
by DGR News Service | May 19, 2021 | Biodiversity & Habitat Destruction, Colonialism & Conquest, Culture of Resistance, Direct Action, Indigenous Autonomy, Listening to the Land, Lobbying, Mining & Drilling, Movement Building & Support, Obstruction & Occupation, Repression at Home, Toxification, White Supremacy
In this statement, Atsa koodakuh wyh Nuwu (the People of Red Mountain), oppose the proposed Lithium open pit mines in Thacker Pass. They describe the cultural and historical significance of Thacker Pass, and also the environmental and social problems the project will bring.
We, Atsa koodakuh wyh Nuwu (the People of Red Mountain) and our native and non-native allies, oppose Lithium Nevada Corp.’s proposed Thacker Pass open pit lithium mine.
This mine will harm the Fort McDermitt Paiute-Shoshone Tribe, our traditional land, significant cultural sites, water, air, and wildlife including greater sage grouse, Lahontan cutthroat trout, pronghorn antelope, and sacred golden eagles. We also request support as we fight to protect Thacker Pass.
”Lithium Nevada Corp. (“Lithium Nevada”) – a subsidiary of the Canadian corporation Lithium Americas Corp. – proposes to build an open pit lithium mine that begins with a project area of 17,933 acres. When the Mine is fully-operational, it would use 5,200 acre-feet per year (equivalent to an average pumping rate of 3,224 gallons per minute) in one of the driest regions in the nation. This comes at a time when the U.S. Bureau of Reclamation fears it might have to make the federal government’s first-ever official water shortage declaration which will prompt water consumption cuts in Nevada. Meanwhile, despite Lithium Nevada’s characterization of the Mine as “green,” the company estimates in the FEIS that, when the Mine is fully-operational, it will produce 152,703 tons of carbon dioxide equivalent emissions every year.
Mines have already harmed the Fort McDermitt tribe.
Several tribal members were diagnosed with cancer after working in the nearby McDermitt and Cordero mercury mines. Some of these tribal members were killed by that cancer.
In addition to environmental concerns, Thacker Pass is sacred to our people. Thacker Pass is a spiritually powerful place blessed by the presence of our ancestors, other spirits, and golden eagles – who we consider to be directly connected to the Creator. Some of our ancestors were massacred in Thacker Pass. The name for Thacker pass in our language is Peehee mu’huh, which in English, translates to “rotten moon.” Pee-hee means “rotten” and mm-huh means “moon.” Peehee mu’huh was named so because our ancestors were massacred there while our hunters were away. When the hunters returned, they found their loved ones murdered, unburied, rotting, and with their entrails spread across the sage brush in a part of the Pass shaped like a moon. To build a lithium mine over this massacre site in Peehee mu’huh would be like building a lithium mine over Pearl Harbor or Arlington National Cemetery. We would never desecrate these places and we ask that our sacred sites be afforded the same respect.
Thacker Pass is essential to the survival of our traditions.
Our traditions are tied to the land. When our land is destroyed, our traditions are destroyed. Thacker Pass is home to many of our traditional foods. Some of our last choke cherry orchards are found in Thacker Pass. We gather choke cherries to make choke cherry pudding, one of our oldest breakfast foods. Thacker Pass is also a rich source of yapa, wild potatoes. We hunt groundhogs and mule deer in Thacker Pass. Mule deer are especially important to us as a source of meat, but we also use every part of the deer for things like clothing and for drumskins in our most sacred ceremonies.
Thacker Pass is one of the last places where we can find our traditional medicines.
We gather ibi, a chalky rock that we use for ulcers and both internal and external bleeding. COVID-19 made Thacker Pass even more important for our ability to gather medicines. Last summer and fall, when the pandemic was at its worst on the reservation, we gathered toza root in Thacker Pass, which is known as one of the world’s best anti-viral medicines. We also gathered good, old-growth sage brush to make our strong Indian tea which we use for respiratory illnesses.
Thacker Pass is also historically significant to our people.
The massacre described above is part of this significance. Additionally, when American soldiers were rounding our people up to force them on to reservations, many of our people hid in Thacker Pass. There are many caves and rocks in Thacker Pass where our people could see the surrounding land for miles. The caves, rocks, and view provided our ancestors with a good place to watch for approaching soldiers. The Fort McDermitt tribe descends from essentially two families who, hiding in Thacker Pass, managed to avoid being sent to reservations farther away from our ancestral lands. It could be said, then, that the Fort McDermitt tribe might not be here if it wasn’t for the shelter provided by Thacker Pass.
We also fear, with the influx of labor the Mine would cause and the likelihood that man camps will form to support this labor force, that the Mine will strain community infrastructure, such as law enforcement and human services. This will lead to an increase in hard drugs, violence, rape, sexual assault, and human trafficking. The connection between man camps and missing and murdered indigenous women is well-established.
Finally, we understand that all of us must be committed to fighting climate change. Fighting climate change, however, cannot be used as yet another excuse to destroy native land. We cannot protect the environment by destroying it.
Sign the petition from People of Red Mountain: https://www.change.org/p/protect-thacker-pass-peehee-mu-huh
Donate: https://www.classy.org/give/423060/#!/donation/checkout
For more on the Protect Thacker Pass campaign
#ProtectThackerPass #NativeLivesMatter #NativeLandsMatter

by DGR News Service | May 13, 2024 | ACTION, Mining & Drilling, The Problem: Civilization
BY KATIE FITE / COUNTERPUNCH
A recent financial Webinar features Jindalee mining company executive Lindsay Dudfield selling the company’s plan for an immense lithium mining project that would tear apart the heart of irreplaceable Sage-grouse habitat at McDermitt Creek in southeast Oregon. Australian miner Jindalee has spun itself off as a US company, just as Lithium Americas did when it formed Lithium Nevada Corporation (LNC) to mine Thacker Pass further south in the McDermitt caldera. This positions the miners for federal loan largesse as they pursue mining destruction of the sagebrush sea. I wrote about the extraordinary McDermitt Creek values at stake, and the damage and habitat fragmentation already inflicted by 70 or so previous Jindalee exploration drilling sites here.
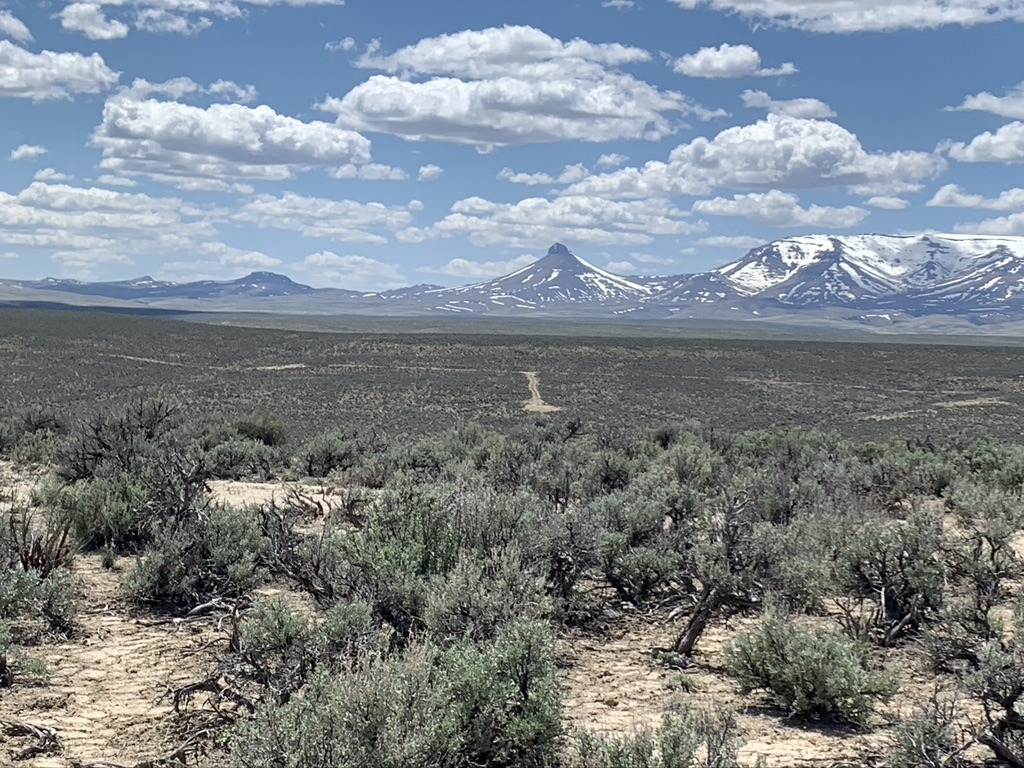

Distant view of scar from a new road and just one of Jindalee’s past McDermitt drill sites. Look at how wide open and unencumbered by hills this country is – maximizing the distance any mining disturbance sights and sounds will travel.
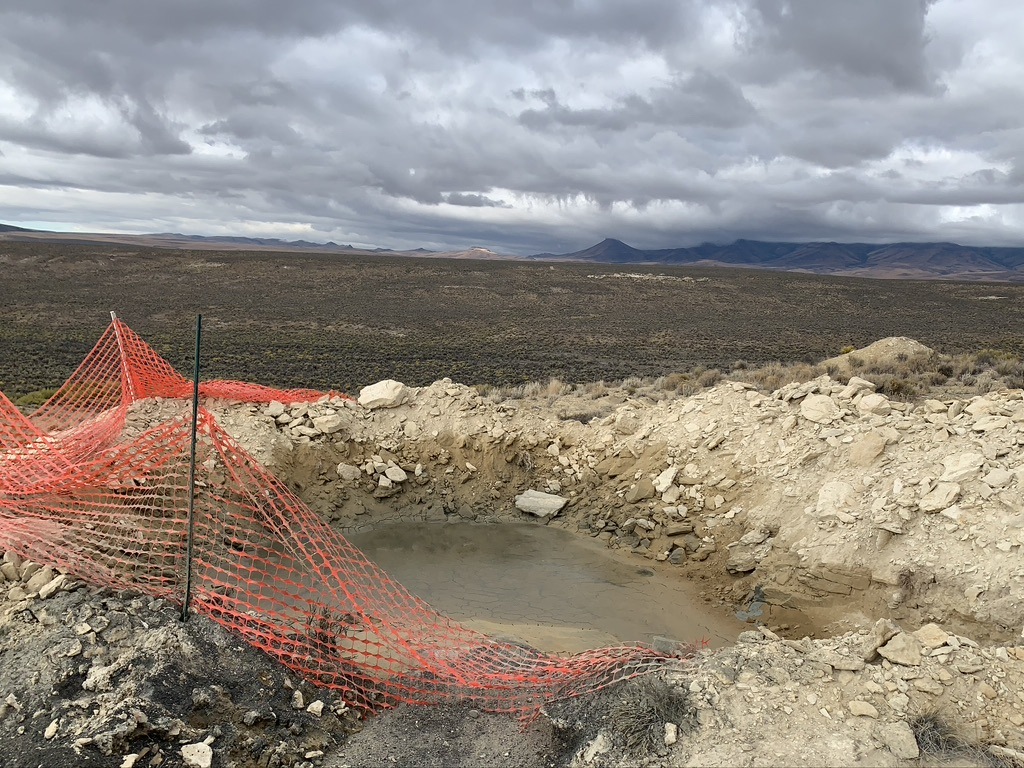

Jindalee drill hole sump. Drilling waste water left to seep into the ground, Wildlife “exclusion” fence fallen down.
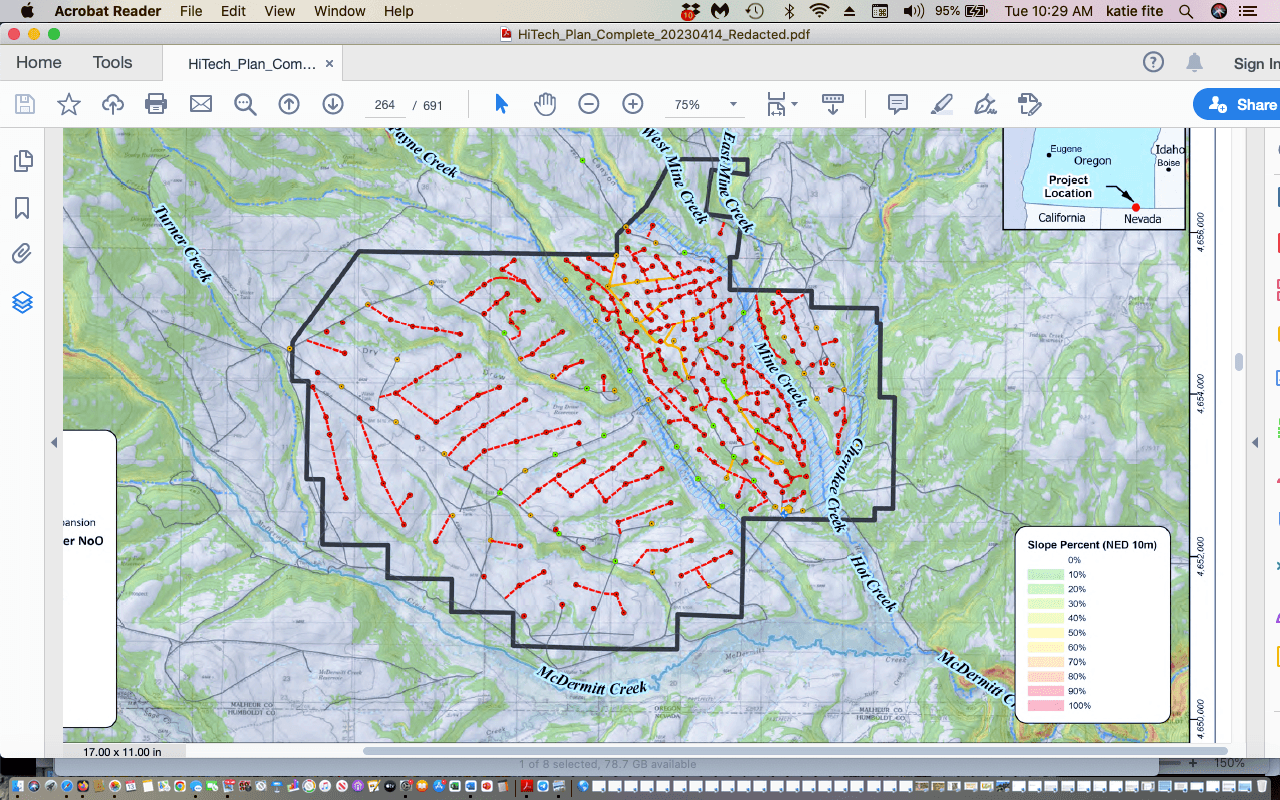 This is a map of the ghastly 2023 Jindalee exploration plan to punch in 267 new drill hole and sump sites and construct 30 miles of new roads. It would fragment an area with a very high density of nesting sagebrush songbirds of all kinds. Birds like Sagebrush Sparrow require continuous blocks of dense mature or old growth big sagebrush. Jindalee boasts its consultant environmental and cultural studies have found “no show-stoppers” and “no red flags”. Industry gets the results it wants when it pays for mine consultant work. Federal and state agencies, after a bit of pro forma sniping, acquiesce to what the mine comes up with.
This is a map of the ghastly 2023 Jindalee exploration plan to punch in 267 new drill hole and sump sites and construct 30 miles of new roads. It would fragment an area with a very high density of nesting sagebrush songbirds of all kinds. Birds like Sagebrush Sparrow require continuous blocks of dense mature or old growth big sagebrush. Jindalee boasts its consultant environmental and cultural studies have found “no show-stoppers” and “no red flags”. Industry gets the results it wants when it pays for mine consultant work. Federal and state agencies, after a bit of pro forma sniping, acquiesce to what the mine comes up with.
No red flags? Does the company really expect us to believe they or their consultants aren’t aware of the plight of Sage-grouse, and the importance of the stronghold habitat they would wipe out? The 2015 BLM Sage-grouse plan found the entire McDermitt Creek area and nearly all caldera lands were essential for the bird’s survival. BLM determined that a federal mineral withdrawal was necessary to protect this Focal habitat and to ensure Sage-grouse species survival. The withdrawal never happened, stopped first by mining and cattle industry litigation. BLM then began a stand-alone NEPA analysis for the withdrawal. Trump terminated that withdrawal analysis process. Then after a court ruled his action unlawful, BLM foot-dragging has stalled the most recent withdrawal process at the NEPA scoping stage and it appears merged with a cumbersome major plan revision.
Jindalee’s new exploration proposal – a prelude to a mine – would tragically rip apart the Basin heart. A full blown mine here would obliterate it. Mining noise and visual disturbance emanating outward would make the remaining sage ringing the mine site uninhabitable. The site is surrounded by dozens of leks.
The impossibility of mitigating a mega-mine at McDermitt Creek just blasted further into the stratosphere. Mounting scientific evidence shows how seriously the sight and sound disturbance footprint of industrial projects harms the birds. New research examined geothermal energy development impacts from Ormat plants at Tuscarora Nevada and McGinness Hills/Grass Valley near Austin. (I remember the Battle Mountain BLM manager extolling Ormat’s virtues when the McGinness project was pushed through and then later expanded to take a bigger bite out of sage habitat). New research found:
“… sage-grouse population numbers declined substantially in years following the development of a geothermal energy plant … sage-grouse abundance at leks [breeding sites] decreased within five kilometers of the infrastructure and leks were completely abandoned at significantly higher rates within about two kilometers. So, we looked at the mechanisms responsible for declines in numbers and lek abandonment, and we found adverse impacts to survival of female sage-grouse and their nests”.
This reinforces common sense: “Nests located farther from the plant tended to experience higher rates of survival. Interestingly, where hills were located between sage-grouse nests and infrastructure [high topographic impedance], we found the distance effect to be less important. Under those circumstances topography was compensating for the lack of distance and likely serving to reduce effects of light and sound”.
“The physical footprint of geothermal energy infrastructure is small relative to other renewable energy … but noise and light pollution emanating from these power plants likely cause larger adverse direct impacts to wildlife populations than infrastructure alone”.
There aren’t big hills to block a lithium mine’s 24 hour a day sight and sound impacts in the McDermitt bowl. The mined area would suffer outright sage obliteration. Surrounding sagebrush would be exposed to unimpeded straight line 24 hour a day mine operation visual impacts and noise of all kinds.
Jindalee must know of the indigenous opposition and resistance to the Thacker Pass lithium mine in the southern caldera, located in similarly unceded Paiute-Shoshone ancestral lands. Controversy and lawsuits over Thacker Pass have been in the headlines for years. It’s a pre-eminent example of an unjust transition to alternative energy and the green-washing of air and water polluting habitat wrecking dirty hard rock mining. Unfortunately, a District Court Judge’s ruling did not halt the Thacker Pass mine construction. However, the lawsuits by environmental groups, Tribes and a local rancher opposing the mine continue. The District Court decision was appealed to the Ninth Circuit, where a hearing is scheduled for June 26.
Thacker Pass mine development would destroy a Traditional Cultural Property, where Paiute-Shoshone ancestors were massacred. This spring, it’s been the site of the indigenous Ox Sam Women’s Camp, Newe Momokonee Nokotun, set up in protest. Descendants of Ox Sam, a survivor of a US cavalry massacre at Thacker Pass, helped establish it.
Jindalee Webinar statements also hint at efforts afoot to alter Oregon state mining processes. After lamenting the project wasn’t in Nevada, Jindalee said it was talking to politicians and the head of the state mining Department (DOGAMI).
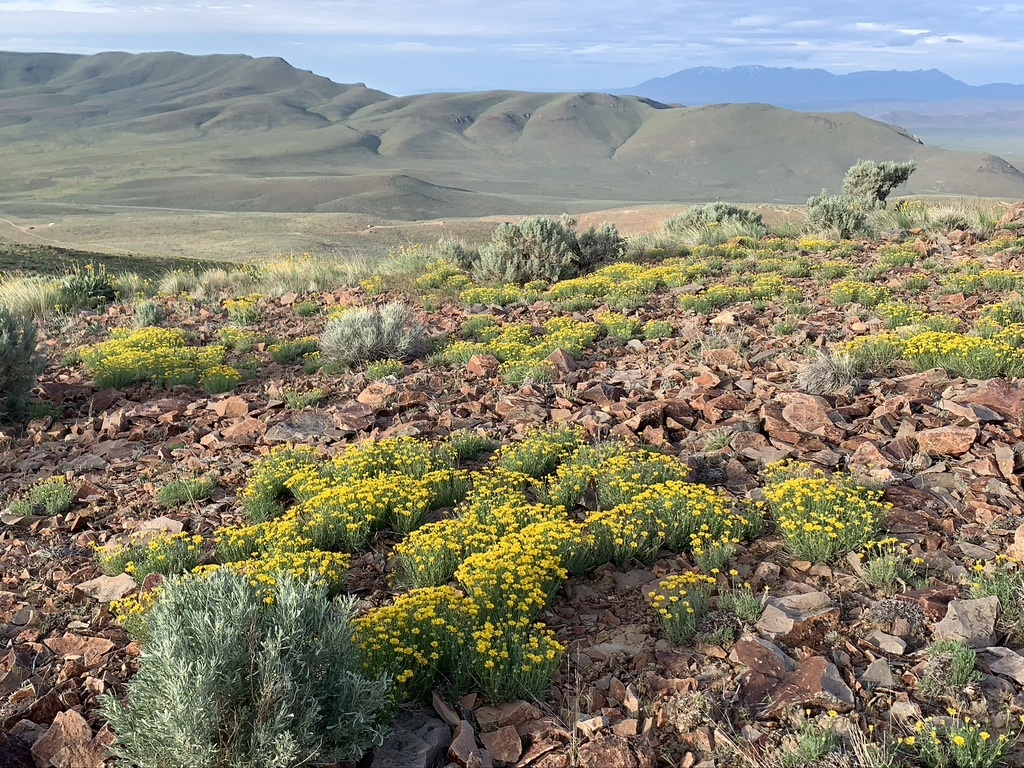
The company’s braggadocio made me blow off deadlines and go once again to McDermitt Creek to document its great biodiversity values. I then went from the beauty of singing sagebrush songbirds, newly hatched Sage-grouse chicks and peaking rare plant blooms at McDermitt Creek (photos below) and down into the Montana Mountains by Thacker Pass.


Sagebrush Sparrows abound at McDermitt Creek. They’re great little birds and often sing throughout the day. And they’re vanishing from many places. A biologist just told me he thinks they may be extirpated in Morrow County Oregon where he’s long inventoried bird. No larger continuous blocks of lower elevation sage = no Sagebrush Sparrows.
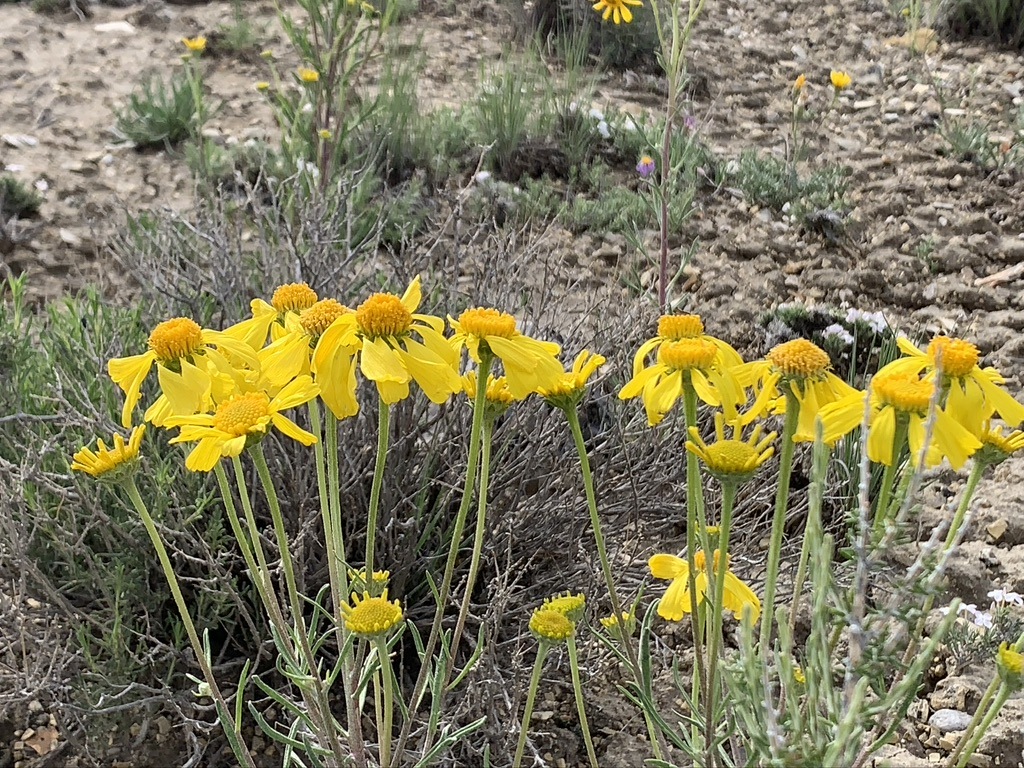

Hymenoxys, an Oregon sensitive plant growing on clay soils.

Humboldt Mountains Milkweed, a medicinal plant, on clay soils.
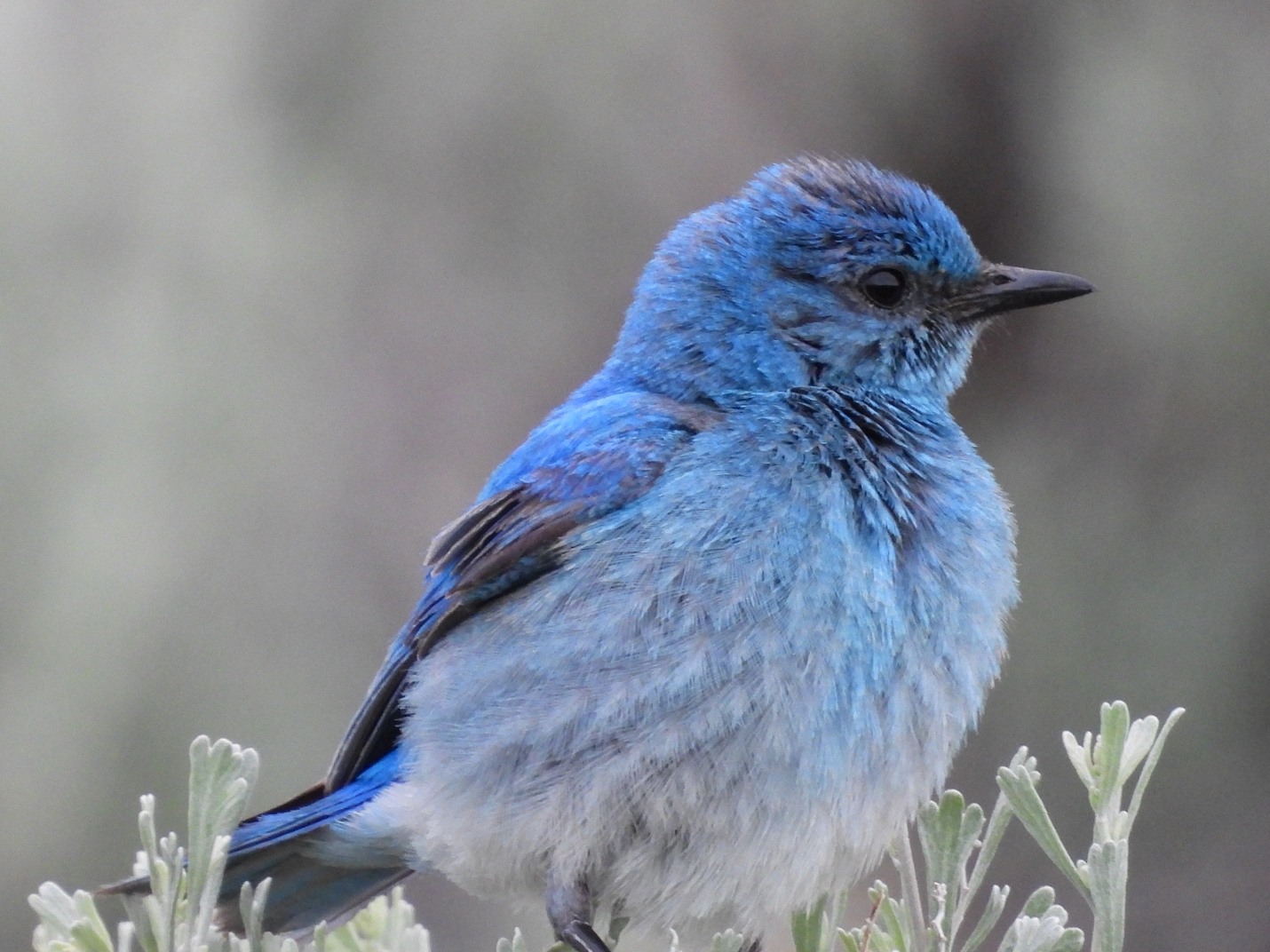

Mountain Bluebird.
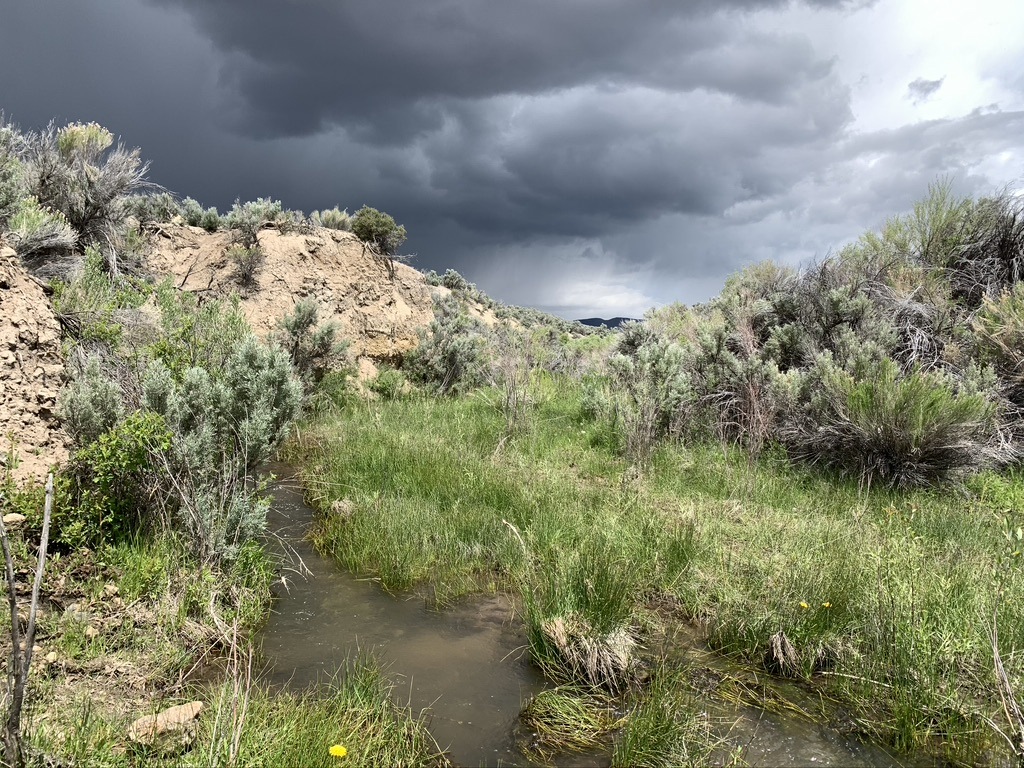

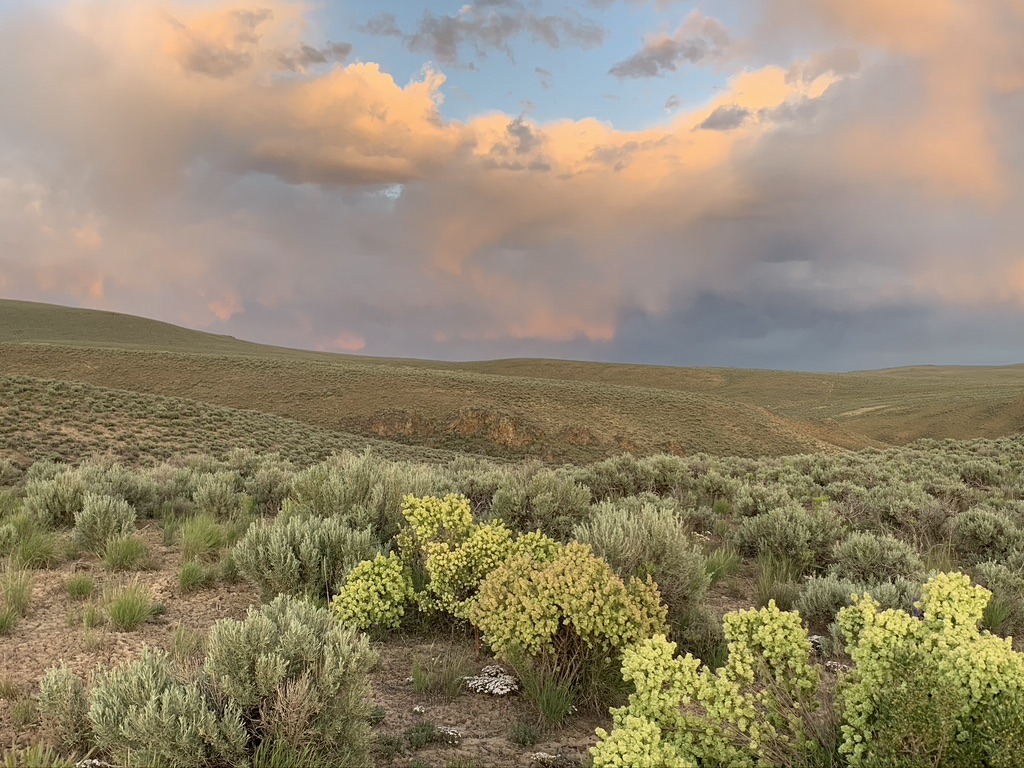
Sky drama all spring long.

Short-horned Lizard – a master of invisibility.

Gray Flycatcher. They nest in head high Basin big sagebrush, which is becoming as scarce as hen’s teeth.
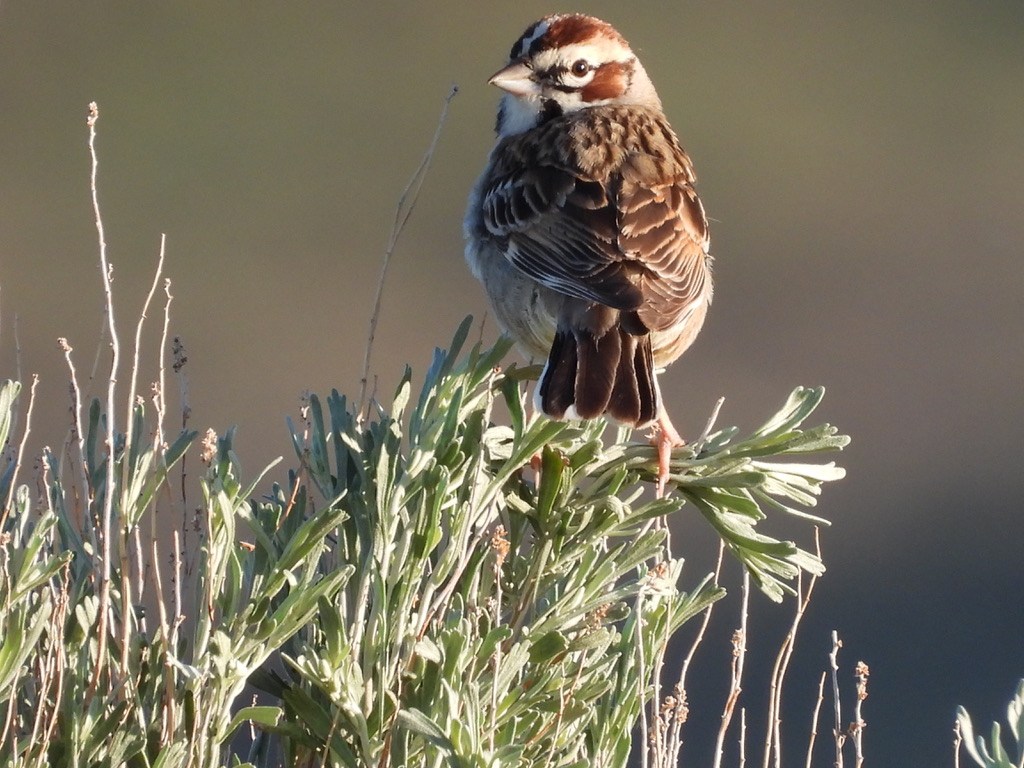

Lark Sparrow. They’re exuberant singers and are dining on Mormon crickets at McDermitt Creek.

An indescribable Indian paintbrush hue.
We’re supposed to sit back and let all this beauty and biodiversity be destroyed for a lithium mine? No way.
Thacker Pass – Turmoil, Land Mutilation, Montana Mountains
I drove south to Orovada and headed west to the turn-off from the state highway into Pole Creek road, the main access to the Montana Mountains. Thacker Pass lies at the southern base of these mountains. A maroon Allied Security company truck squarely blocked the road. Chain link fencing with No Trespassing and No Drone Zone signs was placed off to both sides.
 I stopped, got out and approached a security guard who appeared at the truck. He refused to let me pass. After several minutes of my insistent repetition that this was a public road, the BLM mine EIS said this road would always be open, and that blocking use of this road indicated the EIS, the BLM and Lithium Americas had lied, the security guard relented and said he would call the head of security.
I stopped, got out and approached a security guard who appeared at the truck. He refused to let me pass. After several minutes of my insistent repetition that this was a public road, the BLM mine EIS said this road would always be open, and that blocking use of this road indicated the EIS, the BLM and Lithium Americas had lied, the security guard relented and said he would call the head of security.
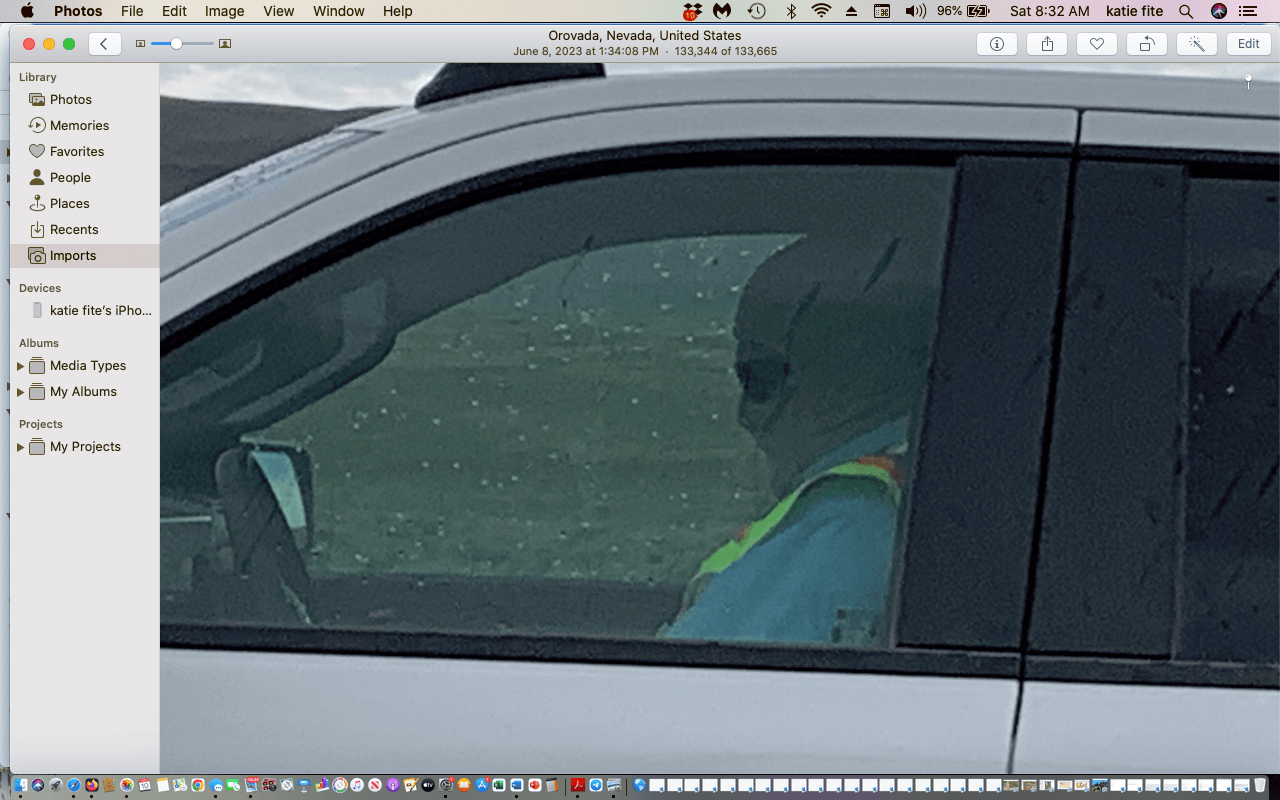 The boss pulled up in a white truck as a sudden rain whirlwind bore down. His face was obscured, and identity concealed by a tan balaclava-like hood and dark sunglasses. When he first arrived, he got out of his truck and pointed a camera device at me. I thought WTF is this – a security firm mercenary decked out for Operation Iraqi Freedom? Abu Ghraib in Orovada? I again repeated repeatedly that this was a public access road, and I was going up into the Montana Mountains to camp. He retreated to his pickup, likely to run me and my license plates through some creepy database. Finally, I was allowed to pass through.
The boss pulled up in a white truck as a sudden rain whirlwind bore down. His face was obscured, and identity concealed by a tan balaclava-like hood and dark sunglasses. When he first arrived, he got out of his truck and pointed a camera device at me. I thought WTF is this – a security firm mercenary decked out for Operation Iraqi Freedom? Abu Ghraib in Orovada? I again repeated repeatedly that this was a public access road, and I was going up into the Montana Mountains to camp. He retreated to his pickup, likely to run me and my license plates through some creepy database. Finally, I was allowed to pass through.
Just up the road was the Ox Sam Protest Camp site, located on a huge mine water pipeline gash that the lithium company had gouged into the earth. The pipeline gash runs right by the sacred Sentinel (or Nipple) Rock. The tents appeared lifeless, flaps blowing open in the rain squall as I drove by. With better cell phone service up in the mountains, I called Winnemucca BLM, asked to talk to a Manager, Assistant Manager, somebody, and told the receptionist that the mine was trying to block the public access road. She said there was no one to talk with. I asked for a Manager’s e-mall address. She refused to give me an address and shunted me to the general BLM mailbox where public comments go to be ignored. Winnemucca is the BLM outpost in charge of enforcing LNC’s compliance with EIS requirements. They’ll be sure to jump on enforcement actions when the public brings potential mining violations to their attention over the next 45-years.
Later I saw a Google alert for “Thacker Pass”, and read that the camp had been raided after an incident. Underscore News/Report for America writes: “On Wednesday, police from the Humboldt County Sheriff’s Office and private security for Lithium Nevada, a subsidiary of Lithium Americas, cleared the camp and arrested one protester.
When I left the next day, the chain link fence with No Trespassing signs was still up by the sides of the access route. The security truck was gone, and I drove on through. A local resident pulled up. We chatted, gazing up at the mountains that were witnessing the lithium mine destruction unfold. He knows the country like the back of his hand. He said you could see over 20 mountain ranges from the Montanas. Our presence generated the interest of security guards who came by to check us out as we stood by the state road right of way. A project worker came and moved the chain link fence with its No Trespassing signs away – at least for now.
Allied Security’s aggressive approach to security has gained notoriety. The Denver city council canceled their contract after two Allied guards beat a black man so hard they caused him permanent brain damage. In May, Time magazine profiled a long troubling history of Allied incidents.
How fitting. Lithium Americas came in claiming Thacker Pass was some kind of great “green” mine, as cover for plain old dirty open pit mining and a noxious lithium processing plant. Now they’ve hired a security firm prone to violence. I don’t know what went down with the Ox Sam camp. But I do know that having the security boss decked out in black ops head gear is an effort to intimidate, and an indication the security firm may have things to hide. Security personnel concealing their identity or playing gatekeeper on a public lands access road in this way have no place at a project on public lands. Months before the Ox Sam camp was set up, LNC had established a manned compound with a building and fencing and what looked like cameras right by the Pole Creek access road. Driving up into the mountains in April to trek across the snow to the Montana-10 lek had already felt like running a gauntlet. I wager that anyone going in or out that public road gets recorded.
LNC has many mining claims staked up in the mountains in Sage-grouse stronghold habitat including at the Montana 10 lek. This makes efforts to limit access or intimidate people so they don’t go up there more concerning. Back home, I consulted the Thacker Final EIS:
“SR 293, Pole Creek Road, Crowley Creek Road and Rock Creek Road are the main transportation routes in the Project area. Under Alternative A, LNC would not close, block, or limit in any manner access along these routes”. FEIS at 494-495. The EIS also constrained use of these access roads for certain types of mine activities.
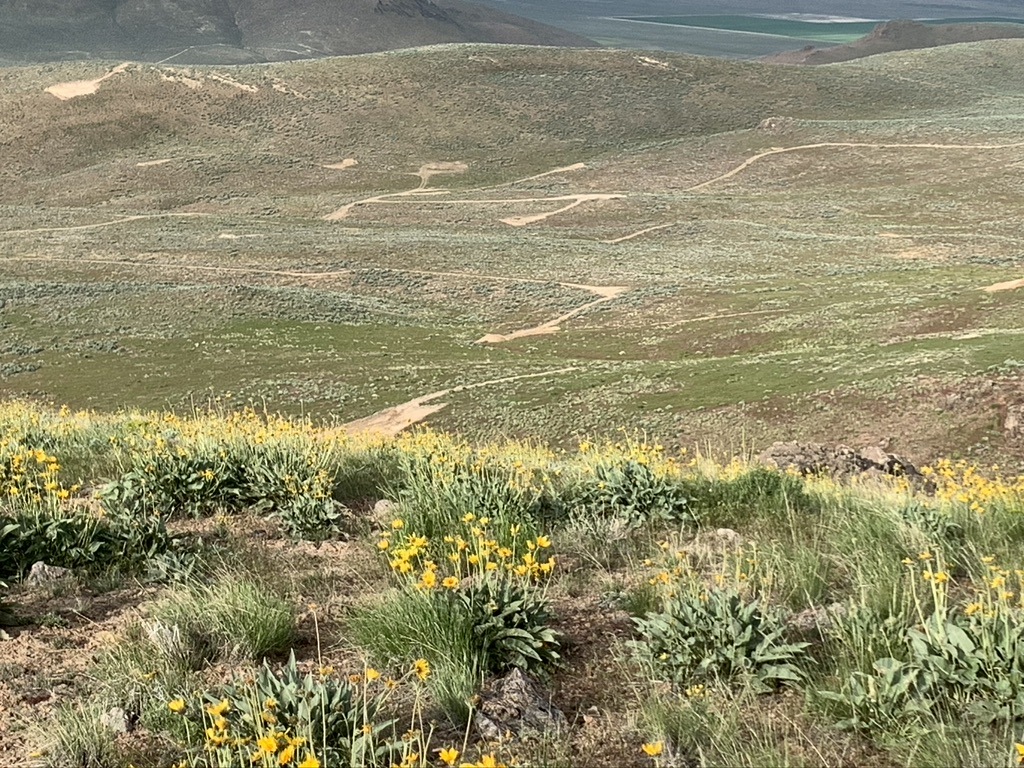
Photos below from up in the Montana Mountains looking down on spring 2023 LNC scars from drilling and bulldozing in migratory bird nesting season. The drilling is creeping upslope. It’s hard to tell if some may be outside the project boundary. Nevada BLM uses in-front-of-the-bulldozer bird survey protocols that are deeply flawed with transects spaced 100 ft. apart – a distance far too wide to detect cryptic sagebrush birds that are experts at concealment. You practically have to step on or by a nest to detect it. The only way to avoid migratory bird “take” is for the mine to not destroy the bird habitat in spring.
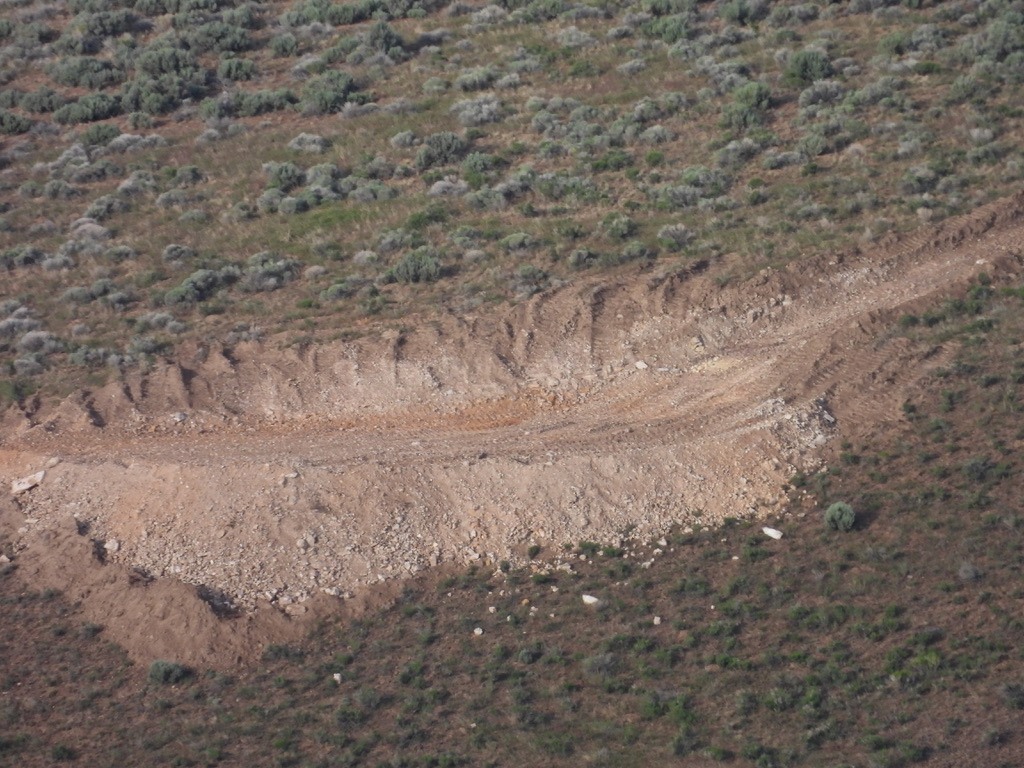


 LNC’s drill scarring is a mere prelude to the destruction that’s planned – 5,694 acres of outright destruction in a 17,933 acre project zone. The enormity and scale of the planned mine is mind boggling – a deep open pit, a waste rock pile, all types of infrastructure, a lithium smelter/sulfuric acid plant on-site using huge volumes of waste sulfur shipped into a new railroad off-loading site by the Winnemucca airport. The latter was just announced a few months ago, to the dismay of nearby residents who find themselves facing living by a hazardous materials zone. Hundreds of tons of off-loaded material will be trucked to Thacker Pass and burned every day in a plant whose air scrubber design wasn’t even finalized before the Thacker decision was signed by BLM. What stink and toxic pollution will this lithium processing generate? McDermitt caldera soils contain uranium and mercury. Mine water use is estimated to be 1.7 billion gallons annually. Enormous volumes of diesel fuel will be used throughout the mine’s operation. What’s green about all this?
LNC’s drill scarring is a mere prelude to the destruction that’s planned – 5,694 acres of outright destruction in a 17,933 acre project zone. The enormity and scale of the planned mine is mind boggling – a deep open pit, a waste rock pile, all types of infrastructure, a lithium smelter/sulfuric acid plant on-site using huge volumes of waste sulfur shipped into a new railroad off-loading site by the Winnemucca airport. The latter was just announced a few months ago, to the dismay of nearby residents who find themselves facing living by a hazardous materials zone. Hundreds of tons of off-loaded material will be trucked to Thacker Pass and burned every day in a plant whose air scrubber design wasn’t even finalized before the Thacker decision was signed by BLM. What stink and toxic pollution will this lithium processing generate? McDermitt caldera soils contain uranium and mercury. Mine water use is estimated to be 1.7 billion gallons annually. Enormous volumes of diesel fuel will be used throughout the mine’s operation. What’s green about all this?

Think of the volume of water that will be sucked through these pipes.
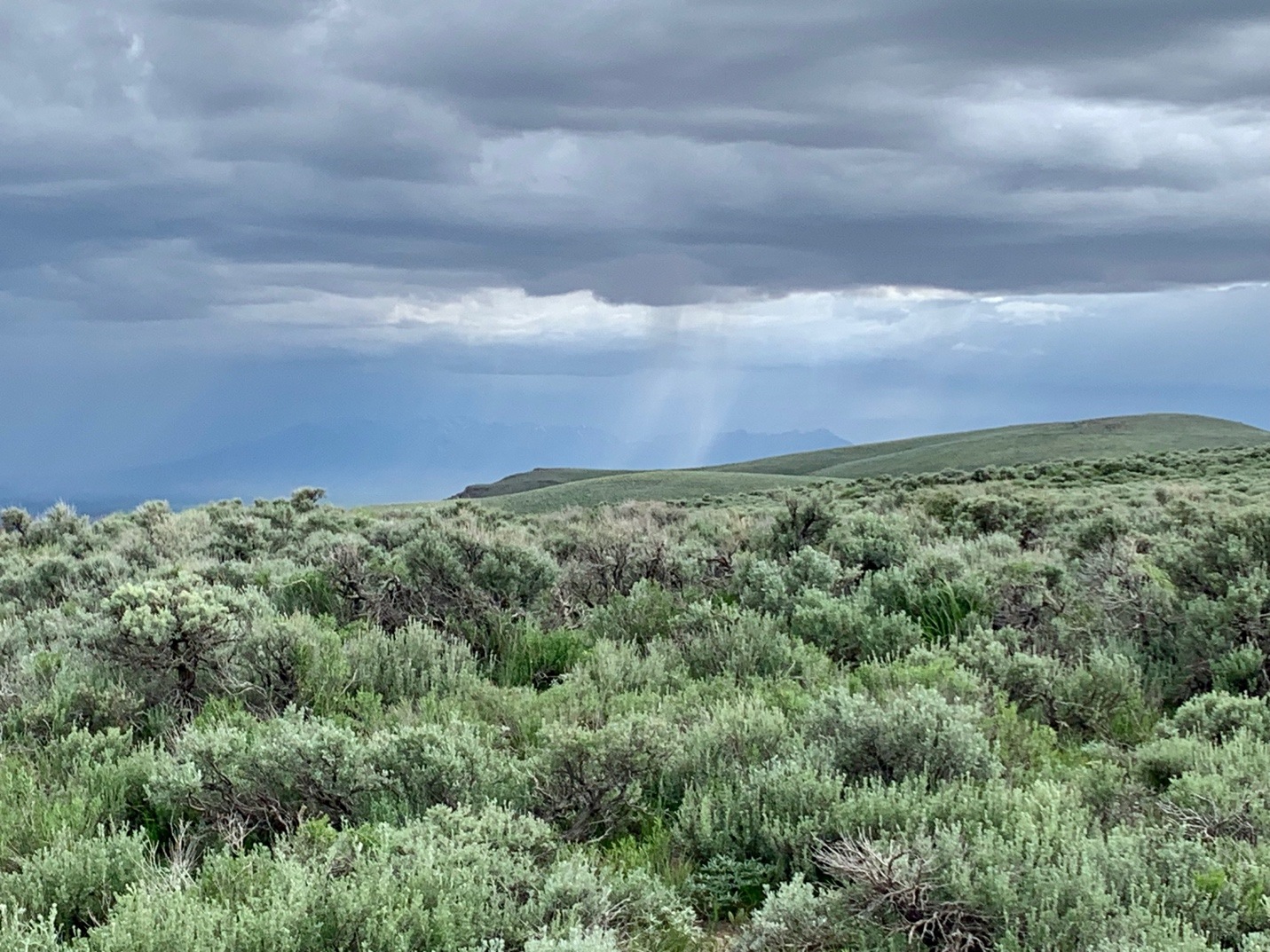

Beautiful dense big sagebrush full of Sage Thrashers, Brewer’s Sparrows, and Sage-grouse sign, up in the mountains where LNC has claims galore.

 Sacrificing the Interior West for Corporate Energy Dominance While Energy Conservation Lags or Is Forgotten Altogether
Sacrificing the Interior West for Corporate Energy Dominance While Energy Conservation Lags or Is Forgotten Altogether
Big Green environmental groups and outdoor interests who’ve been silent on the unfolding lithium mine destruction at Thacker Pass, or the tragic destruction of Mojave Desert Tortoise habitat for Big Solar and many other brewing “green” energy controversies better wake up. The lithium boom plague that’s descended on the West is hard rock mining at its worst. Thousands of acres at each mine site become essentially privatized (with security guards) for 40 or 50 years. Much of the land is reduced to waste rock rubble piles, gaping pits, infrastructure all over the place. Local water is used up for processing and for suppressing clouds of dust, and mine pollutants contaminate the air and ground water.
US taxpayers are helping finance these colonialist lithium mines. LNC received commitments for a $600 million dollar loan investment of US tax dollars. General Motors, while continuing to pump out gargantuan trucks and EV Hummers priced at $110,000, provided LNC with a $600 million dollar injection. In the Jindalee Webinar, executive Dudfield assured a questioner that their company will also be “in queue” for similar handouts. The miners are gobbling up funds for a battery technology that may soon be outdated. China is zooming past the US with its development of sodium batteries and is introducing them in low-end vehicles, a sane path forward. Why aren’t these funds going to research alternatives to lithium and safer less earth-wrecking technologies? Why isn’t Nevada Senator Catherine Cortez-Masto directing her attention to spurring new technologies and sustainability? Instead she’s using “critical minerals” mantra to justify introducing a bill to make the 1872 Mining Law even worse, and a wholesale giveaway to mining companies.
Jindalee’s Webinar talk said the company embraced “social license and responsibility”, then later emphasized that McDermitt Creek was “a long, long way” from Oregon population centers like Salem and Portland. This highlights how lithium mine pollution, cultural site desecration, community de-stabilization and ecological damage will be out of sight and out of mind of urban elites.
US government policy is now based on greatly accelerating energy colonialism of all types within our own borders, and especially on willy-nilly sacrifice of the public lands of the Interior West. This allows massively subsidized corporations (often tied to a foreign mothership) and billionaires to retain a chokehold on energy. Conservation is paid lip service. BLM’s Tracy Stone-Manning just announced a new proposed rule making it easier for BLM to hand over public lands to wind and solar developers, furthering de facto public lands privatization for half a human lifespan.
But people are catching on. A surprising thing recently happened in Idaho. The entire Idaho legislature (all the Republicans and the hand full of Democrats alike) voted in favor of a Resolution opposing the BLM Lava Ridge Wind Farm, with its 400 turbines standing 800 feet tall sprawling across 3 counties. Lava Ridge’s plan managed to offend or disgust everybody – from agricultural operations and home site impacts, to Golden Eagle and rare bat killing, to destroying the stark setting of the Minidoka Japanese Internment Camp Monument and marring the Dark Skies and wildness of Craters of the Moon.
The same Legislators, who in a normal year would be inviting Land Grab proponents from Utah to speak in the session, were pushing protection of public lands from this behemoth of LS Power’s subsidiary Magic Valley Energy. It’s facilitated by the planned new LS Power SWIP North renewables-focused transmission line. Idaho Power and PacifiCorp’s Gateway “green” transmission line has also resulted in a stampede for more wind and solar
leases in south-central Idaho.
If you live in the West and love the outdoors, be very afraid of what the Biden administration’s breakneck push for many more of these “green” lines will do to public lands, and your access to areas beyond – once projects feeding energy into the line are built and the fencing goes up. It’s the sagebrush sea equivalent of building a road through the Amazon.
While there are no huge wind farms yet on public lands in Idaho, there are many smaller scale turbine arrays on private lands across the Snake River Plain. It’s become quite apparent that industrial wind is not benign. Above all else, folks realized how badly Idaho was getting screwed by the Lava Ridge project and its export of energy to benefit coastal populations. The Legislature said No to Lava Ridge exploitation of Idaho as an energy colony. Counties in the Mojave Desert are now starting to resist some industrial solar developments overrunning public lands. Remotely sited “renewable” energy or “critical minerals” projects amount to public land privatization. They cause profound losses of many kinds – scarring the land, sucking it dry, extinguishing the wildlife that’s managed to persist in the face of merciless domination since White settlement, trenching a massacre site.
 I’m outraged at the ecocidal stupidity with which this “energy transition” is being carried out. Will we soon see Jindalee get US tax dollars to wipe out the McDermitt Creek Sage-grouse stronghold? How ironic that would be. Interior just announced funding for major sagebrush habitat restoration using Infrastructure Bill funds in High Priority sagebrush areas. It turns out one of the sites chosen is the Montana Mountains area. Mapping shows it includes the Thacker Pass mine area too, where nearly all the sage is on the verge of being destroyed by LNC. Close review of maps for Interior’s Montana “restoration” project shows it encompasses the McDermitt Creek watershed, hence the entire area coveted by Jindalee for massive new drilling followed by open pit mining. It would be absurd to greenlight Jindalee’s ghastly exploration plan in primo habitat, when the Interior Department has identified this very same landscapeto be among the highest priority for restoration – because so much sage has already been lost already. The caldera is also key for connectivity between Sheldon and Owyhee Sage-grouse populations and for biodiversity preservation.
I’m outraged at the ecocidal stupidity with which this “energy transition” is being carried out. Will we soon see Jindalee get US tax dollars to wipe out the McDermitt Creek Sage-grouse stronghold? How ironic that would be. Interior just announced funding for major sagebrush habitat restoration using Infrastructure Bill funds in High Priority sagebrush areas. It turns out one of the sites chosen is the Montana Mountains area. Mapping shows it includes the Thacker Pass mine area too, where nearly all the sage is on the verge of being destroyed by LNC. Close review of maps for Interior’s Montana “restoration” project shows it encompasses the McDermitt Creek watershed, hence the entire area coveted by Jindalee for massive new drilling followed by open pit mining. It would be absurd to greenlight Jindalee’s ghastly exploration plan in primo habitat, when the Interior Department has identified this very same landscapeto be among the highest priority for restoration – because so much sage has already been lost already. The caldera is also key for connectivity between Sheldon and Owyhee Sage-grouse populations and for biodiversity preservation.
How long before rejection of lithium and other “critical mineral” mines grips communities, especially as promised jobs evaporate with increased mine automation and robot technology, and as the environment goes to hell? But hey, as LNC is showing us, there’s always a bright future as a security guard– at least until the lithium company gets itself a pack of Robodogs.

Katie Fite is a biologist and Public Lands Director with WildLands Defense.
![The Long Shadow of the Tar Sands: Lithium Mining and Tar Sands Sulfur [Dispatches from Thacker Pass]](https://dgrnewsservice.org/wp-content/uploads/sites/18/2021/04/Shadows-980x652-1.jpg)
by DGR News Service | Apr 18, 2021 | Biodiversity & Habitat Destruction, Indigenous Autonomy, Listening to the Land, Mining & Drilling, Movement Building & Support, Obstruction & Occupation, Toxification
In this article, Max Wilbert talks about his experience in fighting tar sand mining in Washington and Utah, and how this is related to the current campaign against lithium mining in Nevada. “I think it’s wrong to blow up a mountain for tar sands. I think it’s wrong to blow up a mountain for lithium, too. I guess I’m just stubborn like that.”
by Max Wilbert
It’s often said that solar panels, wind turbines, and the lithium-ion batteries that store their energy and power electric vehicles will save the planet.
What most people don’t know is that producing lithium has direct links to the Alberta Tar Sands (also known as the Athabasca tar sands), the largest and most destructive industrial project on the planet.
This is a personal issue for me. I have fought the tar sands for over a decade. Starting in 2010, I began campaigning for the city of Bellingham, Washington to forbid a spur of the Trans Mountain pipeline which carries “dilbit” (diluted bitumen, AKA unrefined tar sands to which gas has been added so it’ll flow easily through a pipeline) under the city.
After months of campaigning, Bellingham became the first city in the nation to unanimously pass a resolution declaring tar sands fuel to be harmful. But despite overwhelming public opposition, the city’s attorneys said they couldn’t prevent the pipeline from operating using the law. What that says about the state of democracy is worth a whole different article. And perhaps a revolution. But I digress.
After my years in Bellingham, I lived in Salt Lake City, where I took part in the campaign to protect the Tavaputs Plateau in northeastern Utah from tar sands strip mining. As part of that work, I took part in public meetings, family camp-outs on the site, disruptive protests, and several direct actions against the U.S. Oil Sands Corporation.
For the last three months, I’ve been in Nevada, on Northern Paiute territory, holding down a protest camp established on the proposed site of an open-pit lithium mine. I’m an equal opportunity land defender. I think it’s wrong to blow up a mountain for tar sands. I think it’s wrong to blow up a mountain for lithium, too. I guess I’m just stubborn like that.
But as I’ve implied, these projects are directly related. It turns out, the proposed mine at Thacker Pass would likely rely directly on materials sourced from the Alberta tar sands as the key chemical ingredient in their production process.
According to the Final Environmental Impact Statement, the proposed Thacker Pass mine would produce 5,800 tons of sulfuric acid per day for use in refining lithium. That would require importing 1,896 tons of sulfur per day. That’s nearly 700,000 tons per year, roughly equivalent to the mass of two Empire State Buildings annually. This would be brought in to Thacker Pass on dozens of (diesel-fueled) semi-trucks each carrying 3,800 gallons of molten sulfur.
Most sulfur comes from oil and gas refineries, where it’s a byproduct of producing low-sulfur fuels to meet air-quality regulations. And here’s the punchline: according the U.S. Geological Survey, tar sands contain 11 times as much sulfur as conventional heavy crude oil. There are literal “mountains” of sulfur piling up in Alberta, and at other refineries which process tar sands fuel.
That includes the refineries in Anacortes, Washington, which refines the “dilbit” from the pipelines running underneath Bellingham, my old home. These two refineries are major sources of sulfur for the entire western United States, shipping out millions of tons annually.
According to Lithium Americas Corp. Vice President of Global Engineering, the proposed lithium mine at Thacker Pass would purchase sulfur on the bulk commodity market, and it would be delivered by rail to Winnemucca (60 miles south), then brought by truck to Thacker Pass. That bulk commodity market sources nearly 100% of its elemental sulfur from oil and gas refineries.
And so we come full circle: the lithium destined for lithium-ion batteries that will be extracted from Thacker Pass, will almost certainly be directly connected to the total destruction of Alberta’s boreal forest, the poisoning of the water across thousands of square miles, the epidemic of cancers and rare diseases in that region, the wave of missing and murdered indigenous women in Alberta, and all the other harms that come from the tar sands. And, lest we forget, the tar sands are a major contributor to global warming. Canadian greenhouse gas emissions have skyrocketed over recent decades, as tar sands oil production has expanded.
Revenue from sales of sulfur is not unimportant to the economics of tar sands oil extraction. One report from 2018 found that as much as half a million barrels per day of tar sands product would be economical to extract if legal levels of sulfur allowed in bunker fuel were lowered. Another report found that “developing a plan for storing, selling or disposing of the sulphur will help to ensure the profitability of oil sands operations.”
All this points to a relatively simple conclusion: extraction of lithium at Thacker Pass would directly support the economics of extracting additional sulfur-rich crude oil and bitumen at the tar sands, further incentivizing the destruction of the planet.
Why do we defend the land here at Thacker Pass? There are so many reasons. It is important habitat. It is sacred ancestral land for our Northern Paiute friends from the nearby Fort McDermitt tribe. It is beautiful. But we also stand to protect this place because we stand for the truth. Lithium mining, and by extension, much of the so-called “green economy” that is being developed is not separate from fossil fuels. It is firmly dependent on fossil fuels.
Besides the sulfur, this project would burn tens of thousands of gallons of diesel fuel per day — operating heavy equipment made of steel that was produced with metallurgical coke, a type of coal. That same steel makes up the frame of the electric cars, too. The roads into the mine site would likely be made of asphalt concrete. You know what another name for asphalt is? Bitumen. AKA tar sands.
The idea of a “green” electric car is a fantasy. The sooner we face that reality, the sooner we can put a stop to false greenwashing projects like the Lithium Americas/Lithium Nevada Thacker Pass mine. The sooner we face reality, the sooner we can recognize that to shut down the tar sands, we actually have to shut down the tar sands, not just blow up other mountains elsewhere and hope that leads to the end of the tar sands.
Do not fool yourself. This is not some great green transition. It is more of the same. More destroyed land, more poisoned water, more decimated wildlife.
It’s beautiful here at Thacker Pass. Yesterday morning, I woke before 5am to visit the Greater sage-grouse “lek” — mating ground — on top of the mountain directly above the proposed mine. I watched the male grouse strut and dance, and thought about the new USGS report showing that grouse populations have declined by 80% since 1965, and nearly 40% since 2002. That comes on top of previous population collapses. The population was 16 million a century ago. Now, it’s closer to 200,000. That’s a 99% decline. This region, the northwestern Great Basin, has been particularly hard hit.
It is possible for humans to live sustainably. Our ancestors managed it for hundreds of thousands of years. Is it possible to live sustainably, and drive cars? No, I don’t believe it is. You may not like it, but there’s a thing about the natural laws of the universe: they don’t give a damn if you like them or not. Gravity exists. Ecological constraints exist. If you ignore them, you will pay the price.
We cannot afford to ignore the truth, and because of this, we must stop the Thacker Pass mine — and the tar sands. We need your help. If you can contribute to this campaign, or to the broader transformation of society that is needed, reach out to us at https://ProtectThackerPass.org. Construction might begin very soon. If that happens, Thacker Pass will die. The water will be poisoned. And the truth will be crushed along with the sagebrush, under the hard metal treads of the bulldozers. Stand with us.
#ProtectThackerPass #BrightGreenLies #TarSands #Greenwashing #Lithium #EVs #EnergyStorage #KeepItInTheGround

Photo: Large sulfur pile — byproduct of tar sands oil refining. By Leonard G., Creative Commons ShareAlike 1.0.

by DGR News Service | Apr 7, 2021 | Biodiversity & Habitat Destruction, Climate Change, Colonialism & Conquest, Indigenous Autonomy, Listening to the Land, Mining & Drilling, Movement Building & Support, Toxification
Contact: Daranda Hinkey
775-544-2839
darandahinkey@gmail.com
Fort McDermitt, Nevada — Opposition to lithium mining is growing in native communities in Nevada. On Monday, the Fort McDermitt Paiute and Shoshone Tribe formally resolved to cancel a Project Engagement Agreement with mining company Lithium Nevada, citing threats to land, water, wildlife, hunting and gathering areas, and sacred sites.
The Tribal Council also agreed to initiate a lawsuit against the Bureau of Land Management for violations of federal law in permitting the Thacker Pass lithium mine project to proceed.
These moves, from a tribal council which was previously supportive or neutral towards the mine, come after pressure from traditionalists in the Fort McDermitt community. On March 22, these traditionalists brought a petition to the tribal government asking that they “stop all partnerships with any mining company and to file a lawsuit against Lithium Nevada Corp LNC, Lithium America, Jindalee Resources Limited and any other company associated to stop the development of the proposed Lithium Mine at Thacker Pass, Nevada.”
The group cited violations of the American Indian Religious Freedom Act, the Native American Graves Protection and Repatriation Act, and other laws.
Opposition to the Thacker Pass mine has been growing since January 15th, when the Bureau of Land Management approved the federal permit for the project and—on the same day—a protest camp was established on the proposed mine site. Members of the Fort McDermitt tribe have played an important role in resupplying and overseeing the camp, which is located on their traditional lands. Over the past two months, community members, elders, families, and spiritual leaders have spent time at Thacker Pass engaging in ceremony, including a 273-mile prayer walk ending at the site, and visitors have come from many nearby reservations.
The Thacker Pass mine is also broadly opposed by residents of Orovada and King’s River, two nearby unincorporated communities. One rancher has filed a lawsuit, citing impacts to groundwater, streams, and to threatened Lahontan cutthroat trout, and a local community group, “Thacker Pass Concerned Citizens,” has formed with the majority of members expressing opposition or serious concerns. A coalition of four environmental groups has also filed a lawsuit against the project, and the group “Protect Thacker Pass” setup the protect camp nearly three months ago.
The lithium industry is booming worldwide as governments shift subsidies towards electric vehicles, which are powered by lithium-ion batteries, and towards wind and solar power which often require battery storage for periods when wind stops and nighttime or clouds block the sun.
There are numerous proposed lithium mine projects in Nevada and the United States. The petition filed Monday night also mentions Jindalee Resources, an Australian mining company currently exploring for lithium deposits just north of the Oregon border, near Fort McDermitt. Another proposed lithium mine located at Rhyolite Ridge, further south in Nevada, has attracted major opposition due to an endangered wildflower on the site.
###

by DGR News Service | Mar 8, 2021 | Education, Movement Building & Support, Repression at Home, Strategy & Analysis
In this article Max Wilbert outlines the political and environmental need for security culture. He offers recommendations to secure communications.
By Max Wilbert
For 50 days, the Protect Thacker Pass camp has stood here in the mountains of northern Nevada, on Northern Paiute territory, to defend the land against a strip mine.
Lithium Americas, a Canadian corporation, means to blow up, bulldoze, or pave 5,700 acres of this wild, biodiverse land to extract lithium for “green” electric cars. In the process, they will suck up billions of gallons of water, import tons and tons of waste from oil refineries to be turned into sulfuric acid, burn 11,000 gallons of diesel fuel per day, toxify groundwater with arsenic, antimony, and uranium, harm wildlife from Golden eagles and Pronghorn antelope to Greater sage-grouse and the endemic King’s River pyrg, and lay waste to traditional territories still used by people from the Fort McDermitt reservation and the local ranching and farming communities.
The Campaign to Protect Thacker Pass
They claim this is an “environmentally sustainable” project. We disagree, and we mean to stop them from destroying this place.
Thus far, our work has been focused on outreach and spreading the word. For the first two weeks, there were only two of us here. Now word has begun to spread. The campaign is entering a new stage. There are new opportunities opening, but we must be cautious.
How Corporations Disrupt Grassroots Resistance Movements
Corporations, faced with grassroots resistance, follow a certain playbook. We can look at the history of how these companies respond to determine their strategies and the best ways to counteract them.
Corporations like Lithium Americas Corporation generally do not have in-house security teams, beyond basic security for facilities and IT/digital security. Therefore, when faced with growing grassroots resistance, their first move will be to hire an outside corporation to conduct surveillance, intelligence gathering, and offensive operations.
Private Military Corporations (PMCs) are essentially mercenaries acting largely outside of government regulation or democratic control. They are hired by private corporations to assist in their interests and act as for-hire businesses with few or no ethical considerations. Some examples of these corporations are TigerSwan, Triple Canopy, and STRATFOR.
PMCs are often staffed with U.S. military veterans, and employ counterinsurgency techniques and skills honed during the invasions of Iraq and Afghanistan, or other military operations. And in many cases, these PMCs collaborate with public law enforcement agencies to share information, such that law enforcement is essentially acting as a private contractor for a corporation.
Disruption Tactics Used by Corporate Goon Squads
PMCs can be expected to deploy four basic tactics.
- Intelligence Gathering
First, they will attempt to gather as much information on protesters as possible. This begins with what is called OSINT — Open Source Intelligence. This simply means combing through open records on the internet: Googling names, scrolling through social media profiles and groups, and compiling information that is publicly available for anyone who cares to look.
Other methods of information gathering are more active, and include physical surveillance (such as flying a helicopter overhead, as occurred today), signals intelligence (attempting to capture cell phone calls, emails, texts, and website traffic using a device like a Stingray also known as an IMSI catcher), and infiltration or human intelligence (HUMINT). This last is perhaps the most important, the most dangerous, and the most difficult to combat.
- Disruption
Second, they will attempt to disrupt the protest. This is often done by using the classic tactics of COINTELPRO to plant rumors, false information, and foment infighting to weaken opposition.
During the protests against the Dakota Access Pipeline, one TigerSwan infiltrator working inside the protest camps wrote to his team that
“I need you guys to start looking at the activists in your area and see if there are individuals who are vulnerable. They’re broke, always talking about needing gas money or whatever. Maybe they’re disillusioned, depressed a little. Life is fucking them over. We can buy them a bus ticket to any camp they want if they’re willing to provide intel. We win no matter what. If they agree to inform for pay, we get intel. If they tell our pitchman to go f*** himself/herself, the activist will start wondering who did take the money and it’ll cause conflict within the activist groups and it won’t cost us anything.”
In 2013, there was a leak of documents from the private intelligence company STRATFOR, which has worked for the American Petroleum Institute, Dow Chemical, Northrup Grumman, Coca Cola, and so on. The leaked documents revealed one part of STRATFOR’s strategy for fighting social movements. The document proposes dividing activists into four groups, then exploiting their differences to fracture movements.
“Radicals, idealists, realists and opportunists [are the four categories],” the leaked documents state. “The Opportunists are in it for themselves and can be pulled away for their own self-interest. The Realists can be convinced that transformative change is not possible and we must settle for what is possible. Idealists can be convinced they have the facts wrong and pulled to the Realist camp. Radicals, who see the system as corrupt and needing transformation, need to be isolated and discredited, using false charges to assassinate their character is a common tactic.”
As I will discuss later on, solidarity and movement culture is the best way to push back against these methods.
Other examples of infiltration and disruption have often focused on:
- Increasing tensions around racist or sexist behavior
- Targeting individuals with drug or alcohol addictions to become informants
- Using sex appeal and relationship building to get information
- Acting as an “agent provocateur” to encourage protesters to become violent, even to the point of supplying them with bombs, in order to secure arrests
- Spreading rumors about inappropriate behavior to sew discord and mistrust
- Intimidation
The third tactic used by these companies is intimidation. They will use fear and paranoia as a deliberate form of psychological warfare. This can include anonymous threats, shows of force, visible surveillance, and so on.
- Violence
When other methods fail, PMCs and public law enforcement will ultimately resort to direct violence, as we have seen with Standing Rock and many other protest movements.
As I have written before, colonial states enforce their resource extraction regimes with force, and we should disabuse ourselves of notions to the contrary. Vigilante violence is also always a concern. When people seek to defend land from destruction, men with guns are usually dispatched to arrest them, remove them from the site, and lock them in cages.
How to Resist Against Surveillance and Repression
There are specific techniques we can deploy to protect ourselves, and by extension, protect the land at Thacker Pass. These techniques are called “security culture.”
Security culture is a set of practices and attitudes designed to increase the safety of political communities. These guidelines are created based on recent and historic state repression, and help to reduce paranoia and increase effectiveness.
Security culture cannot keep us 100% safe, all the time. There is risk in political action. But it helps us manage risks that do exist, and take calculated risks when necessary to achieve our goals.
The first rule of security culture is this: be cautious, but do not live in fear. We cannot let their intimidation be effective. Creating paranoia is a key goal for PMCs and other repressive organizations. When they make us so paranoid we no longer take action, reach out to potential allies, or plan and carry out our campaigns, they win using only the techniques of psychological warfare. When we are fighting to protect the land and water, we are doing something righteous, and we should be proud and stand tall while we do this work.
The second rule of security culture is that solidarity is how we overcome paranoia, snitchjacketing, and rumor-spreading. We must act with principles and in a deeply ethical and honorable way. Work to build alliances, friendships, and trust—while maintaining good boundaries and holding people accountable. This is the foundation of a good culture.
In regards to infiltration, security culture recommends the following:
- It’s not safe nor a good idea to generally speculate or accuse people of being infiltrators. This is a typical tactic that infiltrators use to shut movements down.
- Paranoia can cause destructive behavior.
- Making false/uncertain accusations is dangerous: this is called “bad-jacketing” or “snitch-jacketing.”
- Build relationships deliberately, and build trust slowly. Do not share sensitive information with people who don’t need to know it. There is a fine line between promoting a campaign and sharing information that could put someone at risk.
- Good security culture focuses on identifying and stopping bad behavior.
- Do not talk to police or law enforcement unless you are a designated liaison.
Secure communications are an important part of security culture.
Here are some basic recommendations to secure your communications.
- Email, phone calls, social media, and text messages are inherently insecure. Nothing sensitive should be discussed using these platforms.
- Preferably, use modern secure messaging apps such as Signal, Wire, or Session. These apps are free and easy to use.
- We recommend setting up and using a VPN for all your internet access needs at camp. ProtonVPN and Firefox VPN are two reputable providers. These tools are easy to use after a brief initial setup, and only cost a small amount. Invest in security.
We must also remember that secure communications aren’t a magic bullet. If you’re communicating with someone who decides to share your private message, it’s no longer private. Use common sense and consider trust when using secure communications tools.
Security culture also warns us not talk about some sensitive issues, including:
- Your or someone else’s participation in illegal action.
- Someone else’s advocacy for such actions.
- Your or someone else’s plans for a future illegal action.
- Don’t talk about illegal actions in terms of specific times, people, places, etc.
Note: Nonviolent civil disobedience is illegal, but can sometimes be discussed openly. In general, the specifics of nonviolent civil disobedience should be discussed only with people who will be involved in the action or those doing support work for them. It’s still acceptable (even encouraged) to speak out generally in support of monkeywrenching and all forms of resistance as long as you don’t mention specific places, people, times, etc.
Conclusion
Security is a very important topic, but is challenging. There are so many potential threats, and we are not used to acting in a secure way. That’s why we are working to create a “security culture”—so that our communities of resistance are always considering security, assessing threats, studying our opposition, and creating countermeasures to their methods.
This article is only a brief introduction to the topic of security culture. Moving forward, we will be providing regular trainings in security culture to Protect Thacker Pass participants.
Most importantly, do not let this scare you, and do not be overwhelmed. Simply take one security measure at a time, begin to study it, and then implement better protocols one by one. We use the term “security culture” because security is a mindset that should be developed and shared.
Resources:
Recommended topics of study:


 This is a map of the ghastly 2023 Jindalee exploration plan to punch in 267 new drill hole and sump sites and construct 30 miles of new roads. It would fragment an area with a very high density of nesting sagebrush songbirds of all kinds. Birds like Sagebrush Sparrow require continuous blocks of dense mature or old growth big sagebrush. Jindalee boasts its consultant environmental and cultural studies have found “no show-stoppers” and “no red flags”. Industry gets the results it wants when it pays for mine consultant work. Federal and state agencies, after a bit of pro forma sniping, acquiesce to what the mine comes up with.
This is a map of the ghastly 2023 Jindalee exploration plan to punch in 267 new drill hole and sump sites and construct 30 miles of new roads. It would fragment an area with a very high density of nesting sagebrush songbirds of all kinds. Birds like Sagebrush Sparrow require continuous blocks of dense mature or old growth big sagebrush. Jindalee boasts its consultant environmental and cultural studies have found “no show-stoppers” and “no red flags”. Industry gets the results it wants when it pays for mine consultant work. Federal and state agencies, after a bit of pro forma sniping, acquiesce to what the mine comes up with.









 I stopped, got out and approached a security guard who appeared at the truck. He refused to let me pass. After several minutes of my insistent repetition that this was a public road, the BLM mine EIS said this road would always be open, and that blocking use of this road indicated the EIS, the BLM and Lithium Americas had lied, the security guard relented and said he would call the head of security.
I stopped, got out and approached a security guard who appeared at the truck. He refused to let me pass. After several minutes of my insistent repetition that this was a public road, the BLM mine EIS said this road would always be open, and that blocking use of this road indicated the EIS, the BLM and Lithium Americas had lied, the security guard relented and said he would call the head of security. The boss pulled up in a white truck as a sudden rain whirlwind bore down. His face was obscured, and identity concealed by a tan balaclava-like hood and dark sunglasses. When he first arrived, he got out of his truck and pointed a camera device at me. I thought WTF is this – a security firm mercenary decked out for Operation Iraqi Freedom? Abu Ghraib in Orovada? I again repeated repeatedly that this was a public access road, and I was going up into the Montana Mountains to camp. He retreated to his pickup, likely to run me and my license plates through some creepy database. Finally, I was allowed to pass through.
The boss pulled up in a white truck as a sudden rain whirlwind bore down. His face was obscured, and identity concealed by a tan balaclava-like hood and dark sunglasses. When he first arrived, he got out of his truck and pointed a camera device at me. I thought WTF is this – a security firm mercenary decked out for Operation Iraqi Freedom? Abu Ghraib in Orovada? I again repeated repeatedly that this was a public access road, and I was going up into the Montana Mountains to camp. He retreated to his pickup, likely to run me and my license plates through some creepy database. Finally, I was allowed to pass through.

 LNC’s drill scarring is a mere prelude to the destruction that’s planned – 5,694 acres of outright destruction in a 17,933 acre project zone. The enormity and scale of the planned mine is mind boggling – a deep open pit, a waste rock pile, all types of infrastructure, a lithium smelter/sulfuric acid plant on-site using huge volumes of waste sulfur shipped into a new railroad off-loading site by the Winnemucca airport. The latter was just announced a few months ago, to the dismay of nearby residents who find themselves facing living by a hazardous materials zone. Hundreds of tons of off-loaded material will be trucked to Thacker Pass and burned every day in a plant whose air scrubber design wasn’t even finalized before the Thacker decision was signed by BLM. What stink and toxic pollution will this lithium processing generate? McDermitt caldera soils contain uranium and mercury. Mine water use is estimated to be 1.7 billion gallons annually. Enormous volumes of diesel fuel will be used throughout the mine’s operation. What’s green about all this?
LNC’s drill scarring is a mere prelude to the destruction that’s planned – 5,694 acres of outright destruction in a 17,933 acre project zone. The enormity and scale of the planned mine is mind boggling – a deep open pit, a waste rock pile, all types of infrastructure, a lithium smelter/sulfuric acid plant on-site using huge volumes of waste sulfur shipped into a new railroad off-loading site by the Winnemucca airport. The latter was just announced a few months ago, to the dismay of nearby residents who find themselves facing living by a hazardous materials zone. Hundreds of tons of off-loaded material will be trucked to Thacker Pass and burned every day in a plant whose air scrubber design wasn’t even finalized before the Thacker decision was signed by BLM. What stink and toxic pollution will this lithium processing generate? McDermitt caldera soils contain uranium and mercury. Mine water use is estimated to be 1.7 billion gallons annually. Enormous volumes of diesel fuel will be used throughout the mine’s operation. What’s green about all this?


 Sacrificing the Interior West for Corporate Energy Dominance While Energy Conservation Lags or Is Forgotten Altogether
Sacrificing the Interior West for Corporate Energy Dominance While Energy Conservation Lags or Is Forgotten Altogether I’m outraged at the ecocidal stupidity with which this “energy transition” is being carried out. Will we soon see Jindalee get US tax dollars to wipe out the McDermitt Creek Sage-grouse stronghold? How ironic that would be. Interior just announced funding for major sagebrush habitat restoration using Infrastructure Bill funds in High Priority sagebrush areas. It turns out one of the sites chosen is the Montana Mountains area. Mapping shows it includes the Thacker Pass mine area too, where nearly all the sage is on the verge of being destroyed by LNC. Close review of maps for Interior’s Montana “restoration” project shows it encompasses the McDermitt Creek watershed, hence the entire area coveted by Jindalee for massive new drilling followed by open pit mining. It would be absurd to greenlight Jindalee’s ghastly exploration plan in primo habitat, when the Interior Department has identified this very same landscapeto be among the highest priority for restoration – because so much sage has already been lost already. The caldera is also key for connectivity between Sheldon and Owyhee Sage-grouse populations and for biodiversity preservation.
I’m outraged at the ecocidal stupidity with which this “energy transition” is being carried out. Will we soon see Jindalee get US tax dollars to wipe out the McDermitt Creek Sage-grouse stronghold? How ironic that would be. Interior just announced funding for major sagebrush habitat restoration using Infrastructure Bill funds in High Priority sagebrush areas. It turns out one of the sites chosen is the Montana Mountains area. Mapping shows it includes the Thacker Pass mine area too, where nearly all the sage is on the verge of being destroyed by LNC. Close review of maps for Interior’s Montana “restoration” project shows it encompasses the McDermitt Creek watershed, hence the entire area coveted by Jindalee for massive new drilling followed by open pit mining. It would be absurd to greenlight Jindalee’s ghastly exploration plan in primo habitat, when the Interior Department has identified this very same landscapeto be among the highest priority for restoration – because so much sage has already been lost already. The caldera is also key for connectivity between Sheldon and Owyhee Sage-grouse populations and for biodiversity preservation.



![The Long Shadow of the Tar Sands: Lithium Mining and Tar Sands Sulfur [Dispatches from Thacker Pass]](https://dgrnewsservice.org/wp-content/uploads/sites/18/2021/04/Shadows-980x652-1.jpg)


