
by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Jun 23, 2016 | Biodiversity & Habitat Destruction
By Will Falk / Deep Green Resistance
The Swamp Cedars in Spring Valley, Nevada have grown long memories. They stand on the valley floor under the bright Great Basin stars where the skies are still unspoiled by the encroaching glow of electricity. Beneath the trees’ branches, the blue petals of wild irises flutter in the breeze. All of them – the trees, the flowers, the stars – sway to the soft melodies played by the valley’s bubbling springs.
Most of the Swamp Cedars’ memories are pleasant. Carried by glaciers to the valley floor sometime in the last two and a half million years, the Swamp Cedars remember when wooly mammoths plodded through the Great Basin. The wind through their leaves whispers of a time when the Swamp Cedars trembled under the shadow of great teraton birds who rode the skies with their 25-foot wingspans. When wild horses stop at the springs to share a drink with the Swamp Cedars, the trees tell stories of the fleet native horses and camels that once ran the open spaces of North America.
Dawn in Spring Valley still carries the hint of curiosity the Swamp Cedars felt on that morning so many thousands of years ago when they watched the first humans walk from the foothills to rest in the welcome shade the trees offered. They learned to expect the humans regularly as they gathered under the trees for sacred ceremonies. They listened as the humans called themselves “Newe” and the trees learned that the word meant, “people.”
The Newe returned often to the Swamp Cedars for their ceremonies and the trees took delight with the Newe as old friends embraced after several seasons apart, as young people became lovers, and as information was shared about the year’s pinyon pine nut harvest.
A few of the memories are extremely painful. The Swamp Cedars recall when a different kind of human first arrived in Spring Valley. These humans were pale of skin and rode what the trees recognized as horses though they were a different species of horse than the native horses that had long since been lost. At first, there were just a few of the pale humans, but the trickle turned into a flood. The Swamp Cedars wince as they relive their first experience of steel – the excruciating pain that came when the first ax drove deep into living Swamp Cedar wood.
Worst of all, the Swamp Cedars witnessed the Newe screaming as the blue-clad humans on horses rode them down, the puffs of white smoke that turned into a haze, and the sharp cracks of rifle fire. The Swamp Cedars still recoil from the taste of blood in the soil when the bubbling springs turned red.
***
Dr. Ronald Lanner, one of the foremost experts on Great Basin trees explains the Swamp Cedars’ uniqueness: “…within the borders of Nevada, Rocky Mountain juniper is found in 39 mountain ranges but in only one valley – Spring Valley.” The Swamp Cedars carry an aura of magic. In fact, they are not cedars at all. They are actually Rocky Mountain junipers (juniperus scopulorum) and Rocky Mountain junipers always grow on dry, rocky mountain slopes or in somewhat shaded canyons. Always – except for the Swamp Cedars. Mysteriously, the Swamp Cedars grow in valley bottom woodlands that are flooded part of the year.
The Swamp Cedars of Spring Valley are likely on their way to evolving into a distinct species. Lanner describes, “…it is very likely the swamp cedars comprise a distinct ecotype of Rocky Mountain juniper. An ecotype is a genetically differentiated population that has evolved in adaptation to a distinctively different environment than characterizes that of the main population of its species.”
The Swamp Cedars are sacred to the Shoshone (Newe in their own language) peoples. According to Shoshone elder Delaine Spilsbury, Nevada’s Native peoples were hunter-gatherers who roamed the region in small familial groups while they searched for food. The Swamp Cedars were centrally located in the Shoshone’s traditional territories and offered ample shade during the hot Great Basin summers. Beneath the trees are a series of springs. Water from the springs encouraged plants and animals to proliferate. The Shoshone found many game birds and animals, medicinal plants, and fish in the nearby streams and ponds. Not far away from the Swamp Cedars, pinyon pine forests grew bounties of pine nuts. With these conditions, the Swamp Cedars became the favorite gathering place for the Shoshone and a sacred ceremonial site.
The Swamp Cedars are a massacre site. Three times over. Spilsbury explains that two of the massacres are of official military record while the last massacre happened at the hands of vigilantes with no military record.
The first two massacres happened in the 1860s. In the first massacre, most of the Shoshone escaped when American cavalry horses became mired in the mud created by the valley’s springs. The second massacre was much worse and Spilsbury says the written reports “state that men’s penises were cut off and shoved into their mouths and tree branches were shoved into women’s vaginas.”
The third massacre happened in 1897. This massacre is only remembered because two little girls hid in a ditch and were not discovered by the white vigilantes who murdered everyone else. The two little girls walked south to the Swallow Ranch. One of the two survivors was named Mamie by the Swallow family. Later, she married one of the Swallows’ hired hands – a Paiute man from Shivits, Utah named Joe Joseph. Spilsbury is the granddaughter of Mamie and Joe Joseph and, therefore, a direct descendant of a survivor of the last Swamp Cedar massacre.
The massacres cursed the Swamp Cedars with a bloody historical significance, but the massacres also endowed the trees with a deep, spiritual significance. According to Spilsbury, “Newe believe that because of their violent deaths, the spirits of the victims remain in the Sacred Trees.”
***
The Swamp Cedars are under attack. Close to 300 miles south of Spring Valley, the City of Las Vegas sprang up in the desert. Las Vegas’ population continues to grow in an arid landscape and the city is running out of water. Instead of restricting development, Sin City encourages residents and businesses to move to the city promising them access to the water they’ll need.

In 1991, the Southern Nevada Water Authority (SNWA) was created through a cooperative agreement among seven water and wastewater agencies in Southern Nevada including Big Bend Water District, City of Boulder City, City of Henderson, City of Las Vegas, City of North Las Vegas, Clark County Water Reclamation District, and the Las Vegas Valley Water District.
From the SNWA website: “SNWA officials are charged with managing the region’s water resources and providing for Las Vegas Valley residents’ and businesses’ present and future water needs.” To do this, SNWA has proposed a “Groundwater Development Project.”
The bulk of this plan hinges on a large pipeline from Las Vegas to rural eastern Nevada. The main pipeline is estimated to include 263 miles of buried water pipelines while an estimated 96 to 254 miles of collector pipelines will feed water to the main pipeline. The entire pipeline will pump 27 billion gallons of water from the desert annually. Between 71 and 88 wells will have to be dug in fragile ecosystems while somewhere between 96 and 254 miles of overhead distribution power lines will be built in a region famous for wildfires. The water will be taken primarily from 4 desert valleys – Spring, Cave, Dry Lake, and Delamar Valleys.
In other words, SNWA’s Groundwater Development Plan would destroy much of the Great Basin, would destroy Spring Valley and would destroy the Swamp Cedars.
According to Dr. David Charlet, in his study “Effects of Interbasin Water Transport on Ecosystems of Spring Valley, White Pine County, Nevada,” “Ecosystems of Spring Valley, like most valleys in Nevada, are stressed. Overgrazing, particularly during the late 1800s, water diversion, and groundwater pumping have weakened the plant communities.”
This means human activities are already undermining life in the area.
Charlet makes horrifying predictions for the Swamp Cedars, writing, “The groundwater development proposed by the SNWA for the Spring Valley will doom the populations of swamp cedars. It is unlikely that they will live long past the first 20 yr [sic] of drawdown…” In fact, Charlet believes the Swamp Cedars will act as the canaries in the coal mine as he describes what he thinks will happen, “The swamp cedars will be the first plant species in the valley to become locally extinct, and I imagine that they would not be able to hang on for more than 50 yr. The next species to follow the swamp cedars will be the greasewood, followed shortly by big Great Basin sagebrush, and finally by rabbitbrush.”
Dr. Lanner agrees with Dr. Charlet in Lanner’s study “The Effect of Groundwater Pumping Proposed by the Southern Nevada Water Authority on the ‘Swamp Cedar’ of Spring Valley, Nevada.” He writes, “Despite the fact that the swamp cedars are not currently considered at risk of extinction by state or federal authorities, they are vulnerable to groundwater pumping leading to lowering of the water table and loss of surface flooding. The granting of pumping permits would make it logical, however, for such listing to be initiated.”
Even more terrifying than Charlet’s 20-year prediction, Lanner gives the Swamp Cedars 2 years. He explains, “Since the swamp cedars’ root systems are concentrated in the upper one foot of soil, and almost entirely in the upper two feet, drawdown of water from this part of the soil profile can be expected to be devastating to the trees. I would expect trees to die within no more than two years following the pumping of water from their root zone, even if there is ample rainfall to keep surface roots alive.”
***
What will the world lose if SNWA has its way?

Wild irises and Swamp Cedars, Spring Valley
There are the obvious answers. The world will lose the Swamp Cedars, Spring Valley’s ability to support life, and a place of cultural significance for a historically oppressed people. Las Vegas will swell and, as it gets bigger, will require ever more water to support itself. Eventually, the city will reach farther and farther to steal water destroying community after community until it cannot find enough. Then, it will collapse. Many of those who have been forced to rely on the city’s infrastructure for the necessities of life will perish. These will be grievous wounds, of course. And they give us all the reason we need to know that SNWA must be stopped.
There are wounds that strike even deeper than these, though. They are wounds that scrape our spirits. They are aimed at our souls. They erase our collective memory and chill our courage to resist. Understanding the Swamp Cedars, listening to their stories, and sharing their memories helps us to regain our own memories. Regaining our memories will enable us to see more clearly.
What will we see when we see clearly?

We will see that this culture’s pattern of abuse is not inevitable. Las Vegas’ water shortage is the result of a complex of stories, institutions, and artifacts that both leads to and springs from the growth of cities. Cities are groups of people living in place in populations high enough to require the importation of the necessities of life like water. This is a way of life built on drawdown and can never be sustainable.
Contrast this to the hunter/gatherer culture practiced by the Shoshone – the people who will suffer the most from SNWA’s water grab. The Shoshone lived sustainably in places like Spring Valley for thousands of years without destroying the land. The dominant culture, on the other hand, has been in the area since the 1850s. And, already in this comparatively short time, the Great Basin is on the verge of collapse.
Central to Shoshone culture is the idea that the Swamp Cedars are sacred. As the Shoshone teach that the victims of the Swamp Cedars massacres remain in the trees, they ensure that the lessons of these massacres will never be forgotten so long as both the Shoshone and the Swamp Cedars survive.
It is in the Swamp Cedars’ sacredness that we find one of the prime motivations for the dominant culture’s destruction of the Swamp Cedars, for the destruction of indigenous peoples’ sacred places around the world, and ultimately for the annihilation of every last indigenous culture. In destroying the Swamp Cedars, in destroying sacred places, and in destroying indigenous cultures, the dominant culture destroys examples of true sustainability. The dominant culture wants to erase all memory that there are other, more beautiful ways to live.
For the vast majority of human history and in lands around the world, humans built cultures based on the notion that all living beings are sacred. Fish, birds, and animals were our kin. Mountains housed gods, rivers spoke the mysteries of existence, and spirits lived in the trees. When every living being is sacred, it is sacrilegious to destroy wantonly and the kind of total annihilation we face today is simply unthinkable.
When a small minority of human cultures banished the sacred to abstract sky gods or denied the possibility of the sacred in any form, they turned a living, speaking world into so much material to use. Surrounded, as this small minority was, by humans who still remembered the sacredness of all life, this small minority was incredibly insecure. To maintain the lies, they had to destroy the reminders. Natural community after natural community, species after species have fallen victim to this culture. The dominant culture operates as a serial killer. And, just like a serial killer, the dominant culture will destroy every last scrap of the evidence of its crimes if we let it.
The Swamp Cedars, by their sacredness to the Shoshone, by the memories they carry, by their very existence, betray the unspeakable evils committed by this culture. The dominant culture cannot afford for the Swamp Cedars to continue teaching the world about life. The Swamp Cedars must survive. We must stop the SNWA water grab and biocidal projects everywhere.
For more information about stopping the SNWA water grab, please see the Great Basin Water Network and Deep Green Resistance Southwest Coalition.

by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Feb 28, 2016 | Biodiversity & Habitat Destruction, Indirect Action
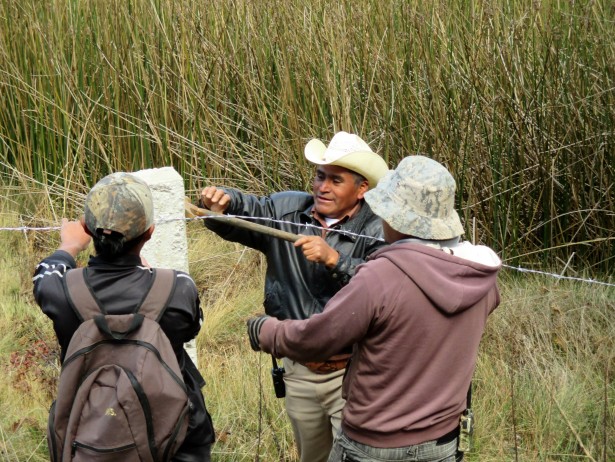
Featured image: Candelaria residents erect a fence around the Suyul Lagoon to help protect it from intruders. (Waging Nonviolence/Sandra Cuffe)
By Sandra Cuffe / Waging Nonviolence
The reeds and grasses are as tall as Sebastián Pérez Méndez, if not taller. The vegetation is so thick it’s hard to see the water in the Suyul Lagoon that he and other local Maya Tzotzil residents are working hard to protect. Pérez Méndez crosses the road to point out where aquatic plants serve as a natural filter for the water as it flows out the lagoon, located in the highlands of Chiapas, in southern Mexico.
“The water is under threat,” he said. Pérez Méndez is the top authority of the Candelaria ejido, a tract of communally-held land in the municipality of San Cristóbal de las Casas. “We’re not going to allow it.”
Communities in Chiapas are organizing to protect the Suyul Lagoon and communal lands from a planned multi-lane highway between the city of San Cristóbal de las Casas and Palenque, where Mayan ruins are a popular tourist destination. Candelaria residents continue to take action locally to protect the lagoon. They also traveled from community to community along the proposed highway route, forming a united movement opposing the project.
It all started back in 2014 when government officials showed up in Candelaria looking for ejido authorities, including Pérez Méndez’ predecessor. It was the first residents had heard about plans for the highway. The indigenous inhabitants had not been consulted and were not shown detailed plans.
“They realized that [the government officials] were only seeking signatures,” Pérez Méndez said.
No one person or group is authorized to make a decision that would affect ejido lands, however, and there are strict conditions in place to ensure elected ejido leaders are accountable to members, he explained. An extraordinary assembly was held to discuss the highway project.
The Candelaria ejido was established in 1935, a year after a new agrarian law enacted during the Lázaro Cárdenas administration led to widespread land reform throughout Mexico. More than 2,000 people live in the 1,600-hectare ejido, and more than 800 of them are ejidatarios — legally recognized communal land holders whose rights have been passed down for generations. Only ejidatarios as a whole have the power to make decisions on issues like the highway project.
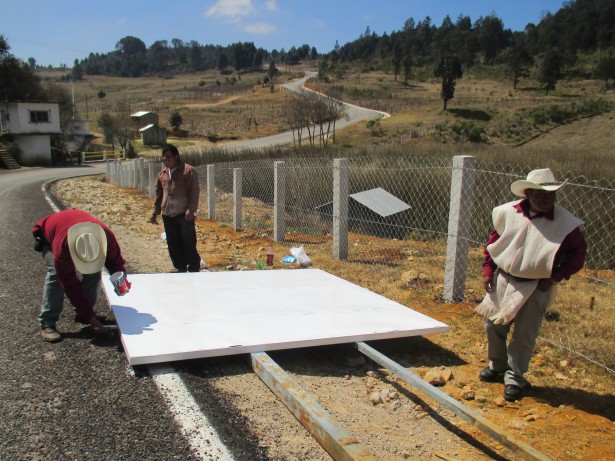

Candelaria residents paint over graffiti to fix up a roadside sign proclaiming their opposition to the highway project. (Waging Nonviolence/Sandra Cuffe)
“The ejido said no,” said Guadalupe Moshan, who works for the Fray Bartolomé de Las Casas Human Rights Center, or FrayBa, supporting Candelaria and other communities in Chiapas. “They didn’t sign.”
Candelaria leaders sought assistance from FrayBa in 2014, after they were approached by government officials and pressured to sign a document indicating their consent to the highway project that would involve a 60-meter-wide easement through communally-held lands. Officials told community members that the highway was already approved and that they would be well compensated, but that there would consequences if they refused to sign, Moshan said.
“They told them they would suspend government programs and services,” she explained. In the days following the extraordinary ejido assembly rejecting the project, there was unusual activity in the area, according to Moshan. Helicopters flew over theejido, unknown individuals entered at night, and trees were marked, she said.
Protecting the Suyul Lagoon remains at the heart of Candelaria’s opposition to the planned highway. The lagoon provides potable water not only for Candelaria, but also for several nearby communities, said ejido council secretary Juan Octavio Gómez. Aside from the highway itself, project plans eventually shown to the community leaders include a proposed eco-tourism complex right next to the lagoon. That isn’t in the communities’ interest, Gómez explained.
“Water is life. We can’t live without it,” he said. “Without this lagoon, we don’t have another option for water.”
Fed by a natural spring, the Suyul Lagoon never runs dry. Local residents are careful to protect the water and lands in the ejido, where the majority of residents live from subsistence agriculture, sheep rearing and carpentry. They engage in community reforestation, but have plans to plant more trees, Gómez said.
The Suyul Lagoon is also sacred to local Maya Tzotzil. Ceremonies held every three years in its honor involve rituals, offerings, music and dance.
“It is said that it’s the navel of Mother Earth,” Pérez Méndez said.
Candelaria residents didn’t sit back and relax after rejecting the highway project in their extraordinary assembly. They have been organizing ever since. The Suyul Lagoon lies just outside the Candelaria ejido, but it belongs to ejidatarios by way of an agreement with the supportive land owner. Aside from the highway project and potential eco-tourism complex, the lagoon has caught the attention of companies, whose representatives have turned up in the area expressing interest in establishing a bottling plant.
It’s cold in February up in the highlands, but community members have been out all day, erecting a fence around the Suyul Lagoon to protect it from intruders. White fence posts are visible under the treeline across the sea of reeds. Like so many other local initiatives, fence materials are collectively financed by the ejido and the labor is all voluntary, communal work.
While residents continue stringing barbed wire from post to post, others take paintbrushes to one of their roadside signs. Locals have erected large signs next to roads in and around their ejido, announcing their opposition to the tourist highway.

A sign along the road leading to Candelaria informs passers-by of opposition to the planned super-highway. (Waging Nonviolence/Sandra Cuffe)
“We’re also already organized with the other communities,” Pérez Méndez said. “All the communities reject the super-highway.”
After they were approached by government officials, Candelaria ejido residents traveled from community to community along the entire planned highway route. Some communities hadn’t heard of the project at all, while others said they were pressured into signing documents indicating their consent, Pérez Méndez said. As a result of Candelaria’s visits, community organizing along the highway route led to the formation of a united front of opposition, the Movement in Defense of Life and Territory.
Candelaria also recently got together with other indigenous communities in the highlands to issue a joint statement rejecting the tourist super-highway and a host of other government and corporate projects and policies.
“Our ancestors, our grandfathers and our grandmothers have always taken care of these blessed lands, and now it’s our turn to [not only take] care of the lands, but also to defend them,” reads the February 10 communiqué.
“The neoliberal capitalist system, in its ambition to exploit natural assets, invades our lands,” the statement continues. “The government and transnational companies are violently imposing their mega-projects.”
Back along the edge of the Suyul Lagoon, Candelaria residents continue to string barbed wire from post to post. They’ve been at it for a while now, according to Pérez Méndez, but they’ve now stepped up their efforts and hope to finish the fence by the end of the month.
Pérez Méndez surveys the progress, protected from the unrelenting sun and icy wind by his hat and white sheep’s wool tunic. He becomes pensive when asked if he thinks communities will be able to defeat the highway project.
“Yes,” the ejido leader said, after giving it some thought. “We can stop it.”

by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Feb 11, 2016 | Colonialism & Conquest, Toxification
Featured image: Figure from EPA Pacific Southwest Region 9 Addressing Uranium Contamination on the Navajo Nation
By Courtney Parker / Intercontinental Cry
Recent media coverage and spiraling public outrage over the water crisis in Flint, Michigan has completely eclipsed the ongoing environmental justice struggles of the Navajo. Even worse, the media continues to frame the situation in Flint as some sort of isolated incident. It is not. Rather, it is symptomatic of a much wider and deeper problem of environmental racism in the United States.
The history of uranium mining on Navajo (Diné) land is forever intertwined with the history of the military industrial complex. In 2002, the American Journal of Public Health ran an article entitled, “The History of Uranium Mining and the Navajo People.” Head investigators for the piece, Brugge and Gobel, framed the issue as a “tradeoff between national security and the environmental health of workers and communities.” The national history of mining for uranium ore originated in the late 1940’s when the United States decided that it was time to cut away its dependence on imported uranium. Over the next 40 years, some 4 million tons of uranium ore would be extracted from the Navajo’s territory, most of it fueling the Cold War nuclear arms race.
Situated by colonialist policies on the very margins of U.S. society, the Navajo didn’t have much choice but to seek work in the mines that started to appear following the discovery of uranium deposits on their territory. Over the years, more than 1300 uranium mines were established. When the Cold War came to an end, the mines were abandoned; but the Navajo’s struggle had just begun.
Back then, few Navajo spoke enough English to be informed about the inherent dangers of uranium exposure. The book Memories Come to Us in the Rain and the Wind: Oral Histories and Photographs of Navajo Uranium Miners and Their Families explains how the Navajo had no word for “radiation” and were cut off from more general public knowledge through language and educational barriers, and geography.
The Navajo began receiving federal health care during their confinement at Bosque Redondo in 1863. The Treaty of 1868 between the Navajos and the U.S. government was made in the good faith that the government – more specifically, the Bureau of Indian Affairs (BIA) – would take some responsibility in protecting the health of the Navajo nation. Instead, as noted in “White Man’s Medicine: The Navajo and Government Doctors, 1863-1955,” those pioneering the spirit of western medicine spent more time displacing traditional Navajo healers and knowledge banks, and much less time protecting Navajo public health. This obtuse, and ultimately short-sighted, attitude of disrespect towards Navajo healers began to shift in the late 1930’s; yet significant damage had already been done.
Founding director of the environmental cancer section of the National Cancer Institute (NCI), Wilhelm C. Hueper, published a report in 1942 that tied radon gas exposure to higher incidence rates of lung cancer. He was careful to eliminate other occupational variables (like exposure to other toxins on the job) and potentially confounding, non-occupational variables (like smoking). After the Atomic Energy Commission (AEC) was made aware of his findings, Hueper was prohibited from speaking in public about his research; and he was reportedly even barred from traveling west of the Mississippi – lest he leak any information to at-risk populations like the Navajo.
In 1950, the U.S. Public Health Service (USPHS) began to study the relationship between the toxins from uranium mining and lung cancer; however, they failed to properly disseminate their findings to the Navajo population. They also failed to properly acquire informed consent from the Navajos involved in the studies, which would have required informing them of previously identified and/or suspected health risks associated with working in or living near the mines. In 1955, the federal responsibility and role in Navajo healthcare was transferred from the BIA to the USPHS.
In the 1960’s, as the incidence rates of lung cancer began to climb, Navajos began to organize. A group of Navajo widows gathered together to discuss the deaths of their miner husbands; this grew into a movement steeped in science and politics that eventually brought about the Radiation Exposure Compensation Act (RECA) in 1999.
Cut to the present day. According to the US EPA, more than 500 of the existing 1300 abandoned uranium mines (AUM) on Navajo lands exhibit elevated levels of radiation.
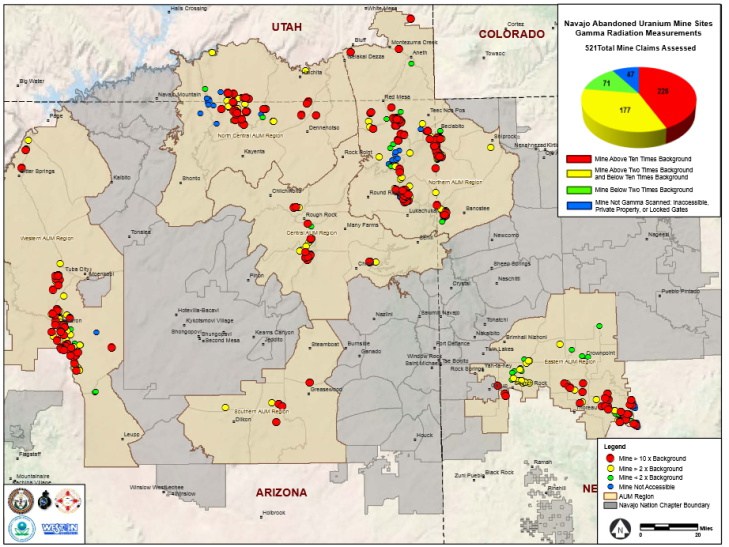
Navajo abandoned uranium mines gamma radiation measurements and priority mines. US EPA
The Los Angeles Times gave us a sense of the risk in 1986. Thomas Payne, an environmental health officer from Indian Health Services, accompanied by a National Park Service ranger, took water samples from 48 sites in Navajo territory. The group of samples showed uranium levels in wells as high as 139 picocuries per liter. Levels In abandoned pits were far more dangerous, sometimes exceeding 4,000 picocuries. The EPA limit for safe drinking water is 20 picocuries per liter.
This unresolved plague of radiation is compounded by pollution from coal mines and a coal-fired power plant that manifests at an even more systemic level; the entire Navajo water supply is currently tainted with industry toxins.
Recent media coverage and spiraling public outrage over the water crisis in Flint, Michigan has completely eclipsed the ongoing environmental justice struggles of the Navajo. Even worse, the media continues to frame the situation in Flint as some sort of isolated incident.
Madeline Stano, attorney for the Center on Race, Poverty & the Environment, assessed the situation for the San Diego Free Press, commenting, “Unfortunately, Flint’s water scandal is a symptom of a much larger disease. It’s far from an isolated incidence, in the history of Michigan itself and in the country writ large.”
Other instances of criminally negligent environmental pollution in the United States include the 50-year legacy of PCB contamination at the Mohawk community of Akwesasne, and the Hanford Nuclear Reservation (HNR) situated in the Yakama Nation’s “front yard.”
While many environmental movements are fighting to establish proper regulation of pollutants at state, federal, and even international levels, these four cases are representative of a pervasive, environmental racism that stacks up against communities like the Navajo and prevents them from receiving equal protection under existing regulations and policies.
Despite the common thread among these cases, the wave of righteous indignation over the ongoing tragedy in Flint has yet to reach the Navajo Nation, the Mohawk community of Akwesasne, the Yakama Nation – or the many other Indigenous communities across the United States that continue to endure various toxic legacies in relative silence.
Current public outcry may be a harbinger, however, of an environmental justice movement ready to galvanize itself towards a higher calling, one that includes all peoples across the United States, and truly shares the ongoing, collective environmental victories with all communities of color.

by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Jan 13, 2016 | Alienation & Mental Health
By Will Falk / Deep Green Resistance Great Basin
Featured image: Utah snow by Max Wilbert
Sitting on the patio at the Park City Library on a crisp September afternoon, I admire the beauty of this season’s new dusting of snow on mountains awash in the golds, reds, and greens of fall. I arrived in Park City last week thinking I will live in Utah again for the first time in almost 10 years.
The mountains’ timelessness makes it hard to believe it’s been 10 years since I packed my parents’ 1992 black Chevy suburban on a cold December night in Cedar City in 2005 before making the long drive to Iowa to be closer to my family in the Midwest. The joy that the sight of new snow has always produced for me makes it hard to believe its been 10 years since I last watched the good, thick Utah snow gather behind me to cloud the scene from my rear-view mirror as I pulled away softening the reminders of what and who I left behind.
Almost immediately after recognizing this beauty, I feel a deep pang of anxiety. I have been reading about the impacts climate change will have on Utah’s snow. I know, for example, that many scientists agree with Porter Fox, the author of DEEP: The Story of Skiing and the Future of Snow, that there will be no snow in Utah by the end of this century if climate change cannot be stopped.
My memories make it incredibly painful to imagine a Utah without snow, but this is the reality confronting us. Loving the snow as I do and understanding what the snow means to both humans and non-humans in Utah, I cannot help but call human-produced climate change “suicidal.”
***
I am intimately familiar with suicide. Sometime in the ten years after leaving Utah, I developed what my doctors have called “major depressive disorder.” When I was a public defender in Kenosha, WI, I tried to kill myself in April, 2013 and, again, in August, 2013.
I have spent the last two years trying to understand the darknesses that led me to attempt to take my own life those two times. I’ve always possessed a certain type of melancholy, but it takes more than a simple disposition for melancholy to develop suicidal depression.
Many theories exist for why I took the road to attempted suicides.
First, I have a history of traumatic head injuries including a brain contusion I suffered in a high school football game. I cannot remember what happened, but I do remember watching the game film the next morning and seeing my head bounce like a ball on the turf after I was knocked completely off my feet. I do not know if I suffered full-blown concussions playing college football at the University of Dayton, but I do remember my head hurting an awful lot. This theory supports the view that depression is truly a mental illness. My doctors tell me my brain struggles to recycle serotonin, and that this could be a result of the head injuries.
Another theory roots the depression I experience in my history of disconnection from any one place. I’ve never lived anywhere for long and this perpetual moving creates a feeling of spiritual vertigo for me. I was born in Evansville, IN, moved to Bedford, IN, moved to Salt Lake City, went to Cedar City, UT, re-joined my family in Waterloo, IA, headed to Dayton for college, then Madison, WI for law school, and on to Milwaukee to work in the public defender’s office. I lived in all of these places before I was 26. Each uprooting came with its own specific pains. Eventually, however, like a plant who will not take to new soil, I rejected the idea I could ever grow roots anywhere.
The final theory for my suicide attempts – and the one that makes the most sense to me – points to an overwhelming mixture of exhaustion, guilt, and despair I built as a public defender watching client after client dragged away to prison while I woke every morning to read news reports of ever more environmental destruction. I worked 60 and 70 hour weeks and it never seemed to matter. I could not keep my clients out of prison. I brought my case files home and some nights woke up at 3 AM to get a head start on the day. The more I lost, the stronger my feelings of guilt grew. It was my fault. I needed to work harder. The harder I worked, the more exhausted I became. The more exhausted I became, the harder it was to fight the guilt. The more guilt I felt, the harder I told myself I needed to work.
On top of this, I recognized – and still do – the fact that the planet’s life support systems are under attack by forces like climate change causing a growing number of scientists to predict human extinction by as soon as 2050. Carcinogens have seeped so deeply into the earth that every mother in the world has contaminants like dioxin in her breast milk; humans have successfully poisoned the most sacred physical bond between mother and child.
Meanwhile, nearly 50 percent of all other species are disappearing. Between 100-200 species a day are going extinct around the world. One quarter of the world’s coral reefs have been murdered. In the United States, alone, 95% of old growth forests are gone. In 70 countries worldwide there are no longer any original forests at all.
I often try to apologize for listing off these facts, or explain that perhaps I fixate on these things because I have a mental illness. I will not do that any longer. These atrocities are happening. Unless you are a sociopath, to truly contemplate these facts, to understand what they mean, to feel their implications comes with a profound emotional cost. I might have a mental illness, but it is natural to feel despair when confronted with the possibility of the destruction of all life on the planet.
***
I return to Utah after spending two years on the road supporting indigenous-led land-based environmental struggles. Why, just months after trying to commit suicide, did I set out for the front lines of the environmental movement?
Well, my experiences tell me that emotional states like despair, by themselves, are illusions and cannot hurt me on their own. Afflicted as I often am with a poor self-esteem and feelings of inadequacy, I learned that even when those thoughts arise, I do not have to entertain them. I can let them flash across the movie screen in my mind without ever attaching any meaning to them.
Despair by itself cannot kill me. I can kill me. Feeling the despair, I can grind several pills into powder, snort the powder to numb the pain, and then drink down the rest of the pills. Similarly, feeling the despair, I could put a gun to my temple or jump from a bridge. But, in each of these cases, it will not be the despair that kills me. It will be a physical action that kills me.
I find this realization to be deeply empowering. While I cannot always control my emotional state, I can control my actions. No matter how much despair I feel, I can refuse to act on that despair. Following this idea, I started to understand that I was not going to heal my mental illness with thoughts alone. I was not going to think my way out of depression. In order to heal, I needed to take tangible steps to alleviate the despair I was feeling.
First, I went up to central British Columbia to volunteer at the Unist’ot’en Camp. The Unist’ot’en Camp is an indigenous cultural center and pipeline blockade on the traditional, unceded territory of the Unist’ot’en clan of the Wet’suwet’en First Nation. I helped to build a bunkhouse on the precise GPS coordinates of a pipeline that would carry fossil fuels from the Fort McMurray tar-sands in Alberta over Unist’ot’en territory to a refinery in Kitimat, BC where the fossil fuels would be processed and shipped to be burned in markets world wide. I helped to break trails and walked the trapline on Unist’ot’en territory in the winter. Most of my time was spent sleeping on floors and couches in Victoria, BC as I volunteered for fundraising and organizing efforts to support the Camp.
I ran out of money in Canada and found it difficult to find work as a non-citizen, so I returned to my parents’ home in San Ramon, CA. Before long, though, I was encouraged to head to Hawai’i to write about Kanaka Maolis’ (native Hawaiians’) efforts to prevent the Thirty Meter Telescope from being constructed on the summit of their most sacred mountain, Mauna Kea. I spent 37 nights at 9,200 feet sleeping on the cold ground. I saw more snow than beaches in Hawai’i and was present when the police tried to force a way through 800 Kanaka Maoli as they blocked the construction equipment from gaining Mauna Kea’s summit. The police arrested 12 people that day, but were forced to turn back when boulders were rolled into the one road leading to the construction site.
Sometimes people try to thank me for my environmental activism. I always want to tell them not to thank me. I had to do it. All the thanks should go to the Unist’ot’en Clan and Kanaka Maoli for their bravery in protecting the Earth.
There’s a darker side to my decision to give up on a mainstream lifestyle to more effectively support environmental causes. I quit my job, gave up my apartment lease, sold my car, and broke up with the woman I was dating (a woman who stayed with me through the suicide attempts) in order to take off for Canada. It was not long before my money ran out and I was relying entirely on the generosity of others to help me along the way.
There are times when I wonder if it really is all that brave to turn my back on the normal responsibilities adults in this culture must attend to for basic survival. Getting a real job terrifies me. Maybe all I was doing on the road was avoiding putting my life back together after the suicide attempts?
***
While I ponder the snow from the Park City Library, I am reminded that I should be working on several of the online content writing gigs I have taken in an effort to re-build a sustainable income for myself. While I was on the road, I got sick of being broke. I became profoundly lonely for familiar places. I began to crave consistency in my day-to-day life.
I have a friend here in Park City, for example – the truest kind of friend who earned my trust after years of selfless communication and sincere concern for my well-being – who reminded me while I was on the road that I was always welcome in Utah. Her words were deeply encouraging, but I also knew I might not have enough money to get to Utah to see her. The truth is, to maintain relationships, you have to – at least sometimes – see those with whom you seek relationship.
The content writing gigs are a reminder of the long path facing me back to financial self-sufficiency. I would be lying if I did not confess the despair I sometimes feel when I realize just how out of control I let my personal life get. My student loans did not pay themselves. My resume can not magically produce an explanation for the hole in my work history. I still do not have enough money in my bank account to pay a first month rent and deposit to secure my own place to live.
Looking at my situation, the darkness begins to creep back in. I feel a deep sense of guilt wondering if I’ve sold out the environmental movement in order to build a community for myself. What right do I have to slow down right now? How can I look the Unist’ot’en Clan or Kanaka Maoli in the eye while their homes are under attack and I’m writing content for personal injury lawyers? Seeing the beauty of the snow on Park City’s peaks, knowing Utah may soon be too hot for snow to exist, why am I not running back to the front lines?
When these thoughts begin to spiral, I know I am in danger. I begin to hear that old whispering, suggesting a way out. I remember that there is a route to numb this confusion. It would not take too much of an effort to make it all fade away.
There the snow is again, though, and I know I will never try to kill myself again. I see the dark, heavy clouds weighing on the mountains’ shoulders. The chill in the air is a comfort because it brings the promise of water. As the powder spreads down the mountainsides, I know for another season, at least, there will be snowmelt, the streams will swell, and life will flourish across the land.
The snow in Park City brings a lesson. The snow is the future. Where there is snow, there is water and where there is water, there is life. Despair is the inability to see a livable future. Those who are destroying the planet are also destroying our future. When they clear-cut a forest, they clear-cut the future for those living in the forest. When they dam a river, they dam that river’s future. When they burn their fossil fuels and boil the Earth’s temperatures so that the snow in Park City disappears, they’re burning and boiling Park City’s future.
The snow, then, gives me my medicine for despair. The snow is the future. Fight for the snow, fight to ensure that the snow will continue to fall, and seeing the snow fall will bring the ability to see a livable future.

Colorado Plateau, southern Utah
Thoughts of suicide still sometimes fleet across my mind. Suicide’s mystique fades after you’ve gone through the spiritual process and the physical actions to produce your own death. The scariest part about it is that it really isn’t that scary at all. Suicide can come so easily.
But, the snow falls, and I know I cannot help the snow if I am dead. I am still engaged in war with my own demons and have had to re-consider my capacity, but if I can defeat those demons maybe I can become a stronger activist than I ever thought possible. The snow is too beautiful, the joy I feel seeing the snow is too strong, and the first stirrings of a feeling of belonging in Park City are too compelling for me to ever give in like that again.
Will Falk is a former public defender turned environmental writer and activist. He has been engaged in support for aboriginal sovereignty on the front lines at the Unist’ot’en Camp in so-called British Columbia and on Mauna Kea in Hawai’i. He is in the process of moving to Park City, Utah.

by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Nov 11, 2015 | Biodiversity & Habitat Destruction, Mining & Drilling, Toxification

Elvira Nascimento
Cyntia Beltrão reports from Brazil on what may be the country’s worst environmental disaster ever, at the Samarco open pit project jointly owned by Vale and BHP Billiton:
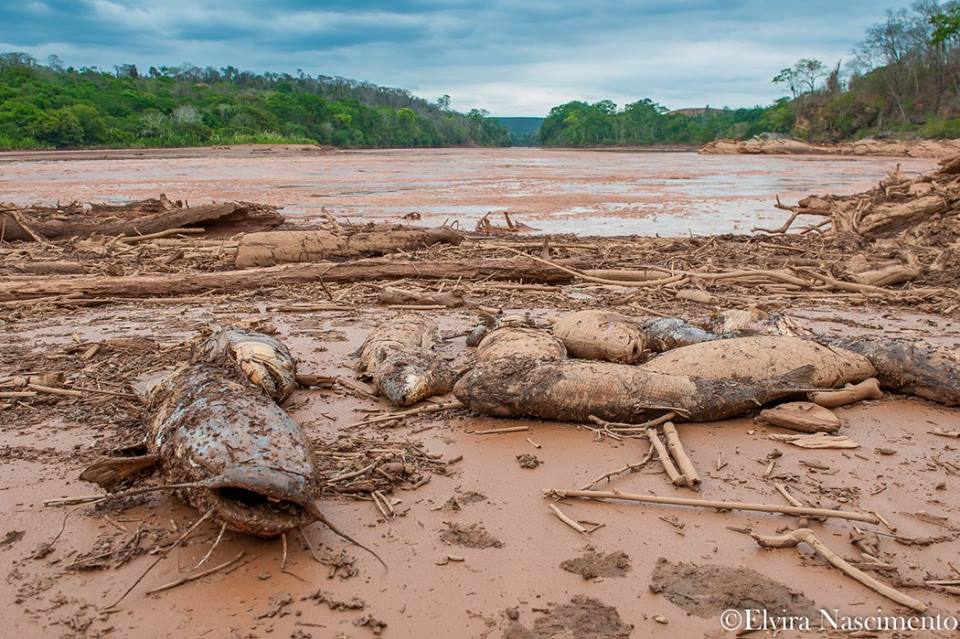
Last Thursday, November 5th, two dams containing mine tailings and waste from iron ore mining burst, burying the small historic town of Bento Rodrigues, district of Mariana, Minas Gerais state. The village, founded by miners, used to gain its sustenance from family farming and from labor at cooperatives. For many years, the people successfully resisted efforts to expel them by the all-powerful mining company Vale (NYSE: VALE, formerly Vale do Rio Doce, after the same river now affected by the disaster). Now their land is covered in mud, with the full scale of the death toll and environmental impacts still unknown.
Officially there are almost thirty dead, including small children, with several still missing. The press and the government hide the true numbers. Independent journalists say that the number of victims is much larger.
The environmental damage is devastating. The mud formed by iron ore and silica slurry spread over 410 miles. It reached one of the largest Brazilian rivers, the Rio Doce (“Sweet River”), at the center of our fifth largest watershed. The Doce River already suffers from pollution, silting of margins, cattle grazing in the basin land, and several eucalyptus plantations that drain the land. This year Southeastern Brazil, a region with a normally mild climate, endured a devastating drought. Authorities imposed water rationing on several major cities. Meanwhile, miners contaminate ground water and exploit lands rich in springs. The Doce River, once great and powerful, is now almost dry, even in its estuary. The mud of mining waste further injures the life of the river.
We do not know if the mud is contaminated by mercury and arsenic. Samarco / Vale says it isn’t, but we know that its components, iron ore and silica, will form a cement in the already dying river. This “cement” will change the riverbed permanently, covering the natural bed and artificially leveling its structure. The mud is sterile, and nothing will grow where it was deposited. A fish kill is already occuring. We do not know the full extent of impacts on river life or for those who depend on the river’s waters.
Soon the dirty mud will reach the sea, where it will cause further damage, to the important Rio Doce estuary and to the ocean.
 Some resources in Portuguese to learn more and get active:
Some resources in Portuguese to learn more and get active:















