
by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Nov 5, 2018 | Protests & Symbolic Acts
by Honduras Solidarity Network
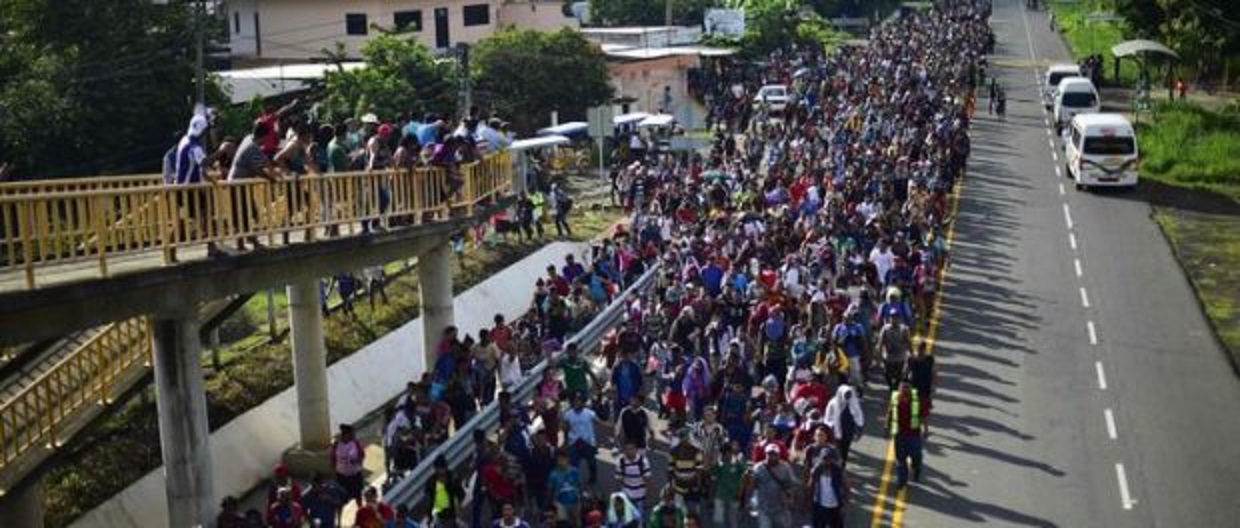
On October 12, 2018, hundreds of women, men, children, youth and the elderly decided to leave Honduras as a desperate response to survive. The massive exodus that began in the city of San Pedro Sula, reached more than 3 thousand people by the time the group crossed to Guatemala. The caravan, which is headed north to Mexico first, and to the United States as the goal- is the only alternative this people have to reach a bit of the dignity that has been taken from them. They are not alone in their journey. Various waves of Hondurans, whose numbers increase every hour, are being contained by Honduran security forces on their border with El Salvador and Guatemala.
The Honduras Solidarity Network in North America condemns any threats and acts of repression against the refugee caravan, human rights activists and journalists that accompany their journey. The conditions of violence, marginalization and exploitation in which this refugee crisis find its origins, have been created, maintained and reproduced by US-backed social, economic and military interventionist policies, with the support of its Canadian and regional allies. We call on people in the US to reject the criminalization, prosecution, detention, deportation and family separation that threaten the members of this march and the lives of all those refugees forced from their homes in the same way. We urge a change of US policy in Honduras and to cut off security aid to stop human rights abuses and government violence against Hondurans.
This refugee crisis has been exacerbated by the governments of Guatemala and Mexico, who subservient to Donald Trump’s administration, have chosen the path of repression. Bartolo Fuentes, a Honduran journalist and spokesperson for the refugees, has been detained in Guatemala. Meanwhile the Mexican government has sent two planeloads of its National Police to the border with Guatemala. Irineo Mujica, a migrant rights activist and photojournalist, was arrested in Chiapas by agents of the Mexican National Institute of Migration when he was getting ready to support the Honduran migrant march. Today (Friday) in the afternoon, tear gas was fired into the group as they tried to come into Mexico on the border bridge. Honduran human rights organizations report that a 7 month old baby was killed.
The massive forced flight of people from Honduras is not new; it is the legacy of US intervention in the country. Since the 2009 US-backed coup in Honduras, the post-coup regime has perpetuated a system based on disregard for human rights, impunity, corruption, repression and the influence of organized crime groups in the government and in the economic power elite. Since the coup, we have seen the destruction of public education and health services through privatization. The imposition of mining, hydro-electric mega-projects and the concentration of land in agro-industry has plunged 66 percent of the Honduran population into poverty and extreme poverty. In the last 9 years, we have witnessed how the murder of Berta Cáceres and many other activists, indigenous leaders, lawyers, journalists, LGBTQ community members and students has triggered a humanitarian crisis. This crisis is reflected in the internal displacement and the unprecedented exodus of the Honduran people that has caught the public’s eye during recent days.
The fraudulent November 2017 elections, in which Juan Orlando Hernández -president since questionable elections in 2013- was re-elected for a second term in violation of the Honduran constitution, sparked a national outrage. The people’s outrage was confronted by an extremely violent government campaign with military and US-trained security forces to suppress the protests against the fraud. The result of the repression was more than 30 people killed by government forces, more than a thousand arrested and there are currently 20 political prisoners being held in pre-trial prison.
To the repression, intimidation and criminalization faced by the members of the refugee caravan, we respond with a call for solidarity from all the corners of the world. In the face of the violence that has led to the mass exodus of hundreds of thousands of Hondurans, we demand an end to US military and security aid to Juan Orlando’s regime, not as the blackmail tool used by Donald Trump, but as a way to guarantee the protection of the human rights of the Honduran people. We demand justice for Berta Cáceres, for all the victims of political violence as a consequence of the post coup regime, and the approval of the Berta Cáceres Human Rights in Honduras Act H.R. 1299. We demand freedom for all the political prisoners in Honduras. We demand the US end the criminalization, imprisonment, separation, deportation and killing of migrants and refugees.
Today we fight so that every step, from Honduras to the north of the Americas, is dignified and free
Honduras Solidarity Network of North America

by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Aug 10, 2016 | Strategy & Analysis
Featured image by Vanessa Vanderburgh
By Joanna Pinkiewicz / Deep Green Resistance Australia
Most people in the industrial civilized world will come to a point of crisis, loosely translated from its Greek origin as: “testing time” or “an emergency event.”
An ongoing feeling of pressure, instability or a threat can all bring on such crisis. These events shake our whole being, alarm our physical bodies and rupture our rational mind. The advice for dealing with a crisis that is perceived as “personal” or “individual” often follows a set of clear, practical steps:
- Slow your breath to anchor yourself in the present
- Take a note of your emotions or bodily sensations
- Open up and express your thoughts
- Pursue a valued course of action
The last step is particularly interesting, as it suggests questioning: What do I value the most? What do I stand for? How do I want to see myself respond?
As much as a crisis brings many negatives, such as anxiety and depression, it also brings an opportunity to re-examine our lives and expand our understanding of what is happening in the world or to the world around us. It forces us to examine and to make a choice: are we going to be a bystander or are we going to become courageous in the face of a looming threat?
Research on the psychology of resistance suggests, that access to support and the right type of information is crucial to help those wanting to understand what is really happening to us and the world, as well as, what can be done to address it.
The authors of Courageous Resistance, The Power of Ordinary People list certain factors that contribute to ordinary people becoming resisters in the face of injustice or impending threat. These include a combination of:
- Preconditions: previous attitudes, experiences and internal resources
- Networks: ongoing relationships with people that offered information, resources and assistance and
- The Context itself: political climate, severity of the situation
We understand courageous resistance to be a conscious process of decision making, which is affected not only by who the decision maker is, but where they are and who they know at the particular time they become aware of a grave injustice…
We define “courageous resisters” along three dimensions: First, they are those who voluntarily engage in other-oriented, largely selfless behaviour with significantly high risk or cost to themselves or their associates. Second, their actions are the result of a conscious decision. Third, their efforts are sustained over time. [i]
Humanity today faces ongoing stress from living in the civilized world. By and large, we have managed to adapt to changes that have been imposed on us, such as higher density living and working conditions. However the escalated threat of armed violence and impending effects of climate change bring on new types of crises, which needs not only immediate response, but creation of a completely new culture. The current culture likes us to believe that the crises we are experiencing are “individual,” due to a weakness or an illness. If we choose to believe this, we are more likely to suffer from helplessness and not participate in creating this new culture.
Aric McBay explains this in Deep Green Resistance, Strategy To Save The Planet:
If someone is dissatisfied with the way society works, they say, then it is that individual’s personal emotional problem. Furthermore, the individual traumas perpetuated by those in power on individual people, on groups of people, and on the land, can seem random at first glance. But if we can trace them back to their common roots—in capitalism, in patriarchy, in civilization at large—then we can understand them as manifestations of power imbalance, and we can overcome the learned helplessness…[ii]
To begin to create a culture of resistance individuals must drop loyalty to the oppressive status quo and its systems. Two things may prevent us from fully committing to resistance: fear of punishment or separation from our kin (friends, family). While loss of “belief” in “redeeming” the existing culture is a first step towards resistance, separation from dependency on the existing systems is gradual.
As building an effective resistance culture is a long process involving generations, we must be wise at preserving our health and using our resources.
Listed below are steps that effective groups or communities follow in response to a crisis that is not personal, but wide spread and caused by either natural (earthquake, flood) or man-made circumstances (occupation, oppression, ecocide).
- Prepare: clarify our values, recruit people, gather resources, and devise the strategy
- Respond: assign roles and responsibilities, implement strategy
- Recover: extend support networks, rebuild communities, and establish new organizations
Resilience building will come from commitment and co-operation in all of those stages. After the recovery from a crisis, a group gains valuable experience and is able to refine the “emergency” response plan and train newcomers.
Experience of past resisters demonstrates rise in organisational, strategic and physical skills among individuals as well and rise in strength and independence of a group.
I am thankful for my crisis. Like a loud warning siren it told me that things are not right in the world, that I must increase my awareness and prepare for the future.
My crisis led me to discover techniques and practices that reconnected me with my body. I discovered that reconstruction of mental and physical health goes hand in hand with protecting the environment. By recognising the physical and spiritual nourishment we receive from our forests, rivers, oceans, a commitment to environmental action is born.
Taking responsibility was the first step to my healing and the beginning of an authentic life. Such path does not require perfection, but courage and imagination to create new ways of living and existing. To work as a collective in the name of all nature’s communities is a revolutionary path of resistance we desperately need today.
Deep Green Resistance is a global radical environmental organization with a strategy to address our impending planetary crisis. We have recruited capable and experienced individuals to guide and work together in implementing our strategy and fulfill our vision to dismantle the industrial civilization, assist the planet’s recovery and build sustainable communities with decentralized governance.
Join the many existing chapters or start a new one! Become a conscious resister!
Notes:
[i] Thalhammer, Kristina E.; O’Loughlin, Paula L.; Glazer, Myron Peretz; Glazer, Penina Migdal; McFarland, Sam; Shepela, Sharon Toffey; Stoltzfus, Nathan. Courageous Resistance, The Power of Ordinary People. New York: Palgrave Macmillan, 2007.
[ii] McBay, Aric; Keith, Lierre; and Jensen, Derrick. Deep Green Resistance: Strategy to Save the Planet. New York: Seven Stories Press, 2011.
by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Jul 10, 2016 | Biodiversity & Habitat Destruction, Colonialism & Conquest
By Carlos Enrique Maibeth-Mortimer / Intercontinental Cry
There is a crisis erupting in Nicaragua’s North Caribbean Autonomous Region that spans across all social and economic boundaries, affecting everything from human rights to ecosystem preservation to climate change. The Indigenous Miskitu and Mayagna Peoples, whose traditional cultural practices are inseparably linked to the environment and who exist at the forefront of imminent climate shifts capable of displacing entire communities, are under attack. The situation is one that world doesn’t yet know about. It is incumbent upon all of us to change that–to do what we can to empower the Native Peoples of Nicaragua, and stop the destruction.
Settlers are attacking Indigenous communities with automatic firearms, killing, plundering and forcing residents to flee their ancestral lands. Foreign companies have entered the territory illegally and are burning the region’s precious stronghold of biodiversity and natural resources at an alarmingly rapid rate.
Disturbing reports continually come to light of dozens of killings and kidnappings, particularly of Miskitu Indigenous men and women. Thousands of Indigenous refugees have been forced to flee their communities to the relative safety of more urban areas. With no support services intact to deal with the influx of refugees in the already strained resources of the urban regions, those fleeing the violence continue to suffer a lack of food and lack of medical attention upon arrival. The murderous ‘colonos’ operate with complete impunity. As a result, the attacks continue unrestrained by Nicaraguan law enforcement, contributing to a climate of escalation. There is a real and valid concern regarding the virtual media blackout, in both local and international spheres, where little to no reporting focuses on the critical situation unfolding.
Inhabitants of the Atlantic Coast, or Costeños as they are collectively known to the rest of Nicaragua, represent a unique diversity of ethnic groups including Indigenous Miskitu, Mayagna, and Rama, Garífuna (descended from African slaves and Carib Indians), English-speaking Creoles (descendants of African slaves), and Mestizos (mixed race Latin Americans descended from European colonizers and Native peoples).
The region was deeply impacted – scarred even – by the revolutionary war of the 1980’s, when US-backed counter-revolutionaries mounted attacks against the Sandinistas from military bases in Honduras, just across the Coco (Wangki) River.
In 1987, with the war raging, the Autonomy Statute for the Atlantic Coast was enacted and amended to the Nicaraguan Constitution. The new law recognized the multi-ethnic nature of the communities of the Atlantic coast; and in particular, noted Indigenous peoples’ rights to identity, culture and language. The new Autonomous Regions were divided between the North and the South.
In 2003 the Nicaraguan National Assembly finally passed the Communal Property Regime Law 445 and the Demarcation Law to address Indigenous concerns regarding land demarcation and natural resources after much pressure from international institutions.
Indigenous people have legal ownership to significant portions of their ancestral lands as assured by Nicaraguan law, in addition to the Indigenous and Tribal Peoples Convention 169 ratified by Nicaragua in 2010 and the United Nations Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous People. Yet realities have differed from legalities. Although the Autonomy Agreement recognized collective land holdings, Indigenous people did not actually hold the legal title to their lands for a long time. In recent years, while Indigenous people have been waiting for formal title to be issued to their lands, false titles have been issued in Managua or elsewhere, selling land illegally to settlers from outside the region. It is a sad reality that although Law 445 calls for the removal of illegal settlers from Indigenous lands, it is increasingly undeniable that the exact opposite has taken place.
Violent conflicts over Indigenous land rights have been increasingly erupting in the remote areas of the Northern Caribbean Autonomous Region. Since September 2015, the Miskitu settlements of Wangki, Twi-Tasba Raya, and Li Aubra, have come under especially heavy attack. Reports indicate as many as 80 Miskitu men have been killed or kidnapped from these regions alone; while as many as 2,000 refugees fled their homes and communities in fear for their very lives. These particular villages have been hit especially hard by the violent conflict and, despite pleas for help at municipal and national levels, have received no measure of protection or even investigation, much less prosecution.
Transnational lumber companies siphoning profits from the region’s natural resources have been operating out of nearby Honduras. They are carrying out sophisticated lumbering operations utilizing helicopters and cargo boats to facilitate the rapid export of extracted wood. Nicaragua is home to the Bosawas Biosphere Reserve, one of the largest tropical rainforests in the Americas, second only to the Amazon. The world can no longer stand by while this stronghold of biodiversity and climate-stabilizing carbon-mitigating forest is sacrificed to next quarter’s profits.
Pleas for help have seemed to fall on deaf ears in the capital city of Managua. The Nicaraguan government has not officially acknowledged any of the most recent and most egregious killings, illegal land occupation or deforestation issues. The socialist central government has not offered any plan for addressing this escalating humanitarian crisis, for providing any gestures of protection to the Indigenous communities under attack nor assistance to the refugees. Many Indigenous to the region cannot help but suspect that human rights violations and land rights violations may be happening with the silent consent of the central Nicaraguan government.
While much attention has been given to the Nicaraguan government’s sale of a concession to a Chinese investment firm for an ill-conceived canal to run through the Southern Caribbean Autonomous Region, virtually no media attention has focused on the current urgent crisis in the Northern Region.
Thousands of illegal settlers have clear cut precious rainforest – indifferent to immediate or long term impacts – and have begun to establish cattle ranches and lumber operations that are completely inappropriate to the ecology of the region. The environmental impact mirrors the destructive patterns playing out in the Amazon Basin.
The Bosawas Biosphere Reserve is located in the North Caribbean Autonomous Region in an area historically occupied by Indigenous Mayagna and Miskitu people. The reserve has been designated a UNESCO World Heritage site due to its unique ecological and biocultural significance. The negative impacts on this vulnerable area in particular have consequences not only for Nicaragua, but also for the whole planet. Tropical rainforests hold 50 percent more carbon than trees elsewhere. To this end, deforestation of tropical forests actually causes much more carbon to be released. The problems associated with illegal human migration to the region and its effect on the natural ecology and rates of deforestation are grave, with worldwide ecological consequences.
Although there are differences among settler groups, what they have in common is an environmentally destructive cultural mentality. It is not a coincidence that the settler groups who have inflicted the worst environmental destruction have simultaneously inflicted the worst violence against Indigenous Miskitu and Mayagna.
The critical cultural differences between the Native populations and the non-Indigenous settlers can result in vastly different outcomes for the natural environment. These key cultural differences include: property regimes, expansion patterns, agricultural practices and long-term economic strategies. Indigenous communities hold land in common, meaning that they have collective ownership of their territories. Mestizo settlers, on the other hand, exercise a private property model and parcel out land that they have settled and/or seized.
Significant differences in the use and care of livestock can have a major environmental impacts. On average, only 10 percent of Indigenous families have cattle, whereas mestizo settlers average one cow per family. The low cattle count among Indigenous families, along with their nucleated communities, means that cattle are kept within the limits of the village, along with other livestock like pigs. The Indigenous people of the region contain their animals within the perimeter of their communities, whereas crops are planted in wooded areas up to a two-hour radius from community centers.
When mestizo settlers move into the region they re-shape and redistribute the land with the driving purpose of raising cattle and in anticipation of obtaining even more cattle in the future. After clear-cutting invaluable rainforest land, they immediately begin sowing grass seed and other crops. Within one season, their crop fields are converted into more pasture land. Indigenous farmers, on the other hand, will cut back specific plots of rainforest but will only use these plots for a year or two. They then allow them to grow back and move on to another area to develop communal plots. This traditional Indigenous practice of land management allows the rain forest to regenerate and recover — a sustainable method the Indigenous biostewards of the region have practiced for thousands of years.
On the other hand, mestizo settlers often cause irreversible damage to the rainforest. Settler occupations seem bent on developing as much pasture as possible. If they have the economic means, they raise more cattle and continually increase the herd size. If they do not have the means for raising cattle, they sell this land to settlers who do have cattle. This is the way in which mestizo settlers illegally appropriate traditional Indigenous territory and cash in on the destructive practices they inflict on it soon after. This type of land speculation and ‘economic development’ is almost nonexistent among Indigenous groups, and many view it as a direct challenge to their inherent values. Ironically, many mestizos use this conservative approach to concoct a false narrative that Indigenous people are lazy and undeserving of their vast quantities of land.
Even with growing populations, indigenous communities have a relatively low environmental impact compared to their mestizo non-Indigenous counterparts. The differences in environmental impact and lifestyles between Indigenous and mestizo communities put land tenure and environmental conservation in perspective.
Significant progress towards honoring Indigenous land rights must be a crucial component in the creation of a multi-stakeholder enforced strategy to protect the environmental integrity of the Autonomous Region of Northern Caribbean. It becomes especially critical when considering the overarching role tropical rainforests play in regulating the Earth’s climate.
The two factors of tropical deforestation and human-induced global warming are inextricably connected. There is a definite consensus in the scientific community that deforestation is one of the innate causes behind global warming. According to the Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations, “… Between 25 to 30 percent of the greenhouse gases released into the atmosphere each year —1.6 billion tons — are caused by deforestation.” Contributing to deforestation is by definition contributing to global warming.
It’s important to really drive home the compounding effects of the destruction of tropical rainforest: is it is even more damaging to the environment than destruction of other types of forest because of the unique ecology of rainforests. Compared to boreal forests, which are much more expansive, each square hectare of tropical rainforest holds nearly 50 percent more carbon.
The carbon within tropical rainforests is split pretty evenly between soils and flora. When tropical rainforests are clear-cut,massive amounts of carbon are released. Warmer temperatures cause soil to more rapidly decompose.
Tropical forests sequester more carbon because they grow year round and faster than other forest types. When protected and preserved, tropical rainforests are able to actually take in more carbon than they release into the atmosphere, critically reducing the adverse effects of fossil fuel emissions. To put things in clear perspective, tropical rainforests produce 20 percent of the world’s oxygen and 30 percent of the world’s freshwater.
When tropical forestland is transformed into pasture and overused, it leads to a steady cycle of desertification. Rainforests hold together the soil and ensure that it is saturated with rich nutrients. Over time, cattle grazing on pasture land created by clear-cutting forest will quantifiably weaken the soil. Monsoon seasons that are prevalent in Eastern Nicaragua steadily wash away any topsoil that no longer has forests holding it together or nourishing it. Without trees this lower-level soil cannot adequately absorb water. This further leaves areas more susceptible to flooding and landslides. Manure, fertilizer and pesticide runoff are contaminating and acidifying nearby waterways, killing off flora and fauna that are critical to the integrity of intact forests. During the summer months, this lower-level soil bakes and cracks, slowly developing into desert.
Lest it seem the many and crucial challenges facing the Indigenous people of Nicaragua are insurmountable in the face of such great adversity, Native Miskitu and Mayagna continue to defy the odds and act as trailblazers. Their actions set a prime example of what can be accomplished, even with minimal resources.
Although many of the Native people of Nicaragua are not familiar with the Pan-Indigenous American movement known as Idle No More, their actions are living embodiments of the mantra. They have consistently and repeatedly sought assistance and protection from local and national authorities, yet their pleas for help have fallen on deaf ears. No meaningful action has been taken by any government authority. The problem of Indigenous land rights violations and removal of the settlers has been presented to the OAS (Organization of American States) and the IACHR (Inter-American Court of Human Rights). The issue has even been formally raised at the United Nations Permanent Forums on Indigenous peoples.
NGOs played a supportive role in pressuring the Nicaraguan government to institute necessary jurisprudence in protecting environment and Indigenous land rights; the problem is that the laws are not being respected or enforced. The government continues to ignore the laws both at the national and local level. Mounting anecdotal evidence points to the possibility of corrupt officials contributing to the problem, at virtually every level of government. Through their inexcusable silence and inaction in the face of the escalating crisis, government at all levels is complicit at least in actively undermining Indigenous Peoples’ rights to their legal territories.
This is an ongoing crisis in the Autonomous Region of Northern Caribbean Nicaragua. The Indigenous cultures of the region are inseparably linked to the natural environment. The legal protections for Native people and the rain forest are being flagrantly violated by increasingly violent mestizo colonists (‘colonos’). Government at all levels has proven ineffectual in the face of the crisis. There has been no media coverage of this crisis, the escalation of violence, or the plight of refugees fleeing the areas of conflict.
It’s also important for us to help stop the destruction of the tropical rainforest, which is critically important to all of us. Government inaction in the face of mounting numbers of refugees and killings is morally corrupt and warrants international outcry.
The Indigenous Miskitu and Mayagna are not passive victims, but they are facing a tremendous challenge to address a problem of this magnitude. They are in desperate need of assistance to overcome this crisis.
5 WAYS YOU CAN HELP
- It is very important for international media outlets to focus on what is happening in this remote region. Spreading the word through social media will be key to applying international pressure to help the refugees and stop the killing of both the Indigenous people and the rainforest.
- There is an equal need for conventional media coverage. To that end, you can reach out to your favorite news outlet and encourage them to take on the story
- Costa Rica, Mexico, and the U.S. government have issued travel bans to Nicaragua, nevertheless, there is a growing need for humanitarian aid and witnesses to document what’s happening on the ground.
- If you want to support the Miskitu and Mayagna from home, consider organizing a community event or any kind of online action to make sure the world knows what’s happening.
- You can also ask the Ortega government to do the right thing, by working with the Miskitu and Mayagna to secure their ancestral territory, addressing the ongoing land theft and responding to the brutal attacks that are being carried out at the hands of the Colonos.

by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Mar 31, 2016 | Lobbying, Toxification
Featured Image: Gold miners have been invading Yanomami land for decades. © Fiona Watson/Survival International
Mercury poisoning is devastating tribal peoples across Amazonia, Survival International warned the U.N today.
In a letter to the U.N Special Rapporteur for Health, Survival International highlighted the failure of South American governments to address the contamination.
The unmonitored use of mercury, such as in illegal alluvial gold mining, often takes place on tribal peoples’ lands. Discriminatory attitudes towards tribal peoples mean that little action is taken to control it.
In Peru, 80% of a Nahua community have tested positive for high levels of mercury poisoning. 63% of those affected are children. Symptoms include anemia and renal failure, and one child has already died displaying symptoms consistent with mercury poisoning.
The Peruvian government has known about the mercury contamination since 2014 but has done little to identify the source. It is possible that other tribal peoples in the area have been affected, including uncontacted peoples.
In Brazil, new statistics reveal alarming rates of mercury poisoning amongst the Yanomami and Yekuana. 90% of Indians in one community are severely affected.

Without medical attention, mercury posioning can be lethal. Children and women of child-bearing age are most vulnerable
© Fiona Watson/Survival
Illegal gold miners operate on Yanomami land, polluting the rivers and forest with mercury. Uncontacted Yanomami are particularly in danger as many miners work near where they live.
Indigenous spokesman Reinaldo Rocha Yekuana said: “We are worried about the results of this research. This pollution affects plants, animals, and future generations.”
The Brazilian authorities have known about the mercury contamination since at least the 1980s, yet have failed to put a permanent stop to the illegal gold mining. Little has also been done to treat the affected Indians.
In Venezuela, several tribes including the Yekuana, Yanomami, Piaroa, Hoti and Pemon are also being devastated. 92% of Yekuana women in one region have levels of contamination far exceeding accepted limits.
Survival’s Director, Stephen Corry said: “These governments are sitting on a ticking time bomb. Every week that they fail to act, more and more indigenous peoples are being harmed. When mercury poisoning is identified, the source must be halted immediately and those affected must be treated. The effects will be catastrophic if indigenous peoples’ lands aren’t protected.”

by Deep Green Resistance News Service | Feb 11, 2016 | Colonialism & Conquest, Toxification
Featured image: Figure from EPA Pacific Southwest Region 9 Addressing Uranium Contamination on the Navajo Nation
By Courtney Parker / Intercontinental Cry
Recent media coverage and spiraling public outrage over the water crisis in Flint, Michigan has completely eclipsed the ongoing environmental justice struggles of the Navajo. Even worse, the media continues to frame the situation in Flint as some sort of isolated incident. It is not. Rather, it is symptomatic of a much wider and deeper problem of environmental racism in the United States.
The history of uranium mining on Navajo (Diné) land is forever intertwined with the history of the military industrial complex. In 2002, the American Journal of Public Health ran an article entitled, “The History of Uranium Mining and the Navajo People.” Head investigators for the piece, Brugge and Gobel, framed the issue as a “tradeoff between national security and the environmental health of workers and communities.” The national history of mining for uranium ore originated in the late 1940’s when the United States decided that it was time to cut away its dependence on imported uranium. Over the next 40 years, some 4 million tons of uranium ore would be extracted from the Navajo’s territory, most of it fueling the Cold War nuclear arms race.
Situated by colonialist policies on the very margins of U.S. society, the Navajo didn’t have much choice but to seek work in the mines that started to appear following the discovery of uranium deposits on their territory. Over the years, more than 1300 uranium mines were established. When the Cold War came to an end, the mines were abandoned; but the Navajo’s struggle had just begun.
Back then, few Navajo spoke enough English to be informed about the inherent dangers of uranium exposure. The book Memories Come to Us in the Rain and the Wind: Oral Histories and Photographs of Navajo Uranium Miners and Their Families explains how the Navajo had no word for “radiation” and were cut off from more general public knowledge through language and educational barriers, and geography.
The Navajo began receiving federal health care during their confinement at Bosque Redondo in 1863. The Treaty of 1868 between the Navajos and the U.S. government was made in the good faith that the government – more specifically, the Bureau of Indian Affairs (BIA) – would take some responsibility in protecting the health of the Navajo nation. Instead, as noted in “White Man’s Medicine: The Navajo and Government Doctors, 1863-1955,” those pioneering the spirit of western medicine spent more time displacing traditional Navajo healers and knowledge banks, and much less time protecting Navajo public health. This obtuse, and ultimately short-sighted, attitude of disrespect towards Navajo healers began to shift in the late 1930’s; yet significant damage had already been done.
Founding director of the environmental cancer section of the National Cancer Institute (NCI), Wilhelm C. Hueper, published a report in 1942 that tied radon gas exposure to higher incidence rates of lung cancer. He was careful to eliminate other occupational variables (like exposure to other toxins on the job) and potentially confounding, non-occupational variables (like smoking). After the Atomic Energy Commission (AEC) was made aware of his findings, Hueper was prohibited from speaking in public about his research; and he was reportedly even barred from traveling west of the Mississippi – lest he leak any information to at-risk populations like the Navajo.
In 1950, the U.S. Public Health Service (USPHS) began to study the relationship between the toxins from uranium mining and lung cancer; however, they failed to properly disseminate their findings to the Navajo population. They also failed to properly acquire informed consent from the Navajos involved in the studies, which would have required informing them of previously identified and/or suspected health risks associated with working in or living near the mines. In 1955, the federal responsibility and role in Navajo healthcare was transferred from the BIA to the USPHS.
In the 1960’s, as the incidence rates of lung cancer began to climb, Navajos began to organize. A group of Navajo widows gathered together to discuss the deaths of their miner husbands; this grew into a movement steeped in science and politics that eventually brought about the Radiation Exposure Compensation Act (RECA) in 1999.
Cut to the present day. According to the US EPA, more than 500 of the existing 1300 abandoned uranium mines (AUM) on Navajo lands exhibit elevated levels of radiation.
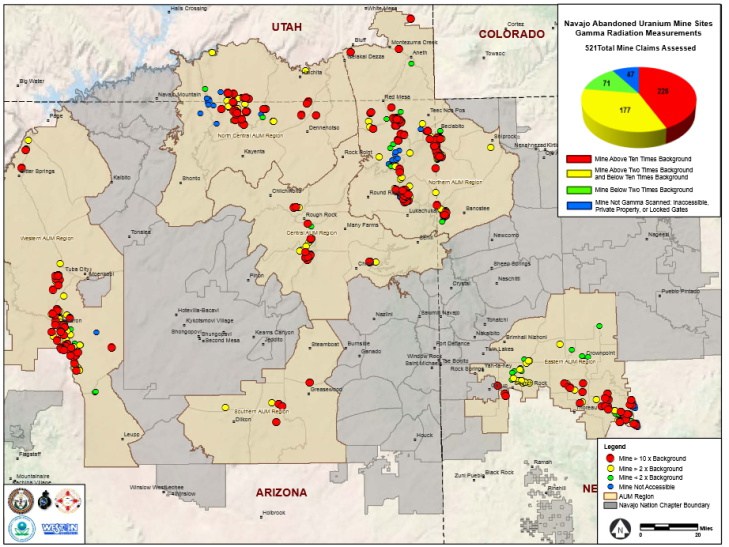
Navajo abandoned uranium mines gamma radiation measurements and priority mines. US EPA
The Los Angeles Times gave us a sense of the risk in 1986. Thomas Payne, an environmental health officer from Indian Health Services, accompanied by a National Park Service ranger, took water samples from 48 sites in Navajo territory. The group of samples showed uranium levels in wells as high as 139 picocuries per liter. Levels In abandoned pits were far more dangerous, sometimes exceeding 4,000 picocuries. The EPA limit for safe drinking water is 20 picocuries per liter.
This unresolved plague of radiation is compounded by pollution from coal mines and a coal-fired power plant that manifests at an even more systemic level; the entire Navajo water supply is currently tainted with industry toxins.
Recent media coverage and spiraling public outrage over the water crisis in Flint, Michigan has completely eclipsed the ongoing environmental justice struggles of the Navajo. Even worse, the media continues to frame the situation in Flint as some sort of isolated incident.
Madeline Stano, attorney for the Center on Race, Poverty & the Environment, assessed the situation for the San Diego Free Press, commenting, “Unfortunately, Flint’s water scandal is a symptom of a much larger disease. It’s far from an isolated incidence, in the history of Michigan itself and in the country writ large.”
Other instances of criminally negligent environmental pollution in the United States include the 50-year legacy of PCB contamination at the Mohawk community of Akwesasne, and the Hanford Nuclear Reservation (HNR) situated in the Yakama Nation’s “front yard.”
While many environmental movements are fighting to establish proper regulation of pollutants at state, federal, and even international levels, these four cases are representative of a pervasive, environmental racism that stacks up against communities like the Navajo and prevents them from receiving equal protection under existing regulations and policies.
Despite the common thread among these cases, the wave of righteous indignation over the ongoing tragedy in Flint has yet to reach the Navajo Nation, the Mohawk community of Akwesasne, the Yakama Nation – or the many other Indigenous communities across the United States that continue to endure various toxic legacies in relative silence.
Current public outcry may be a harbinger, however, of an environmental justice movement ready to galvanize itself towards a higher calling, one that includes all peoples across the United States, and truly shares the ongoing, collective environmental victories with all communities of color.






