen.
The mechanics of the decline and fall of the U.S. American empire have been well documented by others. But what hasn’t been discussed, and what I am interested in exploring here, is the implications of this decline and collapse for revolutionaries.
What will the decline of the American empire mean for those of us fighting for justice?
As revolutionaries, we must be “internationalists.” That is, we must understand and design our strategy in a way that confronts capitalism, civilization, and empire as global systems, not merely national ones. So in this sense, a reorientation of global power is nothing more than that—a shifting of polarity.
We need to be prepared for the international impacts, but also the domestic implications of these shifts. As the axis of global power moves away from Washington and towards “the world island”—Beijing, New Delhi, Moscow—we are seeing a rise in imperial impetuousness, racism, and reaction typified by Trump. Author Richard Powers calls this “a tantrum in the face of a crumbling control fantasy.”
How will the collapse of American empire play out?
Will it (ironically) mirror the decline of the USSR, where Russia now has the most billionaires per capita in the world, an ex-KGB dictator, and an economic system dominated by collaborations between organized crime and corporate capitalism? Will it mirror the more gradual, socially moderated collapse of the UK? Will we see a full-on Children of Men or Elysium-style dystopia?
As society becomes more volatile, those who have best prepared themselves will be the most likely to survive and influence the course of the future. As Vince Emanuele has written, “the next recession will be the icing on the cake. Once the economy collapses and the American Empire is forced to retreat from various parts of the globe, immigrants, Muslims, blacks, and poor whites will be the targets of state and non-state violence. The only way we’ll survive is through community and organizing.”
Vince wrote those words months ago. Now, that recession has now arrived. Times have changed faster than minds have changed.
How should we respond to the current situation?
In crisis lies opportunity. Emergencies clarify things. Bullshit gets less important and truth becomes more self-evident. That is the case now, as well. Reality is imposing itself on us. Any faith in capitalism, in globalization—hell, in the grocery store—has been shattered. The ruling class is weakened. And the lessons are clear.
Globalization is dying. Sure, the system might repair itself and reassemble transnational supply chains. Coronavirus is unlikely to end it all. But the fragility and unreliability of just-in-time industrial food delivery is now obvious. We need to build robust local food systems using sustainable, biodiverse and soil-growing methods.
Organizations already exist that are doing this work. They need funding and support to rapidly scale up. Local governments should be pressured to direct funds towards these projects and make land available for urban and peri-urban gardening, and people should begin volunteer brigades to do the labor.
Food is just the beginning. Globalization isn’t a threat just because it will collapse; it is a threat if it continues as well. Local production of water, clothing, housing, healthcare, and other basic necessities must begin as well. There are cooperative and truly sustainable methods with which this could be done.
Mutual aid is the new rallying cry of the 21st century. There will be no individual survival. Our best hope for creating a better world—and for survival—lies in banding together, building small-scale, localized communities based on human rights and sustainability, pressuring local governments to join—or simply replacing them if they cannot respond—and preparing for the challenges to come.
The longer business as usual continues, the worse off we will be. Governments are already descending into fascism in a vain attempt to be “great again.” Expansions of the surveillance state, police powers, and repression will only deepen as ecological collapse undermines stability.
Each day more forests logged, more carbon in the atmosphere, more species driven extinct. More wealth in the hands of the elite and more poverty, disease, and hopelessness for the people. Remember: the air is cleaner now than you have ever seen it. It can only remain that way if these global supply chains do not re-start.
The sooner we dismantle industrial supply chains, the better off the people and the planet will be. Tim Garrett, a climate scientist at the University of Utah, says that “Only complete economic collapse will prevent runaway global climate change.” He bases this conclusion on climate models he designs. Garrett’s calculations show that industrial civilization is a “heat machine,” and only the total collapse of industrial civilization will permit life on Earth to survive the ongoing mass extinction, and global warming.
To borrow Marxist language, we need to not only seize the means of production away from the ruling class, we need to destroy much of the means of production, because what it produces is ecocide.
Collapse Does Not Have to Be Bad
Some people inaccurately view collapse as a state of total lawlessness; in other words, the disintegration of society. More accurately, collapse refers to a rapid, radical simplification in society, such as the breakdown of “normal” economic, social, and political institutions.
Under this definition, a more or less global collapse of industrial civilization within the next 50 or 100 years—possibly much sooner—is almost a certainty. A NASA-commissioned study in the journal of Ecological Economics found a few years ago that “the system is moving towards an impending collapse” due to destruction of the planet and economic stratification. They write that their model, using conditions “closely reflecting the reality of the world today… find[s] that collapse is difficult to avoid.”
This does not have to be a bad thing. A managed collapse, or reduction in complexity, is the best way to ensure human rights and sustainability moving forward. In the book Deep Green Resistance, the authors advocate for a political movement that could help speed up certain aspects of collapse, while fighting others, to maximize good outcomes. As the book explains:
“Many different mechanisms drive collapse, not all equally desirable. Some [can be] intentionally accelerated and encouraged, while others are slowed or reduced. Energy decline by decreasing consumption of fossil fuels is a mechanism of collapse highly beneficial to the planet and humans, and that mechanism is encouraged. Ecological collapse through habitat destruction and biodiversity crash is also a mechanism of collapse, but is slowed or stopped whenever possible… The collapse of large authoritarian political structures allows small-scale participatory structures. The collapse of global industrial capitalism allows local systems of exchange, cooperation, and mutual aid.”
Uncontrolled collapse is a dire alternative. Even now, local and regional collapses are occurring around the globe. This is especially true in places like Syria, Libya, Pakistan, and Iraq where ecological destruction has combined with war.
But the problems are global. Water shortages, refugee crises, religious extremism, exploding population and consumption, toxification, mass extinction, soil drawdown, desertification, and extreme weather are all driving increased instability. It is emerging first in the poorest countries, but it is spreading fast.
Consider: there may be 1 billion climate refugees by 2050. That’s 30 years from now.
Like revolutions and climate change, collapse is an organic process driven by the interplay of countless human and non-human factors, not a single event.
The world is changing.
We need to plan for tomorrow rather than building strategies purely based on the past. These times call for a two-pronged approach. First, we must build additional resiliency into our communities, relocalizing our food systems and reducing and eliminating reliance on big business and national/state government alike. Second, we must be prepared to take advantage of coming shocks to the economic and political system. We can use these breaks in normality as openings to dismantle oppressive systems of power and the physical infrastructure that is destroying our world.
Max Wilbert is a political organizer and wilderness guide. His essays have been published in Earth Island Journal, Counterpunch, and elsewhere. His second book, Bright Green Lies, is scheduled for release in early 2021.
Featured image by the author.






