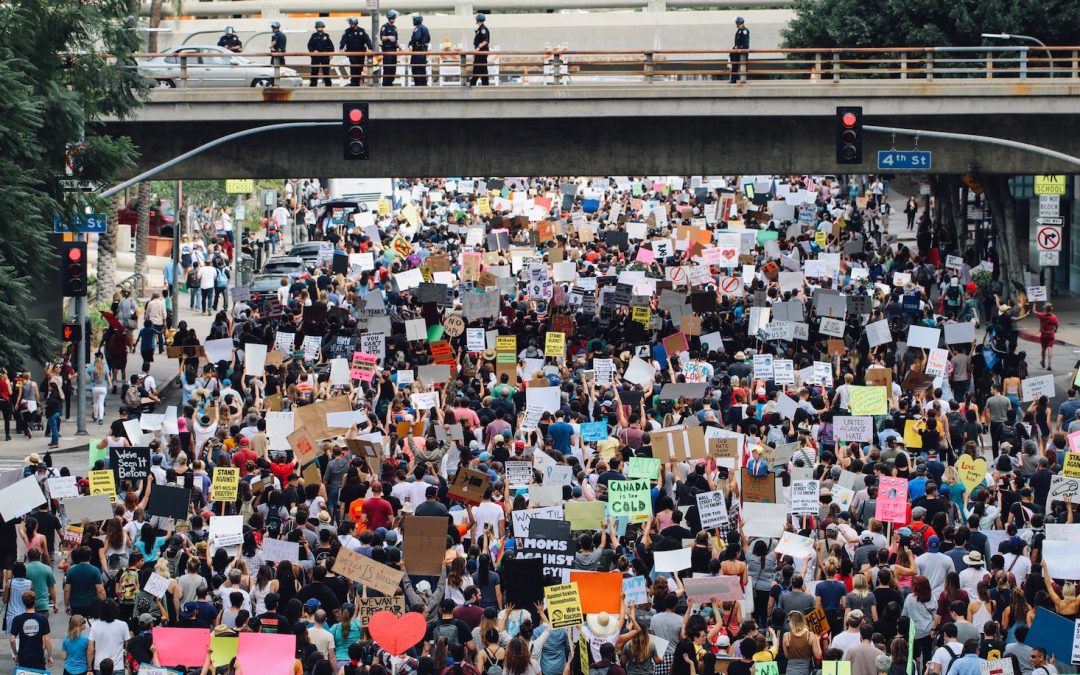

by DGR News Service | Sep 16, 2022 | ACTION, Protests & Symbolic Acts
Editor’s Note: When many people think of political engagement, they think of protests. However, protests are merely one tactic among thousands. Like all tactics, protests can be very effective in contributing to a broader strategy, or they can backfire. Context matters. Protest must play a role in a larger strategic plan if it is to help effect change.
At Deep Green Resistance, we endorse raising political awareness of the destructive nature of civilization and organizing to stop the destruction of our planet. We also believe that aboveground activists need to push for acceptance and normalization of more militant and radical tactics, where appropriate.
This article presents one view on protest, which is not necessarily ours. Nonetheless, this is useful material. For more information on strategy and tactics, we highly recommend reading Chapters 12, 13, and 14 in the book Deep Green Resistance: Strategy to Save the Planet (buy the book or read a free online version here).
By Activist Handbook
Protest marches are a common and accessible way of getting your voice heard and bringing attention to your cause.
In this guide, you will learn how to organise a protest or demonstration. This article for activists explains step by step how to organise an action to draw attention to your cause. Following are 10 suggested steps to organizing an effective protest and some suggestions for taking it to the next level. There are plenty of opinions about how to host a successful and inclusive protest so feel free to read critically and adapt these ideas freely to suit your goals.
If you are new to protesting, we recommend you to read the following articles first:
This guide originally appeared on the Activist Handbook website, a Wikipedia-style collaborative manual created by activists, for activists. The Activist handbook have combined various resources into their wiki. The formatting of the guide has been slightly tweaked by The Commons such as adding images and quotes.
A successful demonstration – one that accomplishes its goals either immediately or over the long term, and that runs the way organizers envisioned – depends upon clarity of purpose, getting people there, getting the message to those who need to hear it, and leaving a sense of success and support for the issue with your target audience, your constituents, the public, and the media.
If you consider beforehand whether a demonstration is the right vehicle for you to get your point across, plan it carefully, carry it out well, and follow up diligently, then you should be able to stage a successful public demonstration.
If your demonstration is to go smoothly and to accomplish its purpose, you’ll need to organize it carefully. There are really four major bases to cover in putting together a public demonstration:
- Planning, planning, planning
- Lead time
- Communication
- Follow-up
If there is a single most important piece to organizing a demonstration, it’s planning it completely beforehand. The demonstration must have a coordinator and a group of organizers who work together before, during, and after the event to plan and carry it out. They need to decide what the demonstration will be like, and to anticipate potential problems and plan for them as well.
As you begin to organize your protest, the more like-minded friends and community members you have at your side, the better! Reach out and ask if they want to help you organize. If your protest issue does not directly impact you, be sure that you are intentionally building relationships with those in your community who are, centring their voices and experiences, and listening to their guidance. It is best if you can co-create your team and action together. Lastly, seek out local or regional organizations that work on your issue and invite them to organize with you. (You may also learn a thing or two from them!)
In this section, we briefly discuss how to define your strategy. But we also have a full chapter about how to define your strategy.
Answer these questions:
- Goals: What do you want to achieve?
- Target: Who has the power to make that happen?
- Action: What kind of action would make them listen to you (tactic)? When and where should you organise this action to make the most impact?
What is (are) the exact goal(s) of the demonstration? It’s important to decide whether you’re advocating for or supporting a position, protesting something, or planning a specific action. Your purpose will help to determine the tone and shape of the demonstration. If advocacy is your goal, the demonstration might be upbeat, singing the praises of whatever you’re advocating for. If your purpose is protest, or righting a wrong, then its tone will be different. Tone is important, because what you accomplish might depend on how the demonstration is viewed. If your demonstration leans too much toward entertainment and feel-good sentiment, it may not be taken seriously. If it’s frightening, people may not listen to its message.
Ask yourselves what you are trying to achieve through this advocacy lane. Are you trying to build awareness? Do you aim to build a larger coalition to continue work on your issue? Are you trying to be seen and heard by an elected official or influential figure? Be clear with yourself and others about the objectives behind your actions. This will help you develop the best strategy, and later reflect on elements that can be improved.
With your goals in mind, try to imagine the most effective protest to achieve those goals and focus on making that protest happen. Ask yourselves: when and where will you hold the protest and why? What type of protest is required to achieve your goal? The most common modes of protest are marches and rallies. But protests can take many forms: sit-ins, walk-outs, vigils, and more sophisticated efforts like encampments and choreographed or theatrical expressions.
Demonstrations may be meant to serve one or more different goals, depending upon the timing of the demonstration, the issues involved, who’s doing the organizing, and what else has gone before. Setting out your goal clearly is important, because it will often dictate what form the demonstration should take, at whom it should be directed, and other crucial elements. Common goals for demonstrations include…
- Advocacy: To urge legislators or the public to look favorably on a bill, adopt a particular idea or policy or service, or pay attention to the needs of a particular group of people (welfare recipients or people with disabilities, for instance).
- Support: To express agreement or solidarity with a person or group, with an idea or policy, or with a particular issue. For example, a group of organizations offering different services might hold a community demonstration to support the proposed establishment of more and better services for the homeless in the community.
- Protest: To speak against some injustice, event, public figure, potential occurrence, etc. A group might demonstrate against the possible establishment of a hazardous waste treatment plant in their community, or to protest the treatment of community residents by police.
- Counter-demonstration: To respond to a demonstration or other public event already scheduled by another, antagonistic organization. A civil rights group might organize a demonstration to balance one by the Ku Klux Klan, for instance; or a group of demonstrators might organize to counter a rally for a politician whose views they disagree with.
- Public Relations: To advertise or put in a good light an event, issue, organization, segment of the population, etc.
- Action: To actually accomplish a specific substantive purpose, prevent or change a particular event, or to influence the course of events. Such actions might include workers on a picket line blocking replacement workers’ access to a factory, or peace activists chaining themselves to the gates of a military base; it can also include demonstration participants breaking up into constituent groups to visit their legislators.
- A combination of any or all of the above.
In reality, most demonstrations serve more than one purpose. Regardless of their other goals, most organizers seek media coverage for the demonstration, for instance, in order to draw attention to their cause. Most demonstrations either advocate for and support, or protest against, something. The difference is in the emphasis, which may have a great effect on the form and timing of the demonstration.

Decide who you’re trying to reach with the demonstration’s message, and who you want to attend. Contact other organizations, coalitions, etc. long before and get them to endorse (and attend) the demonstration. The time, place, and program should be geared to the desired audience.
- Legislators or other elected officials: The demonstration should be where they are — City Hall, the State House–on a day when they’re in session. Elected officials pay attention to voters. This is a great situation for members of the target population, especially those from key legislators’ districts, to tell their stories, and for advocates to use their knowledge of statistics to underline the magnitude of the issue and the size of the constituency affected by it.
- General public: If you’re aiming your message at the general public, then you might want a very large demonstration, or one that’s particularly unusual or interesting, staged in a public place at a busy time, so that it will attract both onlookers and media attention. It’s even better if there’s a draw, in the form of entertainment and/or celebrities. And the demonstration should be advertised publicly, through flyers and posters in neighborhoods, public service announcements on radio and TV, clubs and churches, etc.
- Target population: If you’re trying to publicize an initiative with those you hope will take advantage of it, it should be in their neighborhood, and in their language as well. It might help if children and families are encouraged to come, and if familiar figures from the target group itself are part of the program. Presentations should be aimed at providing practical information and helping people understand the issue and how it relates to them.
Decide where the demonstration will be. Your decision will depend on timing, on how large a space you need (How many people do you expect or hope for?), on whether your demonstration is a reaction to something specific in a specific place, and on who you want to reach with your message. However, there are some important general questions you need to answer in choosing a place. Is it available for the time you need it? Do you need, and can you get, a permit to use it? Will it cost you anything, and can you afford it? Is it accessible to those with disabilities? The answers to these questions will help you determine where to hold the demonstration.
Decide on a specific day, date and time. Sometimes, the day, date, and time are determined for you: a counter-demonstration, for example, will happen at the same time as the demonstration it is meant to counter; a particular vote in the legislature will take place on a particular day. But in general, these elements are determined by three things:
- The availability of the people you want to reach (A rally at the State House on Saturday won’t attract many legislators, nor will the ‘solidarity with Working Mothers’ demonstration attract many working mothers if it’s on Tuesday at 2:00 PM… when most of them are working.)
- The weather (You might not want to hold an outdoor demonstration in Minnesota in January… or in Florida in July). Do you need a rain or snow date?
- Conflicts with other events (You don’t want to compete with the free Rolling Stones concert in Central Park).
Learn more about this in our strategies chapter.
In this section, we briefly discuss different tactics you can use. Make sure to also read our chapter with a list of tactics for protests.
Plan your program
What you’re actually going to do at the demonstration also depends upon what you want to accomplish and who your audience is. There needs to be a clear structure for what will happen, and everything in the program should be geared directly to the desired results of the demonstration. Block out the schedule to the minute, and let participants know well beforehand how long they have in the program.
Some possibilities for programs or program elements:
- Speeches may convince some people and bore others, although some speakers and speeches (Martin Luther King’s “I Have a Dream” comes immediately to mind) are so powerful that they electrify anyone hearing them. Celebrity speakers may draw people and attention to the demonstration and to your issue. Speeches may be meant to convey information, convert the unconvinced, or simply fire up the crowd and supporters. Members of a target population (people who’ve learned to read as adults, AIDS sufferers, etc.) may be the most eloquent spokespersons for their issue.
- Marches or other movement of demonstrators can serve to show the extent of support for your issue, and can dramatize–by the route chosen–where a problem is located, and who should be involved in a solution. They can also help to build group spirit, to expose large numbers of people to the existence of the issue, and to attract media attention.
- Entertainment. Music may energize people, address their emotions, and help to develop group spirit. It’s usually geared to the subject of the rally, with songs written for the occasion, for instance. Theater can be used to ridicule ideas being protested, as was done very effectively for years by such groups as the San Francisco Mime Troupe. If the entertainment is particularly good or includes celebrity performers, it’s almost sure to attract media and bystanders.
- A symbolic activity, such as each person lighting a candle, group song or chanting of slogans, the display of a picture or document, prayer, etc. can be a powerful way to communicate a message, solidify a group, and gain public attention. It can also be seen as nothing more than an attention-grabbing device. This kind of activity has to make sense for your particular issue and demonstration.
- Picketing may be used simply to make a point, or to discourage people from entering or patronizing a particular building or space because of their sympathy with the picketers’ issue. In either case, it requires a high degree of organization, but it creates a vivid picture in people’s minds, and makes a strong point. It can also make your organization seem more militant than it is, or than you want it to be perceived.
- Civil actions or civil disobedience can range from legal actions designed to accomplish a specific purpose (large numbers of people witnessing an event that the perpetrators would have preferred to keep quiet, such as the destruction of a neighborhood landmark) to a few people engaging in a symbolic action designed to get them arrested or otherwise challenged (chaining themselves to the gate of a government building, refusing publicly to pay taxes, etc.) to mass actions like civil rights marches or the blocking of troop movements in Tien An Men Square. Demonstrators taking part in civil disobedience must be willing to be arrested and face punishment, and organizers must train them beforehand to respond appropriately to the police and to the whole arrest procedure. Organizers must also be aware of the impact of these actions on how their issue is perceived by the public.
Read more in our tactics chapter.

Work out the logistics. Logistics are the nuts and bolts of any event, the who and how and when of what gets done. Each demonstration presents its own logistical questions, but some important ones are:
- Do you need, how will you pay for, who will be in charge of, and where will you get… A sound system that works? Toilets? Medical facilities and personnel in case of emergency? Parking? Trash disposal? Signs or banners? A way of getting speakers or performers to and from the demonstration and the platform?
- How do people in general get to and from the demonstration, and in and out of the space?
- How do they get home?
- Is there a need for crowd control (i.e. a potential for violence, or for horrendous traffic problems), before during, and/or after the demonstration?
- Is clean-up needed? Who cleans up, and how?
- What are the plans for meeting with the media before, during and after the event?
- Are there plans for post-demonstration activities (constituent meetings with legislators, on-site vaccination of young children, registration for literacy classes, etc.)? If so, how will all this be handled?
Try to think of every possible thing that can go wrong that you haven’t already addressed, and figure out what to do about it. Where are you going to get toilets if the ones you ordered aren’t delivered? What if there’s a counter-demonstration? What if only a few people show up? What if the media doesn’t show, or leaves too soon?
Anything you can anticipate and plan for is another crisis you don’t have to worry about: you’ll know what to do.

Be ready and have a contingency plan. If your local police tend toward clearing protests quickly or even violence, you will want to share tips about self-protection against, for example, tear gas or pepper spray. If you are expecting extreme hot or cold weather, provide suggestions for staying safe. During the protest, everyone’s safety should be your number one priority. Ask folks how they’re feeling.
Decide on what specific things you’d like to actually happen — and not happen — at the demonstration. How do people get to the space where the demonstration will be held? How easily can they leave? How do you want them to behave while they’re there? Will there be some sort of action, and will it possibly lead to arrest or other confrontation with the authorities? How will you handle that? A crowd can be kept happy with food and entertainment, or angered by aggressive speechmaking: it’s up to the organizers to think through what they want.
It’s important to confer with the authorities beforehand about use of space, to obtain the proper permits, and to work out with police and other officials how things will be handled, so that there are no misunderstandings. Make sure that those who are likely to attend the demonstration know what to expect and what you expect of them. If people understand that violence is unacceptable, or that it’s important that everyone follow a certain route, they’re more likely to behave accordingly.
So, you’ve decided that you have some good reasons for using a public demonstration as part of your initiative. We’ve already seen that timing is important. Later, we’ll discuss how much time you might need to plan your demonstration: that’s a major concern. But assuming that that’s taken care of, when will a demonstration be most effective? If you can, it makes the most sense to schedule it to coincide with an event or time that will help draw attention to your cause, or that needs to be brought to public attention. Some possibilities include…
- Just before or during a major event that the demonstration can influence. A local, state, or national vote on a bill affecting your issue, an election, or a campaign for the establishment of a local service might all provide appropriate times to stage a public demonstration.
- The local visit of a political or controversial figure or group. The visitor might be seen as an ally, an antagonist, or as someone who could be influenced by a demonstration. The character of the demonstration itself would of course depend on how you view the person or group.
- A demonstration by another group opposed to your cause or point of view. In this circumstance, you might plan your counter-demonstration to begin before the other group’s, thus drawing media attention away from their message and to yours. Scheduling your major speaker or event toward the middle of your demonstration may also serve to hold the media there during the start of the other demonstration.
- A national day honoring or commemorating your issue. May 1st, Labor Day in every country but the United States, has traditionally been the occasion for marches of workers and speeches by labor advocates in much of the world. National Literacy Day, in September, often sees upbeat public demonstrations by literacy programs and advocates.
- As part of a funding drive for your organization or issue. In the late 1980’s, when public human service budgets were being cut and money was scarce, a county human service coalition kicked off a local fundraising effort with a well-staged piece of street theater about some of the things that were actually being funded instead of human services. The cleverness and timeliness of the performance attracted statewide attention, and enhanced local fundraising efforts.
- As part of a publicity campaign for your organization or issue. A group trying to immunize all toddlers in the area might hold a public demonstration emphasizing the importance of immunization, and trying to make the whole process look like non -threatening fun for kids. Such an event could include clowns, facepainting, people in hypodermic costumes, etc., as well as information for parents on where, when, and how to get shots for their children.
Learn what local authorities require for public demonstrations in your community. You can often find specific permit requirements and guidelines on your local government’s website or by calling your town hall. Do you need a permit and what are its requirements? Are there restrictions such as amplified sound restrictions or fines for littering? When talking to the authorities, don’t shy from being clear about your needs, for example, to clear a road of traffic or provide a portable toilet.
You be the judge if you should adhere to the terms of the local requirements; violating those terms could invite confrontation, which your invitees may not be interested in or prepared for at all. Make it clear to the authorities, and your supporters, that safety is a priority. Ask the authorities to maintain contact with your group during the protest, and tell them how to do so.
Learn more in our legal rights chapter.
Decide on how you’ll get people to come. To some extent, this depends on how much time and money you have to publicize the event, and how many people you want to attract. You have to reach people through methods they’ll pay attention to, in language they’re comfortable with. If possible, it’s best to get the message out many times in different ways, and to reach as many people as possible personally. Methods might include flyers, posters, phone calls, mailings, ads in newspapers and local church and organizational newsletters, public service announcements on local radio and TV, announcements in churches, clubs, and agencies, etc.
Assuming your objective is to have the largest turnout possible, you will reach more people by diversifying your outreach. You may want a versatile graphic to draw people’s eyes to your invitations. Get the word out through every social media channel that will reach your intended audience. (One of the benefits of working with an established group is they can broaden your social media reach.) Put up posters where people can see them like public bulletin boards and lamp posts. Ask shops if you can put posters up in their windows. But nothing beats face-to-face outreach. Time permitting, visiting neighbors and personally inviting them with fliers in hand is a highly effective way of growing a protest.
Invite local television stations, newspapers, radio stations, and bloggers to your protest. Tell them what’s special about your protest and give them the most precise information about the protest you can. Encourage your invitees to post videos and photos to social media and give them a hashtag.

Learn more in our communication chapter.
Every stage of protest planning is an opportunity to build solidarity and community. Keep an intentional lens on inclusion and intersection. Invite a wider circle of friends over for planning meetings. Sign-making parties are a great way to build relationships in advance of your protest.
You don’t want your invitees or spoilers to ruin your plans by damaging property or starting fights. Designate peace marshals within your team. A peace marshal’s job is to keep an eye out for anyone who is creating risks for your protests such as provoking police, vandalizing, etc. If tension rises, your peace marshals will step in and deescalate. You may also want to invite your local Lawyers Guild or other independent observers if you are concerned about keeping the peace or the police response.
Leaving a mess is not a good look for your team or your cause. Make sure people know your expectations up front about discarding signs and literature. Set an example by picking up litter from your group. When you see someone littering, point them to the nearest garbage can. You want to learn from your experiences so you do an even better job organizing your next protest. After your team has had some time to reflect (but not too long after your protest) get your organizing team together to discuss how the protest went. Review how you did with each of the ten steps. Document the conversation for the next time you plan a protest. And finally, be proud of what you have accomplished; you organized your first protest.
Protest is, in its own way, storytelling. We use our bodies, our words, our art, and our sounds both to tell the truth about the pain that we endure and to demand the justice that we know is possible. It is meant to build and to force a response. – DeRay Mckesson, Civil rights activist
If possible, it is best to allow more than enough time in planning a demonstration to handle all the details and pull everything together. Celebrities or public figures of any kind generally are booked far ahead, and unless (or even if) this is their pet project, they’re not going to show up without adequate advance knowledge (at least several months, not several weeks). Sometimes acquiring, or even finding, a space to use can take longer than you’d think possible. Planning how to handle large numbers of people is difficult, and carrying out your planning is even more so (the sound system you need may not be available from the first or second company you talk to; and what do you do when it doesn’t appear on the agreed-upon day?)
It’s vital to build extra time into your planning if you can. More than enough lead time is usually measured in months, and there’s no such thing as too much.
Sometimes, however, a demonstration has to be planned in days, or even hours. The key to planning something successful under any circumstances is to be honest with yourself. What can you really do effectively in the time you have? Don’t overreach, and there’s a good chance you’ll end up with a demonstration that may be modest, but accomplishes your goals. Aim for the moon without adequate time to get there, and you’re likely to miss entirely.
Also make sure to check out our chapter on communication for more details.
Design an effective general communication system. The most important thing you can do when you begin planning a demonstration is, if you don’t already have one, to set up an efficient and usable communication system. This system should be available not only for demonstrations and emergencies, but for general use as well among people directly involved in and connected to your issue.
Systems like this prove their worth when there is a need to quickly sway the opinion of legislators. One person, emailing or calling a number of organizations, can, in a matter of hours, generate hundreds, or even thousands, of phone calls and letters to government offices. Fifty letters or calls on an issue is generally considered a large number by legislative staffs. If they get hundreds, that’s a groundswell; a thousand or more is a landslide.
The ideal communication system has an individual or small committee as a central coordinator. In the best of all possible worlds, the coordinator would use email, which can reach large numbers of people with a single transmission, for fast and efficient communication. If email isn’t available to everyone in the loop, the next best possibility is a phone tree that the coordinator can activate by calling a small number of reliable individuals who then call a number of others who then call others, until everyone on the list has gotten the message. These systems aren’t perfect, but they greatly increase the chances that you’ll be able to quickly reach everyone you need to. The coordinator should also maintain an up-to-date, computer -based if possible, mailing list from which to do mailings of general interest or importance.
Develop a plan for publicizing the demonstration
The coordinator would be the point person in informing supporters, the desired audience, and the public about the demonstration. Depending upon whom you were trying to reach, the coordinator could make up and assign the distribution of flyers; send out one or more large mailings from the computer list of supporters and relevant organizations; prepare and distribute press releases, news stories, and/or print, radio, and TV ads; post to an email list; activate the phone tree; and facilitate anything else necessary to get the word out. The coordinator doesn’t have to do everything himself; but it’s important that there be one place where the publicity and communication buck stops.
Orchestrate media coverage of the event
Again, one person–probably either the communications coordinator or an organizer of the demonstration–should oversee media coverage. One good way to guarantee accurate coverage before the event is to write your own stories about it, either as press releases, or, if you have a good relationship with media representatives, in some other form.
If you haven’t already done so, you should begin to cultivate a long-term relationship with the media, so that when you need them–as you do now–they’ll respond. Be generous with your time and information when they ask for it, and volunteer information when you can. Position yourself as the “expert” on your particular issue, so that you’re the person they’ll turn to when they want information about it. Try to establish personal relationships with reporters from different media; they’re more likely to be sympathetic to your cause if they know your organization and have some direct contact with the issue.
Make sure that reporters and media outlets know exactly when and where the demonstration will be, and what they’re likely to find there. Make organizers, speakers, celebrities, members of the target population, etc. available for comment before, during, and after the event. Think about photo and TV opportunities: if you want pictures or TV coverage, the demonstration has to provide the visual images. Try to make it as easy as possible for media representatives to do their jobs: find them places from which they can see, hear, film, etc. easily; assign a person (perhaps the same person who has coordinated media coverage) to take care of their needs; introduce them to the appropriate people; help them get around. If you want good coverage, then it’s up to you to make the event as media-friendly as possible.
Ensure good communication before, during, and after the demonstration
It is vital that organizers be able to communicate with one another, with program participants, and with the crowd while the event is forming, going on, and winding down, especially if it’s being held in a large outdoor area. Explaining changes in program, relaying instructions about traffic flow or trash pickup, and contacting individuals in emergencies are only some of the reasons why good communication is essential. Organizers and other key individuals should have cell phones, pagers, or some other means of quick communication with them. It might also make sense, depending on the situation, to appoint a group of “runners,” people who can carry messages and run errands while the event is going on. Good communication could mean the difference between a successful demonstration and a disaster.
Immediate follow-up
Your job isn’t done when the demonstration is over.
There’s making sure the demonstration breaks up in an orderly way, that everything’s cleaned up, that people are able to get home. There may be other events scheduled right after the demonstration (visiting legislators, signing up for immunizations, etc.) It might be important to make sure that media representatives get to talk to celebrity participants, members of the target population, and/or demonstration organizers. And there may be organizational or legal issues — paying suppliers or government permit offices, for instance — that have to be taken care of before you can call it a day.
Long-term follow-up
The demonstration itself is only a first step toward something. If you don’t continue the work you’ve started, you might as well not have bothered. First, it’s important to go over the demonstration with organizers and others who were involved, to assess how things went, and to evaluate the event as a whole. Questions that need to be answered include…
- Was the demonstration successful (i.e. did it come off the way you intended, and did it accomplish what you wanted it to)?
It’s important to remember that a demonstration is usually only one piece of a larger effort to publicize and/or affect policy on your issue. The law might not change right away; the service might not become available instantly. A successful demonstration may not immediately show obvious results, but it may help to build a foundation for what will happen later.
If it runs smoothly and seems to have strong public support, then your organization might be seen as a force that the powers that be need to deal with. You might find yourself invited to meetings you couldn’t get into before, and asked for advice by policy makers who formerly ignored you. That’s success, too. You may need to wait a while before you can determine exactly how successful your demonstration was.
- What went well, and what didn’t? How could you do things better in the future?
- Who did their jobs well, or particularly well? (You might want to give them more responsibility next time.)
- Was a demonstration the right way to get your point across? Should you have used some other method instead?
- Would you do it again, and what would you change?
The next step in long-term follow-up is to build on the success and momentum of the demonstration. There are a number of possible ways to do this:
- Follow up with the intended audience of the demonstration (legislators, for example) by continuing to bring up the issue, and referring to the demonstration as evidence of support for it.
- Follow up with your own constituents (target population, supporters, etc.), using the energy generated by the demonstration to get them involved in keeping the issue before the public.
- Publicize your success. Use your contacts with the media to publicize how big and powerful your demonstration was.
- Try to get the media to do a series of stories on the issue. If there are celebrities who are willing, they might also be involved in this effort.
- Organize other events to address the issue.
- Institutionalize the demonstration. Many cities have walks to raise money for hunger, AIDS, or other causes that started out as demonstrations. Now they happen every year, attract thousands of walkers and tens of thousands of sponsors, raise huge amounts of money, and bring the issue to the public in an unavoidable way.
- Keep up the Momentum
Your protest is likely to draw many new folks who want to get further involved in the cause. Use the protest to make sure they know what the next action is. Hand out flyers for your next general meeting or for another protest. If you don’t have an immediate next step for them, get your clipboards out and collect email addresses with the promise of further action.
- Get Creative
Find a time or location that helps bolster your message. For example, a marijuana decriminalization march could be held at 4:20pm or a rally against police militarization could be held with armored vehicles behind the speakers. Be theatrical if you want; great photos spread faster and help get your message out. Puppets, themed costumes, or other artistic expressions help draw attention. Some organizations, like PETA, are known for their powerful protest theater, soaking themselves in fake animal blood. Even with a small attendance, their protests garner international attention.
- Go Deep on Your Strategy
You may be trying to influence a politician or other influential figure. If this figure has not responded to protest in the past, consider another approach. Everyone with power draws that power from someone else (donors, for example). You may want to consider protesting the origin of their power, for example, protesting a politician’s top donor or a university president’s allies on the board of directors.
- Don’t Be Afraid of Disruption
While many people equate disruption with violence or beyond the scope of constitutionality, disrupting the daily rhythms of life—especially for corporate or government officials—is precisely what the founding fathers had in mind: colonial-era riots, the burning of effigies, and dumping crates of tea in the bay. Disruption gets people talking about your protest and draws more media attention. Disruptive protest is more likely to lead to arrests. Be sure all of your invitees know what they are signing up for and that you research best practices incivil disobedience and disseminate that information to all participants.
- Be Spontaneous
If a protest is not pre-planned or expected by authorities, it can draw urgency to your cause and, as it grows, can give a feeling of momentum. Of course, to draw a crowd and the press to a spontaneous protest, more work will have to be done in a shorter amount of time. An inspirational (and effective) example of spontaneous protests were the large, widespread airport protests after President Trump announced his “muslim ban”. Many municipalities waive permit requirements if a protest forms in response to a recent or ongoing event but it’s worth checking with your local officials so you don’t put your invitees at risk of arrest.
Potential Impact
Reach
Whether or not your protest march will be covered in local/national/international news media depends on the number of people participating and the novelty of the cause that you are advocating. If it is something for which there already have been a lot of protests, you will need to step up your game to make the march interesting enough to cover.

Photograph by Peter Cahill
Since a march is a moving protest, a lot of bystanders may see your action, but it is harder to start one-on-one conversations with them. Take pictures, record videos and livestream during the march, so you can reach additional people via social media.
Engagement
A protest march is a relatively accessible action format, so it is a good way to get people who have never protested before involved. Make sure you have clear follow up actions though, so that participants of the march will take up more active roles within your movement after the march.
People who see your action as bystanders or hear about in in news media might also get involved. Note this is a very small percentage of the total number of people reached. You can improve this by handing out leaflets during the march and making it easy for people to find your website and get involved.
Disruptiveness
A protest march is usually not very disruptive. You are usually only taking up some space for a few hours. And because it is a moving protest, traffic will be able to continue their travels as you move away, though with a large number of participants this may take a while.
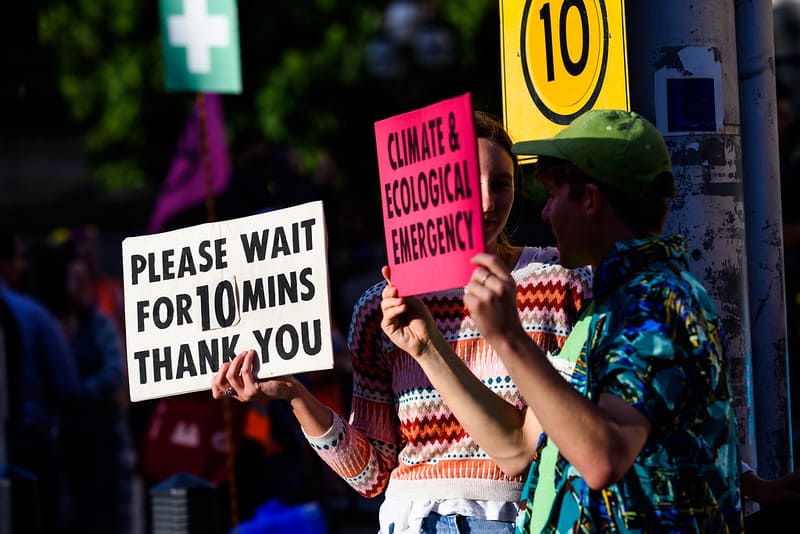

You are temporarily taking up a certain physical space, depending on the number of people participating and duration of the march and you are creating disturbance with noise. These are some ways to make it more disruptive: march on a frequent basis, march a longer distance, make more noise (for example, by asking people to bring pots and pans), or engage in cultural disruption (for example, march naked).
Because a protest march is not very disruptive generally speaking, it is unlikely that decision makers will feel forced to respond to your demands based on the disruption alone (though they may feel forced through public pressure as the result of your reach in news media). Being a relatively undisruptive tactic, this also means that the authorities are less likely to try to stop you by means of police force.
Creativity
The tactic of marching to draw attention to a certain cause is very commonly used. Unless you add something special, a protest march is not very creative. This means that news media will be less interested, because it misses the aspect of novelty. These are some ways to use creativity to make a march more interesting: wear special clothing, bring art objects (for example a brightly painted boat or paper mâché skeletons) or have a group of people play theatre.
About the Author
Activist Handbook is a Wikipedia-like site for everyone to exchange knowledge and experiences about activism. It’s written by activists for activists. Visit the website to contribute to their wiki and learn more about other fundraising means and other topics including:
- ⏳Theory of change: Here we explain what activism is. We argue anyone can be an activist. Even though you might not refer to yourself as an ‘activist’, we believe this handbook can be useful for anyone who would like to achieve societal change.
- ⚡️ Organising: We believe that change-makers are more successful together. Learn how to set up an inclusive movement, how to make decisions democratically and how to mobilise people and keep them engaged.
- 💡 Campaign strategy: Social change can be achieved in various ways. Here we showcase different types of strategies depending on local political and social contexts.
- 📣 Action tactics: Guides on how to: protests, creative actions, digital activism, storytelling and more
Explore Further
Featured image via Unsplash.
Featured

by DGR News Service | Jul 11, 2022 | ANALYSIS, Biodiversity & Habitat Destruction
Editor’s note: The dominant global culture (“industrial civilization”) is built on resource extraction and forced conversion of habitat to exclusive human use, and this has serious consequences.
Both global warming and the ongoing mass extermination of life on the planet (which has been deemed “the sixth mass extinction”), as well as other ecological crises (aquifer depletion, toxification of the total environment, ecosystem collapse, oceanic dead zones, etc.) are symptoms of humanity’s broken relationship to the planet. In plain terms: this way of life is killing the planet.
Today’s article reminds us that these crises are deeply interlinked, and so are solutions. While we are a revolutionary organization, every small step in the right direction also matters. And as a biocentric organization, we are in favor of actions to protect the natural world rather than putting our faith in technological Bright Green Lies.
By Tara Lohan / The Revelator
Mass extinction lurks beneath the surface of the sea. That was the dire message from a study published in April in the journal Science, which found that continuing to emit greenhouse gases unchecked could trigger a mass die-off of ocean animals that rivals the worst extinction events in Earth’s history.
The findings serve as just the latest reminder that climate change and biodiversity loss are interconnected crises — even if they’re rarely addressed in tandem by policymakers.
Toward that point, the Science study came with a dose of hopeful news: Action to curb greenhouse gas emissions and keep warming below 2 degrees Celsius could cut that extinction risk by 70%.
Additional research published in Global Change Biology offers another encouraging finding. The study, by an international team of scientists, found that not only can we do better at addressing biodiversity issues — we can do it while also targeting climate change.
“Many instances of conservation actions intended to slow, halt or reverse biodiversity loss can simultaneously slow anthropogenic climate change,” the researchers wrote in the study.
Their work looked at 21 proposed action targets for biodiversity that will be the focus of this fall’s international convening of the Convention on Biological Diversity in Kunming, China — a meeting delayed two years by the COVID-19 pandemic. The researchers found that two-thirds of those biodiversity targets also support climate change mitigation, even though they weren’t explicitly designed for that goal. The best opportunities to work on these crises together were actions to avoid deforestation and restore degraded ecosystems. Of particular focus, the study found, should be coastal ecosystems such as mangroves, seagrass and salt marshes, which can store large amounts of carbon and support a diversity of animals.
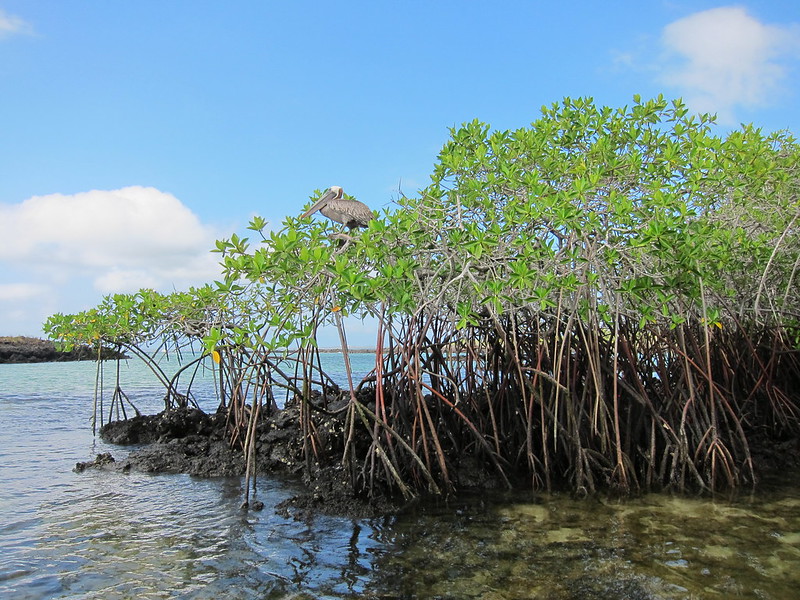 A pelican enjoys a perch in a mangrove stand in the Galapagos. Photo: Hans Johnson (CC BY 2.0)
A pelican enjoys a perch in a mangrove stand in the Galapagos. Photo: Hans Johnson (CC BY 2.0)
Also important is restoring forests and woodlands, but doing so with native species is critical. Planting monocultures of nonnative trees won’t boost biodiversity, the researchers point out, despite such endeavors being incentivized as a climate change solution.
Another target is reducing runoff into rivers, lakes and coastal waters from excess nutrients — including nitrogen and phosphorus — that cause algal blooms and oxygen-depleted waters. This eutrophication, combined with warming, may increase greenhouse gas emissions in freshwater bodies, in addition to harming fish and other animals.
Expanding and connecting the network of protected areas is another mutualistic target. Globally, we’ve protected about 15% of land and 7% of marine habitats. But we need to bump those numbers up considerably. As the researchers behind the Global Change Biology study put it, “There is a substantial overlap of 92% between areas that require reversing biodiversity loss and the areas needing protection for enhancing carbon storage and drawdown.”
Working on these issues in tandem can help boost the benefits.
We’re also spending large sums of money in all the wrong places. The study lists the reduction or elimination of subsidies that are harmful to biodiversity and the climate as “one of the most important and urgent reforms.”
We spend 10 times more on subsidies for environmentally harmful practices than on biodiversity conservation, the researchers note. Brazil, for example, spends 88 times more on subsidizing activities linked to deforestation than on those that may help stop it.
Other target areas to boost biodiversity and climate work include recovering and conserving wild species; greening urban areas; eliminating overfishing; reducing food and agricultural waste; and shifting diets to include more plant-based foods and less meat and dairy.
And, the researchers say, we need to “mainstream” the issues together — embedding both climate and biodiversity targets and metrics into policy, business and consumer practices.
Understanding these issues should start early, too. A study of school curricula in 46 countries found that fewer than half addressed climate change, and a paltry one-fifth referenced biodiversity. Both these subjects should be covered more and integrated together, the researchers say.
It’s not possible, after all, to tackle one crisis without addressing the other.
To fight climate change, we need fully functioning ecosystems with healthy populations of native plants and animals.
“And climate change is damaging this capacity,” said Hans-Otto Pörtner, a study coauthor and climate researcher at the Alfred Wegener Institute, Helmholtz Centre for Polar and Marine Research. “Only when we succeed in drastically reducing emissions from fossil fuels can nature help us to stabilize the climate.”

by DGR News Service | Jun 25, 2022 | ANALYSIS, The Problem: Civilization
Editor’s note: Marxism and Collapse is a new organization formed “for information and debate on the scientific sources surrounding the existential problems facing humanity in the short term (ecological crisis, energy collapse, overpopulation, resource depletion, pandemics, atomic war) and the need for a new strategic programmatic framework in the face of an inevitable nearby process of civilisational collapse and human extinction.” They reached out to Deep Green Resistance member Max Wilbert recently and invited him to participate in this written debate with Noam Chomsky and Miguel Fuentes. His comments are published here for the first time.
A few notes. First, while it is impossible to work for social change without contending with Marx and his legacy, Deep Green Resistance is not a Marxist organization. Although several of our organizers do consider themselves Marxists, others reject Marxism. Nonetheless, we see great value in dialogue with Marxist organizations and communities, just as we value in dialogue with Conservative or Libertarian organizations. Open dialogue, debate, and discussion is essential, and we are glad to see some strains of Marxism beginning to seriously contend with the unfolding ecological crisis.
Second, this debate includes comments from Guy McPherson, a man who Deep Green Resistance cut ties with after allegations surfaced of sexual misconduct. We would have preferred to remove McPherson’s comments, but left them here at the insistence of Marxism and Collapse. Be wary of this man.
This is part 1 of a 2 part written debate.
Introduction
The following is the first part of the interview-debate “Climate Catastrophe, Collapse, Democracy and Socialism” between the linguist and social scientist Noam Chomsky, one of the most important intellectuals of the last century, the Chilean social researcher and referent of the Marxist-Collapsist theoretical current Miguel Fuentes, and the American scientist Guy McPherson, a specialist in the topics of the ecological crisis and climate change. One of the most remarkable elements of this debate is the presentation of three perspectives which, although complementary in many respects, offer three different theoretical and political-programmatic approaches to the same problem: the imminence of a super-catastrophic climate change horizon and the possibility of a near civilisational collapse. Another noteworthy element of this debate is the series of interpretative challenges to which Chomsky’s positions are exposed and that give this discussion the character of a true “ideological contest” between certain worldviews which, although as said before common in many respects, are presented as ultimately opposed to each other. In a certain sense, this debate takes us back, from the field of reflection on the ecological catastrophe, to the old debates of the 20th century around the dilemma between “reform or revolution”, something that is undoubtedly necessary in the sphere of contemporary discussions of political ecology.
Question 1:
Marxism and Collapse: In a recent discussion between ecosocialist stances and collapsist approaches represented by Michael Lowy (France), Miguel Fuentes (Chile) and Antonio Turiel (Spain), Lowy constantly denied the possibility of a self-induced capitalist collapse and criticized the idea of the impossibility of stopping climate change before it reaches the catastrophic level of 1.5 centigrade degrees of global warming. Do you think that the current historical course is heading to a social global downfall comparable, for example, to previous processes of civilization collapse or maybe to something even worse than those seen in ancient Rome or other ancient civilizations? Is a catastrophic climate change nowadays unavoidable? Is a near process of human extinction as a result of the overlapping of the current climate, energetic, economic, social and political crisis and the suicidal path of capitalist destruction, conceivable? (1) (Marxism and Collapse)
Noam Chomsky:
The situation is ominous, but I think Michael Lowy is correct. There are feasible means to reach the IPPC goals and avert catastrophe, and also moving on to a better world. There are careful studies showing persuasively that these goals can be attained at a cost of 2-3% of global GDP, a substantial sum but well within reach – a tiny fraction of what was spent during World War II, and serious as the stakes were in that global struggle, what we face today is more significant by orders of magnitude. At stake is the question whether the human experiment will survive in any recognizable form.
The most extensive and detailed work I know on how to reach these goals is by economist Robert Pollin. He presents a general review in our joint book Climate Crisis and the Global Green New Deal. His ideas are currently being implemented in a number of places, including some of the most difficult ones, where economies are still reliant on coal. Other eco-economists, using somewhat different models, have reached similar conclusions. Just recently IRENA, —the International Renewable Energy Agency, part of the UN– came out with the same estimate of clean energy investments to reach the IPCC goals.
There is not much time to implement these proposals. The real question is not so much feasibility as will. There is little doubt that it will be a major struggle. Powerful entrenched interests will work relentlessly to preserve short-term profit at the cost of incalculable disaster. Current scientific work conjectures that failure to reach the goal of net zero Carbon emissions by 2050 will set irreversible processes in motion that are likely to lead to a “hothouse earth,” reaching unthinkable temperatures 4-5º Celsius above pre-industrial levels, likely to result in an end to any form of organized human society.
Miguel Fuentes:
Noam Chomsky highlights the possibility of a global warming that exceeds 4-5 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels within this century in his previous response, which according to him could mean, literally, the end of all forms of organised human society. Chomsky endorses what many other researchers and scientists around the world are saying. A recent report by the Breakthrough National Centre for Climate Restoration, for example, points to 2050 as the most likely date for the onset of widespread civilisational collapse. The central idea would be that, due to a sharp worsening of the current climate situation, and the possible transformation by the middle of this century of a large part of our planet into uninhabitable, a point of no return would then be reached in which the fracture and collapse of nation states and the world order would be inevitable . At the same time, he states that the needed goals to avert this catastrophe which will lay the foundations for a transition to “clean energy”, and a more just society, would still be perfectly achievable. Specifically, Chomsky says that this would only require an investment of around 2-3% of world GDP, the latter within the framework of a plan of “environmental reforms” described in the so-called “Green New Deal” of which he is one of its main advocates.
Let’s reflect for a moment on the above. On the one hand, Chomsky accepts the possibility of a planetary civilisational collapse in the course of this century. On the other hand, he reduces the solution to this threat to nothing more than the application of a “green tax”. Literally the greatest historical, economic, social, cultural and even geological challenge that the human species and civilisation has faced since its origins reduced, roughly speaking, to a problem of “international financial fundraising” consisting of allocating approximately 3% of world GDP to the promotion of “clean energies”. Let’s think about this again. A danger that, as Chomsky puts it, would be even greater than the Second World War and could turn the Earth into a kind of uninhabitable rock, should be solved either by “international tax collection” or by a plan of limited “eco-reforms” of the capitalist economic model (known as the “Green New Deal”).
But how is it possible that Chomsky, one of the leading intellectuals of the 20th century, is able to make this “interpretive leap” between accepting the possibility of the “end of all organised human society” within this century and reducing the solution to that threat to what would appear to be no more than a (rather timid) cosmetic restructuring of international capitalist finance? Who knows! What is certain, however, is that Chomsky’s response to the climate threat lags far behind not only those advocated by the ecosocialist camp and even traditional Marxism to deal with the latter, based on posing the link between the problem of the root causes of the ecological crisis and the need for a politics that defends the abolition of private ownership of the means of production as a necessary step in confronting it. Moreover, Chomsky’s treatment of the ecological crisis seems to be inferior to that which characterises all those theoretical tendencies which, such as the theory of degrowth or a series of collapsist currents, advocate the imposition of drastic plans of economic degrowth and a substantial decrease in industrial activity and global consumption levels. The latter by promoting a process of “eco-social transition” which would not be reduced to a mere change in the energy matrix and the promotion of renewable energies, but would imply, on the contrary, the transition from one type of civilisation (modern and industrial) to another, better able to adapt to the new planetary scenarios that the ecological crisis, energy decline and global resource scarcity will bring with them.
But reducing the solution of the climate catastrophe to the need for a “green tax” on the capitalist market economy is not the only error in Chomsky’s response. In my view, the main problem of the arguments he uses to defend the possibility of a successful “energy transition” from fossil fuels to so-called “clean energy” would be that they are built on mud. First, because it is false to say that so-called “clean energies” are indeed “clean” if we consider the kind of resources and technological efforts required in the implementation of the energy systems based on them. Solar or wind energy, for example, depend not only on huge amounts of raw materials associated for their construction with high polluting extractive processes (e.g., the large quantities of steel required for the construction of wind turbines is just one illustration of this), but also on the use of extensive volumes of coal, natural gas or even oil. The construction of a single solar panel requires, for instance, enormous quantities of coal. Another striking example can be seen in the dependence of hydrogen plants (specially the “grey” or “blue” types) on vast quantities of natural gas for their operations. All this without it ever being clear that the reduction in the use of fossil fuels that should result from the implementation of these “clean” technologies will be capable of effectively offsetting a possible exponential increase in its “ecological footprint” in the context of a supposedly successful energy transition .
Secondly, it is false to assume that an energy matrix based on renewable energies could satisfy the energy contribution of fossil fuels to the world economy in the short or medium term, at least, if a replication of current (ecologically unviable) patterns of economic growth is sought. Examples of this include the virtual inability of so-called “green hydrogen” power plants to become profitable systems in the long term, as well as the enormous challenges that some power sources such as solar or wind energy (highly unstable) would face in meeting sustained levels of energy demand over time. All this without even considering the significant maintenance costs of renewable energy systems, which are also associated (as said) with the use of highly polluting raw materials and a series of supplies whose manufacture also depend on the use of fossil fuels .
But the argumentative problems in Chomsky’s response are not limited to the above. More importantly is that the danger of the climate crisis and the possibility of a planetary collapse can no longer be confined to a purely financial issue (solvable by a hypothetical allocation of 3% of world GDP) or a strictly technical-engineering challenge (solvable by the advancement of a successful energy transition). This is because the magnitude of this problem has gone beyond the area of competence of economic and technological systems, and has moved to the sphere of the geological and biophysical relations of the planet itself, calling the very techno-scientific (and economic-financial) capacities of contemporary civilisation into question. In other words, the problem represented by the current levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, or those related to the unprecedented advances in marine acidification, Arctic melting, or permafrost decomposition rates, would today constitute challenges whose solution would be largely beyond any of our scientific developments and technological capabilities. Let’s just say that current atmospheric carbon dioxide levels (already close to 420 ppm) have not been seen for millions of years on Earth. On other occasions I have defined this situation as the development of a growing “terminal technological insufficiency” of our civilisation to face the challenges of the present planetary crisis .
In the case of current atmospheric CO2 concentrations, for example, there are not and will not be for a long time (possibly many decades or centuries), any kind of technology capable of achieving a substantial decrease of those concentrations. This at least not before such concentrations continue to skyrocket to levels that could soon guarantee that a large part of our planet will become completely uninhabitable in the short to medium term. In the case of CO2 capture facilities, for instance, they have not yet been able to remove even a small (insignificant) fraction of the more than 40 billion tonnes of carbon dioxide emitted each year by industrial society . Something similar would be the situation of other ecological problems such as the aforementioned increase in marine acidification levels, the rise in ocean levels or even the increasingly unmanageable proliferation of space debris and the consequent danger it represents for the (immediate) maintenance of contemporary telecommunication systems. In other words, again, increasing threatening problems for which humanity has no effective technologies to cope, at least not over the few remaining decades before these problems reach proportions that will soon call into question our very survival as a species.
Unsolvable problems, as unsolvable as those that would confront anyone seeking to “restore” a clay pot or a glass bottle to its original state after it has been shattered into a thousand fragments by smashing it against a concrete wall! To restore a glass of the finest crystal after it has been smashed to pieces? Not even with the investment of ten, a hundred world GDPs would it be possible! This is what we have done with the world, the most beautiful of the planetary crystals of our solar system, blown into a thousand pieces by ecocidal industrialism! To restore? To resolve? Bollocks! We have already destroyed it all! We have already finished it all! And no “financial investment” or “technological solution” can prevent what is coming: death! To die then! To die… and to fight to preserve what can be preserved! To die and to hope for the worst, to conquer socialism however we can, on whatever planet we have, and to take the future out of the hands of the devil himself if necessary! That is the task of socialist revolution in the 21st century! That is the duty of Marxist revolutionaries in the new epoch of darkness that is rising before us! That is the mission of Marxism-Collapsist!
Max Wilbert:
Throughout history, all civilizations undermine their own ecological foundations, face disease, war, political instability, and the breakdown of basic supply chains, and eventually collapse.
Modern technology and scientific knowledge does not make us immune from this pattern. On the contrary, as our global civilization has harnessed more energy, expanded, and grown a larger population than ever before in history, the fall is certain to be correspondingly worse. What goes up must come down. This is a law of nature. The only question is, when?
Professor Chomsky’s argument that collapse of civilization can be averted at a relatively minor cost by diverting 2-3% of global GDP to transition to renewable energy and fund a *Global Green New Deal* does not contend with the physical constraints civilization faces today. The global energy system, which powers the entire economy, is the largest machine in existence and was built over more than a century during a period of abundant fossil fuels and easy-to-access minerals and raw materials. It was powered by the *last remnants of ancient sunlight*, fossil fuels condensed into an extremely dense form of energy that is fungible and easily transportable.
That era is over. Accessible reserves of minerals, oil, and gas are gone, and we are long since into the era of extreme energy extraction (fracking, deepwater drilling, arctic drilling, tar sands, etc.). Simply replacing fossil fuels with solar and wind energy and phasing out all liquid and solid fuel (which still makes up roughly 80% of energy use) in favor of electrification of transportation, heating, etc. is not a simple task in an era of declining energy availability, increasing costs, extreme weather, political and financial instability, and resource scarcity. And these so-called “renewable” technologies still have major environmental impacts (for example, see solar impacts on desert tortoise, wind energy impacts on bat populations, and lithium mining impacts on sage-grouse), even if they do reduce carbon emissions—which is not yet proven outside of models.
In practice, renewable energy technologies seem to be largely serving as a profitable investment for the wealthy, a way to funnel public money into private hands, and a distraction from the scale of the ecological problems we face (of which global warming is far from the worst) and the scale of solutions which are needed. This is, as Miguel Fuentes points out, a rather timid cosmetic restructuring of the dominant political and economic order.
In our book *Bright Green Lies: How the Environmental Movement Lost Its Way and What We Can Do About It*, my co-authors and I call this “solving for the wrong variable.” We write: “Our way of life [industrial modernity] doesn’t need to be saved. The planet needs to be saved from our way of life… we are not saving civilization; we are trying to save the world.” Scientists like Tim Garrett at the University of Utah model civilization as a “heat engine,” a simple thermodynamic model that will consume energy and materials until it can no longer do so, then collapse. Joseph Tainter, the scholar of collapse, writes that “in the evolution of a society, continued investment in complexity as a problem-solving strategy yields a declining marginal return.” This is our reality.
Whether sanity prevails and we succeed in building a new politics and new societies organized around rapidly scaling down the human enterprise to sustainable levels, or we continue down the business-as-usual path we are on, the future looks either grim or far more dire. Global warming will continue to worsen for decades even if, by some miracle, we are able to dismantle the fossil fuel industry and restore the ecology of this planet. The 6th mass extinction event and ecological collapse aren’t a distant future. We are in the depths of these events, and they’ve been getting worse for centuries. The question is not “can we avoid catastrophe?” It’s too late for that. The question is, “how much of the world will be destroyed?” Will elephants survive? Coral reefs? Tigers? The Amazon Rainforest? Will humans? What will we leave behind?
I want to leave behind as much biodiversity and ecological integrity as possible. Human extinction seems unlikely, at least in coming decades, unless runaway global warming accelerates faster than predicted. “Unlikely” is not “impossible,” but there are 8 billion of us, and we are profoundly adaptable. I am far less worried about human extinction than about the extinction of countless other species—100 per day. I am far more worried about the collapse of insect populations or phytoplankton populations (which provide 40% of all oxygen on the planet and are the base of the oceanic food web). The fabric of life itself is fraying, and we are condemning unborn human generations to a hellish future and countless non-humans to the extinction. Extinction will come for humans, at some point. But at this point, I am not concerned for our species, but rather for the lives of my nephews and their children, and the salmon on the brink of extermination, and the last remaining old-growth forests.
Guy McPherson:
There is no escape from the mass extinction event underway. Only human arrogance could suggest otherwise. Our situation is definitely terminal. I cannot imagine that there will be a habitat for Homo sapiens beyond a few years in the future. Soon after we lose our habitat, all individuals of our species will die out. Global warming has already passed two degrees Celsius above the 1750 baseline, as noted by the renowned Professor Andrew Glikson in his October 2020 book “The Event Horizon”. He wrote on page 31 of that book: “During the Anthropocene, greenhouse gas forcing increased by more than 2.0 W/m2, equivalent to more than > 2°C above pre-industrial temperatures, which is an abrupt (climate change) event taking place over a period not much longer than a generation”.
So yes. We have definitely passed the point of no return in the climate crisis. Even the incredibly conservative Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) has already admitted the irreversibility of climate change in its 24 September 2019 “Special Report on the Ocean and Cryosphere in a Changing Climate”. A quick look around the globe will also reveal unprecedented events such as forest fires, floods and mega-droughts. The ongoing pandemic is just one of many events that are beginning to overwhelm human systems and our ability to respond positively.
All species are going extinct, including more than half a dozen species of the genus Homo that have already disappeared. According to the scientific paper by Quintero and Wiens published in Ecology Letters on 26 June 2013, the projected rate of environmental change is 10.000 times faster than vertebrates can adapt to. Mammals also cannot keep up with these levels of change, as Davis and colleagues’ paper published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences on 30 October 2018 points out. The fact that our species is a vertebrate mammal suggests that we will join more than 99% of the species that have existed on Earth that have already gone extinct. The only question in doubt is when. In fact, human extinction could have been triggered several years ago when the Earth’s average global temperature exceeded 1.5 degrees Celsius above the 1750 baseline. According to a comprehensive overview of this situation published by the European Strategy and Policy Analysis System in April 2019, a “1.5 degree increase is the maximum the planet can tolerate; (…) in a worst-case scenario, [such a temperature increase above the 1750 baseline will result in] the extinction of humanity altogether”.
All species need habitat to survive. As Hall and colleagues reported in the Spring 1997 issue of the Wildlife Society Bulletin: “We therefore define habitat ‘as the resources and conditions present in an area that produce occupancy, including survival and reproduction, of a given organism. Habitat is organism-specific; it relates the presence of a species, population or individual (…) to the physical and biological characteristics of an area. Habitat implies more than vegetation or the structure of that vegetation; it is the sum of the specific resources needed by organisms. Whenever an organism is provided with resources that allow it to survive, that is its habitat’”. Even tardigrades are not immune to extinction. Rather, they are sensitive to high temperatures, as reported in the 9 January 2020 issue of Scientific Reports. Ricardo Cardoso Neves and collaborators point out there that all life on Earth is threatened with extinction with an increase of 5-6 degrees Celsius in the global average temperature. As Strona and Corey state in another article in Scientific Reports (November 13, 2018) raising the issue of co-extinctions as a determinant of the loss of all life on Earth: “In a simplified view, the idea of co-extinction boils down to the obvious conclusion that a consumer cannot survive without its resources”.
From the incredibly conservative Wikipedia entry entitled “Climate change” comes this supporting information: “Climate change includes both human-induced global warming and its large-scale impacts on weather patterns. There have been previous periods of climate change, but the current changes are more rapid than any known event in Earth’s history.” The Wikipedia entry further cites the 8 August 2019 report “Climate Change and Soils”, published by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). The IPCC is among the most conservative scientific bodies in history. Yet it concluded in 2019 that the Earth is in the midst of the most rapid environmental change seen in planetary history, citing scientific literature that concludes: “These rates of human-driven global change far exceed the rates of change driven by geophysical or biospheric forces that have altered the trajectory of the Earth System in the past (Summerhayes 2015; Foster et al. 2017); nor do even abrupt geophysical events approach current rates of human-driven change”.
The Wikipedia entry also points out the consequences of the kind of abrupt climate change currently underway, including desert expansion, heat waves and wildfires becoming increasingly common, melting permafrost, glacier retreat, loss of sea ice, increased intensity of storms and other extreme environmental events, along with widespread species extinctions. Another relevant issue is the fact that the World Health Organisation has already defined climate change as the greatest threat to global health in the 21st century. The Wikipedia entry continues: “Under the 2015 Paris Agreement, nations collectively agreed to keep warming ‘well below 2.0 degrees C (3.6 degrees F) through mitigation efforts’”. But Professor Andrew Glikson already pointed out as we said in his aforementioned book The Event Horizon that the 2 degrees C mark is already behind us. Furthermore, as we already indicated, the IPCC also admitted the irreversibility of climate change in its “Special Report on the Ocean and Cryosphere in a Changing Climate”. Therefore, 2019 was an exceptional year for the IPCC, as it concluded that climate change is abrupt and irreversible.
How conservative is the IPCC? Even the conservative and renowned journal BioScience includes an article in its March 2019 issue entitled “Statistical language supports conservatism in climate change assessments”. The paper by Herrando-Perez and colleagues includes this information: “We find that the tone of the IPCC’s probabilistic language is remarkably conservative (…) emanating from the IPCC’s own recommendations, the complexity of climate research and exposure to politically motivated debates. Harnessing the communication of uncertainty with an overwhelming scientific consensus on anthropogenic climate change should be one element of a broader reform, whereby the creation of an IPCC outreach working group could improve the transmission of climate science to the panel’s audiences”. Contrary to the conclusion of Herrando-Perez and colleagues, I cannot imagine that the IPCC is really interested in conveying accurate climate science to its audiences. After all, as Professor Michael Oppenheimer noted in 2007, the US government during the Reagan administration “saw the creation of the IPCC as a way to prevent the activism stimulated by my colleagues and me from controlling the political agenda”.
Question 2:
Marxism and Collapse: Have the human species become a plague for the planet? If so, how can we still conciliate the survival of life on Earth with the promotion of traditional modern values associated with the defence of human and social rights (which require the use of vast amounts of planetary resources) in a context of a potential increase of world’s population that could reach over twelve billion people this century? The latter in a context in which (according to several studies) the maximum number of humans that Earth could have sustained without a catastrophic alteration of ecosystems should have never exceeded the billion. Can the modern concept of liberal (or even socialist) democracy and its supposedly related principles of individual, identity, gender, or cultural freedom survive our apparent terminal geological situation, or it will be necessary to find new models of social organization, for example, in those present in several indigenous or native societies? Can the rights of survival of living species on Earth, human rights, and the concept of modern individual freedom be harmoniously conciliated in the context of an impending global ecosocial disaster?
Noam Chomsky:
Let’s begin with population growth. There is a humane and feasible method to constrain that: education of women. That has a major effect on fertility in both rich regions and poor, and should be expedited anyway. The effects are quite substantial leading to sharp population decline by now in parts of the developed world. The point generalizes. Measures to fend off “global ecosocial disaster” can and should proceed in parallel with social and institutional change to promote values of justice, freedom, mutual aid, collective responsibility, democratic control of institutions, concern for other species, harmony with nature –values that are commonly upheld by indigenous societies and that have deep roots in popular struggles in what are called the “developed societies” –where, unfortunately, material and moral development are all too often uncorrelated.
Miguel Fuentes:
Chomsky’s allusions to the promotion of women’s education and the social values of justice, freedom, mutual aid, and harmony with nature, as “moral values” disconnected from a broader critique of the industrial system, capitalism, and the class society within which threats such as global warming have been generated and aggravated, become mere phrases of good intentions. On the contrary, the realization of these principles must be thought within a context of a large-scale world social transformation. The latter if those principles are to be effective in combatting the challenges facing humanity today and the kind of civilisational crisis that is beginning to unfold as a product of the multiple eco-social (ecological, energy and resource) crises that are advancing globally. In other words, a process of historical transformation that can envisage the abolition of the current ecocidal industrial economic system, and its replacement by one in which production, exchange and distribution can be planned in accordance with social needs.
But even a traditional socialist approach to these problems, such as the one above, also falls short of accounting for the kind of planetary threats we face. Let’s put it this way, the discussion around the ecological crisis and the rest of the existential dangers hanging over the fate of our civilisation today really only begins, not ends, by giving it a proper Marxist contextualisation. One of the underlying reasons for this is that the traditional socialist project itself, in all its variants (including its more recent ecosocialist versions), would also already be completely insufficient to respond to the dangers we are facing as a species. That is, the kind of dangers and interpretative problems that none of the Marxists theoreticians of social revolution over the last centuries had ever imagined possible, from Marx and Engels to some of the present-day exponents of ecosocialism such as John Bellamy Foster or Michael Lowy .
One of these new types of problems that revolutionary theories are facing today is that of the current uncontrolled demographic growth rates of humanity. A problem that would already confer on us, amongst other things, the condition of one of the worst biological (or, in our case, “biosocial”) plagues existing to this day. This if we consider the absolutely devastating role that our species has been exerting on the biosphere in the last centuries. A plague that would be even comparable in its destructive power to that represented by the cyanobacteria that triggered the first mass extinction event on Earth some 2.4 billion years ago, although in our case at an even more accelerated and “efficient” pace than the latter. Is this statement too brutal? Maybe, from a purely humanist point of view, alien to the kind of problems we face today, but not from an eminently scientific perspective. Or can there be any doubt about our condition as a “planetary plague” for any ecologist studying the current patterns of behaviour, resource consumption and habitat destruction associated with our species? Too brutal a statement? Tell it to the more than 10.000 natural species that become extinct every year as a result of the role of a single species on the planet: ours! Tell it to the billions of animals killed in the great fires of Australia or the Amazon a few years ago! Tell it to the polar bears, koalas, pikas, tigers, lions, elephants, who succumb every year as a product of what we have done to the Earth! Very well, we are then a “plague”, although this term would only serve to classify us as a “biological species”, being therefore too “limited” a definition and lacking any social and historical perspective. Right?
Not really. The fact that we possess social and cultural systems that differentiate us from other complex mammals does not mean that our current status as a “plague of the world” should be confined to the biological realm alone. On the contrary, this just means that this status could also have a certain correlation in the social and cultural dimension; that is, in the sphere of the social and cultural systems particular to modern society. To put it in another way, even though our current condition of “plague of the world” has been acquired by our species within the framework of a specific type of society, mode of production and framework of particular historical relations, characteristic of industrial modernity, this does not mean that this condition should be understood as a merely historical product. That is, excluding its biological and ecological dimension. In fact, beyond the differentiated position and role of the various social sectors that make up the productive structure and the socio-economic systems of the industrial society (for example, the exploiting and exploited social classes), it is indeed humanity as a whole: rich and poor, entrepreneurs and workers, men and women, who share (all of us) the same responsibility as a species (although admittedly in a differentiated way) for the current planetary disaster. An example of the above. Mostly everything produced today by the big multinationals, down to the last grain of rice or the last piece of plastic, is consumed by someone, whether in Paris, London, Chisinau or La Paz. And we should also remember that even biological plagues (such as locusts) may have different consumption patterns at the level of their populations, with certain sectors being able to consume more and others consuming less. However, just because one sector of a given biological plague consumes less (or even much less), this sector should not necessarily be considered as not belonging to that plague in question.
Another similar example: it is often claimed in Marxist circles (sometimes the numbers vary according to each study) that 20% of humanity consumes 80% of the planetary resources. This means that approximately 1.600.000.000.000 people (assuming a total population of 8 billion) would be the consumers of that 80% of planetary resources; that is, a number roughly equivalent to three times the current European population. In other words, what this sentence really tells us is that a much larger segment of the world’s population than the capitalist elites (or their political servants) would also bear a direct, even grotesque, responsibility for the unsustainable consumption patterns that have been aggravating the current planetary crisis. Or, to put it in more “Marxist” terms, that a large percentage (or even the totality) of the working classes and popular sectors in Europe, the United States, and a significant part of those in Latin America and other regions of the so-called “developing countries”, would also be “directly complicit”, at least in regards of the reproduction of the current ecocidal modern urban lifestyle, in the destruction of our planet.
But let us extend the discussion to the remaining 80% of humanity; that is, to the approximately 6.400.000.000.000 people who consume 20% of the planetary resources used in a year. To begin with, let us say that 20% of global resources is not a negligible percentage, representing in fact a fifth of them and whose production would be associated with substantial and sustained levels of environmental destruction. The latter in the context of an ever-growing world population that possibly should never have exceeded one billion inhabitants, so that we would have been in a position today to stop or slow down the disastrous impact we are having on ecosystems. Let us not forget that the number of people included in this 80% of the world’s population is more than four times higher than the entire human population at the beginning of the 20th century, which means that the number of basic resources necessary for the survival of this sector is an inevitable pressure on the earth’s natural systems, even if consumption levels are kept to a minimum.
In short, there is therefore no doubt that humanity has indeed become one of the worst planetary plagues in the history of terrestrial life, constituting this a (fundamental) problem in itself for contemporary revolutionary thought and, more generally, for the human and social sciences as a whole. In other words, a problem that today would not be solved by a mere change in the mode of production, the class structure, or the socio-political system, but would be associated with the very “genetics” of the development of industrial society. That is to say, a society based on a particularly destructive (voracious) form of human-nature relationships, which would be at the same time the “structural basis” of all possible and conceivable models of it (capitalists, socialists or any other type). Whether in the framework of a neo-liberal market economy or a socialist and/or collectivist planned economy, it is the industrial system and modern mass society in all its variants, whether capitalist or socialist, its mega-cities, its productive levels, its consumption patterns and lifestyles, its “anthropocentric spirit”, structurally associated with certain demographic patterns in which the Earth is conceived as a mere space for human consumption and reproduction… that is the main problem.
Is it possible to reconcile current levels of overpopulation with the survival requirements of our species? No. We have become a planetary plague and will remain a planetary plague until such time as, by hook or by crook (almost certainly by crook) our numbers are substantially reduced and remain at the minimum possible levels, for at least a few centuries or millennia. Is it possible to solve the problem of overpopulation and at the same time defend the legitimacy of traditional modern values associated with the promotion of human and social rights, at least as these values have been understood in recent centuries? No. Modernity has failed. Modernity is dead. We are going to have to rethink every single one of our values, including the most basic ones, all of them. We are going to have to rethink who we are, where we are going and where we come from. The existence of almost 8 billion people on our planet today, and moreover the likely increase of this number to one that reaches 10 or even 12 billion is not only incompatible with the realisation of the very ideals and values of modern democracy in all its variants (capitalists or socialists), but also with the very survival of our species as a whole and, possibly, of all complex life on Earth. This simply because there will be nowhere near enough resources to ensure the realization of these values (or even our own subsistence) in such a demographic context (there simply won’t be enough food and water). Our situation is terminal. Modernity is dead. Democracy is dead. Socialism is dead. And if we want these concepts -democracy or socialism- to really have any value in the face of the approaching catastrophe, then we will have to rethink them a little more humbly than we have done so far.
Modern civilisation has borne some of the best fruits of humanity’s social development, but also some of the worst. We are in some ways like the younger brother of a large family whose early successes made him conceited, stupid and who, thinking of himself as “master of the world”, began to lose everything. We are that young man. We should therefore shut up, put our ideologies (capitalists and socialists) in our pockets, and start learning a little more from our more modest, slower and more balanced “big brothers”; for example, each of the traditional or indigenous societies which have been able to ensure their subsistence for centuries and in some cases even millennia. The latter while industrial society would not even have completed three centuries before endangering its own existence and that of all other cultures on the planet. In a few words, start learning from all those traditional societies that have subsisted in the context of the development of social systems that are often much more respectful of ecological and ecosystemic balances. Those “ecosocial balances” which are, in the end, in the long view of the evolution of species, the real basis for the development of any society… because without species (be they animal or plant), any human culture is impossible. Scientific and technological progress? Excellent idea! But perhaps we could take the long route, think things through a bit more, and achieve the same as we have achieved today in two centuries, but perhaps taking a bit longer, say ten, twenty or even a hundred centuries? Who’s in a hurry? Let us learn from the tortoise which, perhaps because it is slow, has survived on Earth for more than 220 million years, until we (who as Homo sapiens are no more than 250.000 years old) came along and endangered it.
Max Wilbert:
Human population is a hockey-stick graph that corresponds almost exactly with rising energy use. Most of the nitrogen in our diet comes from fossil fuel-based fertilizers. Norman Borlaug, the plant breeder who won the Nobel Peace Prize for his work on the Green Revolution, said in his acceptance speech that “we are dealing with two opposing forces, the scientific power of food production and the biologic power of human reproduction… There can be no permanent progress in the battle against hunger until the agencies that fight for increased food production and those that fight for population control unite in a common effort.”
Ideally, this situation could be dealt with humanely by education and making family planning and women’s health services available. The best example of this actually comes from Iran, where under a religious theocracy in the wake of the Iran-Iraq war, birth rates were reduced from around 7 children per woman to less than replacement in little more than a decade (the policy was since reversed, and Iran’s land and water is paying the price). Technically, it’s quite easy to solve overpopulation humanely; reduce birth rates to less than replacement levels, then wait. Politically, it’s much harder. As we’ve seen with the recent fall of abortion rights in the US, the political battle for control of women’s reproduction is alive and well, and basic ecology is anathema to many political leaders and populations.
Unless we take action to reduce our population willingly, it will happen unwillingly as the planet’s ecology fails to be able to support us. That will be harsh. Any species that exceeds the carrying capacity of the environment it lives in will experience a population crash, usually due to starvation, disease, and predation. That’s our choice. Either we make the right decisions, or we pay the price.
The difference between our situation today and the Indus Valley civilization or the Roman Empire is that today civilization is globalized. The collapse of global industrial civilization, as I wrote above, is coming. I don’t believe it can be stopped at this point; in fact, I believe it is already in progress. But collapse is also not simply an overnight chaotic breakdown of all social order. We can define collapse as a rapid simplification of a complex society characterized by breakdown of political and social institutions, a return to localized, low energy ways of life, and usually a significant reduction in population (which is a nice way of saying, a lot of people die).
Collapse should be looked at as having good and bad elements. Good elements, from my perspective, include reducing consumption and energy use, localizing our lives, and having certain destructive institutions (for example, the fossil fuel industry) fade away. Bad elements might include breakdown of basic safety and rising violence, mass starvation, disease, and, for example, the destruction of local forests for firewood if electricity is no longer available for heating. Some aspects of collapse have elements of both. For example, the collapse of industrial agriculture would be incredibly beneficial for the planet but would lead to mass human die offs.
If collapse is coming regardless of what we want, it’s our moral and ecological responsibility to make the best of the situation by assisting and accelerating the positive aspects of collapse (for example, by working to reduce consumption and dismantle oil infrastructure) and help prevent or mitigate the negative aspects (for example, by working to reduce population growth and build localized sustainable food systems).
As I write this, I am looking into a meadow between 80-year-old oak trees. A deer and her fawn are walking through the grass. Birds are singing in the trees. A passenger jet roars overhead, and the hum of traffic floats over the hills. There is a fundamental contradiction between industrial civilization and ecology, and the organic tensions created by this contradiction are rising. These are dire and revolutionary times, and it is our responsibility to navigate them.
Guy McPherson:
As ecologists have been pointing out for decades, environmental impacts are the result of human population size and human consumption levels. The Earth can support many more hunter-gatherers than capitalists seeking more material possessions. Unfortunately, we are stuck with the latter rather than the former. Ecologists and environmentalists have been proposing changes in human behaviour since at least the early 20th century. These recommendations have fallen on deaf ears. However, even if it is possible to achieve substantial changes in human behaviour, and if they result in an effective slowing down or stopping of industrial activity, it is questionable whether this is a useful means of ensuring our continued survival. One reason for this lies in the knowledge of what the effect of “aerosol masking” could mean for the climate crisis.
The “climate masking” effect of aerosols has been discussed in the scientific literature since at least 1929, and consists of the following: at the same time as industrial activity produces greenhouse gases that trap part of the heat resulting from sunlight reaching the Earth, it also produces small particles that prevent this sunlight from even touching the surface of the planet. These particles, called “aerosols”, thus act as a kind of umbrella that prevents some of the sunlight from reaching the earth’s surface (hence this phenomenon has also been referred to as “global dimming”) . In other words, these particles (aerosols) prevent part of the sun’s rays from penetrating the atmosphere and thus inhibit further global warming. This means, then, that the current levels of global warming would in fact be much lower than those that should be associated with the volumes of greenhouse gases present in the atmosphere today (hence the designation of this phenomenon as “climate masking”). To put it in a simpler way, the global warming situation today would actually be far more serious than is indicated not only by the very high current global temperatures, but also by the (already catastrophic) projections of rising global temperatures over the coming decades. This is especially important if we consider the (overly optimistic) possibility of a future reduction in the amount of aerosols in the atmosphere as a result of a potential decrease in greenhouse gas emissions over the next few years, which should paradoxically lead, therefore, to a dramatic increase in global temperatures.
Global temperatures should then not only be much higher than they are today, but the expected rise in global temperatures will necessarily be more intense than most climate models suggest. According to the father of climate science, James Hansen, it takes about five days for aerosols to fall from the atmosphere to the surface. More than two dozen peer-reviewed papers have been published on this subject and the latest of these indicates that the Earth would warm by an additional 55% if the “masking” effect of aerosols were lost, which should happen, as we said, as a result of a marked decrease or modification of industrial activity leading to a considerable reduction in greenhouse gas emissions. This study suggests that this could potentially lead to an additional (sudden) increase in the earth’s surface temperature by about 133% at the continental level. This article was published in the prestigious journal Nature Communications on 15 June 2021. In conclusion, the loss or substantial decrease of aerosols in the atmosphere could therefore lead to a potential increase of more than 3 degrees Celsius of global warming above the 1750 baseline very quickly. I find it very difficult to imagine many natural species (including our own) being able to withstand this rapid pace of environmental change.
In reality, a mass extinction event has been underway since at least 1992. This was reported by Harvard professor Edward O. Wilson, the so-called “father of biodiversity”, in his 1992 and 2002 books The Diversity of Life and The Future of Life, respectively. The United Nations Environment Programme also reported in August 2010 that every day we are leading to the extinction of 150 to 200 species. This would thus be at least the eighth mass extinction event on Earth. The scientific literature finally acknowledged the ongoing mass extinction event on 2 March 2011 in Nature. Further research along these lines was published on 19 June 2015 in Science Advances by conservation biologist Gerardo Ceballos and colleagues entitled “Accelerated human-induced losses of modern species: entering the sixth mass extinction”. Coinciding with the publication of this article, lead author Ceballos stated that “life would take many millions of years to recover and that our species would probably soon disappear”. This conclusion is supported by subsequent work indicating that terrestrial life did not recover from previous mass extinction events for millions of years. It is true, however, that indigenous perspectives can help us understand ongoing events. However, I am convinced that rationalism is key to a positive response to these events.
Noam Chomsky is an American linguist, philosopher, cognitive scientist, historian, social critic, and political activist. He adheres to the ideas of libertarian socialism and anarcho-syndicalism. He advocates a New Green Deal policy as one of the ways of dealing with the ecological crisis.
Miguel Fuentes is a Chilean social researcher in the fields of history, archaeology, and social sciences. International coordinator of the platform Marxism and Collapse and exponent of the new Marxist-Collapsist ideology. He proposes the need for a strategic-programmatic updating of revolutionary Marxism in the face of the new challenges of the Anthropocene and the VI mass extinction.
Max Wilbert is an organizer, writer, and wilderness guide. He has been part of grassroots political work for 20 years. He is the co-author of Bright Green Lies: How The Environmental Movement Lost Its Way and What We Can Do About It, which was released in 2021. He is the co-founder of Protect Thacker Pass and part of Deep Green Resistance.
Guy McPherson is an American scientist, professor emeritus of natural resources, ecology, and evolutionary biology. He adheres to anarchism and argues the inevitability of human extinction and the need to address it from a perspective that emphasises acceptance, the pursuit of love and the value of excellence.
The final version of this document has been edited by Dutch archaeologist Sven Ransijn.
Notes
The debate between Michael Lowy, Miguel Fuentes, and Antonio Turiel (which also included critical comments by Spanish Marxist ecologist Jaime Vindel, Argentinean left-wing leader Jorge Altamira and Chilean journalist Paul Walder) can be reviewed in full in the debate section of the Marxism and Collapse website at the following link: www.marxismoycolapso.com/debates.














 A pelican enjoys a perch in a mangrove stand in the Galapagos. Photo: Hans Johnson (CC BY 2.0)
A pelican enjoys a perch in a mangrove stand in the Galapagos. Photo: Hans Johnson (CC BY 2.0)