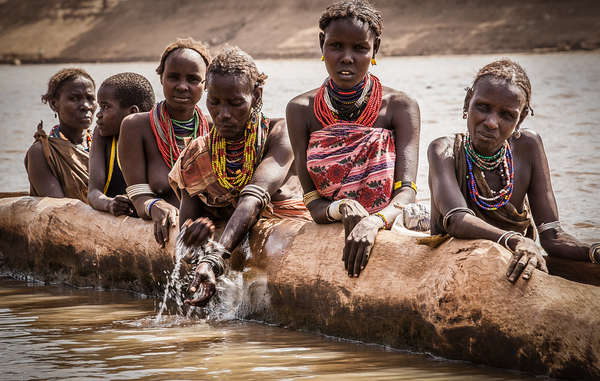by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Apr 13, 2016 | Biodiversity & Habitat Destruction, Indigenous Autonomy
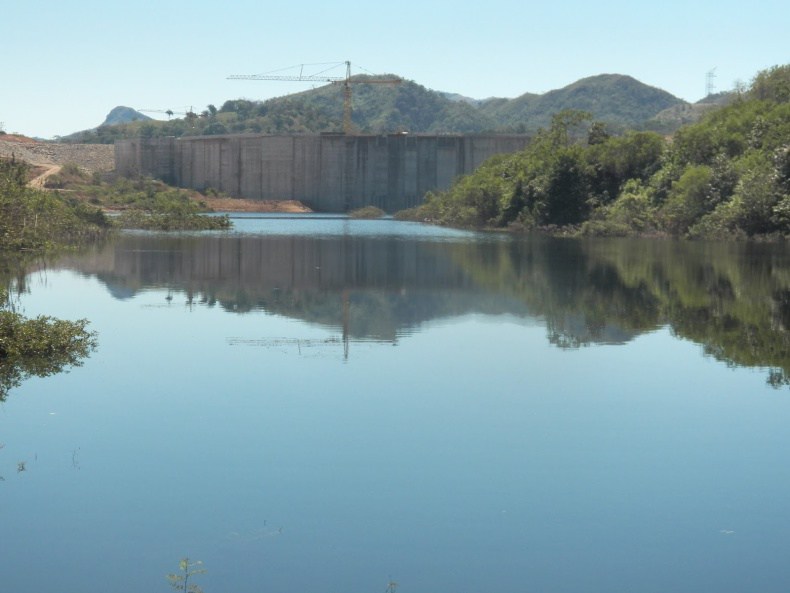
Featured image: The Barro Blanco Dam will have a disastrous effect on Ngäbe communities inside the Comarca Ngäbe-Bugle and campesino communities also living on the banks of the river. Photo Oscar Sogandares
By Jennifer Kennedy/ Intercontinental Cry
Ngäbe communities in western Panama are calling for support from the international community after officials from the Honduran-owned energy company, GENISA, warn that they will soon be evicted from their homes to make way for the flooding of the Barro Blanco hydro dam reservoir.
Ricardo Miranda, a spokesperson from the Movimiento 10 De Abril (M10) resistance movement, told IC, “The situation for the Ngäbe people is critical and tense with the imminent closure of the Barro Blanco gates. The government has announced that the gates will be closed in April and before that people will be evicted.”
The 28.84 megawatt dam is being constructed by GENISA on the Tabasará River in the western province of Chiriquí. Although located in Chiriquí, the dam will have a disastrous impact on Ngäbe communities inside the Comarca Ngäbe-Bugle and campesino communities also living on the banks of the river.
Once the gates are closed and the reservoir is filled, the subsistence fishing practices of all nearby communities will take a severe hit; cultivable land will be irrecoverably lost and the Ngäbe themselves will lose their school, their cultural centre and two sets of ancient petroglyphs that are of considerable cultural and archaeological importance.
Before this happens, Ngäbe-Bugle and campesino communities in the impact area will be forced from their homes.

A celebratory gathering to honor the petroglyphs. Photo: Oscar Sogandares
GENISA officials have reportedly claimed that the dam’s reservoir will be filled on April 15.
M10 has been fighting relentlessly to halt the project since the movement was founded in 1999, when a group of Ngäbe protesters were arrested for opposing the dam. Working along side them is Movimiento De Septiembre 22 (M22), an independent Ngäbe movement whose members follow Mama Tata, a religion that’s centered on cultural revival. M22 made international headlines in 2015 when they blocked the entrance to the dam for 38 consecutive days, until riot police, claiming to act in self-defense, unleashed pepper spray and batons on the Ngäbe activists, women and children among them.

Edilma Pinto, 17, suffered a fractured foot during the 2015 police crackdown. (Photo: Oscar Sogandares
Silvia Carrera, chief of the Comarca Ngäbe-Bugle, who is currently in negotiations with the government, was initially supportive of M10 and M22’s resounding calls to cancel the project. However, Carrera changed her position after the July crackdown, signing a document with the government in favour of the project.
Under that document, the dam is forbidden to proceed until an agreement is reached with the region’s indigenous and campesino stakeholders. Unfortunately, this provision appears to have slipped off the table. Flood tests are now taking place and according to the international NGO Carbon Market Watch (CMW), there remains a worrying lack of requisite dialogue between the government and the communities affected by the hydro dam.
GENISA itself has never sought the free, informed, and prior consent (FPIC) of the indigenous communities living on the banks of the Tabasará river.
Miranda says affected communities are as adamant as ever that the project be stopped. Together, they are urgently calling on the international community for support.
“We are asking for international solidarity in the struggle for water and the Tabasará River. We are asking people to demand the definitive cancellation of Barro Blanco and to demand an end to the violence against the Ngäbe which is being inflicted by the project,” he said.
GENISA isn’t the only one that’s failing to live up to stakeholder expectations.
The US$78M project, registered under the United Nation’s CDM carbon offsetting mechanism, has received significant financing from The Netherlands Development Finance Company (FMO), The German Investment & Development Company (DEG) and the Central American Bank for Economic Integration (CBIE).
The FMO and DEG previously admitted to failing their own due diligence tests during the course of financing. A report published in May 2015 by FMO’s internal Independent Complaints Mechanism (ICM) states, “Lenders should have sought greater clarity on whether there was consent to the project from the appropriate indigenous authorities prior to project approval.”
In June 2015, however, the lenders took things one step further by threatening the Panamanian government when it temporarily suspended Barro Blanco’s construction.
Denouncing the developments banks, Miranda told IC that “the FMO and DEG are complicit in the serious violations of human rights on the Tabasará River.”
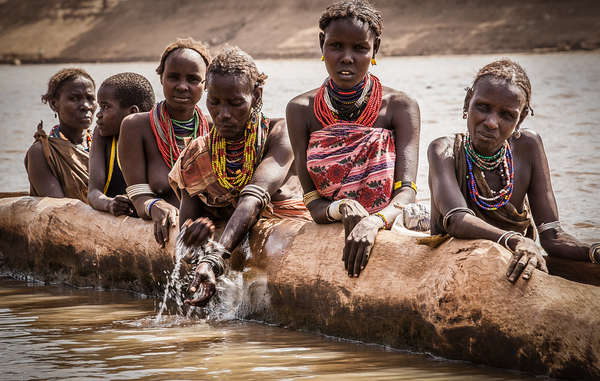
by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Mar 14, 2016 | Biodiversity & Habitat Destruction, Lobbying
Survival International has reported Italian engineering giant Salini to the OECD (Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development) over its construction of a controversial dam which is set to destroy the livelihoods of hundreds of thousands of people in Ethiopia and Kenya.
The dam has cut off the Omo river’s regular flooding, which 100,000 people rely on to water their crops and livestock and a further 100,000 depend on indirectly. According to experts, this could also spell the end for Lake Turkana – the world’s largest desert lake – and disaster for the 300,000 tribespeople living along its shores.
Salini did not seek the consent of local people before building the dam, but claimed that an “artificial flood release” would compensate them for their losses. However, this promised flood never came and thousands of people now face starvation.

Up to half a million people face starvation as a result of the dam Salini has constructed on the Omo river.
© Magda Rakita/Survival International
The region is one of the most important sites in early human evolution, and an area of exceptional biodiversity, with two World Heritage Sites and five national parks. The head of Kenya’s conservation agency said last week that the dam is unleashing “one of the worst environmental disasters you can imagine.”
Survival’s Director Stephen Corry said: “Salini has ignored crucial evidence, made false promises and ridden roughshod over the rights of hundreds of thousands of people. Thousands are now facing starvation because Italy’s largest contractor, and one of its best known companies, didn’t think human rights were worth its time. The real consequences of the Ethiopian government’s devastating policies for its country’s development, which are shamefully supported by western aid agencies like the UK’s DFID and USAID, are plain for all to see. Stealing people’s land and causing massive environmental destruction is not progress, it is a death sentence for tribal peoples.”
by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Jan 18, 2016 | Indigenous Autonomy, Lobbying
By Glenn Scherer, Mongabay
Featured image: Brazilian President Dilma Rousseff visits the construction site of the Belo Monte Dam, 2014. Photo by Ichiro Guerra/Sala de Imprensa licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 2.0 Generic license
The gigantic Belo Monte hydroelectric dam, located on the Xingu River in the heart of the Brazilian Amazon, stood just weeks away from beginning operation this week — but the controversial mega-dam, the third largest on earth, has now been blocked from generating electricity by the Brazilian court system until its builders and the government meet previous commitments made to the region’s indigenous people.
Federal court judge Maria Carolina Valente do Carmo in the city of Altamira, in the state of Pará where the dam is located, has suspended the dam’s operating license. It will not be reinstated, she decided, until the dam’s owner Norte Energia SA, along with Brazil’s government, meet a 2014 court-ordered licensing requirement to reorganize the regional office of Funai, the national agency that protects Brazil’s indigenous groups.
Judge Valente do Carmo has fined the government and company R$900,000 (US$225,000) for non-compliance with the Funai requirement, a provision included in the rules governing Belo Monte when the project was given its preliminary license in 2010.
This is the latest in a series of snafus that have plagued the dam’s construction. Licensing of the project was delayed last September by Brazil’s environmental agency IBAMA, due to a failure to complete agreed to provisions to mitigate the impacts of inundating thousands of acres of Amazon rain forest — flooding that could displace 20,000 people.
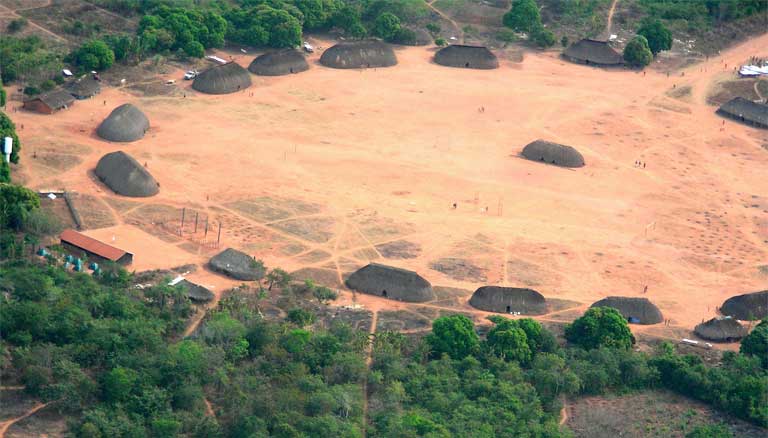

Indigenous village near the Xingu River in the Amazon. Indigenous lands could soon be flooded by the Belo Monte dam. Photo by Pedro Biondi/ABr licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Brazil license.
Earlier in 2015, federal prosecutors found that Norte Energia violated 55 different obligations it had agreed to in order to guarantee the survival of indigenous groups, farmers and fishermen whose homes and lands will be lost.In December, Brazil’s Public Federal Ministry, an independent state body started legal proceedings to have it recognized that the crime of “ethnocide” was committed against seven indigenous groups during the building of the Belo Monte dam.
Indigenous groups have fought the dam since its inception, saying that it will severely impair their water supply and impact fishing and hunting. They especially contend that it will reduce the river’s flow by 80 percent at the Volta Grande (“Big Bend”), where indigenous Juruna and Arara people and sixteen other ethnic groups live, according to the teleSUR television network.
Partially republished with permission of Mongabay. Read the full article at Brazilian court suspends operating license for Belo Monte dam

by DGR Colorado Plateau | Jan 2, 2016 | Colonialism & Conquest, Lobbying
By Sue Branford / Mongabay
Featured image courtesy of Wikipedia under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2
- Brazil’s Federal Public Ministry (MPF) has found the Brazilian federal government and the Norte Energia company guilty of ethnocide for the social and cultural destruction wrought on seven indigenous groups during the Belo Monte dam’s construction.
- The MPF is demanding the courts set up an external commission to prevent future harm, even as the Brazilian government is granted an operational licence for the dam, whose reservoirs are now filling.
- The MPF report states: “What is happening with the Belo Monte dam is a process of ethnic extermination by which the federal government is continuing with the colonial practice of integrating Indians into the hegemonic society.”
Brazil’s Public Federal Ministry (Ministério Público Federal, MPF), an independent state body, has started legal proceedings to have it recognised that the crime of “ethnocide” was committed on seven indigenous groups due to the severe detrimental impacts on their lives made by the building of the giant Belo Monte hydroelectric power station that will soon begin operating on the Xingu River in eastern Amazonia. The charges have been made against Brazil’s federal government and Norte Energia, the contractor that built the dam.
After carrying out a lengthy study that fills 50 books and includes contributions from a wide range of experts, the MPF has concluded that the “social organization, customs, languages and traditions” of the indigenous groups have been destroyed by the construction of the dam.
One of the actions undertaken by Norte Energia about which the MPF is most critical was a plan called “Plano Emergencial”. Under this plan the company set up a distribution center in Altamira, a town that has experienced explosive growth recently as a result of the dam’s construction. Goods and foodstuffs were available here each month for every indigenous village but the Indians had to travel to the town to pick them up. The money for the center came from a budget line for “ethno-development”, which was set up to help the villages become sustainable in food and to develop viable economic activities.
Indians, some of whom had never been to Altamira before, had to stop planting and fishing in order to travel to the town each month. The journey could take days and the whole procedure was very damaging to indigenous culture. The MPF says: “The villages became covered in garbage, with a proliferation of disease as a result, illnesses such as high blood pressure, obesity and diabetes became common because of the change in diet, child mortality surged, along with alcoholism, drug consumption and prostitution.”

The Belo Monte dam was completed at the cost of ethnocide to seven Amazon indigenous groups, according to the MPF. Photo by Pascalg622 licensed under under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2
At the same time Norte Energia began to build cheap houses in villages higher up the Xingu River, without taking into account indigenous culture. “Dozens of houses were built — wooden shacks with fiber cement roofs, like those in urban shanty-towns — with no consultation with Funai [the Indian Agency] or Ibama [the Environmental Agency]”. The building work itself was very harmful: unskilled workers without proper authorization entered the villages, disrupting village life and leaving construction waste behind; timber was illegally felled; a 17-year-old indigenous girl became pregnant from a construction worker.
Partially republished with permission of Mongabay. Read the full article, Brazil’s government charged with ethnocide in building of Amazon dam

by DGR Colorado Plateau | Dec 22, 2015 | Biodiversity & Habitat Destruction, NEWS
By Claire Salisbury / Mongabay
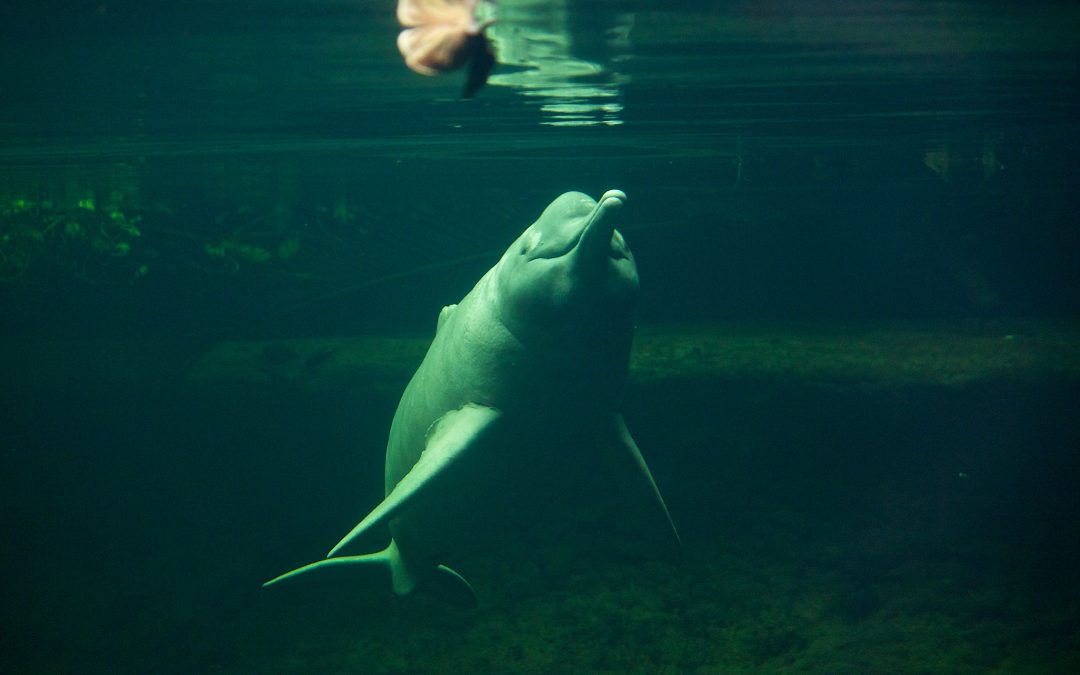
- A new study finds that as many as 26 dams could put the charismatic Amazon River Dolphin and the freshwater Tucuxi Dolphin at risk.
- The research looked at whether particular Amazon dam projects would fragment dolphin populations and affect prey populations.
- Though the public is fascinated by the Amazon’s dolphins, no one knows how many are currently left in the wild, or how the dam building frenzy will impact their numbers.
A dam-building boom is underway in the Amazon. More than 400 hydroelectric dams are in operation, being built, or planned for the river’s headwaters and basin. Scientists know that tropical dams disrupt water flow and nutrient deposition, with negative consequences for aquatic animals, especially migratory species. But little detailed knowledge exists as to the impacts of dams on specific species, or as to the best mitigations to prevent harm.
A recent study that tries to fill in that knowledge gap zeroes in on Brazil’s river dolphins. It found that as many as 26 dams could negatively impact dolphin populations and their prey.
The research, led by Dr Claryana Araújo of the Federal University of Goiás, Brazil, focused on two freshwater species: the Amazon River Dolphin, or boto (Inia geoffrensis), which is sometimes famously pink; and the Tucuxi (Sotalia fluviatilis).
The river dolphins of South America are charismatic emblems of rainforest biodiversity, and have captured the public imagination. Swimming in rivers, lagoons, and among submerged tree trunks in flooded forests to chase down prey, they can be found as far inland as the upper reaches of Amazonian tributaries, more than 2,600 kilometers (1,615 miles) from the Atlantic Ocean.
The two species inhabit Brazil, Peru, Ecuador, and Colombia, and in the case of the Amazon River Dolphin, Bolivia and Venezuela. Their ranges in Brazil extend beyond the limits of the Amazon basin, to include the Araguaia-Tocantins (for the Amazon River Dolphin) and North Atlantic watersheds (for both species).
Despite their status as flagship species in the region, both are classified as Data Deficient by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) due to a current dearth of data. No one knows how many exist in the wild, or population trends over recent decades, and uncertainties remain regarding their ecology, and major threats to the species. This lack of baseline data leaves scientists and governments in the dark regarding the conservation measures needed, and puts the animals at greater risk.
Partially republished with permission of Mongabay. Read the full article, Damming the Amazon: new hydropower projects put river dolphins at risk
“Amazon river dolphin” by Missud is licensed under CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.