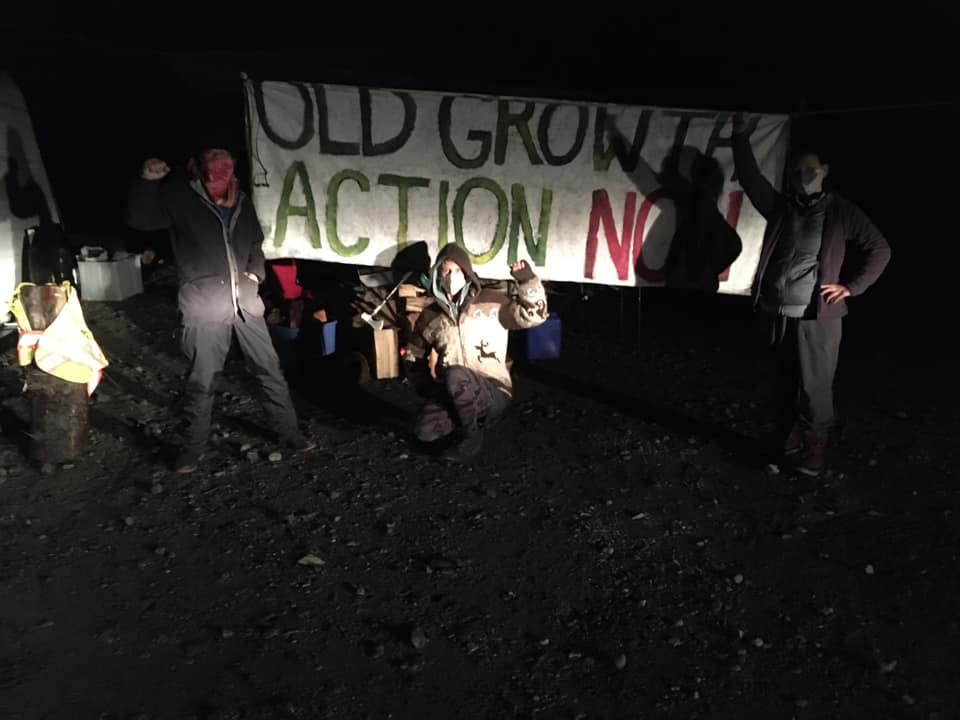by DGR News Service | Apr 6, 2021 | Biodiversity & Habitat Destruction, Colonialism & Conquest, Indigenous Autonomy, The Problem: Civilization
The “Grainway” freight train project cutting through the Brazilian Amazon is expected to receive its first environmental license next month.
This article was originally published on Mongabay. By Jennifer Ann Thomas, translated by Maya Johnson
A controversial project to build a rail line for transporting soybeans and other commodities through Indigenous lands in the Brazilian Amazon may get its environmental license as soon as April.
- Prosecutors in the state of Pará, where the line will terminate at the Miritituba river port, have filed a court request for a suspension of the project until prior consultation with the affected Indigenous communities have been carried out.
- The request seeks to challenge the project on its economic viability, with prosecutors arguing that without detailed data on costs and compensation measures, there is no way of knowing how the project will impact on public coffers.
- This is the first time that prosecutors have highlighted a project’s viability to seek its suspension.
A controversial freight railway line that would cut through Indigenous lands in the Brazilian Amazon looks set to be approved for construction by the federal government as soon as April, despite a lawsuit pending against it by local prosecutors.
The EF-170 railroad, known as the Ferrogrão, or “Grainway,” is a priority project of the federal government and will run 933 kilometers (580 miles) from the municipality of Sinop, in Mato Grosso state, to Miritituba in Pará state. The call for a tender is expected to be released within the first quarter of 2021, and the project is expected to be granted its environmental license in April.
All the freight traffic between the two cities currently flows through the BR-163 highway, bringing produce from Mato Grosso north to the river terminal in Pará. At present, though, more than 70% of Mato Grosso’s harvest is trucked southeast to the Atlantic ports of Santos and Paranaguá for export. With the railroad, the government aims to avoid this arduous step of the journey, instead sending commodities like soybean and corn to the transshipment terminal in Miritituba and onto ships sailing out to the Atlantic via the Tapajós, Tocantins and Amazon rivers. Aside from grains, the government also plans to transport soybean oil, fertilizers, sugar, ethanol, and petroleum products.
While the railroad is considered vital for grain shipping, the way the federal government is pushing ahead with the project has raised concerns.
In particular, the Federal Prosecutor’s Office (MPF) in Pará has challenged the government’s failure to seek the free, prior and informed consent of the Indigenous peoples through whose lands the railway would pass. In October, the MPF and five civil society organizations filed a request with the Federal Court of Accounts, the government accountability office, for the precautionary suspension of the privatization process and for the call for tender to be stopped.
Public prosecutor Felipe Moura Palha said the fact that the federal government has violated the Indigenous communities’ right to participate in discussions about the project risks imposing significant economic losses in the future. “This is the first time that the MPF has called on the Court of Accounts to analyze a large project in the Amazon with an eye on economics,” he said.
The MPF says the lack of data on the real environmental impacts of the project means the cost of compensation could be greater than imagined and possibly lead to losses from the public coffers. “We maintain that prior consultation, analysis and the effect on Indigenous communities in the economic viability analysis for the project is essential,” Palha said.
In response to the request filed by the MPF, the court notified the National Land Transportation Agency (ANTT), the federal regulator for railway and highway infrastructure, and Funai, the federal agency for Indigenous affairs, to carry out consultations with Indigenous peoples along the route of the planned rail line. But even then, the federal government has played foul, according to the MPF: prosecutors allege that the government’s Special Secretariat of the Partnerships and Investments Program (SE-PPI) tried to improperly entice an Indigenous Munduruku leader to act on behalf of the tribe.
The Munduruku people, with a population of about 13,700 occupying territories along the Tapajós River, have their own political organizations. According to the MPF, the government sought out a single person to be “the speaker granted representation to articulate the interests of his people.” On Dec. 14, the MPF recommended that the prior consultation process also include the project’s impacts on the Indigenous peoples in the state of Mato Grosso who would be directly or indirectly affected by the Grainway. The recommendation was aimed at Funai and IBAMA, the federal environmental protection agency.
Indigenous people ignored
Melillo Dinis is a lawyer with the Instituto Kabu, representing 12 communities of the Mẽbêngôkre-Kayapó people, including some 12,000 Kayapós. He said the Indigenous people have yet to form an opinion about the Grainway because the project has not yet even been presented to them. Dinis said there are currenty three issues under debate: the right to prior consultation and fulfillment of Indigenous protocol, neither of which were acknowledged by the government of President Jair Bolsonaro; the need for thorough social and environmental evaluation of the degradation, deforestation and growing tensions over territory in the region; and the fact that representatives of governmental agencies affirmed that Indigenous rights would be respected but did not carry out their promises.
“The context that has been presented to us until now is completely disrespectful of Indigenous peoples,” he said. “They have been living here for around 10,000 years. We will fight until the end.”
Dinis noted that the project has been dragged out over previous administrations; the Grainway was proposed in 2016, under the watch of then-president Dilma Rousseff, who was later that year impeached and replaced by Michel Temer. Temer was succeeded by Bolsonaro.
“Before, they would listen to us but wouldn’t pay any attention,” Dinis said of the Rousseff and Temer administrations. “This administration won’t even listen to us. So the outcome is the same.”
Prosecutor Palha said there’s no way to stipulate a ceiling on spending on the project without knowing how much to allocate for environmental compensation.
“We are not opposed to development projects,” he said. “Our request is: carry out the prior consultation before claiming that the project is viable so it can be discussed.”
He cited the case of the Belo Monte dam in the state of Pará as an example. A significant decline in the flow rate of the Xingu River now threatens the viability of the dam, raising the prospect of new power plants, likely fired by fossil fuels, needing to be built.
“We want to avoid this situation with the Grainway, having a project already installed that hasn’t been properly planned,” Palha said. “This is why the Court of Accounts is carrying out an unprecedented economics analysis.”
Controversy over the Grainway began in 2016 when it was announced that studies would be carried out to make the project viable. In 2018, Mongabay reported that the Kayapó people had expressed their concern over the potential threats posed by the railway and had written a letter to the ANTT. In it, tribal chief Anhe Kayapó said:
“The Grainway cannot be built without reinforcing controls, protection and vigilance in the Conservation Units and Indigenous Lands [along its route].”
This article was written by Jennifer Ann Thomas and translated by Maya Johnson; it was published in the Mongabay Series: Amazon Infrastructure
This story was first reported by Mongabay’s Brazil team and published here on the Brazil site on Feb. 26, 2021.
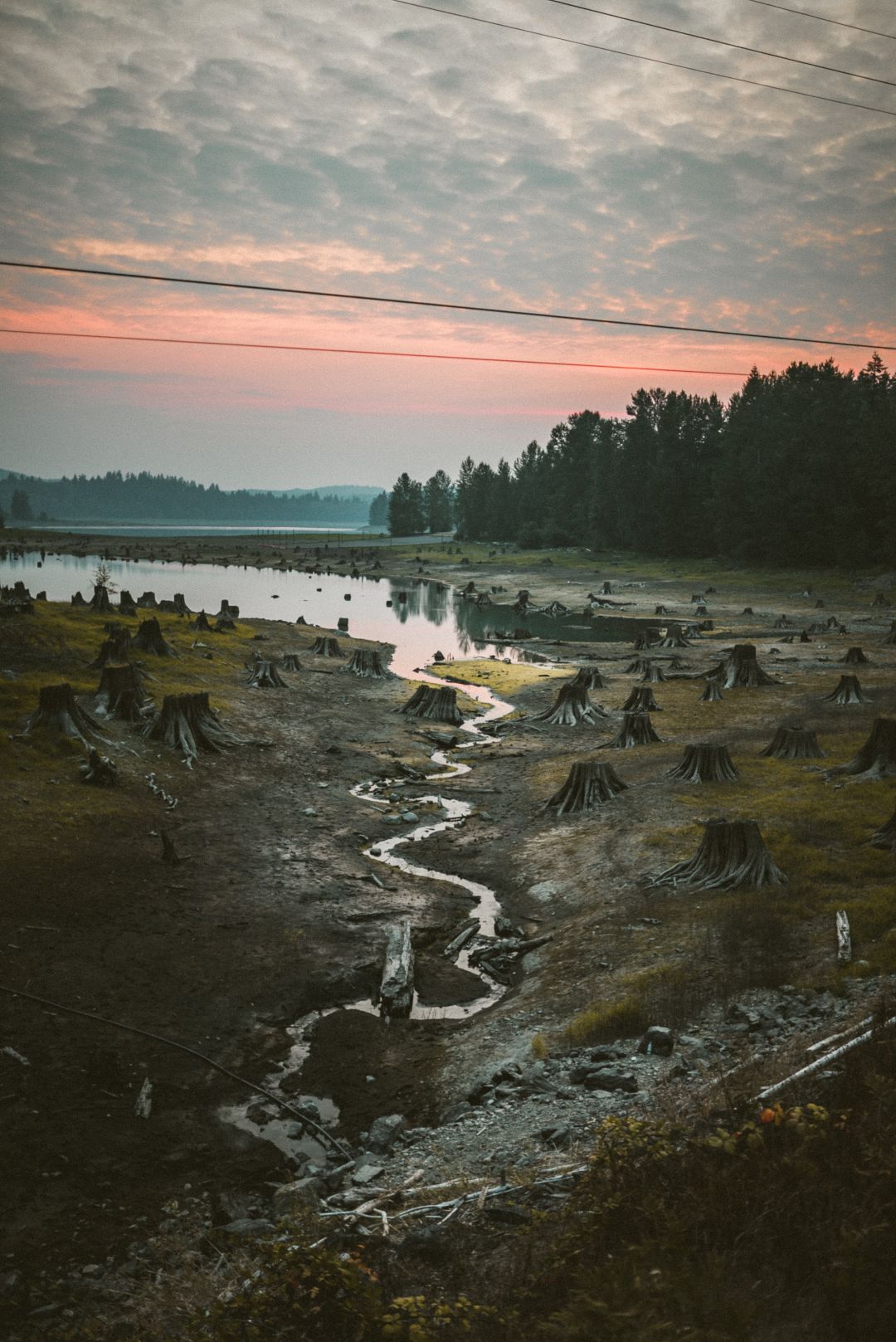

by DGR News Service | Mar 23, 2021 | Agriculture, Biodiversity & Habitat Destruction, Climate Change, The Problem: Civilization
In this article, Erik Molvar outlines the serious nature of climate change. He offers evidence-based clarity on why destroying fragile woodlands, that holds carbon in place, needs to stop.
The dawn breaks each morning on a hundred different mountain ranges in the Great Basin, with few human eyes to see it.
Many of these mountain chains will be unfamiliar to most – the Toquimas, the Wah Wahs, the Goshutes, the Sheeprocks, the Fox Range – but the one thing they all have in common is their juniper woodlands that have been here for thousands of years. On the mesas and tablelands of the Colorado Plateau, guarding the slickrock canyons and mazes of badlands that are American icons, are the fragile woodlands (don’t bust the crust!) of pinyon and juniper that perfume the air with that ineffable scent of wild country. Today, just as the world awakens to the reality that we need as much carbon sequestration as possible, these arid woodlands are under assault from a coordinated campaign to deforest the West, orchestrated by the livestock industry.
Action to address climate change has been announced as a central policy priority with the Biden administration, putting the significant role of domestic livestock in climate disruption in the spotlight. Methane emissions (both from the four-chambered digestion system that allows ruminants to digest cellulose, and from the breakdown of manure) get the lion’s share of the attention, in keeping with America’s end-of-tailpipe fixation on measuring pollution. But the carbon cycle is circular, and livestock exacerbate climate disruption at many points in the cycle. One key effect is by bankrupting soil carbon reserves by eliminating deep-rooted perennial plants and replacing them with annual weeds, and another is through deforestation to create cattle pasture. While deforestation for livestock is widely-recognized as a major climate problem in the Amazonian rainforests, deforestation of pinyon-juniper woodlands is ramping up across the American West, and similarly contributes to the climate catastrophe.
The real reason that pinyon-juniper woodlands are so aggressively targeted for “control” and “treatment,” even though they are an ecologically important and natural component of western ecosystems, comes down to the almighty dollar. A recent survey of Bureau of Land Management employees by Public Employees for Environmental Responsibility contains this clue: “with ranchers, one employee noted that the current excuse to cut pinyon juniper and sagebrush to prevent wildfire, which have been the native species for thousands of years, has no scientific reasoning. Instead, it’s to benefit cattle.”
During the dying days of the Trump administration, an all-out war on juniper woodlands was underway under the guise of fire prevention. The Tri-State Fuel Breaks Project planned almost a thousand miles of strips; scientists criticized the project, predicting it
“will not achieve success and may in fact exacerbate degradation of the native flora and fauna of the region.”
The Idaho portion was approved in May of 2020, authorizing
“manual, mechanical, and chemical treatments, along with targeted grazing and prescribed fire.”
The Great Basin Fuel Breaks Project was even bigger, authorizing 11,000 miles of fuel breaks in April of 2020. The selected alternative authorized wiping out 121,000 acres of woodlands. And for what? A federal review of the science found inconclusive benefits from fuel breaks constructed throughout the West over the past five decades. In effect, these are make-work projects that, while causing significant ecosystem destruction and habitat fragmentation, have little or no benefit in reducing the extent or intensity of fires.
Fuel breaks are but the tip of the deforestation iceberg.
In January 2021, during the twilight of the Trump presidency, a program called “Fuels Reduction and Rangeland Restoration for the Great Basin” was completed. Under this plan, more than 26 million acres would be targeted for a variety of environmentally destructive projects euphemistically labeled “vegetation treatments” as if the native vegetation is somehow sick. “Targeted grazing” is one such treatment authorized, even though a federal court ruled that livestock grazing actually increases the spread of flammable cheatgrass, instead of reducing fire risk, after hearing expert testimony on both sides of the issue.
Pinyon-juniper woodlands would bear the brunt of the projects, facing chainsaws, chaining with bulldozers, and herbicides. Some 3,088,468 acres of pinyon-juniper woodlands are now scheduled for “restoration treatments.” The Administration pre-approved this massive program habitat destruction under a single Environmental Impact Statement, which could allow the agency to approve future projects without analyzing the site-specific impacts, or perhaps even public notification.
The drive to get rid of pinyon and juniper woodlands began several years ago.
Senators Hatch and Heinrich slipped a rider into the 2018 Farm Bill instructing the Bureau of Land Management to create a “Categorical Exclusion” exempting pinyon-juniper logging and chaining projects of up to 4,500 acres from having to go through environmental analysis otherwise required by the National Environmental Policy Act. This legislation was pushed by sportsman groups, spearheaded by the Mule Deer Foundation. Western Watersheds Project and other conservationists warned that pinyon-juniper removal was bad for wildlife – including mule deer – but these warnings were ignored by Congress. Ironically, several months after Hatch-Heinrich passed, a new scientific study was published demonstrating that pinyon-juniper woodlands were an essential habitat component for mule deer, and that juniper removals have a negative effect on the species.
Then the Trump administration took it a giant leap farther, authorizing that pinyon-juniper removals as large as 10,000 acres could be approved under a Categorical Exclusion.
Cutting down juniper woodlands is often promoted as a method to create or improve habitat for the imperiled sage grouse, which requires undisturbed sagebrush steppe habitats and avoids trees of any kind. While juniper removal might seem to make sense, the reality is that logged-off juniper woodlands seldom result in sage grouse habitat. Mature and old-growth stands of junipers typically have very little understory at all, neither sagebrush nor native grasses. When bulldozers and other heavy equipment move in and the trees are torn down, what you get is disturbed bare ground. It’s the perfect breeding ground for the non-native invasive weed, cheatgrass.
If the goal is fuel reduction, cheatgrass infestations are the worst possible outcome.
When livestock add their impacts into the mix (as they almost always do), suppressing native bunchgrasses and breaking up fragile soil crusts, cheatgrass proliferates. Highly flammable, cheatgrass predictably dies each July (escaping the drought stress of high summer in seed form). Drying out, it creates the perfect tinder for fires to burn, and those fires wipe out sagebrush and other fire-intolerant shrubs creating a monoculture of cheatgrass that fuels a cycle of frequent wildfires in perpetuity.
There is a widespread myth that pinyon pines and juniper are an “invasive species” that are unnaturally expanding their range as a result of human activities like fire suppression or heavy livestock grazing. The reality is that these woodlands have been expanding and contracting for thousands of years in a natural cycle, following changes in precipitation patterns.
In addition to mule deer, there are a number of other native wildlife species that benefit from pinyon-juniper woodlands. Scott’s oriole, juniper titmouse, and Bewick’s wren are a few of the songbird species that are considered juniper obligates. Pinyon jays are pinyon obligates, as their name suggests. Obligate species are animals that require a specific type of habitat to sustain their populations.
As for the climate impacts, when you replace juniper woodlands – or sagebrush-bunchgrass steppes – with cheatgrass, it reverses the enormous carbon sequestration capability of western desert shrublands, hemorrhaging soil carbon into the atmosphere. We typically think of forests as the most important carbon immobilizers, but desert shrublands can pull even more carbon out of the atmosphere and safely lock it away in the soil.
The removal of pinyon-juniper woodlands across the American West draws a direct parallel with rainforest destruction to create livestock pastures in the Amazon Basin. It’s all about the fool’s errand of trying to mow down native ecosystems and replace them with idyllic grassy pastures ideal for adding pounds and profits to beef cattle. Nevermind that cattle are ill-adapted to arid environments, and do so poorly on western public lands that the vast acreage dedicated to beef production on western federal lands amounts to little more than two or three percent of the nation’s beef production. Even if western public lands had no recreational value to the Americans for whose benefit they are supposed to be managed, the carbon sequestration value of juniper woodlands would still eclipse the scanty private profits that are wrung from marginal western livestock operations.
Climate change is a serious problem, not least of all for the arid West now struggling with protracted drought and decreasing water availability. Let’s stop making it worse by cutting down the fragile woodlands that hold the carbon in place.
This article was written by Eric Molvar and published on Counterpunch on March 12, 2021. You can read the original version here!
Erik Molvar is a wildlife biologist and is the Laramie, Wyoming-based Executive Director of Western Watersheds Project, a nonprofit group dedicated to protecting and restoring watersheds and wildlife on western public lands.
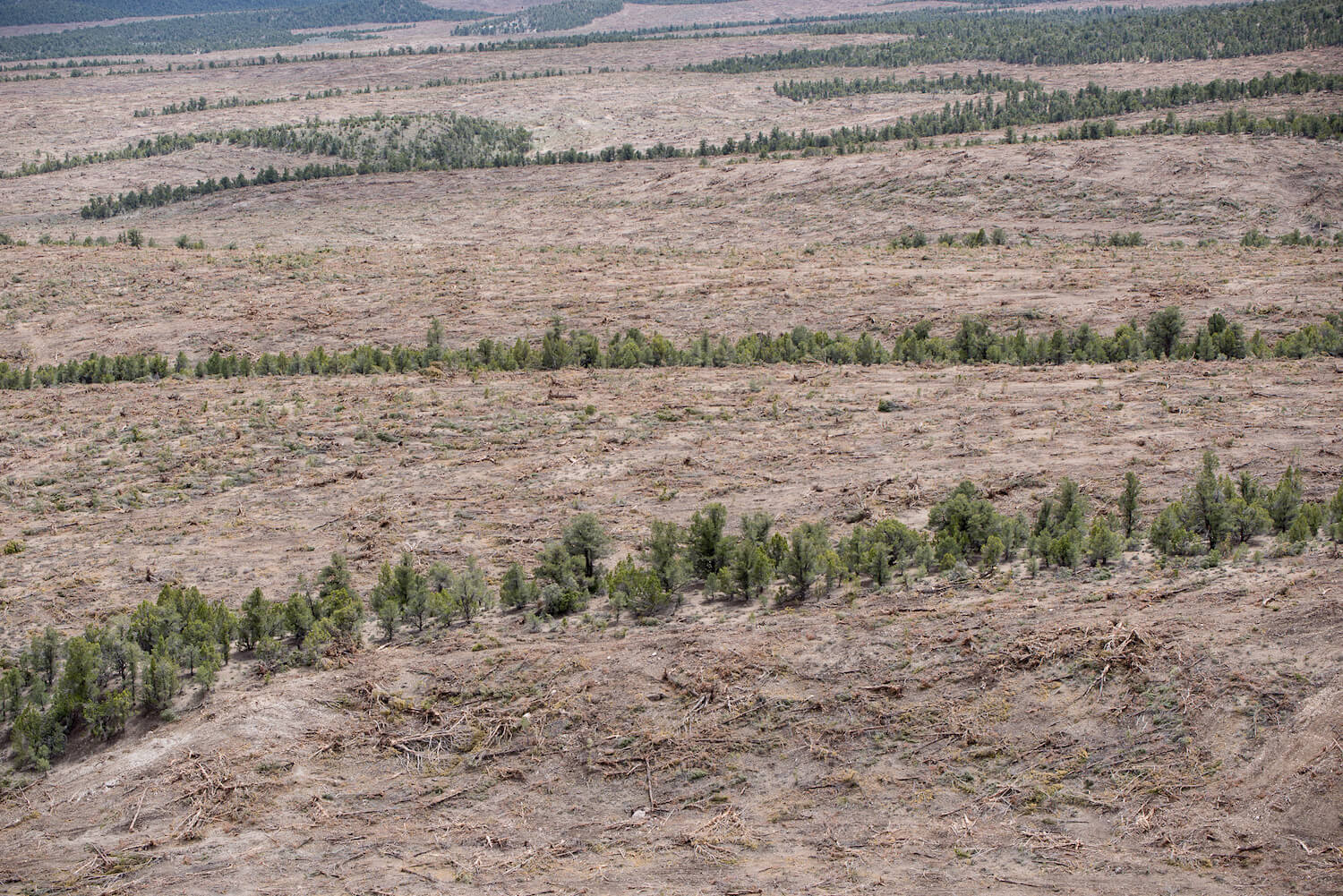

by DGR News Service | Dec 20, 2020 | Biodiversity & Habitat Destruction
In this article Shad Engkilterra exposes plans to expand clearcutting across vast portions of the U.S., to fast track the process, bypass environmental laws and regulations, and destroy forests on a huge scale.
‘Scorched Earth’: In Final Days, Trump Admin Finalizes Sweeping Clearcutting Rule Across West, While Cutting Public out of the Process
by Shad Engkilterra / EnviroNews
Trump and his administration are pushing through policy changes to keep the public in the dark and avoid public input requirements at the Bureau of Land Management (BLM), a group of prominent environmental NGOs decried today in a press release. With just a little over a month left in office, Trump’s BLM is moving forward with plans that will allow fast-track approval on a massive blanket clearcutting initiative for native forests and shrubs throughout the West.
On Dec. 10, 2020, the BLM announced its final “pinyon-juniper categorical exclusion” and its “salvage logging categorical exclusion.” With these two rules finalized today, the agency has enacted five rules and major initiatives designed to allow industrial clearcutting plans to proceed much more quickly by eliminating the public comment period, which the BLM says takes too long.
“The BLM’s massive deforestation schemes will transform much of the West into bleak, cheatgrass-infested and treeless expanses, dealing a huge blow to biodiversity and the survival of many species of migratory birds and other native wildlife,” said Katie Fite of Wildlands Defense, in a joint press release.
Once implemented, the change will skirt the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) and cut the public out of the process. The agency claims “these categorical exclusions will contribute to rural economies, reduce waste of salvageable timber, and reduce future wildfire fuel loads, while diminishing hazards to wildland firefighters, the public, and infrastructure from dead and dying trees.”
But conservation groups are having none of it.
“These are scorched-earth policies with no place in what is supposed to be open, transparent, and science-based management of 245 million acres of public land,” said Kya Marienfeld, Wildlands Attorney with the Southern Utah Wilderness Alliance (SUWA) in a press release. The NEPA-mandated public comment period allows citizens and scientists to review plans set forth by the BLM and other Department of the Interior agencies, and to inform the process by making suggestions or raising concerns. As reported by EnviroNews, allowing citizens to participate in the process oftentimes results in improved land management, above and beyond what the agency initially proposes.
“The removal of public review through these final NEPA exclusions today is especially alarming because many large projects that were withdrawn because of public pressure — including some within Grand Staircase-Escalante National Monument — could now reappear at any time under this new policy and move forward without public review, scientific study, or accountability,” said Marienfeld.
Environmentalists say the beneficiaries of these policies are the industries destroying the western landscape and harming its wildlife populations.
Ranchers, mineral barons, the lumber industry, and oil and gas companies stand to gain now that these policies have been enacted. “This is nothing more than an eleventh-hour attempt by the outgoing administration to shut the public out of public land management and curry favor with Secretary Bernhardt’s industry allies. It has absolutely no basis in science or sound management practices,” said Scott Lake, Nevada Legal Advocate for the Center for Biological Diversity.
The new “pinyon-juniper categorical exclusion” will allow the BLM to clear up to 10,000 acres of pinyon-juniper without any environmental analysis, scientific oversight, or public review and input. The agency can approve projects of this size an unlimited number of times.
“The BLM’s assertion that clearing 10,000 acres of pinyon and juniper forests will not have a significant environmental effect is wrong and incredibly dangerous to ongoing efforts to protect public lands, wildlife, and the general safety and livability of the human environment,” said Logan Glasenapp of New Mexico Wild.
The BLM also says the rules will allow it to better “maintain and restore habitats that are essential to mule deer, sage-grouse, and other important wildlife species.” The sage-grouse is an “umbrella species” spanning the sagebrush sea across 11 western states. Subject of an expansive EnviroNews documentary, the imperiled dancing ground-bird has been at the center of the costliest conservation fight in history.
Mary O’Brien, Utah Forests Program Director for the Grand Canyon Trust disagreed with BLM’s notion that these rule changes are to preserve native wildlife:
“The BLM’s claim that massive clearcutting and mastication of pinyon pine and juniper is ‘solely’ intended to enhance habitat for sage-grouse and mule deer might be believable if science indicated that these ‘[habitat] treatments’ work, or if the BLM didn’t use them as an opportunity to graze the heck out of the newly ripped-up landscape, seeding it with exotic grasses meant for cattle.”
The “salvage logging categorical exclusion” allows the agency to approve logging on up to 3,000 acres of land as long as it determines the trees are “dead or dying.” Lands matching that criteria will be exempt from the NEPA requirements of environmental analysis, scientific oversight, and public input and review.
“The bottom line is that science has to guide the management of our western lands,” said Vera Smith, Senior Federal Lands Policy Analyst with Defenders of Wildlife. “We hope that the Biden Administration will right this wrong by directing the [BLM] to restore science-based decision-making to our public lands and refrain from clearcutting under these new rules.”
The Trump Administration’s BLM has had no shortage of controversies, including in its leadership.
On September 25, a judge ruled that Acting Director William Perry Pendley had served in his position illegally for 424 days in violation of the Federal Vacancies Reform Act. Pendley never received Congressional approval, and was supposed to step down. However, he has made numerous statements that he isn’t going anywhere. The judge in the case also ruled the BLM was to submit which actions Pendley had taken during his time atop the BLM so those actions could be reversed. In October, the court invalidated three of Pendley’s major land-use plans in Montana and warned Pendley against fulfilling the duties of acting director.
EnviroNews has documented the ramping up of a Trump Administration “War on Wildlife,” which has reached a zenith in the last few months of the President’s first, and last, term. From removing the words “climate change” from the White House website, to redefining the word “habitat,” to refusing to give species protections under the Endangered Species Act, to delisting iconic, imperiled species, to allowing drilling in sensitive environments like the Arctic National Wildlife Refuge (ANWR), the Trump Administration has exploited every opportunity to increase access for industry to public lands. Many are concerned that the upward trend in environmental rollbacks will continue until the day he leaves the White House.
This article was written by Shad Engkilterra and published on December 10, 2020 in Environews. You can access the original article here:
https://www.environews.tv/121020-scorched-earth-in-final-days-trump-admin-finalizes-sweeping-clearcutting-rule-across-west-while-cutting-public-out-of-the-process/
Featured image: a freshly-bulldozed native forest of Pinyon Pine and Juniper trees on federal BLM lands just south of Ely, Nevada in 2018. This biodiverse native forest was destroyed in the name of “restoration.”
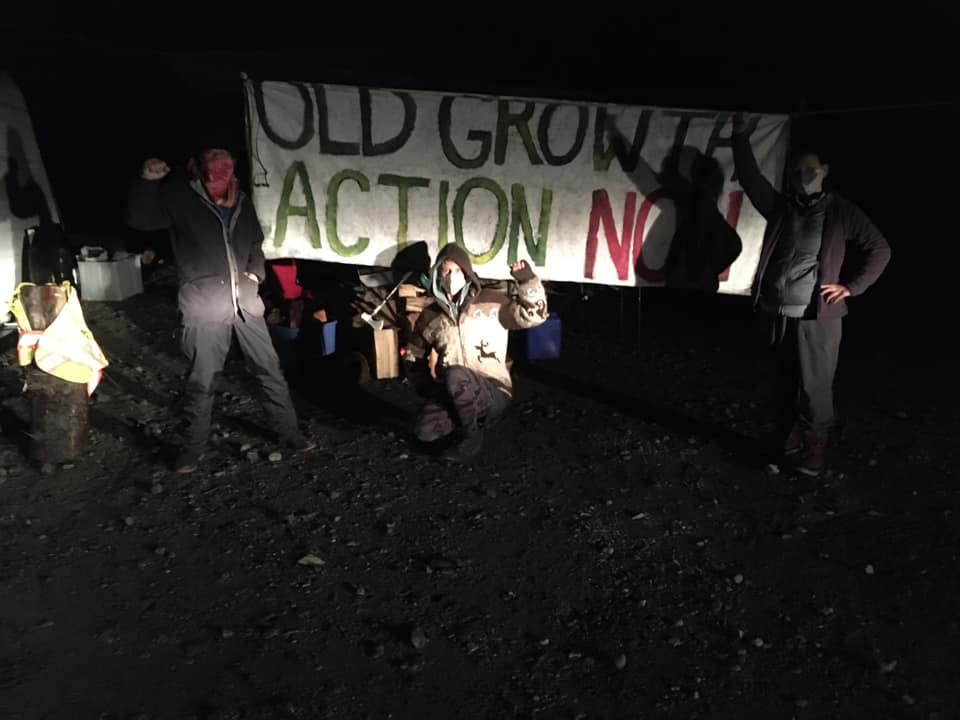
by DGR News Service | Dec 18, 2020 | Obstruction & Occupation
This is an update regarding the chronology of events for the Old Growth Blockade which strives to protect the last old-growth temperate rainforests on Vancouver island, currently facing near-total eradication by the British Columbia government and logging companies.
The Rainforest Flying Squad launches the Bugaboo Creek blockade to prevent road building into the last ancient forests of the watershed.
- Friday, December 11th, a group of Forest Protectors with the Rainforest Flying Squad have moved the Bugaboo Blockade south to block a road adjacent to the world famous Avatar Grove, to prevent road building crews from continued road building into the south side of the Bugaboo’s Ancient Rainforest in Camper Creek on Pacheedaht Territory.
- This comes on the heels of the creation of the first Bugaboo Blockade on December 7, when the Rainforest Flying Squad prevented logging in high elevation old growth western red and yellow cedar forests. Shortly after the creation of that blockade the road building contractor moved their equipment from the north side of the Bugaboo’s Ancient Forest to the south side where another road has been approved into a magnificent stand of Ancient Trees. “The message is simple,” said one of the Squad, “we want no more logging, no more road building into the last of our ancient forests.” After following vehicles moved from the north side of the Bugaboo, and discovering the contractor intended to begin road building on the south side of the rainforest the squad decided to move camp, continuing to monitor the north side as they prevent road building into the southern part of the forest.

- In the meantime another group of Protectors have now mobilized to protect valley bottom old growth forest south of Eden Grove in the Edinburgh Mountain Ancient forest. They have set up a blockade on the bridge leading to Big Lonely Doug, the iconic Douglas Fir tree that stands in an old growth clear-cut on Edinburgh Mountain. This is in response to an application submitted by Teal Jones that would allow for the construction of a logging road into valley bottom old growth forest south of Eden Grove.
- The new Edinburgh Blockade will remain in place as long as it takes to prevent further fragmentation of the Edinburgh Mountain Ancient Forest. The barricades are holding strong at Fairy Creek and meanwhile the Bugaboo Squad will continue to block access and monitor both intrusions into the rainforest until snow pack eliminates the risk of road building into the Bugaboo Ancient Forest. The protesters expect road building crews to remove their equipment in the next few days, they say if the contractors move the equipment back to the north side of the old growth forest, they will be back and blockade there again.
- The blockaders on both blockades are demanding;
- That logging contractor Stone Pacific give up road building into old growth forests in TFL 46 and move their machinery to work on road networks targeting second growth.
- That the Ministry of Forests decline the Teal Jones groups application for new road building on Edinburgh Mountain.
- That the provincial government and Premier John Horgan immediately implement the recommendations of the OGSR and end all old growth logging across British Columbia
- The government immediately shift all forestry operations to sustainable management of silvicultural land-base as a source of long-term employment in local and First Nations communities.
Until these demands are met, the Rainforest Flying Squad will continue to disrupt the timber industry in its attempts to log the last of our Ancient Temperate Rainforests.
#rainforestflyingsquad#savefairycreek
Learn more about the Old Growth Blockade. You can make a donation via GoFundMe. You can also check this other articles regarding the blockade.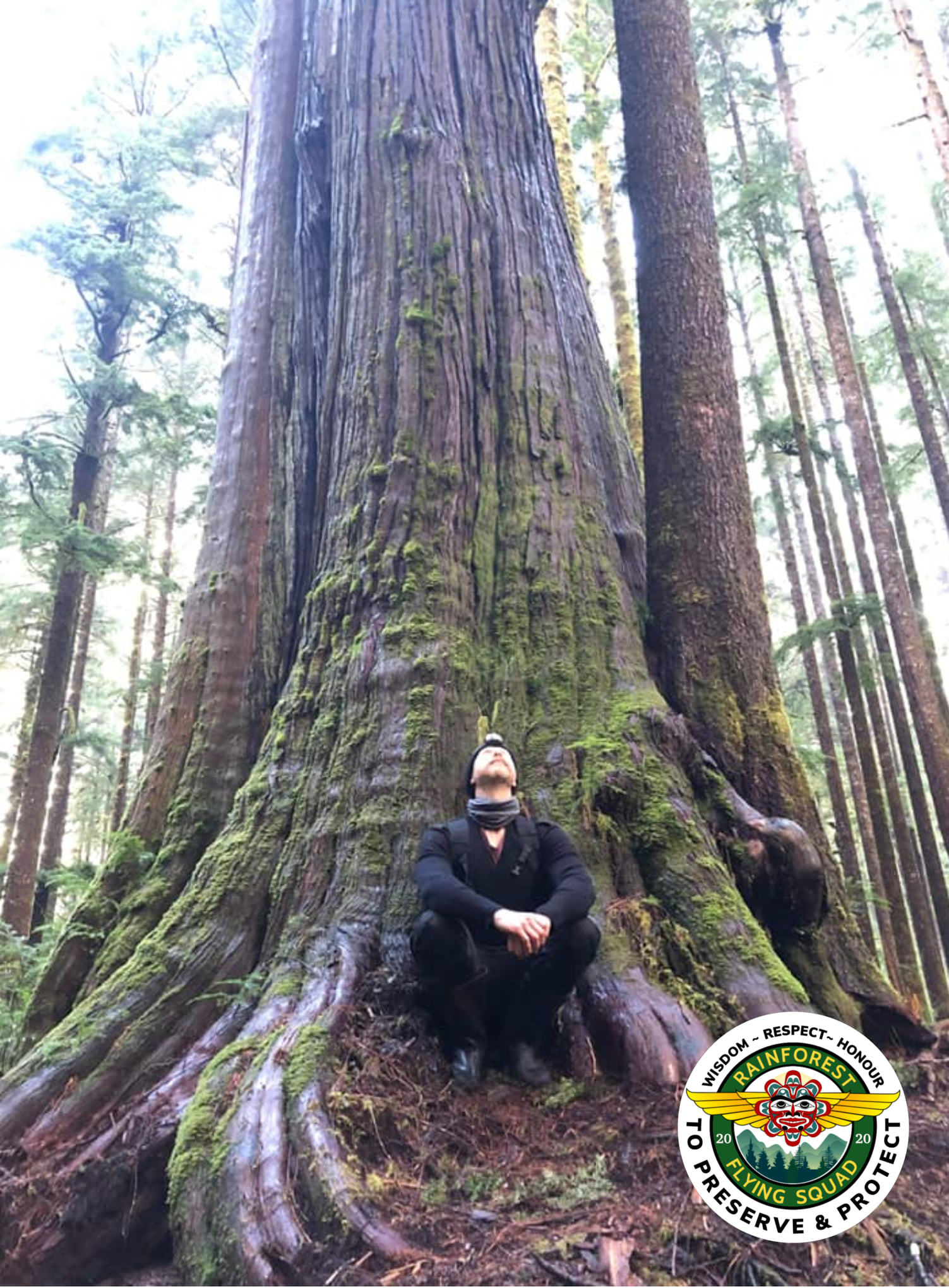

by DGR News Service | Dec 2, 2020 | Biodiversity & Habitat Destruction
Stop Thinning Forests is a community compilation, sponsored by Deep Green Resistance, of research and voices that speak in defense of our forests against the atrocities that are being committed on those communities in the name of “fire mitigation” and “forest health.”
The Forest Service, in partnership with the timber industry, uses propaganda to promote the idea that thinning helps lessen fire severity while improving forest health. The research on the benefits of forest thinning is financially backed by the timber industry, and congressional passing of bills that promote thinning are backed by the lobbying efforts of the industry. The main goal for thinning forests is to increase revenue by allowing the timber industry to get into forests that were previously protected by environmental laws. Recent legislation has allowed the industry to bypass those laws and profit from forest products in the name of “forest health and restoration.” The Forest Service has consistently worked with the timber industry as a result of financial incentives and has been responsible for creating the infrastructure through use of federal tax dollars in the form of subsidies that enable the industry to “get the cut out.”
Individual land owners have recently been encouraged by the Forest Service to thin their lands with available grant monies under the guise of protecting their homes from fire and to improve the health of the forests. The available grant money filters down to the Forest Service from federal legislation that allows industry to get into our treasured, and last remaining, intact forests. Thinning private lands is offered as another incentive that generates money for the Forest Service while creating the appearance that the Forest Service is promoting a policy of “fire mitigation” and “forest restoration,” extending to the wildland/urban interface. Private land owners have the power to become informed and make rational decisions to protect their homes from fire that will not devastate the forest community. It is essential that individuals making these decisions become informed about federal forest policies and the history of the Forest Service before making decisions that will disrupt and harm the forest communities where we live.
Here is a recent on-the-ground report back from Deanna Meyer, a Deep Green Resistance organizer in Colorado:
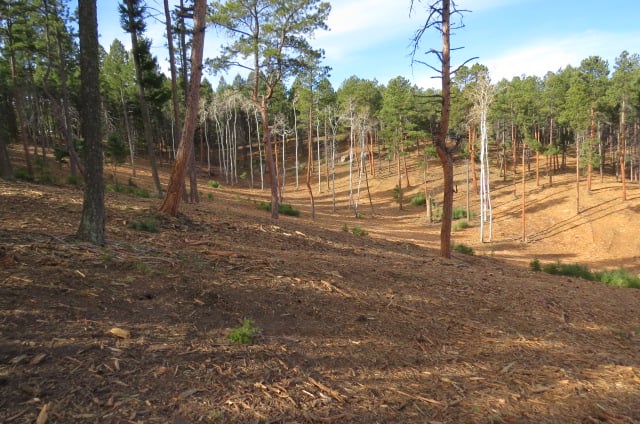
I went up to check on my neighboring forest who is being destroyed as I write with heavy equipment. These photos show some of the results. Pictures could never show the true devastation, and this place, which is very important to me, is now unrecognizable.
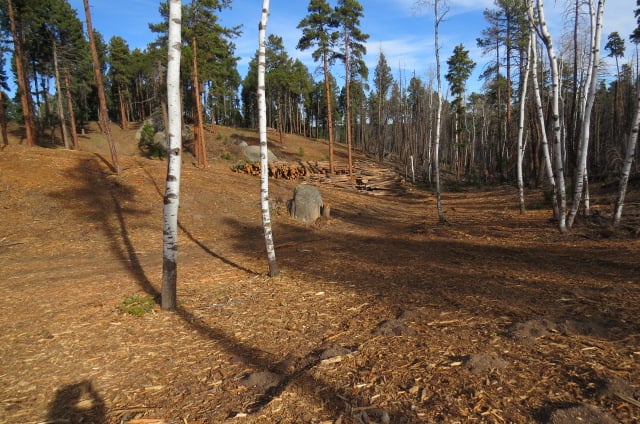

This is at a church in Sedalia, Colorado and this tax exempt church accepted hundreds of thousands of tax payers’ dollars to destroy this forest. All of this is in the name of “fire prevention.” Research analyzing millions of acres throughout the West where fires have occurred shows otherwise.
https://esajournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/ecs2.1492
Here in Colorado, all we need to do is look at the 3 largest fires in our history, all occurring this year, and pay attention to all of the acres that were “thinned” just like this. They did NOT fare any better than the untouched forests and in many areas they burnt even faster and hotter because of wind breaks and dried out soil.
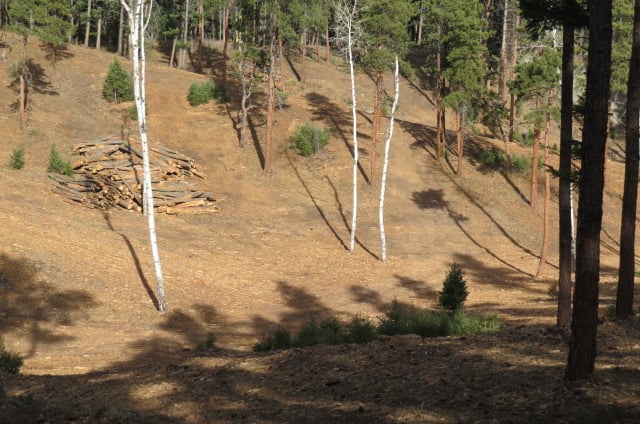

All of this is horrific and heartbreaking, but the soil stands out the most to me. It takes thousands of years to create healthy soil and mycelial networks. This land now is a barren dustbowl with some wood chips thrown on top. The mycelium, grasses, sedges, forbs, and trees who were there and holding the soil together are now completely obliterated from the heavy equipment, mulching and utter destruction of at least a foot of soil who used to be sinking carbon and healing the land.
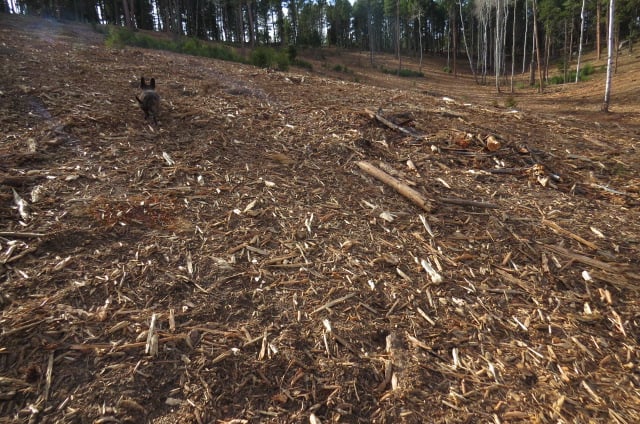

Every time our forests start to heal themselves from the decades of colonizing destruction, the Forest DISservice and private land owners come in and log it again. When you look at the forests that have not been touched for decades, they are healing and thinning themselves out. Just because they look “messy” to colonizers who can’t stand the idea of not having control over every living biome that exists does not alter the fact that the forests know best what to do with themselves and our meddling with them is biocide.