
by DGR News Service | Apr 12, 2022 | Male Supremacy, NEWS
In the United States, the Supreme Court appears poised to overturn Roe v. Wade, the 50-year-old legal precedent that ruled state-level abortion bans are (in many situations) unconstitutional and violate the rights of pregnant women.
Since 1973, legal challenges to Roe v. Wade have weakened the case significantly, most recently allowing for a spate of state-level abortion bans in-all-but-name (notably in Texas, but other states are following suit). Overturning Roe v. Wade is likely to lead to a flood of these state-level abortion bans in roughly half of the United States.
Deep Green Resistance is both ethically and strategically opposed to abortion bans. As a feminist organization, we believe a woman or girl has the right to choose an abortion if that is what she wants. Broadly, these bans disproportionately affect poor women, since wealthier women may be able to travel to a jurisdiction in which abortion is legal, while poor women will not. This entrenches cycles of poverty, since giving birth to and raising a child is extremely expensive and time consuming.
Women’s Loss is Earth’s Loss: Abortion Bans Make Sustainability Impossible
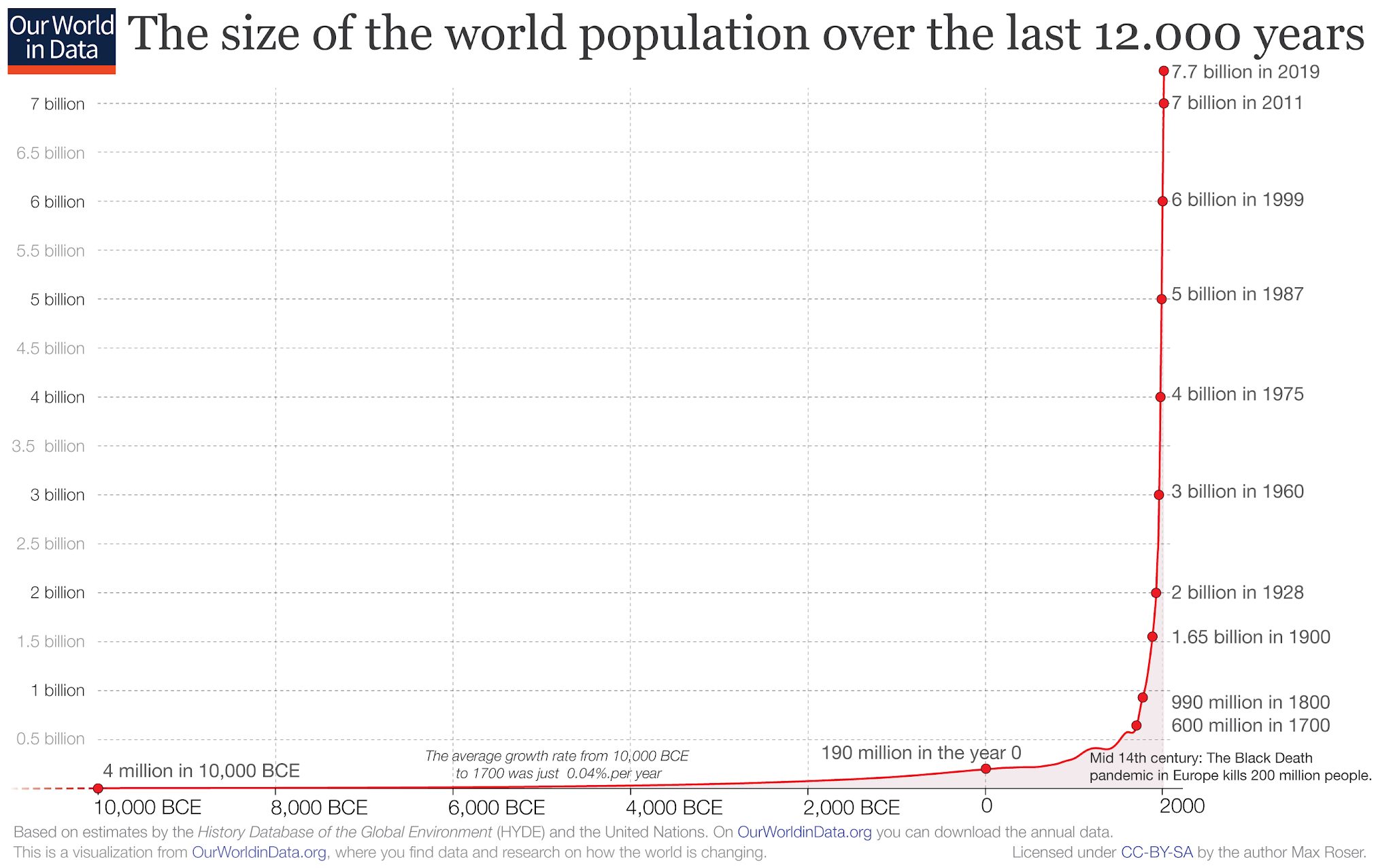
Abortion bans significantly harm the planet, since overpopulation (alongside consumption and technology) is a major driver of the destruction of the natural world.
- The United States population was 31.4 million in 1860. Today, it is more than 331 million.
- As one professor stated, “Since 1960, while human population has doubled, the global economy has quadrupled, and resource consumption quintupled.”
- That was in 1999. Now, twenty-three years later, there are 1.8 billion more people on the planet, equivalent to more than the entire populations of China and the United States combined.
- More than 80 million people are added to the global population annually, the equivalent of ten New York Cities or twenty Los Angeles’s.
- The biomass of mammals on planet Earth is now more than 96% humans and livestock, and only 4% wild animals.
This massive population is only sustained by consuming the planet. Agriculture is rapidly destroying the planet’s remaining soils, and crop yields only remain high due to massive infusions of fossil-fuel derived fertilizers. Dead zones are spreading in the ocean due to pollution from industrial farming running down major rivers. Rainforests are being felled to clear more land for agriculture. Global fish populations are collapsing due to overfishing, pollution, and global warming. Non-renewable aquifers are being overpumped and going dry.
The father of the “Green Revolution” himself, Norman Borlaug, in his Nobel Peace Prize acceptance speech, warned that “There can be no permanent progress in the battle against hunger until the agencies that fight for increased food production and those that fight for population control unite in a common effort.”
Can Overpopulation Be Solved without Violating Human Rights?
Coercive attempts to control population such as China’s one-child policy or forced sterilization policies in different regions of the world have been widely and rightfully condemned as human rights violations. Less widely known are population success stories that do not involve coercion. In Iran, for example, an exploding population in the 1990’s led the government to institute what is often celebrated as the world’s most successful humane birth-rate reduction program (which has since been rolled back in part to encourage economic growth.
Alan Weissman, writing in his 2013 book “Countdown: Our Last, Best Hope for a Future on Earth” in which he travels the world analyzing the issue of overpopulation, describes a conversation with Iranian Obstetrician and Gynecologist Dr. Hourieh Shamshiri Milani:
“There was no covert coercion [in Iran’s family planning program], she’d explain. The sole requirement was that all couples attend premarital classes, held in mosques or in health centers where couples went for prenuptial blood tests. The classes taught contraception and sex education, and stressed the advantages of having fewer children to feed, clothe, and school. The only governmental disincentive was elimination of the individual subsidy for food, electricity, telephone, and appliances for any child after the first three. By 2000, Iran’s total fertility rate reached replacement level, 2.1 children per woman, a year faster than China’s compulsory one-child policy. In 2012, it was 1.7.”
Reducing Birth Rates
To state the obvious, when birth rates are reduced below replacement level (2.1 children per couple), population will gradually and naturally fall over time. Eileen Crist, an associate professor in the Department of Science, Technology, and Society at Virginia Tech and author of a book on population issues, describes that process:
Environmental writers and activists who highlight the calamities connected with overpopulation are motivated by deep concern for the well-being of all life; they also emphasize that a smaller global population can be achieved by policies and actions that promote fundamental human rights. To achieve a sustainable human population, they urge the global community to pursue full gender equity; ensure education for girls (and all children) through secondary schooling and beyond; make high-quality family planning universally available; include comprehensive sexuality education in school curricula; and aggressively oppose the abusive cultural practice of child marriage. With these human rights ambitiously pursued and universally attained, population growth can end sooner (than via ‘the invisible hand’ of globalization) and a smaller global population gradually attained.
And what is the role of abortion in this? Given that roughly 44% of all pregnancies are unintended, and about half of those unintended pregnancies are terminated through abortions, researchers have concluded that no country can effectively reduce its population growth “without the widespread use of abortion.”
We believe that birth control including vasectomies, family planning services, abortion by mail providers, and abortion should be available to all people as part of efforts to defend the planet. Non-abortion family planning measures actually reduce the number of abortions performed, and thus should be supported by everyone regardless of their political beliefs on abortion (for example, today’s abortion rate in the United States is roughly half what it was in the 1980’s, which is believed to reflect easier access to contraceptives such as abortion pills by mail).
For the rights of women, and for environmental reasons, we are opposed to abortion bans.

by DGR News Service | Mar 14, 2022 | ANALYSIS, Building Alternatives, Culture of Resistance, Mining & Drilling, The Problem: Civilization
Editor’s Note: Unquestioned beliefs are the real authorities of any culture, and one of the central authorities in the dominant, globalizing culture is that technological progress is an unmitigated good. We call this “the lie of the techno-fix.”
The lie of the techno-fix is extremely convincing, with good reason. The propaganda promoting this idea is incessant and nearly subliminal, with billions of dollars pouring out of non-profit offices, New York PR firms, and Hollywood production companies annually to inculcate young people into the cult of technology. In policy, technology is rarely (if ever) subjected to any democratic controls; if it can be profitably made, it will be. And damn the consequences. There is money to be made.
Critics of technology and the techno-elite, such as Lewis Mumford, Rachel Carson, Langdon Winner, Derrick Jensen, and many others, have spoken out for decades on these issues. Technological “development,” they warn us, is perhaps better understood as technological “escalation,” since modern industrial technologies typically represent a war on the planet and the poor.
In this article, Helena Norberg-Hodge asks us to consider what values are important to us: progress, or well-being? Breakneck speed, or balance? She articulates a vision of technology as subordinate to ecology and non-human and human communities alike based on her experiences in the remote Himalayan region of Ladakh.
By Helena Norberg-Hodge
The most recent topic explored by the thinkers and activists who make up the Great Transition Network was “Technology and the Future”. As writer after writer posted their thoughts, it was heartening to see that almost all recognize that technology cannot provide real solutions to the many crises we face. I was also happy that Professor William Robinson, author of a number of books on the global economy, highlighted the clear connection between computer technologies and the further entrenchment of globalization today.
As anyone who has followed my work will know, globalization is of particular interest to me: for more than 40 years I’ve been studying its impacts on different cultures and societies around the world. From Ladakh and Bhutan to Sweden and Australia, a clear pattern has emerged: as people are pushed into deepening dependence on large-scale, technological systems, ecological and social crises escalate.
I’m not the only one to have seen this. In the International Forum on Globalization – a network I co-founded in 1992 – I worked with forty writers, journalists, academics and social and environmental leaders from around the world to inform the public about the ways in which “free-trade” treaties, the principal drivers of globalization, have eroded democracy, destroyed livelihoods, and accelerated resource extraction. In countries as disparate as Sweden and India, I have seen how globalization intensifies competition for jobs and resources, leading to dramatic social breakdown – including not only ethnic and religious conflict, but also depression, alcoholism and suicide.
Techno-Fix Failure
Professor Robinson wrote that we are “at the brink of another round of restructuring and transformation based on a much more advanced digitalization of entire global economy”. This is true, but the link between globalization and technological expansion began well before the computer era. Large-scale, technological apparatuses can be understood as the arms and legs of centralized profit-making. And while 5G networks, satellites, mass data-harvesting, artificial intelligence and virtual reality will allow the colonization of still more physical, economic and mental space by multinational corporations, technologies like fossil fuels, global trading infrastructures, and television have already helped to impose a corporate-run consumer-based economy in almost every corner of the globe.
For reasons that are increasingly evident, an acceleration of this process is the last thing we need in a time of serious social and environmental crises. What’s more, the technologies themselves – from the sensors to the satellites – all rely heavily on scarce resources, not least rare earth minerals. Some of the world’s richest corporations are now racing each other to extract these minerals from the deepest seabeds and from the surface of Mars. It has been estimated that the internet alone – with its largely invisible data warehouses (much of it manned by exploited labor in the “developing” world) – will use up a fifth of global electricity consumption by 2025.
Terminating Tradition
And for what? So that we can all spend more time immersed in and addicted to virtual worlds? So that we can automate agriculture, and drive more communities off the land into swelling urban slums? So that drones can deliver our online purchases without an iota of face-to-face contact?
When thinking about technology from within an already high-tech, urban context, we can easily forget that nearly half the global population still lives in villages, still connected to the land. This is not to say that their way of life is not under threat – far from it. Ladakh, the Himalayan region where I lived and worked for several decades, was unconnected to the outside world by even a road until the 1960s. But today you can find processed corporate food, smartphones, mountains of plastic waste, traffic jams and other signs of ‘modernity’ in the capital, Leh. The first steps on this path were taken in the mid-1970s when, in the name of ‘development’, massive resources went into building up the energy, communications and transport infrastructures needed to tie Ladakh to the global economy. Another step involved pulling Ladakhi children out of their villages into western-style schools, where they learned none of the place-based skills that supported Ladakh’s culture for centuries, and instead were trained into the technological-modernist paradigm. Together, these forces are pushing the traditional way of life to the brink of extinction.
While that process began relatively recently in Ladakh, in the west it has been going on far longer, with deeper impacts. But even here, more and more people are becoming aware that the technologization of their personal lives has led to increasing stress, isolation, and mental health struggles. During the pandemic people have been forced to do more online than ever before – from classes to conversations with friends and family – and most have discovered how limited and empty online life can be. There is a clear cultural turning, visible now even in the mainstream, that goes beyond a desire to spend less time on screens. People are also beginning to reject the posturing of the consumer culture and its work-and-spend treadmill, wanting instead to slow down, to cultivate deeper relationships and to engage in more community-oriented and nature-based activities.
Returning Ecology
I see young people all over the world choosing to leave their screen-based jobs to become farmers. (This return to the land is happening in Ladakh, as well, which I find truly inspiring.) Informal networks of mutual aid are arising. Friends are gardening, cooking and baking bread together; families are choosing to live on the land and developing relationships with the animals and plants around them. We are seeing increased respect for indigenous wisdom, for women and for the feminine, and a growing appreciation for wild nature and for all things vernacular, handmade, artisanal and local. There is also an emergence of alternative, ecological practices in every discipline: from natural medicine to natural building, from eco-psychology to ecological agriculture. Although these disciplines have often been the target of corporate co-optation and greenwashing, they have invariably emerged from bottom-up efforts to restore a healthier relationship with the Earth.
All of these are positive, meaningful trends that have been largely ignored by the media, and given no support by policymakers. At the moment, they are running uphill in a system that favors corporate-led technological development at every turn. They testify to enduring goodwill, to a deep human desire for connection.
When viewed from a big-picture perspective, the expansion of digital technologies – which are inherently centralized and centralizing – runs contrary to the emergence of a more humane, sustainable and genuinely connected future. Why should we accept an energy-and mineral-intensive technological infrastructure that is fundamentally about speeding life up, increasing our screen-time, automating our jobs, and tightening the grip of the 1%?
For a better future, we need to put technology back in its place, and favor democratically determined, diverse forms of development that are shaped by human and ecological priorities – not by the gimmicky fetishes of a handful of billionaires.
Helena Norberg-Hodge is founder and director of Local Futures. A pioneer of the “new economy” movement, she has been promoting an economics of personal, social and ecological well-being for over 40 years. She is the producer and co-director of the award-winning documentary The Economics of Happiness, and is the author of Local is Our Future and Ancient Futures: Learning from Ladakh. She was honored with the Right Livelihood Award for her groundbreaking work in Ladakh, and received the 2012 Goi Peace Prize for contributing to “the revitalization of cultural and biological diversity, and the strengthening of local communities and economies worldwide.”
This article first appeared in Local Futures.
Banner image: road sign in Ladakh, via Unsplash.

by DGR News Service | Dec 17, 2021 | Biodiversity & Habitat Destruction, Climate Change, Colonialism & Conquest, Human Supremacy, The Problem: Civilization, The Solution: Resistance
This article was produced by Local Peace Economy, a project of the Independent Media Institute.
By Koohan Paik-Mander
The U.S. military is famous for being the single largest consumer of petroleum products in the world and the largest emitter of greenhouse gases. Its carbon emissions exceed those released by “more than 100 countries combined.”
Now, with the Biden administration’s mandate to slash carbon emissions “at least in half by the end of the decade,” the Pentagon has committed to using all-electric vehicles and transitioning to biofuels for all its trucks, ships and aircraft. But is only addressing emissions enough to mitigate the current climate crisis?
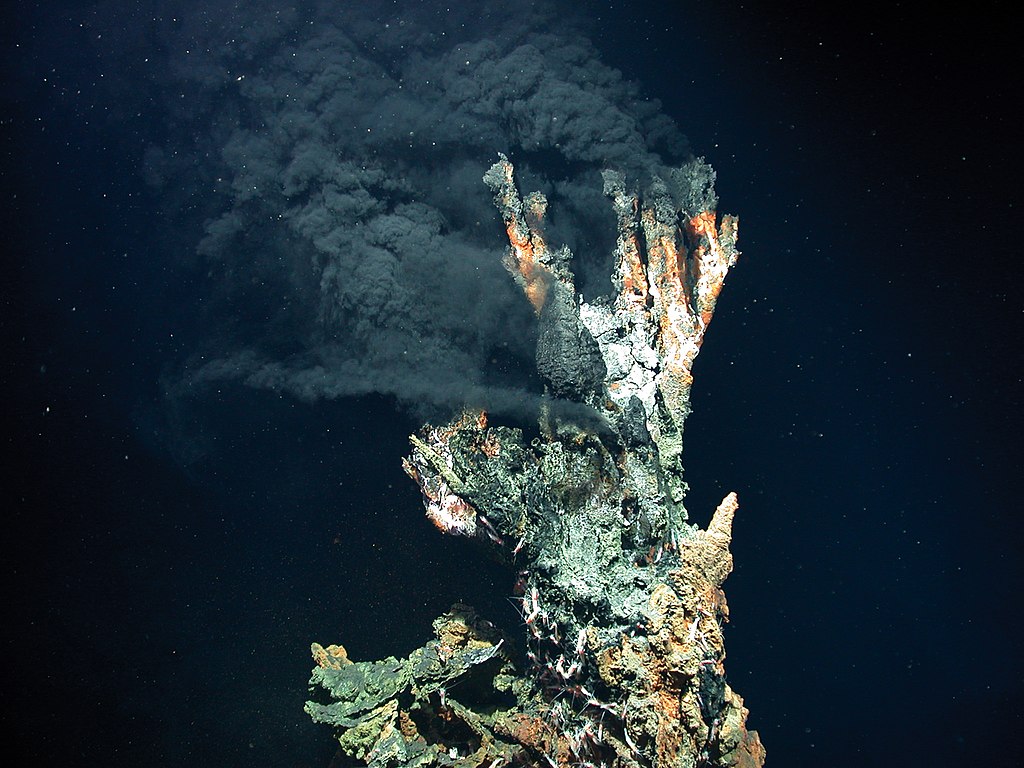
What does not figure into the climate calculus of the new emission-halving plan is that the Pentagon can still continue to destroy Earth’s natural systems that help sequester carbon and generate oxygen. For example, the plan ignores the Pentagon’s continuing role in the annihilation of whales, in spite of the miraculous role that large cetaceans have played in delaying climate catastrophe and “maintaining healthy marine ecosystems,” according to a report by Whale and Dolphin Conservation. This fact has mostly gone unnoticed until only recently.
There are countless ways in which the Pentagon hobbles Earth’s inherent abilities to regenerate itself. Yet, it has been the decimation of populations of whales and dolphins over the last decade—resulting from the year-round, full-spectrum military practices carried out in the oceans—that has fast-tracked us toward a cataclysmic environmental tipping point.
The other imminent danger that whales and dolphins face is from the installation of space-war infrastructure, which is taking place currently. This new infrastructure comprises the development of the so-called “smart ocean,” rocket launchpads, missile tracking stations and other components of satellite-based battle. If the billions of dollars being plowed into the 2022 defense budget for space-war technology are any indication of what’s in store, the destruction to marine life caused by the use of these technologies will only accelerate in the future, hurtling Earth’s creatures to an even quicker demise than already forecast.
Whale Health: The Easiest and Most Effective Way to Sequester Carbon
It’s first important to understand how whales are indispensable to mitigating climate catastrophe, and why reviving their numbers is crucial to slowing down damage and even repairing the marine ecosystem. The importance of whales in fighting the climate crisis has also been highlighted in an article that appeared in the International Monetary Fund’s Finance and Development magazine, which calls for the restoration of global whale populations. “Protecting whales could add significantly to carbon capture,” states the article, showing how the global financial institution also recognizes whale health to be one of the most economical and effective solutions to the climate crisis.
Throughout their lives, whales enable the oceans to sequester a whopping 2 billion metric tons of carbon dioxide per year. That astonishing amount in a single year is nearly double the 1.2 billion metric tons of carbon that was emitted by the U.S. military in the entire 16-year span between 2001 and 2017, according to an article in Grist, which relied on a paper from the Costs of War Project at Brown University’s Watson Institute.
The profound role of whales in keeping the world alive is generally unrecognized. Much of how whales sequester carbon is due to their symbiotic relationship with phytoplankton, the organisms that are the base of all marine food chains.
The way the sequestering of carbon by whales works is through the piston-like movements of the marine mammals as they dive to the depths to feed and then come up to the surface to breathe. This “whale pump” propels their own feces in giant plumes up to the surface of the water. This helps bring essential nutrients from the ocean depths to the surface areas where sunlight enables phytoplankton to flourish and reproduce, and where photosynthesis promotes the sequestration of carbon and the generation of oxygen. More than half the oxygen in the atmosphere comes from phytoplankton. Because of these infinitesimal marine organisms, our oceans truly are the lungs of the planet.
More whales mean more phytoplankton, which means more oxygen and more carbon capture. According to the authors of the article in the IMF’s Finance and Development magazine—Ralph Chami and Sena Oztosun, from the IMF’s Institute for Capacity Development, and two professors, Thomas Cosimano from the University of Notre Dame and Connel Fullenkamp from Duke University—if the world could increase “phytoplankton productivity” via “whale activity” by only 1 percent, it “would capture hundreds of millions of tons of additional CO2 a year, equivalent to the sudden appearance of 2 billion mature trees.”
Even after death, whale carcasses function as carbon sinks. Every year, it is estimated that whale carcasses transport 190,000 tons of carbon, locked within their bodies, to the bottom of the sea. That’s the same amount of carbon produced by 80,000 cars per year, according to Sri Lankan marine biologist Asha de Vos, who appeared on TED Radio Hour on NPR. On the seafloor, this carbon supports deep-sea ecosystems and is integrated into marine sediments.
Vacuuming CO2 From the Sky—a False Solution
Meanwhile, giant concrete-and-metal “direct air carbon capture” plants are being planned by the private sector for construction in natural landscapes all over the world. The largest one began operation in 2021 in Iceland. The plant is named “Orca,” which not only happens to be a type of cetacean but is also derived from the Icelandic word for “energy” (orka).
Orca captures a mere 10 metric tons of CO2 per day—compared to about 5.5 million metric tons per day of that currently sequestered by our oceans, due, in large part, to whales. And yet, the minuscule comparative success by Orca is being celebrated, while the effectiveness of whales goes largely unnoticed. In fact, President Joe Biden’s $1 trillion infrastructure bill contains $3.5 billion for building four gigantic direct air capture facilities around the country. Nothing was allocated to protect and regenerate the real orcas of the sea.
If ever there were “superheroes” who could save us from the climate crisis, they would be the whales and the phytoplankton, not the direct air capture plants, and certainly not the U.S. military. Clearly, a key path forward toward a livable planet is to make whale and ocean conservation a top priority.
‘We Have to Destroy the Village in Order to Save It’
Unfortunately, the U.S. budget priorities never fail to put the Pentagon above all else—even a breathable atmosphere. At a December 2021 hearing on “How Operational Energy Can Help Us Address Logistics Challenges” by the Readiness Subcommittee of the U.S. House Armed Services Committee, Representative Austin Scott (R-GA) said, “I know we’re concerned about emissions and other things, and we should be. We can and should do a better job of taking care of the environment. But ultimately, when we’re in a fight, we have to win that fight.”
This logic that “we have to destroy the village in order to save it” prevails at the Pentagon. For example, hundreds of naval exercises conducted year-round in the Indo-Pacific region damage and kill tens of thousands of whales annually. And every year, the number of war games, encouraged by the U.S. Department of Defense, increases.
They’re called “war games,” but for creatures of the sea, it’s not a game at all.
Pentagon documents estimate that 13,744 whales and dolphins are legally allowed to be killed as “incidental takes” during any given year due to military exercises in the Gulf of Alaska.
In waters surrounding the Mariana Islands in the Pacific Ocean alone, the violence is more dire. More than 400,000 cetaceans comprising 26 species were allowed to have been sacrificed as “takes” during military practice between 2015 and 2020.
These are only two examples of a myriad of routine naval exercises. Needless to say, these ecocidal activities dramatically decrease the ocean’s abilities to mitigate climate catastrophe.
The Perils of Sonar
The most lethal component to whales is sonar, used to detect submarines. Whales will go to great lengths to get away from the deadly rolls of sonar waves. They “will swim hundreds of miles… and even beach themselves” in groups in order to escape sonar, according to an article in Scientific American. Necropsies have revealed bleeding from the eyes and ears, caused by too-rapid changes in depths as whales try to flee the sonar, revealed the article.
Low levels of sonar that may not directly damage whales could still harm them by triggering behavioral changes. According to an article in Nature, a 2006 UK military study used an array of hydrophones to listen for whale sounds during marine maneuvers. Over the period of the exercise, “the number of whale recordings dropped from over 200 to less than 50,” Nature reported.
“Beaked whale species… appear to cease vocalising and foraging for food in the area around active sonar transmissions,” concluded a 2007 unpublished UK report, which referred to the study.
The report further noted, “Since these animals feed at depth, this could have the effect of preventing a beaked whale from feeding over the course of the trial and could lead to second or third order effects on the animal and population as a whole.”
The report extrapolated that these second- and third-order effects could include starvation and then death.
The ‘Smart Ocean’ and the JADC2
Until now, sonar in the oceans has been exclusively used for military purposes. This is about to change. There is a “subsea data network” being developed that would use sonar as a component of undersea Wi-Fi for mixed civilian and military use. Scientists from member nations of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), including, but not limited to Australia, China, the UK, South Korea and Saudi Arabia, are creating what is called the “Internet of Underwater Things,” or IoUT. They are busy at the drawing board, designing data networks consisting of sonar and laser transmitters to be installed across vast undersea expanses. These transmitters would send sonar signals to a network of transponders on the ocean surface, which would then send 5G signals to satellites.
Utilized by both industry and military, the data network would saturate the ocean with sonar waves. This does not bode well for whale wellness or the climate. And yet, promoters are calling this development the “smart ocean.”
The military is orchestrating a similar overhaul on land and in space. Known as the Joint All-Domain Command and Control (JADC2), it would interface with the subsea sonar data network. It would require a grid of satellites that could control every coordinate on the planet and in the atmosphere, rendering a real-life, 3D chessboard, ready for high-tech battle.
In service to the JADC2, thousands more satellites are being launched into space. Reefs are being dredged and forests are being razed throughout Asia and the Pacific as an ambitious system of “mini-bases” is being erected on as many islands as possible—missile deployment stations, satellite launch pads, radar tracking stations, aircraft carrier ports, live-fire training areas and other facilities—all for satellite-controlled war. The system of mini-bases, in communication with the satellites, and with aircraft, ships and undersea submarines (via sonar), will be replacing the bulky brick-and-mortar bases of the 20th century.
Its data-storage cloud, called JEDI (Joint Enterprise Defense Infrastructure), will be co-developed at a cost of tens of billions of dollars. The Pentagon has requested bids on the herculean project from companies like Microsoft, Amazon, Oracle and Google.
Save the Whales, Save Ourselves
Viewed from a climate perspective, the Department of Defense is flagrantly barreling away from its stated mission, to “ensure our nation’s security.” The ongoing atrocities of the U.S. military against whales and marine ecosystems make a mockery of any of its climate initiatives.
While the slogan “Save the Whales” has been bandied about for decades, they’re the ones actually saving us. In destroying them, we destroy ourselves.
Koohan Paik-Mander, who grew up in postwar Korea and in the U.S. colony of Guam, is a Hawaii-based journalist and media educator. She is a board member of the Global Network Against Weapons and Nuclear Power in Space, a member of the CODEPINK working group China Is Not Our Enemy, and an advisory committee member for the Global Just Transition project at Foreign Policy in Focus. She formerly served as campaign director of the Asia-Pacific program at the International Forum on Globalization. She is the co-author of The Superferry Chronicles: Hawaii’s Uprising Against Militarism, Commercialism and the Desecration of the Earth and has written on militarism in the Asia-Pacific for the Nation, the Progressive, Foreign Policy in Focus and other publications.
Banner image: flickr (CC BY-NC-ND 2.0)

by DGR News Service | Nov 24, 2021 | Biodiversity & Habitat Destruction, Human Supremacy, Mining & Drilling, The Problem: Civilization
This story first appeared in Mongabay.
Editor’s note: O Canada! Welcome to the new wild west. If you liked Deepwater Horizon you will love Deep Sea Mining. This statement pretty much sums it up, “countries could have their chance to EXPLOIT the valuable metals locked in the deep sea.” Corporations love to deal with poorer, less developed countries who can do less by way of supervision because they lack greater resources and capacity.
“Like NORI, TOML began its life as a subsidiary of Nautilus minerals, one of the world’s first deep-sea miners. Just before Nautilus’s project in Papua New Guinea’s waters failed and left the country $157 million in debt, its shareholders created DeepGreen. DeepGreen acquired TOML in early 2020 after Nautilus filed for bankruptcy, the ISA said the Tongan government allowed the transfer and reevaluating the company’s background was not required.”
And mining royalties are paid to the ISA. If this doesn’t sound fishy, I don’t know what does. There never should be a question as to what a corporation’s angle is. Their loyalty always is to the stockholders.
By Ian Morse
- Citizens of countries that sponsor deep-sea mining firms have written to several governments and the International Seabed Authority expressing concern that their nations will struggle to control the companies and may be liable for damages to the ocean as a result.
- Liability is a central issue in the embryonic and risky deep-sea mining industry, because the company that will likely be the first to mine the ocean floor — DeepGreen/The Metals Company — depends on sponsorships from small Pacific island states whose collective GDP is a third its valuation.
- Mining will likely cause widespread damage, scientists say, but the legal definition of environmental damage when it comes to deep-sea mining has yet to be determined.
Pelenatita Kara travels regularly to the outer islands of Tonga, her low-lying Pacific Island home, to educate fishers and farmers about seabed mining. For many of the people she meets, seabed mining is an unfamiliar term. Before Kara began appearing on radio programs, few people knew their government had sponsored a company to mine minerals from the seabed.
“It’s like talking to a Tongan about how cold snow is,” she says. “Inconceivable.”
The Civil Society Forum of Tonga, where Kara works, and several other Pacific-based organizations have written to several governments and the International Seabed Authority (ISA) to express concerns that their countries may end up being responsible for environmental damage that occurs in the mineral-rich Clarion-Clipperton Zone, an expanse of ocean between Hawai‘i and Mexico.
“The Pacific is currently the world’s laboratory for the experiment of Deep Seabed Mining,” the groups wrote to the ISA, the U.N.-affiliated body tasked with regulating the nascent industry. As a state that sponsors a seabed mining company, Tonga has agreed to shoulder a significant amount of responsibility in this fledgling industry that may threaten ecosystems that are barely understood. And if anything goes wrong in the laboratory, Kara is worried that Tonga’s liabilities could exceed its ability to pay. If no one can pay for remediation, Greenpeace notes, that may be even worse.
“My concern is that the liability from any problem with deep-sea mining will just be too much for us,” Kara says.
Another Pacific Island state, Nauru, notified the ISA in June that a contractor it sponsors is applying for the world’s first deep-sea mining exploitation permits. The announcement triggered the “two-year rule,” which compels the ISA to consider the application within that period, regardless of whether the exploitation rules and regulations are completed by then.
Among the rules that may not be decided upon by the deadline is liability: Who is responsible if something goes wrong? Sponsoring states like Nauru, Tonga and Kiribati — which all sponsor contractors owned by Canada-based DeepGreen, now The Metals Company — are required to “ensure compliance” with ISA rules and regulations. If a contractor breaches ISA rules, such as causing greater damage to ocean ecosystems than expected, the contractor may be held liable if the sponsoring state did all they could to enforce strict national laws.
However, it’s not yet clear how these countries can persuade the ISA that they enforced the rules, nor how they can prove that they are able to control the contractors, when the company is foreign-owned. The responsibility of sponsoring states to fund potentially billions of dollars in environmental cleanup depends on the legal definitions of terms like “environmental damage” and “effective control,” which may be as murky two years from now as they are at present.
Myriad problems may occur in the mining area: sediment plumes may travel thousands of kilometers and obstruct fisheries, or damage could spread into other companies’ areas. Scientists don’t know all the possible consequences, in part because these ecosystems are poorly understood. The ISA has proposed the creation of a fund to help cover the costs, but it’s not clear who will pay into it.
“The scales of the areas impacted are so great that restoration is just not feasible,” says Craig Smith, an oceanography professor emeritus at the University of Hawai‘i, who has worked with the ISA since its creation in 1994. “To restore tens or hundreds of thousands of square kilometers would be probably more expensive than the mining operation itself.”
Nauru voices concerns
Just over a decade ago, before Nauru agreed to sponsor a deep-sea mining permit, the government worried that it was going to find itself responsible for paying those damages. The government wrote to the International Tribunal for the Law of the Sea, voicing concerns about the liability it could incur. As a sponsoring state with no experience in deep-sea mining and a small budget to support it, the delegation wanted to make sure that the U.N. did not prioritize rich countries in charting this new frontier in mineral extraction. Nauru and other “developing” countries should have just as great an opportunity to benefit from mining as other countries with more experience in capital-intensive projects, they argued.
Sponsoring states like Nauru are required to ensure their contractors comply with the law but, the delegation wrote, “in reality no amount of measures taken by a sponsoring State could ever fully ‘secure compliance’ of a contractor when the contractor is a separate entity from the State.”
Seabed mining comes with risks — environmental, financial, business, political — which sponsoring states are required to monitor. According to Nauru’s 2010 request, “it is unfortunately not possible for developing States to perform their responsibilities to the same standard or on the same scale as developed States.” If the standards of those responsibilities varied according to the capabilities of states, the Nauru delegation wrote, both poor and rich countries could have their chance to exploit the valuable metals locked in the deep sea.
“Poorer, less developed states, it was argued, would have to do less by way of supervision because they lacked greater resources and capacity,” says Don Anton, who was legal counsel to the tribunal during the decision on behalf of the IUCN, the global conservation authority.
The tribunal, issuing a final court opinion the next year, disagreed. Each state that sponsored a deep-sea miner would be required to uphold the same standards of due diligence and measures that “ensure compliance.” Legal experts generally regarded the decision well, because it prevented contractors from seeking sponsorships with states that placed lower requirements on their activities. However, according to Anton, the decision meant that countries with limited budgets like Nauru have only two choices when they consider deep-sea mining: either sponsor a contractor entirely, or avoid the business altogether.
According to the tribunal’s decision, “you cannot excuse yourself as a sponsoring state by referring to your limited financial or administrative capacity,” says Isabel Feichtner, a law professor at the University of Würzburg in Germany. “And that of course raises the question: To what extent can a small developing state really control a contractor who might just have an office in that state?”
Nauru had just begun sponsoring a private company to explore the mineral riches at the bottom of the sea Clarion-Clipperton Zone. Nauru Ocean Resources Inc. (NORI), initially a subsidiary of Canada-based Nautilus Minerals, transferred its ownership to two Nauru foundations while the founder of Nautilus remained on NORI’s board. As a developing state, Nauru said, this kind of public-private partnership was the only way that it could join mineral exploration.
Nauru discussed the tribunal’s decision behind closed doors, according to a top official there at the time, and the government sought no independent consultation, hearing only guidance from Nautilus. Two months after the tribunal gave its opinion, Nauru officially agreed to sponsor NORI.
Control
After the tribunal’s decision, the European Union recognized that writing the world’s first deep-sea mining rules to govern companies thousands of miles away would be a tall order for countries with little capacity to conduct research.
The EU, whose member states also sponsor mining exploration, began in 2011 a 4.4 million euro ($5.1 million) project to help Pacific island states develop mining codes. However, by 2018, when most states had finished drafting national regulations, the Pacific Network on Globalization (PANG) found that the mining codes did “not sufficiently safeguard the rights of indigenous peoples or protect the environment in line with international law.” In addition, in some cases countries enacted legislation before civil society actors were aware that there was legislation, says PANG executive director Maureen Penjueli.
“In our region, most of our legislation assumes impact is very small, so there’s no reason to consult widely,” she says. “We found in most legislations is that it is assumed it’s only where mining takes place, not where impacts are felt.”
For Kara, mining laws are one thing, but enforcement is another. Sponsoring states must have “effective control” over the companies they sponsor, according to mineral exploration rules, but the ISA has not explicitly defined what that means. For example, the exploration contract for Tonga Offshore Mining Limited (TOML) says that if “control” changes, it must find a new sponsoring state. When DeepGreen acquired TOML in early 2020 after Nautilus filed for bankruptcy, the ISA said the Tongan government allowed the transfer and reevaluating the company’s background was not required.
Kara questions whether Tonga can adequately control TOML, its management, and its activities. TOML is registered in Tonga, but its management consists of Australian and Canadian employees of DeepGreen. It is owned by the Canadian company. Since DeepGreen acquired TOML, the only Tongan national in the company is no longer listed in a management role.
“It’s not enough to be incorporated in the sponsoring state. The sponsoring state must also be able to control the contractor and that raises the question as to the capacity to control,” Feichtner says.
When Kara’s Civil Society Forum of Tonga and others wrote to the ISA, they argued Canada should be the state sponsor of TOML, considering TOML is owned by a Canadian firm. In response, the ISA wrote that the Tongan government “has no objection” to the management changes, so no change was needed.
“Of all the work they’re doing in the area, I don’t know whether there’s any Tongan sitting there, doing the so-called validation and ascertaining what they do. We’re taking all of this at face value,” Kara says. With few resources to track down people who live in Canada or Australia, Kara is worried that Tonga will not be able to hold foreign individuals accountable for problems that may arise.
In merging with a U.S.-based company, DeepGreen became The Metals Company and will be responsible to shareholders in the U.S. The U.S., however, has not signed on to the U.N. convention that guides the ISA, and as such is not bound by ISA regulations, the only authority governing mining in the high seas.
“What I think is pretty clear is that ‘effective control’ means economic, not regulatory, control,” says Duncan Currie, a lawyer who advises conservation groups on ocean law. “So wherever it is, it’s not in Tonga.”
The risks
On Sept. 7, Tonga’s delegation to the IUCN’s global conservation summit in France joined 80% of government agencies that voted for a motion calling for a moratorium on deep-sea mining until more was known about the impacts and implications of policies.
“As a scientist, I am heartened by their decision,” says Douglas McCauley a professor of ocean science at the University of California, Santa Barbara. “The passage of this motion acknowledges research from scientists around the world showing that ocean mining is simply too risky a proposition for the planet and people.”
Tonga’s government continues to sponsor an exploration permit for TOML. According to the latest information, Tonga and TOML have agreed that the company will pay $1.25 in royalties for every ton of nodules mined. That may amount to just 0.16% of the value of the activities the country sponsors, according to scenarios presented to the ISA by a group from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Royalties paid to the ISA and then distributed to countries may be around $100,000.
Nauru’s contract with NORI stipulates that the company is not required to pay income tax. DeepGreen has reported in filings to the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission that royalties will not be finalized until the ISA completes the exploitation code. With the two-year rule, NORI plans to apply for a mining permit, regardless of when the code is written.
“The only substantial economic benefit [Nauru] might derive is from royalty payments, and these are not even specified yet. and on the other hand, it potentially incurs this huge liability if something goes wrong,” Feichtner says.
Like NORI, TOML began its life as a subsidiary of Nautilus minerals, one of the world’s first deep-sea miners. Just before Nautilus’s project in Papua New Guinea’s waters failed and left the country $157 million in debt, its shareholders created DeepGreen.
“I am afraid that Tonga will be another Papua New Guinea,” Kara says. “If they start mining and something happens out there, we don’t have the resources, the expertise, because we need to validate what they’re doing.”
DeepGreen has said it is giving “developing” states like Tonga the opportunity to benefit from seabed mining without shouldering the commercial and technical risk. DeepGreen did not respond to Mongabay’s requests for comment.
“I’m still trying to figure out their angle. Personally, I think DeepGreen is using Pacific islanders to hype their image. I’m still thinking that we were never really the target. The shareholders have always been their target,” Kara says.
She says she doubts the minerals at the bottom of the ocean are needed for the world to transition away from fossil fuels. In a letter to a Tongan newspaper, Kara wrote, “Deep-sea mining is a relic, left over from the extractive economic approaches of the ’60s and ’70s. It has no place in this modern age of a sustainable blue economy. As Pacific Islanders already know — and science is just starting to learn — the deep ocean is connected to shallower waters and the coral reefs and lagoons. What happens in the deep doesn’t stay in the deep.”

by DGR News Service | Nov 23, 2021 | Culture of Resistance, Defensive Violence, Direct Action, Repression at Home, Strategy & Analysis, The Solution: Resistance
This story first appeared in Building a Revolutionary Movement
By Adam H
This post briefly describes 25 anarchist thinkers, following on from the political ideology post. I took the list of anarchist thinkers from ‘Demanding the Impossible: A History of Anarchism’ by Peter Marshall.
William Godwin
William Godwin (1756-1836) is said to be the founder of philosophical anarchism. In his book An Enquiry Concerning Political Justice (1793), he argued that “government is a corrupting force in society, perpetuating dependence and ignorance, but that it will be rendered increasingly unnecessary and powerless by the gradual spread of knowledge and the expansion of the human understanding. Politics will be displaced by an enlarged personal morality as truth conquers error and mind subordinates matter. In this development the rigorous exercise of private judgment, and its candid expression in public discussion, plays a central role, motivating his rejection of a wide range of co-operative and rule-governed practices which he regards as tending to mental enslavement, such as law, private property, marriage and concerts.”
Inspired by the optimism of the French Revolution, Godwin believed a time would come when the mind would dominate matter so ‘mental perfectibility’ would take physical form so it would be possible to control illness, ageing resulting in humans becoming immortal. Godwin’s moral theory is described as utilitarian. [1]
Max Stirner
Max Stirner (1806–1856) is the author of Der Einzige und sein Eigenthum (1844). In English, it is known as The Ego and Its Own or The Unique Individual and their Property. It is argued that “the form and content of Stirner’s major work are disconcerting. He challenges expectations about how political and philosophical arguments should be conducted and shakes the reader’s confidence in the moral and political superiority of contemporary civilisation. Stirner provides a sweeping attack on the modern world as increasingly dominated by “religious” modes of thought and oppressive social institutions, together with a much briefer sketch of a radical “egoistic” alternative in which individual autonomy might flourish. The historical impact of The Ego and Its Own is sometimes difficult to assess, but Stirner’s work can confidently be said: to have had an immediate and destructive impact on the left-Hegelian movement; to have played an important contemporary role in the intellectual development of Karl Marx (1818–1883); and subsequently to have influenced significantly the political tradition of individualist anarchism.” [2]
Pierre-Joseph Proudhon
Pierre-Joseph Proudhon (1809 – 1865) was a French socialist, politician, philosopher, economist and the founder of mutualist philosophy. He was the first person to describe himself as an anarchist and is a very influential anarchist thinker, with some describing him as the ‘father of anarchism’.
“Proudhon became a member of the French Parliament after the Revolution of 1848, whereafter he referred to himself as a federalist. Proudhon described the liberty he pursued as “the synthesis of communism and property”. Some consider his mutualism to be part of individualist anarchism while others regard it to be part of social anarchism.
His first major work was What Is Property? (1840), where is asserted that ‘property is theft’. His work interested Karl Marx and they become friends. This ended with their disagreement over Proudhon’s The System of Economic Contradictions, or The Philosophy of Poverty (1846).
Proudhon advocated workers’ councils, associations and cooperatives, plus individual worker/peasant possession over private ownership or the nationalisation of land and workplaces. He believed social revolution was achievable peacefully. “Proudhon unsuccessfully tried to create a national bank, to be funded by what became an abortive attempt at an income tax on capitalists and shareholders. Similar in some respects to a credit union, it would have given interest-free loans.” [3]
Michael Bakunin
Mikhail Bakunin (1814 – 1976) was a Russian revolutionary anarchist, socialist and founder of collectivist anarchism. He is also a very influential anarchist and believed to be the founder of the revolutionary socialist and social anarchist traditions.
His revolutionary politics caused him to move between several countries, be deported from Germany and be imprisoned in Russia. He joined the International Worker Men’s Association and led the anarchist faction. There was a conflict between Bakunin and Marx, with the latter arguing for the use of the state to introduce socialism. “Bakunin and the anarchist faction argued for the replacement of the state by federations of self-governing workplaces and communes.” The anarchists lost the conflict and Bakunin was expelled from the International. Bakunin founded the Anti-Authoritarian International in 1872. From 1870 Bakunin wrote several texts on the State, anarchism and God. He was also involved in several European movements including insurrections in France and Italy.
Bakunin is believed to have “had a significant influence on thinkers such as Peter Kropotkin, Errico Malatesta, Herbert Marcuse, E. P. Thompson, Neil Postman and A. S. Neill as well as syndicalist organizations such as the Wobblies, the anarchists in the Spanish Civil War and contemporary anarchists involved in the modern-day anti-globalization movement.” [4]
Peter Kropotkin
Pyotr Alexeyevich Kropotkin (184 – 1921) was a “Russian anarchist, socialist, revolutionary, economist, sociologist, historian, zoologist, political scientist, human geographer and philosopher who advocated anarcho-communism. He was also an activist, essayist, researcher and writer.”
“Born into an aristocratic land-owning family, Kropotkin attended a military school and later served as an officer in Siberia, where he participated in several geological expeditions. He was imprisoned for his activism in 1874 and managed to escape two years later. He spent the next 41 years in exile in Switzerland, France (where he was imprisoned for almost four years) and England. While in exile, he gave lectures and published widely on anarchism and geography. Kropotkin returned to Russia after the Russian Revolution in 1917, but he was disappointed by the Bolshevik state.”
“Kropotkin was a proponent of a decentralised communist society free from central government and based on voluntary associations of self-governing communities and worker-run enterprises. He wrote many books, pamphlets and articles, the most prominent being The Conquest of Bread and Fields, Factories and Workshops, but also Mutual Aid: A Factor of Evolution, his principal scientific offering. He contributed the article on anarchism to the Encyclopædia Britannica Eleventh Edition[14] and left unfinished a work on anarchist ethical philosophy.” [5]
Élisée Reclus
Jacques Élisée Reclus (1830 – 1905) “was a renowned French geographer, writer and anarchist. He produced his 19-volume masterwork, La Nouvelle Géographie universelle, la terre et les hommes (‘Universal Geography’), over a period of nearly 20 years (1875–1894). In 1892 he was awarded the Gold Medal of the Paris Geographical Society for this work, despite having been banished from France because of his political activism. Reclus advocated nature conservation and opposed meat-eating and cruelty to animals. He was a vegetarian. As a result, his ideas are seen by some historians and writers as anticipating the modern social ecology and animal rights movements.” [6]
Errico Malatesta
Errico Malatesta (14 December 1853 – 22 July 1932) “was an Italian anarchist and revolutionary socialist. He spent much of his life exiled from Italy and in total spent more than ten years in prison. Malatesta wrote and edited a number of radical newspapers and was also a friend of Mikhail Bakunin.”
It has been described that Malatesta had a two-part strategy by the start of the nineteenth century. First, the unification of the anarchist and anti-parliamentary socialists into a new anarchist socialist party as anarchism was a minority movement on the Italian left. The other part was to advocate a syndicalist strategy to encourage socialists into insurrections and to maintain their revolutionary conscience. Malatesta’s form of anarchist communism can be described as ‘anarchism without adjectives’.
Others describe Malatesta’s form of anarchism to be ‘anarchist socialism’, which promoted the socialist character of anarchism and the need for anarchists to regain contact with workers, especially through the labour movement. [7]
Leo Tolstoy
Count Lev Nikolayevich Tolstoy (1828 – 1910) was a Russian writer who is regarded as one of the greatest authors of all time. Born into an aristocratic Russian family and best known for the novels War and Peace (1869) and Anna Karenina (1878).
“In the 1870s, Tolstoy experienced a profound moral crisis, followed by what he regarded as an equally profound spiritual awakening, as outlined in his non-fiction work A Confession (1882). His literal interpretation of the ethical teachings of Jesus, centering on the Sermon on the Mount, caused him to become a fervent Christian anarchist and pacifist. His ideas on nonviolent resistance, expressed in such works as The Kingdom of God Is Within You (1894), had a profound impact on such pivotal 20th-century figures as Mahatma Gandhi and Martin Luther King Jr. He also became a dedicated advocate of Georgism, the economic philosophy of Henry George, which he incorporated into his writing, particularly Resurrection (1899).” [8]
Josiah Warren
Josiah Warren (1798 – 1874) “was an American utopian socialist, individualist philosopher, polymath, social reformer, inventor, musician, printer and author. He is regarded by some as the first American anarchist (although Warren never used the term anarchism himself) and the four-page weekly paper he edited during 1833, The Peaceful Revolutionist, the first anarchist periodical published, was an enterprise for which he built his own printing press, cast his own type, and made his own printing plates.” [9]
Lysander Spooner
Lysander Spooner (1808 – 1887) “was an American individualist anarchist. He was also an abolitionist, entrepreneur, essayist, legal theorist, pamphletist, political philosopher, Unitarian, writer and a member of the First International. Spooner was a strong advocate of the labor movement and anti-authoritarian and individualist anarchist in his political views. His economic and political ideology has usually been identified as libertarian socialism and mutualism. His writings contributed to the development of both left-libertarian and right-libertarian political theory within libertarianism in the United States. Spooner’s writings include the abolitionist book The Unconstitutionality of Slavery and No Treason: The Constitution of No Authority, which opposed treason charges against secessionists. Spooner is also known for competing with the Post Office with his American Letter Mail Company. However, it was closed after legal problems with the federal government.” [10]
Benjamin Tucker
Benjamin Ricketson Tucker (1854 – 1939) “was an American anarchist and libertarian socialist. A 19th-century proponent of individualist anarchism which he called “unterrified Jeffersonianism”, Tucker was the editor and publisher of the American individualist anarchist periodical Liberty (1881–1908) as well as a member of the socialist First International. Tucker harshly opposed state socialism and was a supporter of libertarian socialism which he termed anarchist or anarchistic socialism as well as a follower of mutualism. He connected the classical economics of Adam Smith and the Ricardian socialists as well as that of Josiah Warren, Karl Marx and Pierre-Joseph Proudhon to socialism. Later in his life, Tucker converted to Max Stirner’s egoism.” [11]
Adin Ballou
Adin Ballou (1803 – 1890) “was an American proponent of Christian nonresistance, Christian anarchism and socialism, abolitionism, and the founder of the Hopedale Community. Through his long career as a Universalist and Unitarian minister, he tirelessly advocated for the immediate abolition of slavery, the principles of Christian anarcho-socialism, and promoted the nonviolent theory of praxis (or moral suasion) in his prolific writings. Such writings drew the admiration of Leo Tolstoy, who frequently cited Ballou as a major influence on his theological and political ideology in his non-fiction texts like The Kingdom of God is Within You, along with sponsoring Russian translations of some of Ballou’s works. As well as heavily inspiring Tolstoy, Ballou’s Christian anarchist and nonresistance ideals in texts like Practical Christianity were passed down from Tolstoy to Mahatma Gandhi, contributing not only to the nonviolent resistance movement in the Russian Revolution led by the Tolstoyans, but also Gandhi’s early thinkings on the nonviolent theory of praxis and the development of his first ashram, the Tolstoy Farm. In a recent publication, American philosopher and anarchist Crispin Sartwell wrote that the works by Ballou and his other Christian anarchist contemporaries like William Lloyd Garrison directly influenced Gandhi and Martin Luther King Jr., as well.” [12]
John Humphrey Noyes
John Humphrey Noyes (1811 – 1886) “was an American preacher, radical religious philosopher, and utopian socialist. He founded the Putney, Oneida and Wallingford Communities, and is credited with coining the term ‘complex marriage’.” [13]
Voltairine de Cleyre
Voltairine de Cleyre (1866 – 1912) “was an American anarchist known for being a prolific writer and speaker who opposed capitalism, marriage and the state as well as the domination of religion over sexuality and women’s lives which she saw as all interconnected. She is often characterized as a major early feminist because of her views. Born and raised in small towns in Michigan and schooled in a Sarnia, Ontario, Catholic convent, de Cleyre began her activist career in the freethought movement. Although she was initially drawn to individualist anarchism, de Cleyre evolved through mutualism to what she called anarchism without adjectives, prioritizing a stateless society without the use of aggression or coercion above all else. De Cleyre was a contemporary of Emma Goldman, with whom she maintained a relationship of respectful disagreement on many issues. Many of de Cleyre’s essays were collected in the Selected Works of Voltairine de Cleyre, published posthumously by Goldman’s magazine Mother Earth in 1914.” [14]
Emma Goldman
Emma Goldman (1869 – 1940) “was an anarchist political activist and writer. She played a pivotal role in the development of anarchist political philosophy in North America and Europe in the first half of the 20th century. Goldman was born in Russia and emigrated to the US in 1995. She was attracted to anarchism after the Chicago Haymarket affair and became a write and lecturer on anarchist philosophy, women’s rights and social issues. Goldman and Alexander Berkman attempted to assassinate financier Henry Clay Frick, as an act of propaganda of the deed. It was unsuccessful and Berkman served 14 years in prison. Goldman was imprisoned several times for ‘inciting riots’ and illegally distributing information on birth control. Goldman founded the anarchist journal Mother Earth in 1906. In 1917, Goldman and Berkman were given two-year prison sentences for encouraging people to avoid the First World War draft. Once released they were arrested again and along with 248 others were deported to Russia.
Goldman was initially supportive of the Russian Revolution but following the Kronstadt rebellion, she denounced the Soviet Union for its violent repression of opposing voices. She left the Soviet Union in 1923 and wrote about her experiences. In the 1930’s Goldman moved between England, Canada, France and Spain and wrote her autobiography.
“During her life, Goldman was lionized as a freethinking rebel woman’ by admirers, and denounced by detractors as an advocate of politically motivated murder and violent revolution. Her writing and lectures spanned a wide variety of issues, including prisons, atheism, freedom of speech, militarism, capitalism, marriage, free love, and homosexuality. Although she distanced herself from first-wave feminism and its efforts toward women’s suffrage, she developed new ways of incorporating gender politics into anarchism. After decades of obscurity, Goldman gained iconic status in the 1970s by a revival of interest in her life, when feminist and anarchist scholars rekindled popular interest.” [15]
Alexander Berkman
Alexander Berkman (1870 – 1936) “was a Russian-American anarchist and author. He was a leading member of the anarchist movement in the early 20th century, famous for both his political activism and his writing. Berkman was born in Vilna in the Russian Empire (present-day Vilnius, Lithuania) and immigrated to the United States in 1888. He lived in New York City, where he became involved in the anarchist movement. He was the one-time lover and lifelong friend of anarchist Emma Goldman. In 1892, undertaking an act of propaganda of the deed, Berkman made an unsuccessful attempt to assassinate businessman Henry Clay Frick during the Homestead strike, for which he served 14 years in prison. His experience in prison was the basis of his first book, Prison Memoirs of an Anarchist. After his release from prison, Berkman served as editor of Goldman’s anarchist journal, Mother Earth, and later established his own journal, The Blast. In 1917, Berkman and Goldman were sentenced to two years in jail for conspiracy against the newly instated draft. After their release from prison, they were arrested—along with hundreds of others—and deported to Russia. Initially supportive of that country’s Bolshevik revolution, Berkman and Goldman soon became disillusioned, voicing their opposition to the Soviets’ use of terror after seizing power and their repression of fellow revolutionaries. They left the Soviet Union in late 1921, and in 1925 Berkman published a book about his experiences, The Bolshevik Myth.
While living in France, Berkman continued his work in support of the anarchist movement, producing the classic exposition of anarchist principles, Now and After: The ABC of Communist Anarchism. Suffering from ill health, Berkman committed suicide in 1936.” [16]
Gustav Landauer
Gustav Landauer (1870 – 1919) “was one of the leading theorists on anarchism in Germany at the end of the 19th and the beginning of the 20th century. He was an advocate of social anarchism and an avowed pacifist. In 1919, he was briefly Commissioner of Enlightenment and Public Instruction of the short-lived Bavarian Soviet Republic during the German Revolution of 1918–1919. He was killed when this republic was overthrown. Landauer is also known for his study of metaphysics and religion, and his translations of William Shakespeare’s works into German.” [17]
Johann Most
Johann Joseph “Hans” Most (1846 – 1906) was a German-American Social Democratic and then anarchist politician, newspaper editor, and orator. He is credited with popularizing the concept of ‘propaganda of the deed‘.”
In Germany, he edited several revolutionary socialist newspapers. He argued against patriotism, conventional religion and advocated violent action to bring about revolutionary change. He was forced to leave Germany and moved to France, then London. He founded a new anarchist newspaper there. He was imprisoned by the British state for 18 months for writing about his delight of the assassination of Alexander II of Russia. Following his release, he moved to the US. He continued publishing his newspaper in New York and was imprisoned there too for supporting the assassination of US President McKinley. [18]
Rudolf Rocker
Johann Rudolf Rocker (1873 – 1958) was a German anarchist writer and activist. Some describe him as an anarcho-syndicalist, he described himself as an anarchist without adjectives. He believed that anarchist schools of thought represented “different methods of economy” with the main aim for anarchists was “to secure the personal and social freedom of men”.
As a young man, he joined the SPD and was part of the German labour movement. He was a follower of Bakunin, a revolutionary, radical leftist and anti-Marxist. Rocker moved around Europe in the early twentieth century. He became a regular writer for a syndicalist publication and was part of the 1920 international syndicalist conference that led to the founding of the International Workers Association (IWA) in 1922. Rocker returned to Germany in 1926 and was concerned by the rise of nationalism and fascism. He was later exiled from Nazi Germany.
Rocker published a well-known text, ‘In Pioneers of American Freedom’, “a series of essays, he details the history of liberal and anarchist thought in the United States, seeking to debunk the idea that radical thought was foreign to American history and culture and had merely been imported by immigrants.” [19]
Mohandas Gandhi
Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi (1869-1948) “was an Indian lawyer, anti-colonial nationalist and political ethicist who employed nonviolent resistance to lead the successful campaign for India’s independence from British rule and in turn to inspire movements for civil rights and freedom across the world.
Born and raised in a Hindu family in coastal Gujarat, Gandhi trained in the law at the Inner Temple, London, and was called to the bar at age 22 in June 1891. After two uncertain years in India, where he was unable to start a successful law practice, he moved to South Africa in 1893 to represent an Indian merchant in a lawsuit. He went on to live in South Africa for 21 years. It was here that Gandhi raised a family and first employed nonviolent resistance in a campaign for civil rights. In 1915, aged 45, he returned to India. He set about organising peasants, farmers, and urban labourers to protest against excessive land-tax and discrimination. Assuming leadership of the Indian National Congress in 1921, Gandhi led nationwide campaigns for easing poverty, expanding women’s rights, building religious and ethnic amity, ending untouchability, and above all for achieving swaraj or self-rule.
Also in 1921, Gandhi adopted the use of a short dhoti woven with hand-spun yarn as a mark of identification with India’s rural poor. He began to live in a self-sufficient residential community and to eat simple food; he undertook long fasts as a means of both introspection and political protest. Bringing anti-colonial nationalism to the common Indians, Gandhi led them in challenging the British-imposed salt tax with the 400 km (250 mi) Dandi Salt March in 1930 and in calling for the British to quit India in 1942. He was imprisoned many times and for many years in both South Africa and India.
Gandhi’s vision of an independent India based on religious pluralism was challenged in the early 1940s by a Muslim nationalism which demanded a separate homeland for Muslims within British India. In August 1947, Britain granted independence, but the British Indian Empire was partitioned into two dominions, the Hindu-majority India and the Muslim-majority Pakistan. As many displaced Hindus, Muslims, and Sikhs made their way to their new lands, religious violence broke out, especially in the Punjab and Bengal. Abstaining from the official celebration of independence in Delhi, Gandhi visited the affected areas, attempting to alleviate distress. In the months following, he undertook several hunger strikes to stop the religious violence. The last of these, begun on 12 January 1948 when he was 78, also had the indirect goal of pressuring India to pay out some cash assets owed to Pakistan. Some Indians thought Gandhi was too accommodating to Pakistan. Among them was Nathuram Godse, a Hindu nationalist who assassinated Gandhi on 30 January 1948 by firing three bullets into his chest.” [20]
Herbert Read
Sir Herbert Edward Read, DSO, MC (1893 – 1968) “was an English art historian, poet, literary critic and philosopher, best known for numerous books on art, which included influential volumes on the role of art in education. Read was co-founder of the Institute of Contemporary Arts. As well as being a prominent English anarchist, he was one of the earliest English writers to take notice of existentialism.
Politically, Read considered himself an anarchist, albeit in the English quietist tradition of Edward Carpenter and William Morris. Nevertheless, in 1953 he accepted a knighthood for “services to literature”; this caused Read to be ostracized by most of the anarchist movement. Read was actively opposed to the Franco regime in Spain, and often campaigned on behalf of political prisoners in Spain.
Dividing Read’s writings on politics from those on art and culture is difficult, because he saw art, culture and politics as a single congruent expression of human consciousness. His total work amounts to over 1,000 published titles.
Read’s book ‘To Hell With Culture’ deals specifically with his disdain for the term culture and expands on his anarchist view of the artist as artisan, as well as presenting a major analysis of the work of Eric Gill. It was republished by Routledge in 2002.” [21]
Alex Comfort
Alexander Comfort (1920 – 2000) “was a British scientist and physician known best for his nonfiction sex manual, The Joy of Sex (1972). He was an author of both fiction and nonfiction, as well as a gerontologist, anarchist, pacifist, and conscientious objector.
A pacifist, Comfort considered himself “an aggressive anti-militarist”, and he believed that pacifism rested “solely upon the historical theory of anarchism”.
Comfort was an active member of the Peace Pledge Union (PPU) and Campaign for Nuclear Disarmament, and a conscientious objector in World War II. In 1951 Comfort was a signatory of the Authors’ World Peace Appeal, but later resigned from its committee, claiming the AWPA had become dominated by Soviet sympathisers. Later in the decade he actively endorsed both the Direct Action Committee against Nuclear War, 1957, and the Committee of 100, 1960. Comfort was imprisoned for a month, with Bertrand Russell and other leading members of the Committee of 100, for refusing to be bound not to continue organising the Parliament Square/Trafalgar Square protest of 17 September 1961.
Among the publications by Comfort concerning anarchism is ‘Peace and Disobedience’ (1946), one of many pamphlets he wrote for Peace News and PPU, and ‘Authority and Delinquency in the Modern State’ (1950). He exchanged public correspondence with George Orwell defending pacifism in the open letter/poem, “Letter to an American Visitor”, under the pseudonym “Obadiah Hornbrooke”. Comfort’s book ‘The Joy of Sex’ (1972) earned him worldwide fame and $3 million. But he was unhappy to become known as “Dr. Sex” and to have his other works given so little attention.” [22]
Paul Goodman
Paul Goodman (1911–1972) “was an American author and public intellectual best known for his 1960s works of social criticism. Goodman was prolific across numerous literary genres and non-fiction topics, including the arts, civil rights, decentralization, democracy, education, media, politics, psychology, technology, urban planning, and war. As a humanist and self-styled man of letters, his works often addressed a common theme of the individual citizen’s duties in the larger society, and the responsibility to exercise autonomy, act creatively, and realize one’s own human nature.
Born to a Jewish family in New York City, Goodman was raised by his aunts and sister and attended City College of New York. As an aspiring writer, he wrote and published poems and fiction before receiving his doctorate from the University of Chicago. He returned to writing in New York City and took sporadic magazine writing and teaching jobs, several of which he lost for his outward bisexuality and World War II draft resistance. Goodman discovered anarchism and wrote for libertarian journals. His radicalism was rooted in psychological theory. He co-wrote the theory behind Gestalt therapy based on Wilhelm Reich’s radical Freudianism and held psychoanalytic sessions through the 1950s while continuing to write prolifically.
His 1960 book of social criticism, Growing Up Absurd, established his importance as a mainstream cultural theorist. Goodman became known as “the philosopher of the New Left” and his anarchistic disposition was influential in 1960s counterculture and the free school movement. Despite being the foremost American intellectual of non-Marxist radicalism in his time, his celebrity did not endure far beyond his life. Goodman is remembered for his utopian proposals and principled belief in human potential.” [23]
Murray Bookchin
Murray Bookchin (1921 – 2006) “was an American communalist, political philosopher, trade-union organizer, and educator. A pioneer in the environmental movement, Bookchin formulated and developed the theory of social ecology and urban planning, within anarchist, libertarian socialist, and ecological thought. He was the author of two dozen books covering topics in politics, philosophy, history, urban affairs, and social ecology. Among the most important were ‘Our Synthetic Environment’ (1962), ‘Post-Scarcity Anarchism’ (1971), ‘The Ecology of Freedom’ (1982) and ‘Urbanization Without Cities’ (1987). In the late 1990s, he became disenchanted with what he saw as an increasingly apolitical ‘lifestylism’ of the contemporary anarchist movement, stopped referring to himself as an anarchist, and founded his own libertarian socialist ideology called communalism, which seeks to reconcile Marxist and anarchist thought.
Bookchin was a prominent anti-capitalist and advocate of social decentralization along ecological and democratic lines. His ideas have influenced social movements since the 1960s, including the New Left, the anti-nuclear movement, the anti-globalization movement, Occupy Wall Street, and more recently, the democratic confederalism of Rojava. He was a central figure in the American green movement and the Burlington Greens.” [24]
Noam Chomsky
Avram Noam Chomsky (born 1928) “is an American linguist, philosopher, cognitive scientist, historian, social critic, and political activist. Sometimes called ‘the father of modern linguistics’, Chomsky is also a major figure in analytic philosophy and one of the founders of the field of cognitive science. He is Laureate Professor of Linguistics at the University of Arizona and Institute Professor Emeritus at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), and is the author of more than 150 books on topics such as linguistics, war, politics, and mass media. Ideologically, he aligns with anarcho-syndicalism and libertarian socialism.
Born to Jewish immigrants in Philadelphia, Chomsky developed an early interest in anarchism from alternative bookstores in New York City. He studied at the University of Pennsylvania. During his postgraduate work in the Harvard Society of Fellows, Chomsky developed the theory of transformational grammar for which he earned his doctorate in 1955. That year he began teaching at MIT, and in 1957 emerged as a significant figure in linguistics with his landmark work Syntactic Structures, which played a major role in remodelling the study of language. From 1958 to 1959 Chomsky was a National Science Foundation fellow at the Institute for Advanced Study. He created or co-created the universal grammar theory, the generative grammar theory, the Chomsky hierarchy, and the minimalist program. Chomsky also played a pivotal role in the decline of linguistic behaviorism, and was particularly critical of the work of B. F. Skinner.
An outspoken opponent of U.S. involvement in the Vietnam War, which he saw as an act of American imperialism, in 1967 Chomsky rose to national attention for his anti-war essay “The Responsibility of Intellectuals”. Becoming associated with the New Left, he was arrested multiple times for his activism and placed on President Richard Nixon’s Enemies List. While expanding his work in linguistics over subsequent decades, he also became involved in the linguistics wars. In collaboration with Edward S. Herman, Chomsky later articulated the propaganda model of media criticism in Manufacturing Consent and worked to expose the Indonesian occupation of East Timor. His defense of unconditional freedom of speech, including that of Holocaust denial, generated significant controversy in the Faurisson affair of the 1980s. Since retiring from active teaching at MIT, he has continued his vocal political activism, including opposing the 2003 invasion of Iraq and supporting the Occupy movement. Chomsky began teaching at the University of Arizona in 2017.
One of the most cited scholars alive, Chomsky has influenced a broad array of academic fields. He is widely recognized as having helped to spark the cognitive revolution in the human sciences, contributing to the development of a new cognitivistic framework for the study of language and the mind. In addition to his continued scholarship, he remains a leading critic of U.S. foreign policy, neoliberalism and contemporary state capitalism, the Israeli–Palestinian conflict, and mainstream news media. Chomsky and his ideas are highly influential in the anti-capitalist and anti-imperialist movements.” [25]
Endnotes
- https://plato.stanford.edu/entries/godwin/
- https://plato.stanford.edu/entries/max-stirner/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pierre-Joseph_Proudhon
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mikhail_Bakunin
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Peter_Kropotkin
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/%C3%89lis%C3%A9e_Reclus
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Errico_Malatesta
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Leo_Tolstoy
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Josiah_Warren
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lysander_Spooner
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Benjamin_Tucker
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adin_Ballou
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/John_Humphrey_Noyes
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Voltairine_de_Cleyre
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Emma_Goldman
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alexander_Berkman
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gustav_Landauer
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Johann_Most
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rudolf_Rocker
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mahatma_Gandhi
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Herbert_Read
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alex_Comfort
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Paul_Goodman
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Murray_Bookchin
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Noam_Chomsky






