by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Mar 31, 2016 | Lobbying, Toxification
Featured Image: Gold miners have been invading Yanomami land for decades. © Fiona Watson/Survival International
Mercury poisoning is devastating tribal peoples across Amazonia, Survival International warned the U.N today.
In a letter to the U.N Special Rapporteur for Health, Survival International highlighted the failure of South American governments to address the contamination.
The unmonitored use of mercury, such as in illegal alluvial gold mining, often takes place on tribal peoples’ lands. Discriminatory attitudes towards tribal peoples mean that little action is taken to control it.
In Peru, 80% of a Nahua community have tested positive for high levels of mercury poisoning. 63% of those affected are children. Symptoms include anemia and renal failure, and one child has already died displaying symptoms consistent with mercury poisoning.
The Peruvian government has known about the mercury contamination since 2014 but has done little to identify the source. It is possible that other tribal peoples in the area have been affected, including uncontacted peoples.
In Brazil, new statistics reveal alarming rates of mercury poisoning amongst the Yanomami and Yekuana. 90% of Indians in one community are severely affected.

Without medical attention, mercury posioning can be lethal. Children and women of child-bearing age are most vulnerable
© Fiona Watson/Survival
Illegal gold miners operate on Yanomami land, polluting the rivers and forest with mercury. Uncontacted Yanomami are particularly in danger as many miners work near where they live.
Indigenous spokesman Reinaldo Rocha Yekuana said: “We are worried about the results of this research. This pollution affects plants, animals, and future generations.”
The Brazilian authorities have known about the mercury contamination since at least the 1980s, yet have failed to put a permanent stop to the illegal gold mining. Little has also been done to treat the affected Indians.
In Venezuela, several tribes including the Yekuana, Yanomami, Piaroa, Hoti and Pemon are also being devastated. 92% of Yekuana women in one region have levels of contamination far exceeding accepted limits.
Survival’s Director, Stephen Corry said: “These governments are sitting on a ticking time bomb. Every week that they fail to act, more and more indigenous peoples are being harmed. When mercury poisoning is identified, the source must be halted immediately and those affected must be treated. The effects will be catastrophic if indigenous peoples’ lands aren’t protected.”

by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Feb 21, 2016 | Lobbying, Rape Culture
By Jhonathan F. Gómez / Upside Down World
All photos from Supreme Court trial by Jhonathan F. Gómez
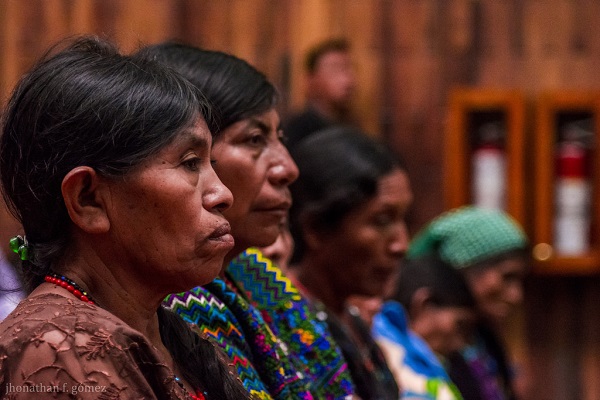
Maya Q’eqchi’ women survivors recently entered the Supreme Court in Guatemala as part of the Sepur Zarco case to demand justice for sexual violence, sexual and domestic slavery, forced disappearances and murder, crimes committed during the internal armed conflict of 1960-1996. On February 1, 2016, Army Lieutenant Colonel Francisco Esteelmer Reyes Girón and military commissioner Heriberto Valdés Asij appeared before the court as another historic trial began.
The Sepur Zarco case is representative of the current state of justice for women in Guatemala. It serves as a reminder that the work towards bringing those responsible for genocide and crimes against humanity is an extensive and challenging process anywhere in the world.
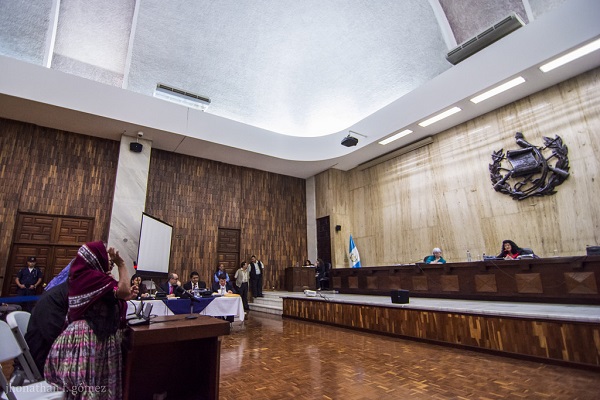

The case goes back to 1982, when the army built a military outpost between the departments of Alta Verapaz and Izabal. Built by forced labor from men of the communities of Panzós and El Estor, it was designated as a resting area for the troops. Late in 1982, the army captured and disappeared Maya Q’eqchi’ men who were fighting for their rights to the land in the area. Consequently, the army took advantage of the widowed women and declared them “alone and available,” forcing them into domestic and sexual slavery. The women were subjected to inhumane conditions, repeatedly raped, gang raped and forced to cook and clean for the army.
These crimes occurred when retired general José Efraín Ríos Mont Ríos Montt was president. Part of his government’s policy was to eliminate the Mayan people by way of displacement, disappearances, murder or forced exile. (Ríos Montt is currently waiting retrial to face justice for his crimes.)

In 1993, the United Nation’s Historical Clarification Commission collected testimonies which allowed for an understanding of what happened. However, a broader understanding of what took place began to surface further in 2000 when the Community Research and Psychosocial Action Team (Equipo de Estudios Comunitarios y Acción Psicosocial, ECAP) conducted psychosocial work with women of the Sepur Zarco region.
The roots of this landmark case are part of a living history which Maya Q’eqchi’ women have been working for years at the community level in the pursuit of justice. In 2009, an independent psychosocial investigation, which led to the publication of a book called Tejidos Que Lleva el Alma (The Weavings that Our Soul Carry) was conducted by ECAP and the National Union of Guatemalan Women (Unión Nacional de Mujeres Guatemaltecas, UNAMG). The book’s aim was to bring the stories of Mayan women survivors into the public consciousness.
In 2010, a symbolic Court of Conscience (Tribunal de Conciencia) against sexual violence for crimes committed during the armed conflict was conducted as a public act by the women survivors. It signaled a breaking of the silence and promoted the sharing of stories with the clear objective that nothing of that nature should ever happen again. The event was organized by various community organizations and with the support of multiple embassies including those from Costa Rica, Spain, Germany Norway and Sweden. Following the symbolic act, the women took a step forward with strategic litigation within the Guatemala justice system.
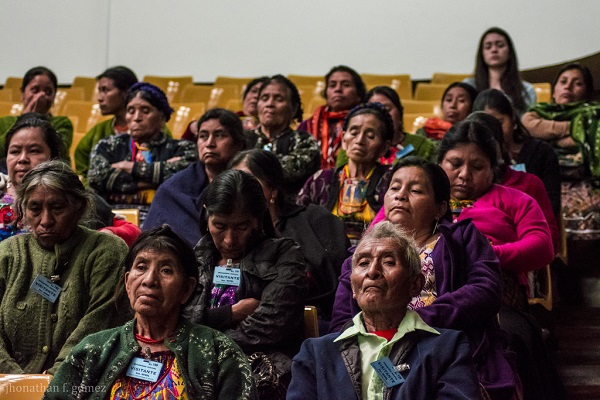

The Breaking the Silence and Impunity Alliance (Alianza Rompiendo el Silencio y la Impunidad), which consists of three grassroots organizations, came together the same year to accompany the legal proceedings of the women survivors. The women survivors have waited over 30 years to see any inclination of justice, and this case can therefore have a large impact in Guatemala and around the world.
The significance of the case cannot be overstated. It is the first time in the world where a national court, in the context of a criminal trial will hear charges against sexual violence during war, as well as the first time a national court will hear charges against sexual and domestic slavery, also in the context of war. The case can set precedents on how sexual violence is judged at a national and international level. Ada I. Valenzuela López from UNAMG states, “In our society, no one else will position sexual violence as an issue in this context. It is a violence which has been silenced for many years. It is almost never at the forefront of any debate in the courts or our society.”
The case stands to move public opinion forward in the struggle for gender justice. It can serve as a step to strengthen trust in a justice system that is capable of hearing the voices of women, and not shaming nor stigmatizing them for speaking out as survivors of sexual violence. It is particularly important for an indigenous population that has been historically discriminated and marginalized to trust in due process. Fifteen women have already testified during the intermediate phase of the case. Many of them have faced threats because of their testimony, yet all of them continue to stand strong because they share a collective understanding of the importance of the trial.
On September 2011, criminal charges were filed in Puerto Barrios, Izabal against military officials Reyes Girón and Valdés Asij. On December, 2011, exhumations were performed at the military outpost. In July of 2012, the prosecutor’s office requested before the Supreme Court that the case be transferred to the High Risk Court. In September of that year, survivors and witnesses presented testimonies before Judge Miguel Ángel Gálvez Aguilar who precedes High Risk Court B.
Arrests were made for Reyes Girón and Valdés Asij in June 14, 2014. On June 23, the first hearing was held and in October, the intermediate phase began which prompted the judge to request a trial date. Immediately after the defense filed a writ of amparo, a legal remedy for the protection of constitutional rights, which was rejected by the Constitutional Court in April of 2015.
In March, April and May of 2015, hearings were suspended because the defense attorneys were not present and because of health problems by Francisco Esteelmer Reyes Girón. Esteelmer Girón had been hospitalized and the defense stated that he was in “poor health.” On June 23, the judge restarted the public debate and the case was sent to the High Risk Court A, comprised by judges Yassmín Barrios, Patricia Bustamante and Gerbi Sical.
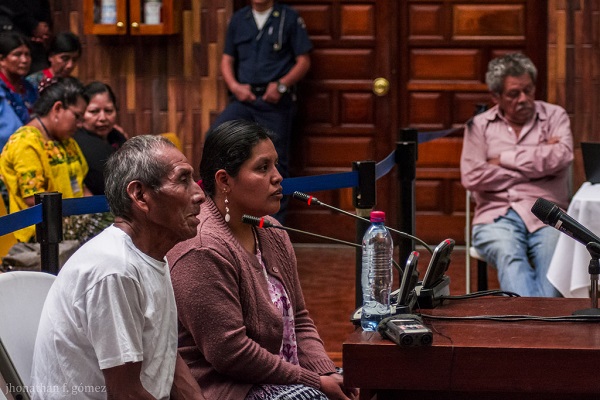

On February 1 of this year, the trial began. It faces many challenges, both in the domain of public opinion, as well as in the trial itself. The defense continues to defame survivors’ organizations, witnesses and uses legal methods to delay the trial. Many organizations have denounced the defense’s methods as a way to evade justice and promote a culture of impunity. Jo-Marie Burt from the Washington Office on Latin America reiterates that “the challenge here is to prove that these types of crimes can be investigated, brought to trial and judged. And to seek to generate mechanism or protocols for the army understand that violence against women cannot be used as an instrument of war, and that women are not war trophies.”
On February 9, the plaintiffs presented over 30 boxes as evidence which contained the remains found in various exhumations which the Forensic Anthropology Foundation of Guatemala (Fundacion de Antropologia Forense de Guatemala, FAFG) conducted. As the contents of the boxes were presented, many people who attended the trial as observers and supporters walked out of the courtroom because of their graphic nature. Evidence of this nature has not always been used at such trials, making it an even more important method of illustrating the magnitude of the crimes.
As a show of support for the Maya Q’eqchi’ women who will be testifying, women from various regions across the country have been present through the trial. As the country watches another historic trial unfold, the survivors are clear on their position. They seek justice and will not rest in peace until justice is served. They want to bring the issue of sexual violence into the public conversation and to show that it is hard for women to speak out against this type of violence. They want their voices to be heard, their truth to be known. They want society to understand that what happened to them was not their fault, and most importantly, that no other woman in Guatemala, or anywhere in the world, experiences what they lived through.
Jhonathan F. Gómez, is a documentary photographer currently living in Guatemala City. He is commitment to documenting the subaltern and diasporic realities of Guatemala as they relate to historic memory, race, class, gender, sexuality, identity and justice.

by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Feb 16, 2016 | Lobbying
Featured image: The Baka have lived sustainably in the central African rainforest for generations as hunter-gatherers
© Selcen Kucukustel/Atlas
By Survival International
Survival International has launched a formal complaint about the activities of the World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF) in Cameroon.
This is the first time a conservation organization has been the subject of a complaint to the OECD (Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development), using a procedure more normally invoked against multinational corporations. Survival International has launched a formal complaint about the activities of the World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF) in Cameroon.
The complaint charges WWF with involvement in violent abuse and land theft against Baka “Pygmies” in Cameroon, carried out by anti-poaching squads which it in part funds and equips.
Before beginning its work in Cameroon, WWF failed to consider what impact it would have on the Baka. As a result, WWF has contributed to serious human rights violations and broken the United Nations Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples. It supports conservation zones on Baka land, to which the Baka are denied access, as well as the anti-poaching squads that have violently abused Baka men and women, and other rainforest tribes, for well over a decade.

Forced out of the forest, many Baka communities complain of a serious decline in their health. Living on the roadside, they are increasingly exposed to malaria and other diseases.
© Survival International
The international conservation organization has thereby violated both OECD human rights guidelines and its own policy on indigenous peoples, and Survival’s legal team has therefore submitted a formal complaint.
Baka have repeatedly testified to Survival about the activities of these anti-poaching squads in the region. In 2015 one Baka man said: “When they came to beat me here in my home, my wife and I were sleeping. They beat me with machetes. They beat my wife with machetes.”
Survival International is calling for a new approach to conservation that respects tribal peoples’ rights. Tribal peoples have been dependent on and managed their environments for millennia. Despite this, big conservation organizations are partnering with industry and tourism and destroying the best conservationists and guardians of the natural world – tribes. They are the environment’s best allies, and should be at the centre of conservation policy.“They are letting the elephants die out in the forest at the same time as they are stopping us from eating,” another Baka man told Survival. Today, the destruction of Baka land through logging, mining and the trafficking of wildlife continues, provoking concern among tribespeople that their land is being destroyed, even as they are denied access to large parts of it in the name of conservation.
Survival’s Director Stephen Corry said today: “WWF knows that the men its supporters fund for conservation work repeatedly abuse, and even torture, the Baka, whose land has been stolen for conservation zones. It hasn’t stopped them, and it treats criticism as something to be countered with yet more public relations. It calls on companies to stick to the same OECD guidelines it routinely violates itself. Both conservation and development have been allowed to trump human rights for decades and millions of people in Africa and Asia have suffered as a result. It’s time the big conservation organizations got their act together. If WWF really can’t stop the guards it funds in Cameroon from attacking Baka, then perhaps it should be asking itself if it has any right to be there at all.”
Survival International is the global movement for tribal peoples’ rights. We help tribal people defend their lives, protect their lands and determine their own futures. Founded in 1969.

by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Jan 21, 2016 | Indigenous Autonomy, Lobbying
NEW REPORT DOCUMENTS CHALLENGES OF DEFENDING INDIGENOUS LAND RIGHTS IN THE PARAGUAYAN CHACO
By Fionuala Cregan / Intercontinental Cry
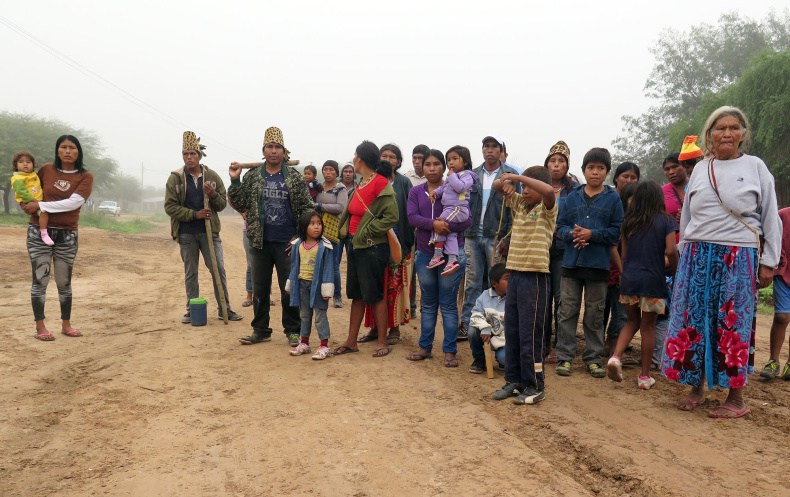
Featured image: Members of the the Ayoreo community of Cuyabia. Photo: Iniciativa Amotocodie
“We don’t care if our struggle involves going to prison or even dying. Our struggle is about justice because the land is ours and our children’s.”
—Alejandro Servín
When Alejandro Servin and five others members of the Enxet Sur indigenous community Kelyenmagategma returned home after two days in the woods hunting and collecting honey, little did they expect to be showered with bullets.
“Three of us were walking ahead when we heard the shots, a bullet just missed me. We ran back into the forest to seek refuge but the employees of the estate managed to catch the youngest member of our group, Francisco, who was 14 years old at the time,” says Servín. “As a result all of us came out. Three hours later a contingent of police arrived, arrested us without a warrant and brought us – in the estate owner’s truck – to the nearest police station.”
Following their arrest, the six indigenous men were transferred to the capital Asuncion where they were held incommunicado for 48 hours without access to a lawyer or contact with their families. They were eventually charged with “theft of cattle” – a crime punishable by up to 10 years in prison under the Paraguayan Constitution. TierraViva – a human rights NGO that provides legal support and advocates for the land rights of indigenous communities in the Chaco region of Paraguay – eventually managed to get the charges dropped due to lack of evidence and the serious legal inconsistencies surrounding the arrest.
It is these as well as an array of other cases documented during more than 20 years of work in the Paraguayan Chaco that lead TierraViva to publish the first ever report on the situation of Human Rights Defenders. The report, released in December of last year, features case studies of illegitimate criminal charges, threats and acts of violence against 19 indigenous leaders and human rights lawyers working on land rights in the Chaco.
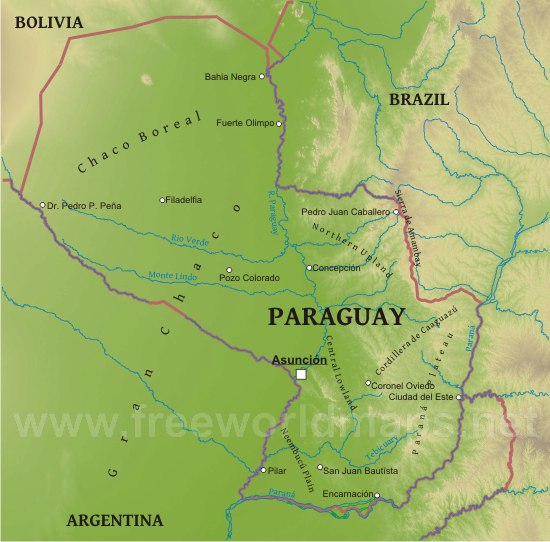
Paraguay is divided into strikingly different eastern and western regions by the Rio Paraguay. The southeastern Paranena region can be generally described as consisting of an area of highlands that slopes toward the Rio Paraguay. The Chaco in the nothwestern region is predominantly lowlands, also inclined toward the Rio Paraguay, that are alternately flooded and parched. Image by freeworldmaps.net.
This arid forested region represents just over 60 percent of Paraguayan territory. It is inhabited by indigenous communities who know it as their ancestral land and private landowners who began to purchase estates from the 1940s onwards, denying the existence of those indigenous communities. This was the case for Kelyenmagategma: the company El Algarrobal SA bought land in 2002 that was inhabited by this Enxet Sur community.
In the past decade, land in the more populated eastern part of the country has become scarce leading to an expansion of the agricultural frontier into the Chaco. The rate of deforestation over the past five years has averaged 500 hectares (equivalent to 500 football fields) per day. In response to this alarming trend, indigenous communities have begun to organize and unite to secure legal title to parts of their ancestral lands to protect what remains of the unique Chaco ecosystem.
Despite the fact that the constitution of Paraguay recognizes the rights of Indigenous Peoples to their ancestral lands, according to Rodrigo Villagra Carron of TierraViva:
“What we see is an undeniable pattern of Government support for the interests of private landowners and the repression of those who defend human rights and national and international legislation related to the rights of Indigenous People.”
This was echoed by Cristina Coronel at the launch of the report in Asuncion in December:
“What this report reveals is [a] world where things are upside down… where indigenous communities and lawyers are defending universal human rights, but instead of protecting them, the police, public prosecutors and other representatives of the government protect the cattle ranchers and agro-industrial companies responsible for illegal deforestation and evictions of Indigenous People from their ancestral lands.”
This can clearly be seen in the case of Unine Cutamurajna from the Ayoreo community of Cuyabia who denounced illegal deforestation by Brandenstein Agro-Forest Investment (BAFI). Cuyabia acquired legal title to 25,000 hectares of land in 1996; but since then it is estimated the community has lost at least 6000 hectares due to land grabs by cattle ranchers. On one occasion, in 2015, the community hijacked a bulldozer that had been clearing vast tracts of forest on land belonging to them. Instead of investigating the illegal actions of BAFI, the Government of Paraguay sent a contingent of police to recover the bulldozer.he community has subsequently suffered threats from heavily armed private security guards working for the company.
“The Government sides with the cattle ranchers because they have money. We Indigenous People don’t have money,” says Unine. “But we will keep defending our land, it doesn’t matter if they continue to threaten us. We will not give up one more single piece of our ancestral land.”
Other cases in the report include:
- Government employee Irma Torales who, while working at the Public Registrar’s Office, refused to become involved in a case of embezzlement of funds destined for the purchase of land for indigenous communities. Her actions lead to the arrest and imprisonment of the former Director of the National Indigenous Institute of Paraguay. Despite this, Irma was subsequently demoted to a more junior role with a significant reduction in her salary.
- Human Rights Lawyer and Director of TierraViva Julia Cabello who faced a possible one-year suspension from practicing law or disqualification from the Paraguay Bar Association for a criticism she made of a Supreme Court Decision to review the constitutionality of a law allowing the return of more than 14,404 hectares of traditional land to the Sawhoyamaxa indigenous community.
TierraViva intends to use the report to carry out continued advocacy and raise awareness of the grave situation of human rights defenders in the Chaco.
According to Villagra Carron:
“This report is a condemnation of the structural inequality in Paraguay and a call to action. The cases documented in it are by no means exhaustive but just a few examples of what is happening in a broader context of rights deprivation. We urgently need to bring this situation and the government’s complicity and/or role in perpetuating it to public attention or the situation risks becoming even more dangerous, serious and unjust.”
The report received support from the Gran Chaco Ecumenical Small Projects Fund which works to strengthen the capacity of civil society organizations, groups and communities in the South American Chaco to transform the conditions of poverty and inequality and promote human rights.
To see the full report in Spanish click here.